Android性能优化之启动耗时测量
Posted bubbleben
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android性能优化之启动耗时测量相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android启动优化之启动耗时测量
本文基于
Android 11.0源码分析,涉及如下文件
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityMetricsLogger.java
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityRecord.java
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStarter.java
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStartController.java
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/WaitResult.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/BasicShellCommandHandler.java
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/BaseCommand.java
frameworks/base/cmds/am/src/com/android/commands/am/Am.java
frameworks/base/cmds/am/src/com/android/commands/am/ActivityManagerShellCommand.java
1. Displayed Time
观察应用启动时间最直观的指标就是logcat中包含的Displayed日志,它的输出行代表从启动应用进程开始到在屏幕上完成应用界面的绘制所用的时间:I/ActivityTaskManager( 1489): Displayed com.tencent.mm/.ui.LauncherUI: +502ms
接下来我们从源码角度来分析下这行日志的打印时机:
1.1 应用启动状态
[-> WaitResult.java]
/**
* Cold launch sequence: a new process has started.
*/
public static final int LAUNCH_STATE_COLD = 1;
/**
* Warm launch sequence: process reused, but activity has to be created.
*/
public static final int LAUNCH_STATE_WARM = 2;
/**
* Hot launch sequence: process reused, activity brought-to-top.
*/
public static final int LAUNCH_STATE_HOT = 3;
首先应用有三种启动状态,每种状态都会影响应用显示所需的时间:冷启动、温启动或热启动。在冷启动中,需要启动应用进程。在另外两种状态中,系统需要将后台运行的进程带入前台。一般我们优化的是冷启动的场景,因为这样也可以提升温启动和热启动的性能;
[-> ActivityMetricsLogger.java]
private void logAppDisplayed(TransitionInfoSnapshot info)
// 仅记录温启动和冷启动的启动时间, 热启动的启动时间需要通过修改源码或其他方式来获取
if (info.type != TYPE_TRANSITION_WARM_LAUNCH && info.type != TYPE_TRANSITION_COLD_LAUNCH)
return;
// 记录event log
EventLog.writeEvent(WM_ACTIVITY_LAUNCH_TIME,
info.userId, info.activityRecordIdHashCode, info.launchedActivityShortComponentName,
info.windowsDrawnDelayMs);
StringBuilder sb = mStringBuilder;
sb.setLength(0);
sb.append("Displayed ");
// 打印Activity的ComponentName
sb.append(info.launchedActivityShortComponentName);
sb.append(": ");
// 打印启动时间,单位是ms
TimeUtils.formatDuration(info.windowsDrawnDelayMs, sb);
Log.i(TAG, sb.toString());
首先logAppDisplayed仅记录温启动(TYPE_TRANSITION_WARM_LAUNCH)和冷启动(TYPE_TRANSITION_COLD_LAUNCH)的启动时间,而不记录热启动(TYPE_TRANSITION_HOT_LAUNCH)的启动时间,它会打印出对应的ComponentName和启动时间;同时也会记录event log:I wm_activity_launch_time: [0,62925681,com.tencent.mm/.ui.LauncherUI,502],它与Displayed打印的时间时一致的;
1.2 应用启动时间计算
[-> ActivityMetricsLogger.java]
private void logAppTransitionFinished(@NonNull TransitionInfo info)
if (DEBUG_METRICS) Slog.i(TAG, "logging finished transition " + info);
// Take a snapshot of the transition info before sending it to the handler for logging.
// This will avoid any races with other operations that modify the ActivityRecord.
// 传入TransitionInfo,并由它来初始化TransitionInfoSnapshot
final TransitionInfoSnapshot infoSnapshot = new TransitionInfoSnapshot(info);
if (info.isInterestingToLoggerAndObserver())
BackgroundThread.getHandler().post(() -> logAppTransition(
info.mCurrentTransitionDeviceUptime, info.mCurrentTransitionDelayMs,
infoSnapshot));
// 后台线程打印Displayed日志
BackgroundThread.getHandler().post(() -> logAppDisplayed(infoSnapshot));
if (info.mPendingFullyDrawn != null)
info.mPendingFullyDrawn.run();
info.mLastLaunchedActivity.info.launchToken = null;
logAppDisplayed在后台线程上运行,并由logAppTransitionFinished调用执行,其中启动时间TransitionInfoSnapshot.windowsDrawnDelayMs由传入的TransitionInfo.mWindowsDrawnDelayMs进行赋值;
TransitionInfoSnapshot notifyWindowsDrawn(@NonNull ActivityRecord r, long timestampNs)
if (DEBUG_METRICS) Slog.i(TAG, "notifyWindowsDrawn " + r);
// 从mTransitionInfoList查找ActivityRecord对应的在notifyActivityLaunched创建的TransitionInfo
final TransitionInfo info = getActiveTransitionInfo(r);
if (info == null || info.allDrawn())
if (DEBUG_METRICS) Slog.i(TAG, "notifyWindowsDrawn no activity to be drawn");
return null;
// Always calculate the delay because the caller may need to know the individual drawn time.
