对保存的vgg16.ckpt模型实现特征图可视化
Posted 大彤小忆
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了对保存的vgg16.ckpt模型实现特征图可视化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在使用NWPU VHR-10数据集训练Faster R-CNN模型之后,可以通过对保存的模型实现特征图可视化来进一步分析模型。
在训练结束后,我们会将一组模型复制到./output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default路径下进行测试。
在对特征图进行可视化前,首先新建一个visual_ckpt.py文件查看vgg16.ckpt文件的内容、参数名称及尺寸,具体代码如下所示。
from tensorflow.python import pywrap_tensorflow
checkpoint_path = 'E:/Remote Sensing/Faster-RCNN_for_NWPU VHR-10/output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default/vgg16.ckpt'
reader = pywrap_tensorflow.NewCheckpointReader(checkpoint_path) # tf.train.NewCheckpointReader
var_to_shape_map = reader.get_variable_to_shape_map()
for key in var_to_shape_map:
print("tensor_name: ", key, reader.get_tensor(key).shape)
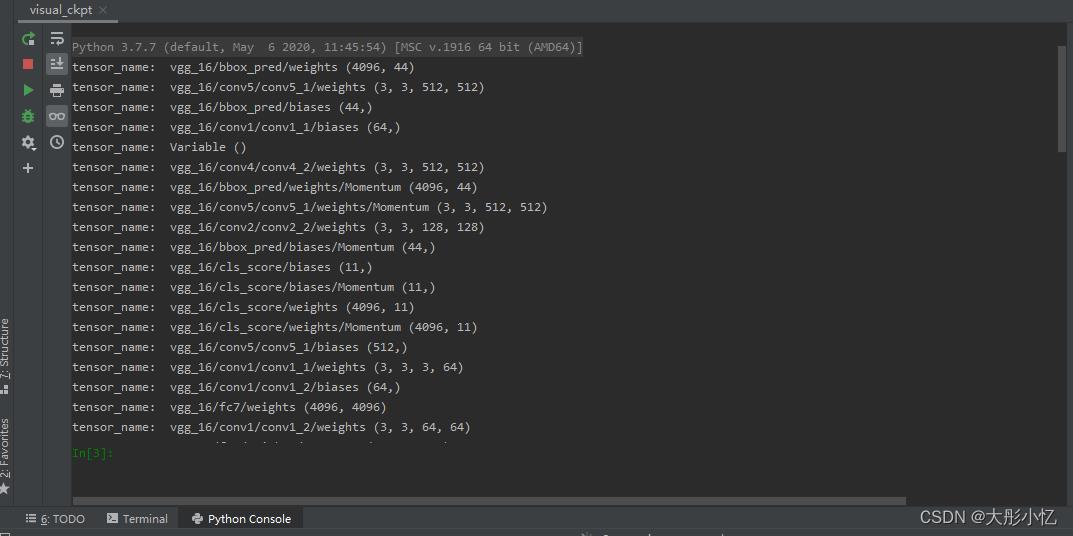
运行代码后得到的结果如下图所示。
然后新建一个ckpt_npy.py文件将vgg16.ckpt文件转为vgg16.npy文件,具体代码如下所示。
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python import pywrap_tensorflow
checkpoint_path = 'E:/Remote Sensing/Faster-RCNN_for_NWPU VHR-10/output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default/vgg16.ckpt' # your ckpt path
reader = pywrap_tensorflow.NewCheckpointReader(checkpoint_path)
var_to_shape_map = reader.get_variable_to_shape_map()
alexnet =
alexnet_layer = ['conv1_1', 'conv1_2', 'conv2_1', 'conv2_2', 'conv3_1', 'conv3_2', 'conv3_3', 'conv4_1', 'conv4_2', 'conv4_3', 'conv5_1', 'conv5_2', 'conv5_3']
add_info = ['weights', 'biases']
alexnet = 'conv1_1': [[], []], 'conv1_2': [[], []], 'conv2_1': [[], []], 'conv2_2': [[], []], 'conv3_1': [[], []], 'conv3_2': [[], []], 'conv3_3': [[], []], 'conv4_1': [[], []], 'conv4_2': [[], []], 'conv4_3': [[], []], 'conv5_1': [[], []], 'conv5_2': [[], []], 'conv5_3': [[], []]
for key in var_to_shape_map:
str_name = key
if str_name.find('Momentum') > -1:
continue
if str_name.find('Variable') > -1:
continue
if str_name.find('rpn') > -1:
continue
if str_name.find('bbox') > -1:
continue
if str_name.find('cls') > -1:
continue
if str_name.find('fc') > -1:
continue
print('tensor_name:', str_name)
if str_name.find('/') > -1:
names = str_name.split('/')
# first layer name and weight, bias
if len(names) > 3:
layer_name = names[2]
layer_add_info = names[3]
else:
layer_name = str_name
layer_add_info = None
if layer_add_info == 'weights':
alexnet[layer_name][0] = reader.get_tensor(key)
elif layer_add_info == 'biases':
alexnet[layer_name][1] = reader.get_tensor(key)
else:
alexnet[layer_name] = reader.get_tensor(key)
# save npy
np.save('E:/Remote Sensing/Faster-RCNN_for_NWPU VHR-10/output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default/vgg16.npy', alexnet)
print('save npy over...')
