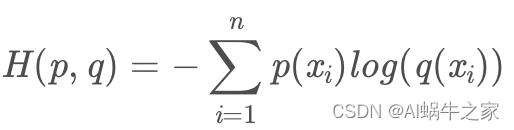IR信息检索前沿梳理
Posted AI蜗牛之家
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了IR信息检索前沿梳理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 检索预训练
1.1 PROP: Pre-training with Representative Words Prediction for Ad-hoc Retrieval
three types of pre-training tasks have been proposed including:
- Inverse Cloze Task (ICT): The query is a sentence randomly drawn from the passage and the document is the rest of sentences;
- Body First Selection (BFS): The query is a random sentence in the first section of a Wikipedia page, and the document is a random passage from the same page;
- Wiki Link Prediction (WLP): The query is a random sentence in the first section of a Wikipedia page, and the document is a passage from another page where there is a hyperlink link to the page of the query.
motivation novelty:
查询似然Query Likelihood
语言模型的假设是:p(R=1|q,d)≈p(q|d,R=1),文档与查询相关的概率约等于 在文档相关的前提下,用户输入q的概率。具体详见:文档排序模型–查询似然Query Likelihood
小编认为,其实原理其实跟TF-IDF差不多,计算query和doc的相似度。
The key idea is inspired by the traditional statistical language model for IR, specifically the query likelihood model [27] which was proposed in the last century. The query likelihood model assumes that the query is generated as the piece of text representative of the “ideal” document [19]. Based on the Bayesian theorem, the relevance relationship between query and document could then be approximated by the query likelihood given the document language model under some mild prior assumption. Based on the classical IR theory, we propose the Representative wOrds Prediction (ROP) task for pretraining. Specifically, given an input document, we sample a pair of word sets according to the document language model, which is defined by a popular multinomial unigram language model with Dirichlet prior smoothing. The word set with higher likelihood is deemed as more “representative” of the document. We then pretrain the Transformer model to predict the pairwise preference between the two sets of words, jointly with the Masked Language Model (MLM) objective. The pre-trained model, namely PROP for short, could then be fine-tuned on a variety of downstream ad-hoc retrieval tasks. The key advantage of PROP lies in that it roots in a good theoretical foundation of IR and could be universally trained over large scale text corpus without any special document structure (e.g. hyperlinks) requirement.
通过查询似然找出两个set,通过加入对比loss,以及Masked Language Model (MLM) 的loss进行训练,这样可以训练出一个跟BERT等价但是更适合检索场景的预训练模型。
1.2.B-PROP: Bootstrapped Pre-training with Representative Words Prediction for Ad-hoc Retrieval
该工作是PROP: Pre-training with Representative Words Prediction for Ad-hoc Retrieval的姊妹篇,motivation是解决PROP中query likelyhood中仅通过unigram没有参考上下文的问题,因此提出用BERT来选择重点词。
最直接的方式就是直接用BERT中CLS与其他token的attention来作为词的权重,但是这样选出来的词经常是一些in, the, of通用词,如下:
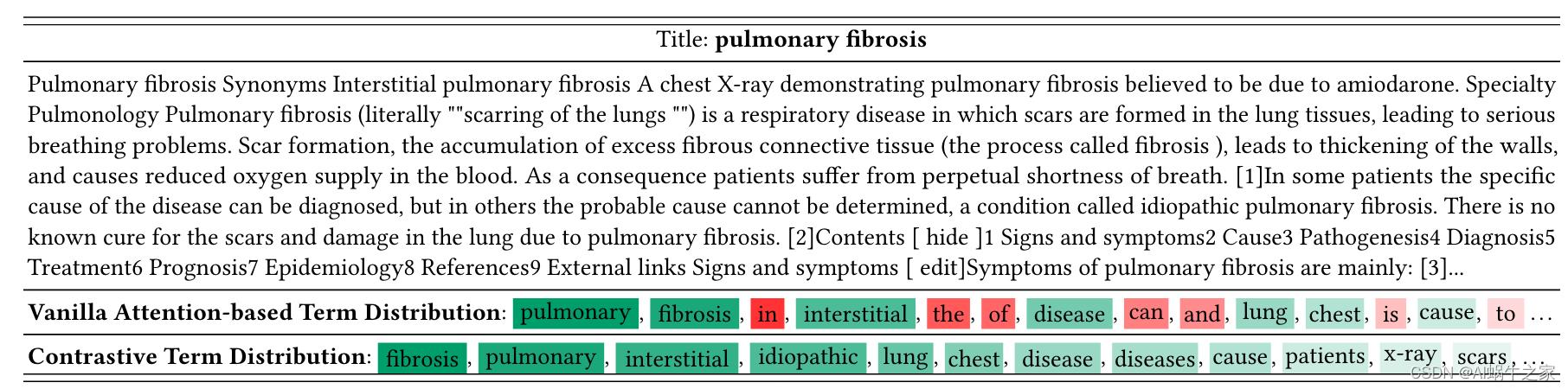
为了解决这个问题,作者采用随机性偏差模型(divergence from randomness),这个是检索里面的一种概率统计模型。所以作者借助于这个理论为立足点,我觉得是这篇文章的一个创新点。
这个地方当时在看文章的时候感觉为什么不用tfidf来过滤呢?其实看完上面这个divergence from randomness这个理论之后发现,采用交叉熵来统计,其实稍加推到就发现跟tfidf基本等价。但是如果写paper的时候直接用tfidf过滤明显就不那么高大上了。这里也不是说B-PROP的作者投机取巧,只是说写作还是需要一定技巧的,只不过这些技巧根植于基本理论体系之上。 关于divergence from randomness
从这里也发现TF-IDF原来跟交叉熵从原理上这么像,放在这里:
TFIDF:
交叉熵: 去掉sum再来看~ (小编小课堂哈哈,详见:Cross-Entropy
其他
- Document Expansion by Query Prediction
identified document expansion terms using a sequence-to-sequence model that generated possible queries for which the given document would be relevant. - Context-Aware Term Weighting For First Stage Passage Retrieval.
used a BERT [12] model to learn relevant term weights in a document and generated a pseudo-document representation
这个方法跟之前在某搜索引擎公司实习时候,挖掘query权重的方法基本类似,通过点击数据获取query中的权重(2018年),不同的是这篇文章中不但给query增加权重,同时还用同样的方式获取document的term weight。从结果上看同样有效。小编的经验:如果点击数量足够大,上述的方法可能效果更好,因为这样的term weight可能更有统计意义。
以上是关于IR信息检索前沿梳理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章