// 根据当前时间戳计算出启动时间
info.mWindowsDrawnDelayMs = info.calculateDelay(timestampNs);
info.removePendingDrawActivity(r);
final TransitionInfoSnapshot infoSnapshot = new TransitionInfoSnapshot(info);
if (info.mLoggeTransitionInfodTransitionStarting && info.allDrawn())
// 最终将更新后的TransitionInfo传递给logAppTransitionFinished
done(false /* abort */, info, "notifyWindowsDrawn - all windows drawn", timestampNs);
return infoSnapshot;
notifyWindowsDrawn用来通知应用的所有窗口已经绘制成功:TransitionInfo.mWindowsDrawnDelayMs在这里被赋值,根据当前时间戳由TransitionInfo.calculateDelay计算得来:
int calculateDelay(long timestampNs)
// Shouldn't take more than 25 days to launch an app, so int is fine here.
return (int) TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(timestampNs - mTransitionStartTimeNs);
其中timestampNs代表当前时间即启动结束的时间,mTransitionStartTimeNs代表启动开始的时间;
/**
* The timestamp of the first @link #notifyActivityLaunching. It can be used as a key for
* observer to identify which callbacks belong to a launch event.
*/
final long mTransitionStartTimeNs;
/** Use @link TransitionInfo#create instead to ensure the transition type is valid. */
private TransitionInfo(ActivityRecord r, LaunchingState launchingState, int transitionType,
boolean processRunning, boolean processSwitch)
mLaunchingState = launchingState;
// 创建TransitionInfo并对mTransitionStartTimeNs进行初始化
mTransitionStartTimeNs = launchingState.mCurrentTransitionStartTimeNs;
mTransitionType = transitionType;
mProcessRunning = processRunning;
mProcessSwitch = processSwitch;
mCurrentTransitionDeviceUptime =
(int) TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toSeconds(SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
setLatestLaunchedActivity(r);
launchingState.mAssociatedTransitionInfo = this;
mTransitionStartTimeNs由LaunchingState.mCurrentTransitionStartTimeNs赋值;
/**
* Notifies the tracker at the earliest possible point when we are starting to launch an
* activity. The caller must ensure that @link #notifyActivityLaunched will be called later
* with the returned @link LaunchingState.
*/
private LaunchingState notifyActivityLaunching(Intent intent, @Nullable ActivityRecord caller,
int callingUid)
final long transitionStartTimeNs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtimeNanos();
TransitionInfo existingInfo = null;
....
if (existingInfo == null)
// Only notify the observer for a new launching event.
launchObserverNotifyIntentStarted(intent, transitionStartTimeNs);
final LaunchingState launchingState = new LaunchingState();
launchingState.mCurrentTransitionStartTimeNs = transitionStartTimeNs;
return launchingState;
existingInfo.mLaunchingState.mCurrentTransitionStartTimeNs = transitionStartTimeNs;
return existingInfo.mLaunchingState;
LaunchingState.mCurrentTransitionStartTimeNs在notifyActivityLaunching中被初始化;
到这里我们已经可以清楚的知道应用启动开始时间以及结束时间是分别在notifyActivityLaunching和notifyWindowsDrawn记录的,接下来我们接着分析它们又是何时被调用的;
1.3 应用启动开始时间
[-> ActivityStarter.java]
int execute()
try
...
final LaunchingState launchingState;
synchronized (mService.mGlobalLock)
final ActivityRecord caller = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(mRequest.resultTo);
// 通过ActivityMetricsLogger.notifyActivityLaunching创建LaunchingState并记录创建Activity开始的时间
launchingState = mSupervisor.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyActivityLaunching(
mRequest.intent, caller);
...
// 执行启动请求
res = executeRequest(mRequest);
...
// Notify ActivityMetricsLogger that the activity has launched.
// ActivityMetricsLogger will then wait for the windows to be drawn and populate
// WaitResult.
// 通过ActivityMetricsLogger.notifyActivityLaunched记录Activity启动完成的时间
mSupervisor.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyActivityLaunched(launchingState, res,
mLastStartActivityRecord);
// 同时将Request.waitResult添加到ActivityStackSupervisor的mWaitingActivityLaunched中,等待窗口绘制完成
return getExternalResult(mRequest.waitResult == null ? res
: waitForResult(res, mLastStartActivityRecord));
finally
onExecutionComplete();
ActivityStarter.execute()会调用ActivityMetricsLogger.notifyActivityLaunching方法并记录启动开始的时间;
static class DefaultFactory implements Factory
@Override
public ActivityStarter obtain()
ActivityStarter starter = mStarterPool.acquire();
if (starter == null)
starter = new ActivityStarter(mController, mService, mSupervisor, mInterceptor);
return starter;
ActivityStarter以对象池的方式进行复用,如果池中没有则创建一个新的ActivityStarter对象;
[-> ActivityStartController.java]
/**
* @return A starter to configure and execute starting an activity. It is valid until after
* @link ActivityStarter#execute is invoked. At that point, the starter should be
* considered invalid and no longer modified or used.