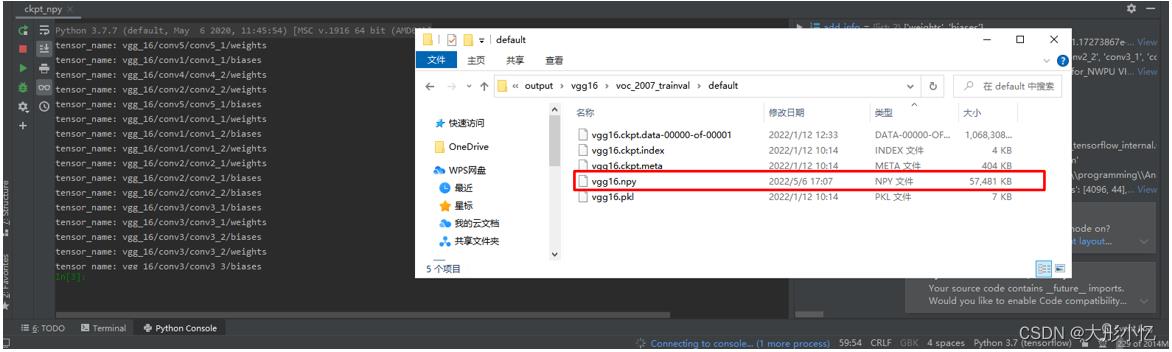
运行代码后得到的结果如下图所示,可以在./output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default路径下得到vgg16.npy文件。
接下来新建一个visual_npy.py文件查看vgg16.npy文件的参数,具体代码如下所示。
import numpy as np
data_dict = np.load('E:/Remote Sensing/Faster-RCNN_for_NWPU VHR-10/output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default/vgg16.npy', encoding='latin1', allow_pickle=True).item()
keys = sorted(data_dict.keys())
# keys: 即为卷积层和全连接层的变量名
print("keys:", keys)
print("-----------------------------------------")
for key in keys:
weights = data_dict[key][0]
biases = data_dict[key][1]
print(key)
print('weights shape: ', weights.shape)
print('biases shape: ', biases.shape)
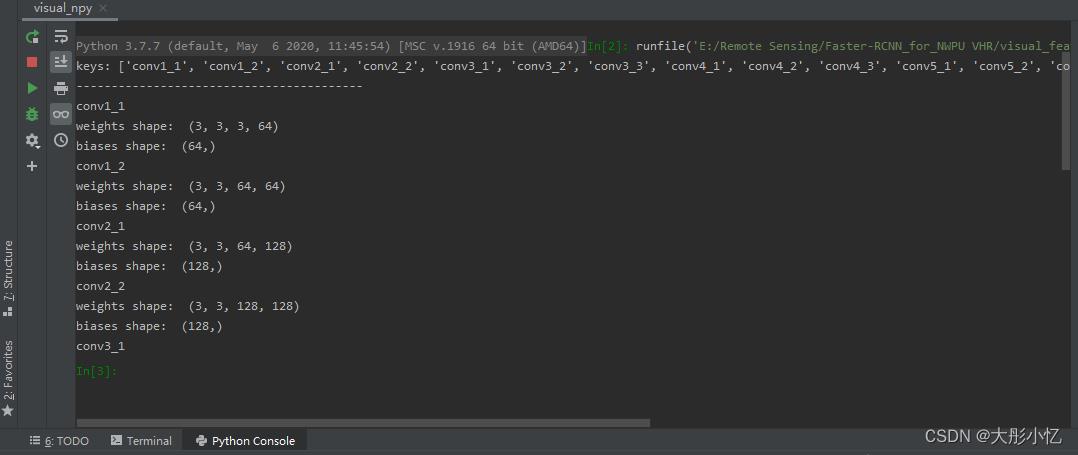
运行代码后得到的结果如下图所示。
最后新建一个visual_feature.py文件对特征提取网络VGG16实现特征图可视化。
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import time
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# VGG 自带的一个常量,之前VGG训练通过归一化,所以现在同样需要作此操作
VGG_MEAN = [102.9801, 115.9465, 122.7717] # rgb 三通道的均值
class VGGNet():
'''
创建 vgg16 网络 结构
从模型中载入参数
'''
def __init__(self, data_dict):
'''
传入vgg16模型
:param data_dict: vgg16.npy (字典类型)
'''
self.data_dict = data_dict
def get_conv_filter(self, name):
'''
得到对应名称的卷积层
:param name: 卷积层名称
:return: 该卷积层输出
'''
return tf.constant(self.data_dict[name][0], name='conv')
def get_fc_weight(self, name):
'''
获得名字为name的全连接层权重
:param name: 连接层名称
:return: 该层权重
'''
return tf.constant(self.data_dict[name][0], name='fc')
def get_bias(self, name):
'''
获得名字为name的全连接层偏置
:param name: 连接层名称
:return: 该层偏置
'''
return tf.constant(self.data_dict[name][1], name='bias')
def conv_layer(self, x, name):
'''
创建一个卷积层
:param x:
:param name:
:return:
'''
# 在写计算图模型的时候,加一些必要的 name_scope,这是一个比较好的编程规范
# 可以防止命名冲突, 二可视化计算图的时候比较清楚
with tf.name_scope(name):
# 获得 w 和 b
conv_w = self.get_conv_filter(name)
conv_b = self.get_bias(name)
# 进行卷积计算
h = tf.nn.conv2d(x, conv_w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
'''
因为此刻的 w 和 b 是从外部传递进来,所以使用 tf.nn.conv2d()
tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu = None, name = None) 参数说明:
input 输入的tensor, 格式[batch, height, width, channel]
filter 卷积核 [filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]
分别是:卷积核高,卷积核宽,输入通道数,输出通道数
strides 步长 卷积时在图像每一维度的步长,长度为4
padding 参数可选择 “SAME” “VALID”
'''
# 加上偏置
h = tf.nn.bias_add(h, conv_b)
# 使用激活函数
h = tf.nn.relu(h)
return h
def pooling_layer(self, x, name):
'''
创建池化层
:param x: 输入的tensor
:param name: 池化层名称
:return: tensor
'''
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], # 核参数, 注意:都是4维
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name=name
)
def fc_layer(self, x, name, activation=tf.nn.relu):
'''
创建全连接层
:param x: 输入tensor
:param name: 全连接层名称
:param activation: 激活函数名称
:return: 输出tensor
'''
with tf.name_scope(name, activation):
# 获取全连接层的 w 和 b
fc_w = self.get_fc_weight(name)
fc_b = self.get_bias(name)
# 矩阵相乘 计算
h = tf.matmul(x, fc_w)
# 添加偏置
h = tf.nn.bias_add(h, fc_b)
# 因为最后一层是没有激活函数relu的,所以在此要做出判断
if activation is None:
return h
else:
return activation(h)
def flatten_layer(self, x, name):
'''
展平
:param x: input_tensor
:param name:
:return: 二维矩阵
'''
with tf.name_scope(name):
# [batch_size, image_width, image_height, channel]
x_shape = x.get_shape().as_list()
# 计算后三维合并后的大小
dim = 1
for d in x_shape[1:]:
dim *= d
# 形成一个二维矩阵
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, dim])
return x
def build(self, x_rgb):
'''
创建vgg16 网络
:param x_rgb: [1, 224, 224, 3]
:return:
'''
start_time = time.time()
print('模型开始创建……')
# 将输入图像进行处理,将每个通道减去均值
r, g, b = tf.split(x_rgb, [1, 1, 1], axis=3)
'''
tf.split(value, num_or_size_split, axis=0)用法:
value:输入的Tensor
num_or_size_split:有两种用法:
1.直接传入一个整数,代表会被切成几个张量,切割的维度有axis指定
2.传入一个向量,向量长度就是被切的份数。传入向量的好处在于,可以指定每一份有多少元素
axis, 指定从哪一个维度切割
因此,上一句的意思就是从第4维切分,分为3份,每一份只有1个元素
'''
# 将 处理后的通道再次合并起来
x_bgr = tf.concat([b - VGG_MEAN[0], g - VGG_MEAN[1], r - VGG_MEAN[2]], axis=3)
# 开始构建卷积层(下面这些变量名称不能乱取,必须要和vgg16模型保持一致)
self.conv1_1 = self.conv_layer(x_bgr, 'conv1_1')
self.conv1_2 = self.conv_layer(self.conv1_1, 'conv1_2')
self.pool1 = self.pooling_layer(self.conv1_2, 'pool1')
self.conv2_1 = self.conv_layer(self.pool1, 'conv2_1')
