PyTorch笔记 - Recurrent Neural Network(RNN) 循环神经网络
Posted SpikeKing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PyTorch笔记 - Recurrent Neural Network(RNN) 循环神经网络相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
循环神经网络,RNN(Recurrent Neural Network):
- 记忆单元分类:RNN(Recurrent Neural Network)、GRU(Gate Recurrent Unit)、LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)
- 模型类别:单向循环、双向循环、多层单向或双向叠加
- 优缺点:
- 优点:可以处理变长序列、模型大小与序列长度无关、计算量与序列长度呈线性增长、考虑历史信息、便于流式输出、权重时不变
- 缺点:串行计算比较慢、无法获取太长的历史信息
- 应用:AI诗歌生成、文本情感分类、词法识别、机器翻译、语音识别/合成、语言模型
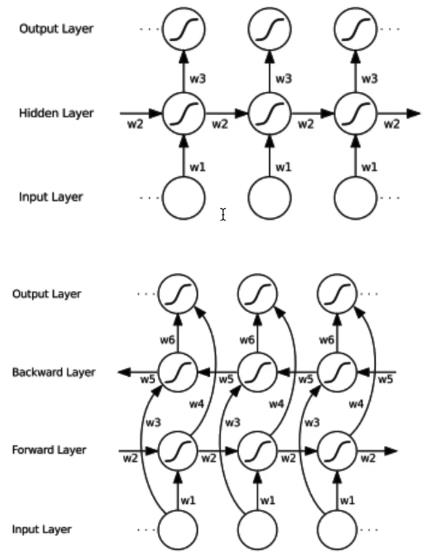
不同类型的RNN效果对比:
- delay 3,预测第1帧时,使用第3帧输入的结果,模型已经看到第1~3帧,看到更多上下文,提升预测效果。

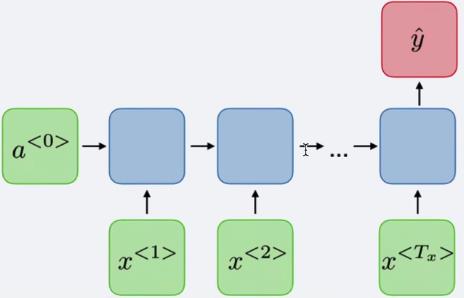
诗歌生成任务:one -> many
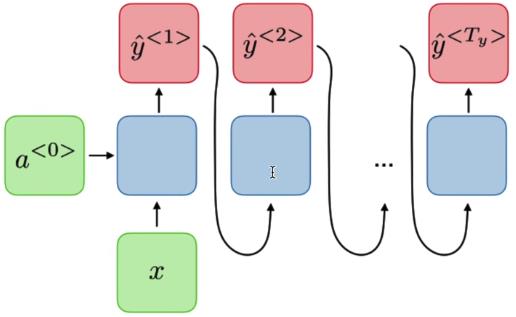
情感分类任务:many -> one
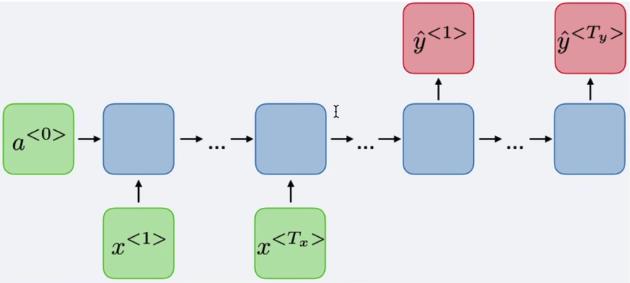
词法识别:

机器翻译:sequence to sequence,AED,Attention Based Encoder-Decoder
PyTorch:torch.nn.RNN
- 当前输入x(t),上一时刻h(t-1)是t-1时刻的隐含状态
- 激活函数tanh