*/
ActivityStarter obtainStarter(Intent intent, String reason)
return mFactory.obtain().setIntent(intent).setReason(reason);
通过工厂模式使用默认的Factory(DefaultFactory)获取ActivityStarter;
[-> ActivityTaskManagerService.java]
private int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
@Nullable String callingFeatureId, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId, boolean validateIncomingUser)
assertPackageMatchesCallingUid(callingPackage);
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivityAsUser");
userId = getActivityStartController().checkTargetUser(userId, validateIncomingUser,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), "startActivityAsUser");
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
// 获取ActivityStarter并执行execute方法
return getActivityStartController().obtainStarter(intent, "startActivityAsUser")
.setCaller(caller)
.setCallingPackage(callingPackage)
.setCallingFeatureId(callingFeatureId)
.setResolvedType(resolvedType)
.setResultTo(resultTo)
.setResultWho(resultWho)
.setRequestCode(requestCode)
.setStartFlags(startFlags)
.setProfilerInfo(profilerInfo)
.setActivityOptions(bOptions)
.setUserId(userId)
.execute();
应用启动之前通过ActivityStartController获取ActivityStarter初始化启动参数,并调用execute方法记录启动开始的时间,以最典型的startActivity(Intent intent)为例,整个调用流程如下:
--> Activity.startActivity
--> Activity.startActivityForResult
--> Instrumention.execStartActivity
--> ActivityTaskManagerService.startActivity
--> ActivityTaskManagerService.startActivityAsUser
注意:这里还并未真正开启Activity的启动流程,只是应用通过Binder跨进程调用ActivityTaskManagerService.startActivityAsUser准备开启真正的启动流程,对于冷启动来讲还需要先启动应用进程然后再启动对应的主Activity,而其余两种启动方式则会直接启动Activity,可以看到启动开始的时间是由系统侧(system_server)记录的;
1.4 应用启动结束时间
[-> ActivityRecord.java]
void onFirstWindowDrawn(WindowState win, WindowStateAnimator winAnimator)
firstWindowDrawn = true;
// We now have a good window to show, remove dead placeholders
removeDeadWindows();
if (startingWindow != null)
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_STARTING_WINDOW, "Finish starting %s"
+ ": first real window is shown, no animation", win.mToken);
// If this initial window is animating, stop it -- we will do an animation to reveal
// it from behind the starting window, so there is no need for it to also be doing its
// own stuff.
win.cancelAnimation();
// 窗口绘制完成,移除starting window
removeStartingWindow();
// 更新窗口可见性并记录启动时间
updateReportedVisibilityLocked();
void updateReportedVisibilityLocked()
...
if (nowDrawn != reportedDrawn)
// 调用onWindowsDrawn记录启动完成的时间
onWindowsDrawn(nowDrawn, SystemClock.elapsedRealtimeNanos());
reportedDrawn = nowDrawn;
...
/** Called when the windows associated app window container are drawn. */
void onWindowsDrawn(boolean drawn, long timestampNs)
mDrawn = drawn;
if (!drawn)
return;
// 调用ActivityMetricsLogger().notifyWindowsDrawn计算启动时间
final TransitionInfoSnapshot info = mStackSupervisor
.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyWindowsDrawn(this, timestampNs);
...
--> WindowStateAnimator.commitFinishDrawingLocked
--> WindowState.performShowLocked
--> ActivityRecord.onFirstWindowDrawn
--> ActivityRecord.updateReportedVisibilityLocked
--> ActivityRecord.onWindowsDrawn
--> ActivityMetricsLogger.notifyWindowsDrawn
应用启动结束的调用流程相对来讲比较复杂,涉及到窗口动画以及surface的切换等,篇幅有限我们只关注最后的流程:即经过上面的调用流程之后,最终将启动完成时间传递给onWindowsDrawn记录;
2. adb shell am start -S -W packageName/ActivityName
我们还可以通过adb命令来测量应用启动时间:它会打印出应用的启动模式LaunchState,启动状态Status,以及TotalTime和WaitTime,接下来我们会从源码角度来分析这几项参数的含义:可以看到通过adb命令打印出来的启动时间(TotalTime)与logcat中打印的启动时间时一致的;
D:\\>adb shell am start -S -W com.android.settings/.Settings
Stopping: com.android.settings
Starting: Intent act=android.intent.action.MAIN cat=[android.intent.category.LAUNCHER] cmp=com.android.settings/.Settings
Status: ok
LaunchState: COLD
Activity: com.android.settings/.Settings
TotalTime: 370
WaitTime: 378
Complete
09-19 09:46:57.474 I/ActivityTaskManager( 1489): Displayed com.android.settings/.Settings: +370ms
2.1 Am
[-> Am.java]
public class Am extends BaseCommand
/**
* Command-line entry point.
*
* @param args The command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
// am命令的入口函数, run方法的实现在其父类BaseCommand中
(new Am()).run(args);
adbd会通过shell调用到具体的命令,包括am,wm,pm和input在内所有的命令都可以在/frameworks/base/cmds/目录下找到对应的实现,其中am的实现在Am.java文件中;
[-> BaseCommand.java]
/**
* Call to run the command.