self.conv2_2 = self.conv_layer(self.conv2_1, 'conv2_2')
self.pool2 = self.pooling_layer(self.conv2_2, 'pool2')
self.conv3_1 = self.conv_layer(self.pool2, 'conv3_1')
self.conv3_2 = self.conv_layer(self.conv3_1, 'conv3_2')
self.conv3_3 = self.conv_layer(self.conv3_2, 'conv3_3')
self.pool3 = self.pooling_layer(self.conv3_3, 'pool3')
self.conv4_1 = self.conv_layer(self.pool3, 'conv4_1')
self.conv4_2 = self.conv_layer(self.conv4_1, 'conv4_2')
self.conv4_3 = self.conv_layer(self.conv4_2, 'conv4_3')
self.pool4 = self.pooling_layer(self.conv4_3, 'pool4')
self.conv5_1 = self.conv_layer(self.pool4, 'conv5_1')
self.conv5_2 = self.conv_layer(self.conv5_1, 'conv5_2')
self.conv5_3 = self.conv_layer(self.conv5_2, 'conv5_3')
print('创建模型结束:%4ds' % (time.time() - start_time))
# 指定 model 路径
vgg16_npy_pyth = 'E:/Remote Sensing/Faster-RCNN_for_NWPU VHR-10/output/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/default/vgg16.npy'
# 内容图像路径
content_img_path = 'E:/Remote Sensing/Faster-RCNN_for_NWPU VHR-10/data/VOCdevkit2007/VOC2007/JPEGImages/000001.jpg'
def read_img(img_name):
'''
读取图片
:param img_name: 图片路径
:return: 4维矩阵
'''
img = Image.open(img_name)
np_img = np.array(img) # 224, 224, 3
# 需要传化 成 4 维
np_img = np.asarray([np_img], dtype=np.int32) # 这个函数作用不太理解 (1, 224, 224, 3)
return np_img
def get_row_col(num_pic):
'''
计算行列的值
:param num_pic: 特征图的数量
:return:
'''
squr = num_pic ** 0.5
row = round(squr)
col = row + 1 if squr - row > 0 else row
return row, col
def visualize_feature_map(feature_batch):
'''
创建特征子图,创建叠加后的特征图
:param feature_batch: 一个卷积层所有特征图
:return:
'''
feature_map = np.squeeze(feature_batch, axis=0)
feature_map_combination = []
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 7))
#plt.figure()
# 取出 featurn map 的数量,因为特征图数量很多,这里直接手动指定了。
num_pic = feature_map.shape[2]
row, col = get_row_col(num_pic)
# 将 每一层卷积的特征图,拼接层 5 × 5
for i in range(0, num_pic):
feature_map_split = feature_map[:, :, i]
feature_map_combination.append(feature_map_split)
plt.subplot(row, col, i + 1)
plt.imshow(feature_map_split)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