RNN参数:
input_size: 输入尺寸hidden_size: 隐含层尺寸num_layers: 循环层数,RNN的堆叠层nonlinearity: 非线性激活bias: 偏置batch_first: 批次在前dropout: 抛弃层bidirectional: 双向RNN结构,输出是2 x hidden_size,头尾都有输出
输入:input和h_0,input -> (L, N, H_in)、h_0 -> (Dxnum_layer, N, H_out),默认是0填充
RNN - PyTorch函数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# step1 单向,单层RNN
# input_size, hidden_size, num_layers
single_rnn = nn.RNN(4, 3, 1, batch_first=True)
input = torch.randn(1, 2, 4) # bs * sl * fs
output, h_n = single_rnn(input) # 不输入h_0,默认是0填充
print(f'output: outp ut.shape')
print(f'h_n: h_n.shape') # 最后一行的值
# step2 双向,单层RNN
bidirectional_rnn = nn.RNN(4, 3, 1, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
bi_output, bi_h_n = bidirectional_rnn(input)
print(f'bi_output: bi_output.shape') # 2个hidden_size
print(f'bi_h_n: bi_h_n.shape') # 最后一行的值,双向中有两个层的状态
实现RNN和BiRNN:
bs, T = 2, 3 # batch_size,输入序列长度
input_size, hidden_size = 2, 3 # 输入特征大小,隐含层特征大小
torch.manual_seed(42)
input = torch.randn(bs, T, input_size) # 随机初始化一个输入特征序列
h_prev = torch.zeros(bs, hidden_size) # 初始隐含状态
# step1 调用PyTorch RNN API
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
rnn_output, state_final = rnn(input, h_prev.unsqueeze(0))
# print(f'rnn_output: \\nrnn_output')
# print(f'state_final: \\nstate_final')
# step2 手写一个rnn_forward函数, 实现RNN的计算过程
def rnn_forward(input, weight_ih, weight_hh, bias_ih, bias_hh, h_prev):
bs, T, input_size = input.shape
h_dim = weight_ih.shape[0]
h_out = torch.zeros(bs, T, h_dim)
for t in range(T):
x = input[:, t, :].unsqueeze(2) # 获取当前时刻输入特征, bs*input_size*1
# weight在不同batch中相同
w_ih_batch = weight_ih.unsqueeze(0).tile(bs, 1, 1) # bs*h_dim*input_size
w_hh_batch = weight_hh.unsqueeze(0).tile(bs, 1, 1) # bs*h_dim*h_dim
w_times_x = torch.bmm(w_ih_batch, x).squeeze(-1) # bs*h_dim
w_times_h = torch.bmm(w_hh_batch, h_prev.unsqueeze(2)).squeeze(-1) # bs*h_dim
h_prev = torch.tanh(w_times_x + bias_ih + w_times_h + bias_hh)
h_out[:, t, :] = h_prev # 更新状态
return h_out, h_prev.unsqueeze(0)
# 验证一下rnn_forward的正确性
# for k, v in rnn.named_parameters():
# print(k, v)
custom_rnn_output, custom_state_final = rnn_forward(input, rnn.weight_ih_l0, rnn.weight_hh_l0,
rnn.bias_ih_l0, rnn.bias_hh_l0, h_prev)
# print(f'custom_rnn_output: \\ncustom_rnn_output')
# print(f'custom_state_final: \\ncustom_state_final')
# step3 手写一个bidrectional_rnn_forward函数,实现双向RNN的计算资源
def bidirectional_rnn_forward(input, weight_ih, weight_hh, bias_ih, bias_hh, h_prev, \\
weight_ih_reverse, weight_hh_reverse, bias_ih_reverse, bias_hh_reverse, h_prev_reverse):
bs, T, input_size = input.shape
h_dim = weight_ih.shape[0]
h_out = torch.zeros(bs, T, h_dim*2)
forward_output = rnn_forward(input, weight_ih, weight_hh, bias_ih, bias_hh, h_prev)[0] # forward layer
backward_output = rnn_forward(torch.flip(input, dims=[1]), weight_ih_reverse, weight_hh_reverse, bias_ih_reverse, bias_hh_reverse, h_prev_reverse)[0]
h_out[:, :, :h_dim] = forward_output # 更新状态
h_out[:, :, h_dim:] = backward_output # 更新状态
return h_out, h_out[:, -1, :].reshape((bs, 2, h_dim)).transpose(0, 1)
# 验证一下bidirectional_rnn_forward的正确性
bi_rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
torch.manual_seed(42)
input = torch.randn(bs, T, input_size) # 随机初始化一个输入特征序列
h_prev = torch.zeros(2, bs, hidden_size) # 初始隐含状态
rnn_output, state_final = bi_rnn(input, h_prev)
print(f'rnn_output: \\nrnn_output')
print(f'state_final: \\nstate_final')
# for k, v in bi_rnn.named_parameters():
# print(k, v)
custom_bi_rnn_output, custom_bi_state_final = \\
bidirectional_rnn_forward(input, bi_rnn.weight_ih_l0, \\
bi_rnn.weight_hh_l0, bi_rnn.bias_ih_l0, \\
bi_rnn.bias_hh_l0, h_prev[0], \\
bi_rnn.weight_ih_l0_reverse, \\
bi_rnn.weight_hh_l0_reverse, \\
bi_rnn.bias_ih_l0_reverse, \\
bi_rnn.bias_hh_l0_reverse, h_prev[1])
print(f'custom_bi_rnn_output: \\ncustom_bi_rnn_output')
print(f'custom_bi_state_final: \\ncustom_bi_state_final')
以上是关于PyTorch笔记 - Recurrent Neural Network(RNN) 循环神经网络的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章