*/
public void run(String[] args)
// 参数有效长度不足时打印命令的使用方法
if (args.length < 1)
onShowUsage(System.out);
return;
try
// 执行Am的onRun方法
onRun();
catch (IllegalArgumentException e)
onShowUsage(System.err);
System.err.println();
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
System.exit(1);
[-> Am.java]
@Override
public void onRun() throws Exception
// 通过ServiceManager获取AMS和PMS
mAm = ActivityManager.getService();
mPm = IPackageManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService("package"));
String op = nextArgRequired();
if (op.equals("instrument"))
runInstrument();
else
// 解析命令参数并执行runAmCmd方法
runAmCmd(getRawArgs());
void runAmCmd(String[] args) throws AndroidException
final MyShellCallback cb = new MyShellCallback();
try
// 调用ActivityManagerService并执行其shellCommand方法
mAm.asBinder().shellCommand(FileDescriptor.in, FileDescriptor.out, FileDescriptor.err,
args, cb, new ResultReceiver(null) );
catch (RemoteException e)
System.err.println(NO_SYSTEM_ERROR_CODE);
throw new AndroidException("Can't call activity manager; is the system running?");
finally
cb.mActive = false;
am命令的功能最终还是通过ActivityManagerService来实现的;
2.2 ActivityManagerService
[-> ActivityManagerService.java]
@Override
public void onShellCommand(FileDescriptor in, FileDescriptor out,
FileDescriptor err, String[] args, ShellCallback callback,
ResultReceiver resultReceiver)
(new ActivityManagerShellCommand(this, false)).exec(
this, in, out, err, args, callback, resultReceiver);
每执行一次am命令,ActivityManagerService都会创建ActivityManagerShellCommand来执行真正的任务;
2.3 ActivityManagerShellCommand
[-> ShellCommand.java]
public abstract class ShellCommand extends BasicShellCommandHandler
public int exec(Binder target, FileDescriptor in, FileDescriptor out, FileDescriptor err,
String[] args, ShellCallback callback, ResultReceiver resultReceiver)
mShellCallback = callback;
mResultReceiver = resultReceiver;
// 继续调用其父类BasicShellCommandHandler的exec方法
final int result = super.exec(target, in, out, err, args);
if (mResultReceiver != null)
mResultReceiver.send(result, null);
return result;
ActivityManagerShellCommand继承于ShellCommand,exec的实现在其父类ShellCommand中;
[-> BasicShellCommandHandler.java]
public int exec(Binder target, FileDescriptor in, FileDescriptor out, FileDescriptor err,
String[] args)
String cmd;
int start;
if (args != null && args.length > 0)
// 获取命令参数
cmd = args[0];
start = 1;
else
cmd = null;
start = 0;
init(target, in, out, err, args, start);
mCmd = cmd;
int res = -1;
try
// 回调子类重写的抽象方法onCommand
res = onCommand(mCmd);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Executed command " + mCmd + " on " + mTarget);
...
return res;
[-> ActivityShellCommand.java]
@Override
public int onCommand(String cmd)
if (cmd == null)
return handleDefaultCommands(cmd);
final PrintWriter pw = getOutPrintWriter();
try
switch (cmd)
case "start":
case "start-activity":
// 如果是start或者start-activity命令,则执行runStartActivity方法
return runStartActivity(pw);
...
default:
return handleDefaultCommands(cmd);
catch (RemoteException e)
pw.println("Remote exception: " + e);
return -1;
am支持多种命令,包括Activity,Service,BroadcasatReceiver的启动等等;
private Intent makeIntent(int defUser) throws URISyntaxException
mWaitOption = false;
mStopOption = false;
return Intent.parseCommandArgs(this, new Intent.CommandOptionHandler()
@Override
public boolean handleOption(String opt, ShellCommand cmd)
if (opt.equals("-D"))
mStartFlags |= ActivityManager.START_FLAG_DEBUG;
else if (opt.equals("-N"))
mStartFlags |= ActivityManager.START_FLAG_NATIVE_DEBUGGING;
else if (opt.equals("-W"))
// 记录mWaitOption
mWaitOption = true;
else if (opt.equals("-S"))
// 记录mStopOption
mStopOption = true;
...
int runStartActivity(PrintWriter pw) throws RemoteException
Intent intent;
try
// 解析命令参数, 我们这里用到了-W和-S, 分别记录在mWaitOption和mStopOption中
intent = makeIntent(UserHandle.USER_CURRENT);
catch (URISyntaxException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
do
if (mStopOption)
String packageName;
...
// 打印Stopping: com.android.settings
pw.println("Stopping: " + packageName);
pw.flush();
// 这里的mInterface是指ActivityManagerService
mInterface.forceStopPackage(packageName, mUserId);
try
// 休眠250ms
Thread.sleep(250);
catch (InterruptedException e)
// 打印Starting: Intent act=android.intent.action.MAIN cat=[android.intent.category.LAUNCHER]
// cmp=com.android.settings/.Settings
pw.println("Starting: " + intent);
pw.flush();
// WaitResult用来记录startActivityAndWait的返回结果
WaitResult result = null;
int res;
// 记录调用startActivityAndWait之前的时间
final long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (mWaitOption)
// 这里的mInterface也是指ActivityManagerService
result = mInternal.startActivityAndWait(null, SHELL_PACKAGE_NAME, null, intent,
mimeType, null, null, 0, mStartFlags, profilerInfo,
options != null ? options.toBundle() : null, mUserId);
res = result.result;
// 记录调用startActivityAndWait之后的时间
final long endTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
PrintWriter out = mWaitOption ? pw : getErrPrintWriter();
boolean launched = false;
switch (res)
// 启动成功
case ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS:
launched = true;
break;
...