def visualize_feature_map_sum(feature_batch):
'''
将每张子图进行相加
:param feature_batch:
:return:
'''
feature_map = np.squeeze(feature_batch, axis=0)
feature_map_combination = []
# 取出 featurn map 的数量
num_pic = feature_map.shape[2]
# 将 每一层卷积的特征图,拼接层 5 × 5
for i in range(0, num_pic):
feature_map_split = feature_map[:, :, i]
feature_map_combination.append(feature_map_split)
# 按照特征图进行叠加代码
feature_map_sum = sum(one for one in feature_map_combination)
plt.imshow(feature_map_sum)
plt.show()
# 读取内容图像
content_val = read_img(content_img_path)
print(content_val.shape)
content = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# 载入模型, 注意:在python3中,需要添加一句: encoding='latin1'
data_dict = np.load(vgg16_npy_pyth, encoding='latin1', allow_pickle=True).item()
# 创建图像的vgg对象
vgg_for_content = VGGNet(data_dict)
# 创建每个神经网络
vgg_for_content.build(content)
content_features = [vgg_for_content.conv1_2,
vgg_for_content.conv2_2,
vgg_for_content.conv3_3,
vgg_for_content.conv4_3,
vgg_for_content.conv5_3,
]
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
content_features = sess.run([content_features],
feed_dict=
content: content_val
)
conv1 = content_features[0][0]
conv2 = content_features[0][1]
conv3 = content_features[0][2]
conv4 = content_features[0][3]
conv5 = content_features[0][4]
# 查看每个特征子图
visualize_feature_map(conv1) # 依次对conv的层数进行修改以得到不同的结果
# 查看叠加后的特征图
visualize_feature_map_sum(conv1)
运行代码后得到的结果如下所示。
-
原图

-
conv1

-
conv2
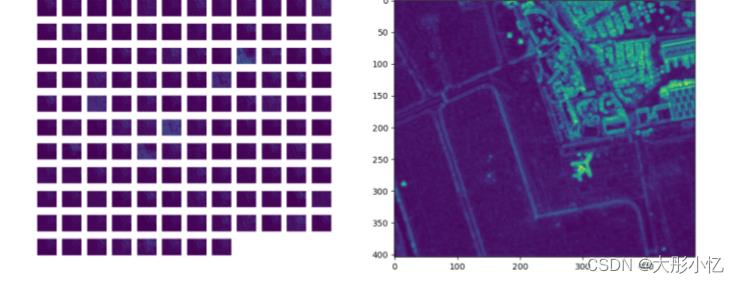
-
conv3

-
conv4
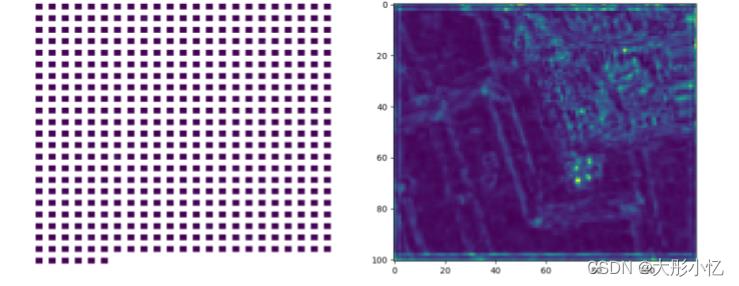
-
conv5
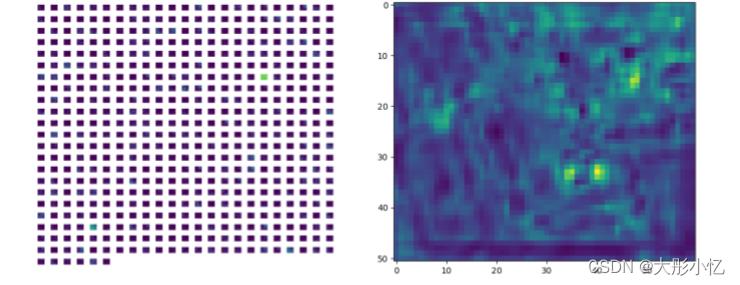
通过分析上面的结果,可以发现浅层特征更多的是对图像边缘的检测,检测到的细节信息更多,随着层次的加深,特征图越来抽象,忽略了很多信息。
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/Vici__/article/details/100626406
https://blog.csdn.net/raby_gyl/article/details/79075716
https://blog.csdn.net/mr_muli/article/details/90677623
https://blog.csdn.net/missyougoon/article/details/85645195
以上是关于对保存的vgg16.ckpt模型实现特征图可视化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
深度学习100例-卷积神经网络(VGG-19)识别灵笼中的人物 | 第7天
深度学习100例-卷积神经网络(VGG-19)识别灵笼中的人物 | 第7天