out.flush();
// 启动成功且指定-W参数,打印启动信息
if (mWaitOption && launched)
// 打印启动结果Status: ok
pw.println("Status: " + (result.timeout ? "timeout" : "ok"));
// 打印启动状态LaunchState: COLD
pw.println("LaunchState: " + launchStateToString(result.launchState));
// 打印TotalTime:TotalTime: 370
if (result.totalTime >= 0)
pw.println("TotalTime: " + result.totalTime);
// 打印WaitTime:WaitTime: 378
pw.println("WaitTime: " + (endTime-startTime));
pw.println("Complete");
pw.flush();
-S参数会指定ActivityManagerService将待启动的应用强行停止以确保其处于冷启动的状态;
-W参数会指定ActivityManagerService以startActivityAndWait的方式启动指定应用的Activity,并根据返回的WaitResult输出启动结果,启动状态以及TotalTime和WaitTime等信息;
WaitTime是ActivityManagerShellCommand执行startActivityAndWait前后的时间差;
TotalTime是执行startActivityAndWait后返回的WaitResult中的totalTime,接下来看下WaitResult中的totalTime是如何计算出来的;
2.4 reportActivityLaunchedLocked
在1.3小节的ActivityStarter.execute方法中,我们已经分析过Activity启动完成后会通过ActivityMetricsLogger.notifyActivityLaunched记录Activity启动完成的时间,同时将Request.waitResult添加到ActivityStackSupervisor的mWaitingActivityLaunched中,等待窗口绘制完成;
[-> ActivityStackSuperVisor.java]
void reportActivityLaunchedLocked(boolean timeout, ActivityRecord r, long totalTime,
@WaitResult.LaunchState int launchState)
boolean changed = false;
for (int i = mWaitingActivityLaunched.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
WaitResult w = mWaitingActivityLaunched.remove(i);
if (w.who == null)
changed = true;
w.timeout = timeout;
if (r != null)
w.who = new ComponentName(r.info.packageName, r.info.name);
// 根据传入的totalTime来更新WaitResult的totalTime
w.totalTime = totalTime;
w.launchState = launchState;
// Do not modify w.result.
if (changed)
mService.mGlobalLock.notifyAll();
reportActivityLaunchedLocked会取出mWaitingActivityLaunched中的WaitResult,并更新totalTime;
[-> ActivityRecord.java]
/** Called when the windows associated app window container are drawn. */
void onWindowsDrawn(boolean drawn, long timestampNs)
mDrawn = drawn;
if (!drawn)
return;
final TransitionInfoSnapshot info = mStackSupervisor
.getActivityMetricsLogger().notifyWindowsDrawn(this, timestampNs);
final boolean validInfo = info != null;
final int windowsDrawnDelayMs = validInfo ? info.windowsDrawnDelayMs : INVALID_DELAY;
final @LaunchState int launchState = validInfo ? info.getLaunchState() : -1;
// The activity may have been requested to be invisible (another activity has been launched)
// so there is no valid info. But if it is the current top activity (e.g. sleeping), the
// invalid state is still reported to make sure the waiting result is notified.
if (validInfo || this == getDisplayArea().topRunningActivity())
mStackSupervisor.reportActivityLaunchedLocked(false /* timeout */, this,
windowsDrawnDelayMs, launchState);
mStackSupervisor.stopWaitingForActivityVisible(this, windowsDrawnDelayMs);
finishLaunchTickingLocked();
if (task != null)
task.setHasBeenVisible(true);
reportActivityLaunchedLocked又是何时被调用的呢?
这里又回到了1.4小节应用启动结束时间的分析:在窗口绘制完成后,会先通过ActivityMetricsLogger.notifyWindowsDrawn打印Displayed时间,然后调用ActivityStackSuperVisor.reportActivityLaunchedLocked更新WaitResult.totalTime,所以可以看到通过adb命令打印出来的TotaTime与logcat中打印的Displayed Time是一致的,至此adb shell am start -S -W命令的源码分析也到此结束了;
3. Systrace
前面两种测量方式都是针对整体的启动过程进行度量,除此之外我们可能还需要进一步细化启动过程中每个阶段的耗时,比如应用进程的创建,Application/Activity的创建,窗口布局的绘制等等,这时就需要使用Systrace来进行分析,在Android性能优化之Perfetto这篇文章中我们分析了Perfetto的使用,鉴于目前Android正在推广Perfetto,所以我们将使用Perfetto来抓取trace;
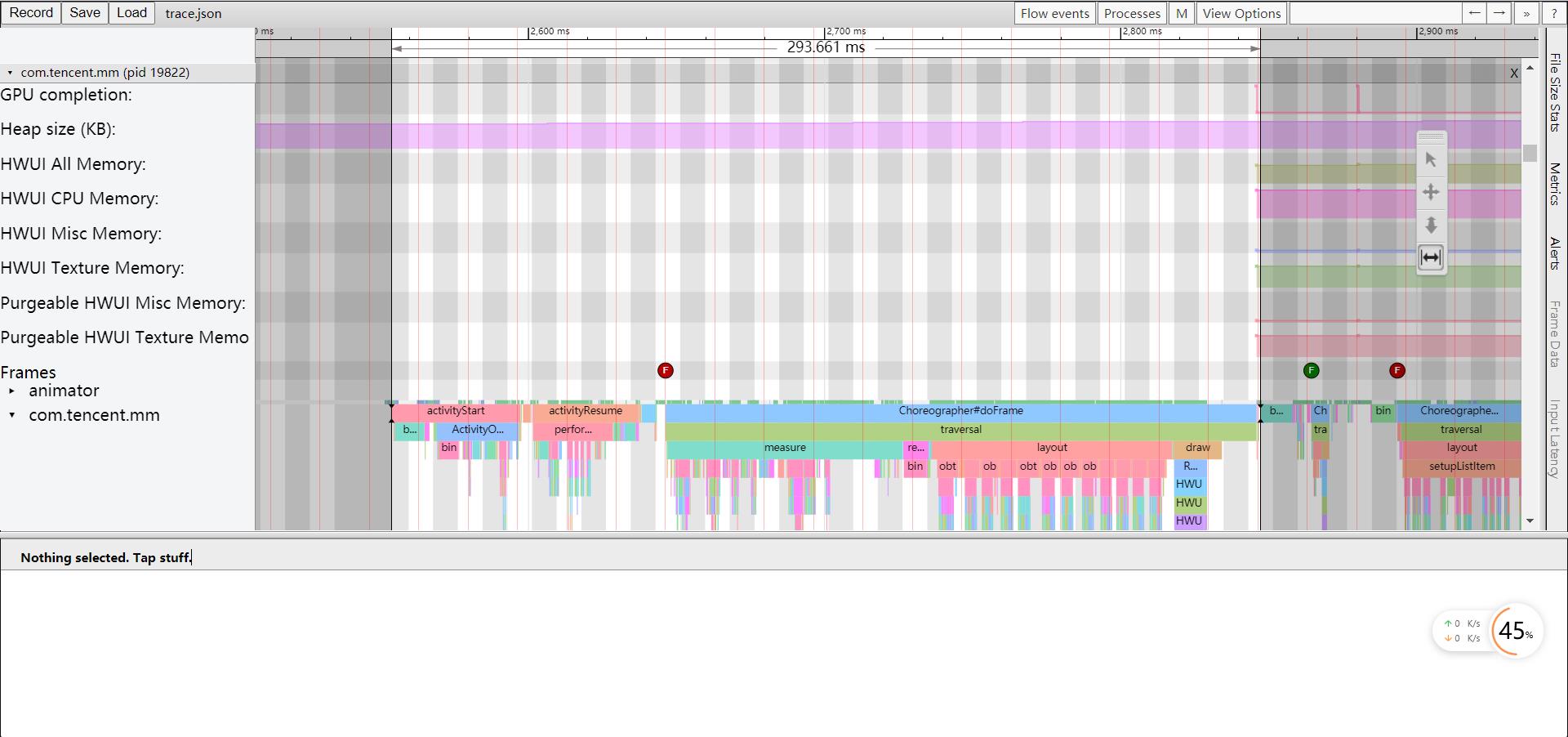
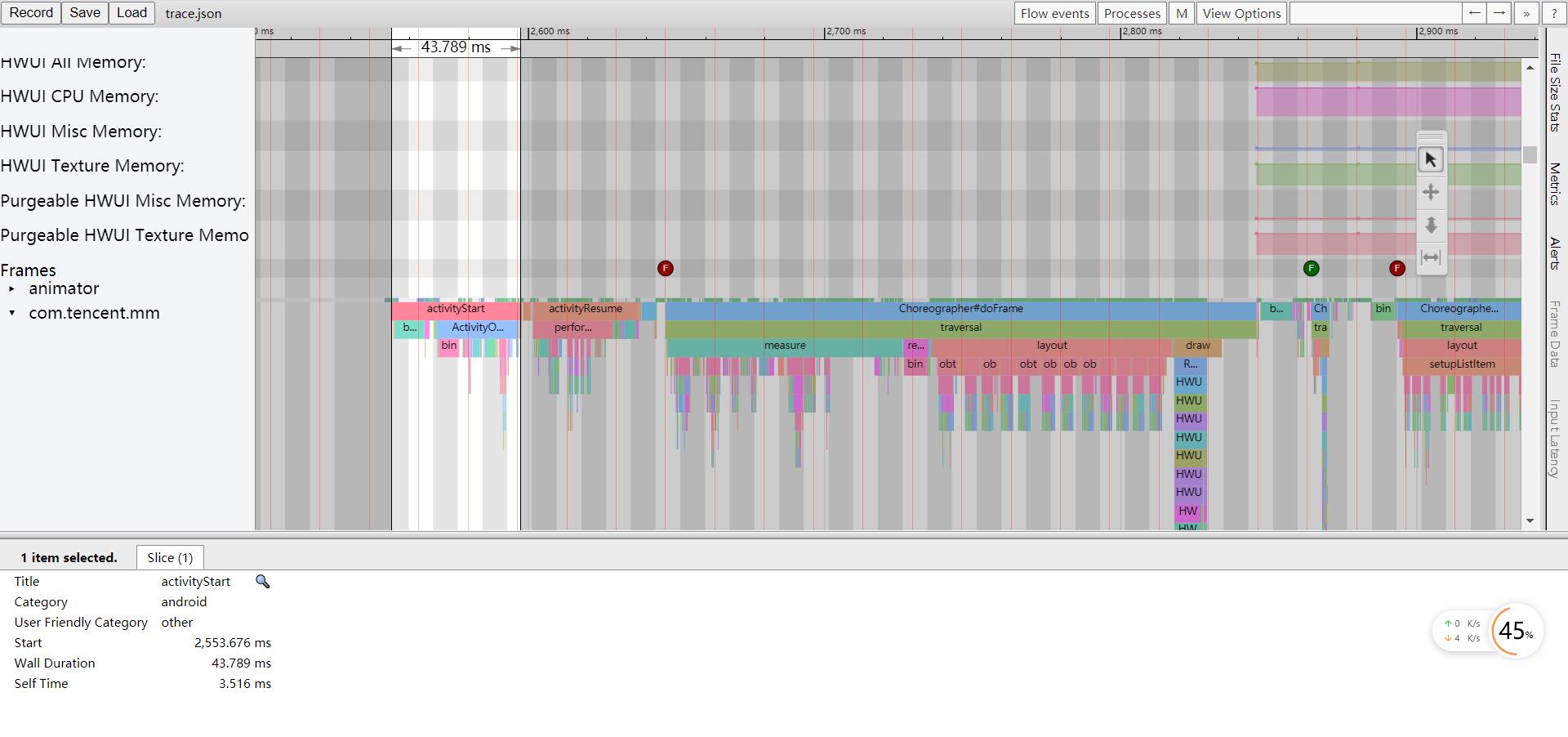
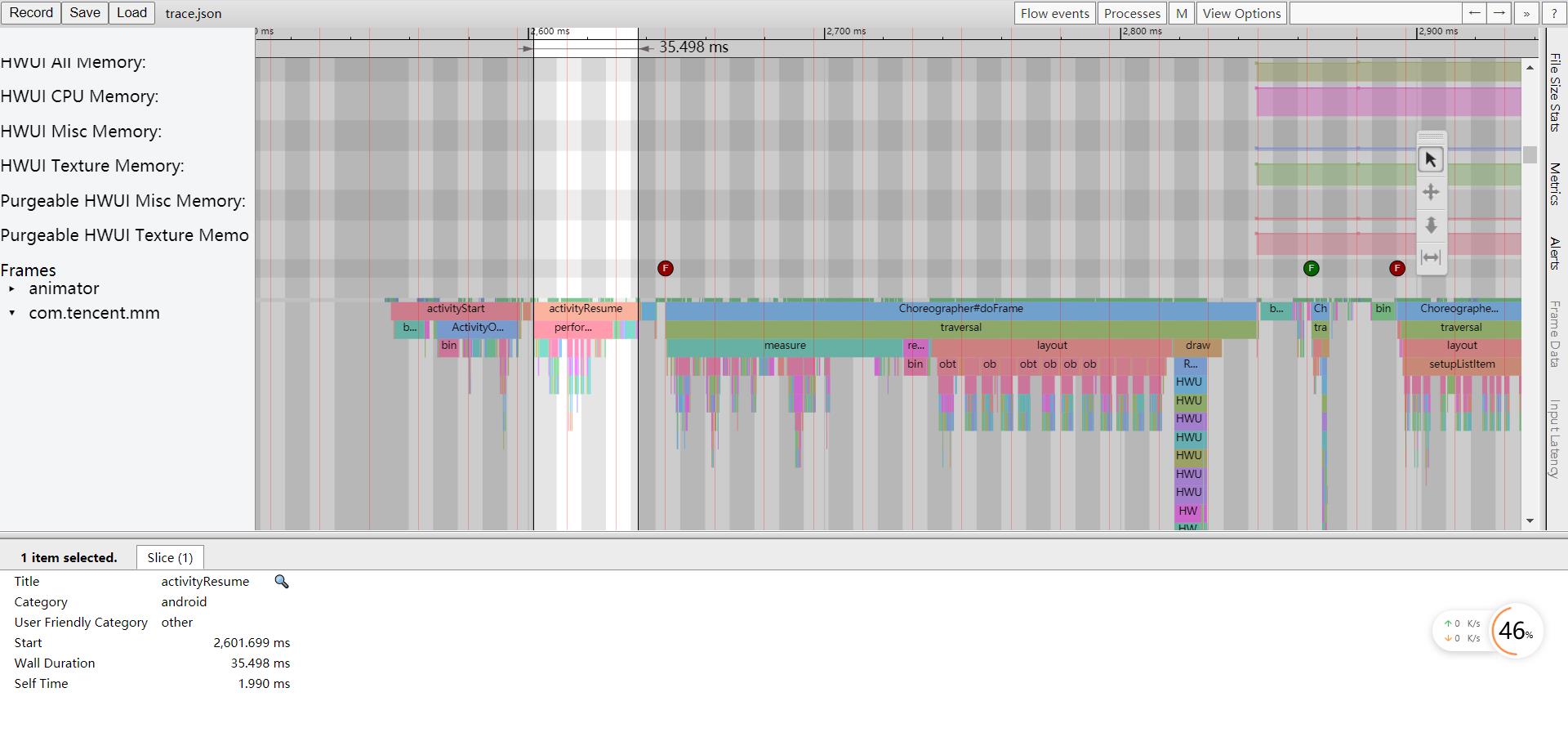
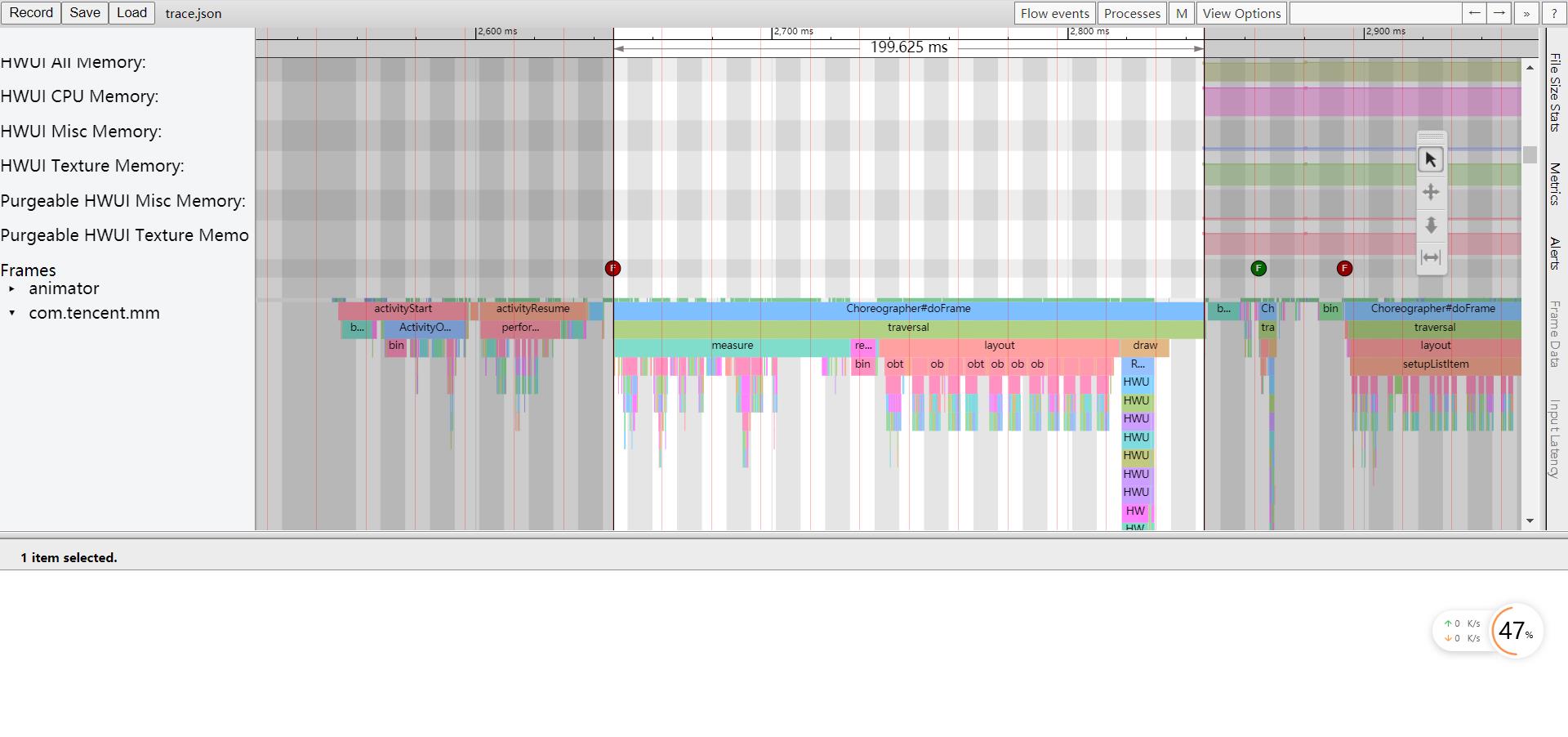
通过Systrace我们可以看到从Activity.onCreate到Activity.onResume,再到第一帧绘制完成的整体耗时,以及各个阶段的耗时情况,同时用户也可以在代码中通过Trace.beginSection()和Trace.endSection()增加trace点进行分析和排查;
4. reportFullyDrawn
5. OnPreDrawListener
[--> ViewTreeObserver.java]
/**
* Interface definition for a callback to be invoked when the view tree is about to be drawn.
*/
public interface OnPreDrawListener
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when the view tree is about to be drawn. At this point, all
* views in the tree have been measured and given a frame. Clients can use this to adjust
* their scroll bounds or even to request a new layout before drawing occurs.
*
* @return Return true to proceed with the current drawing pass, or false to cancel.
*
* @see android.view.View#onMeasure
* @see android.view.View#onLayout
* @see android.view.View#onDraw
*/
public boolean onPreDraw();
6. onWindowFocusChanged
以上是关于Android性能优化之启动耗时测量的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章