struts2基础——需要注意的几点
Posted 小调~
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了struts2基础——需要注意的几点相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
struts是流行和成熟的基于MVC设计模式的web应用程序框架,使用struts可以帮助我们减少运用MVC设计模型来开发web应用的时间。
目录:
一、struts2的工作原理及文件结构
二、三种访问Servlet API的方式
三、struts接收参数的三种方式
四、自定义拦截器
一、struts2的工作原理及文件结构
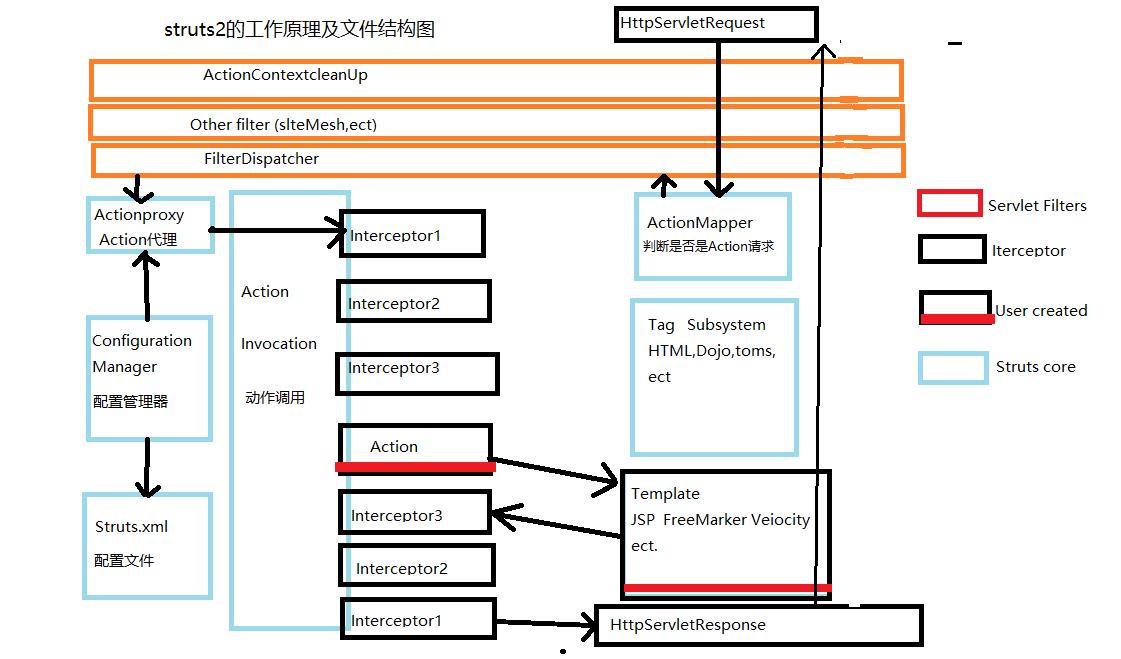
注:FilterDispatcher被替成StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter(如果使用FilterDispatcher过滤器时,程序员自己写的Filter过滤器必须放在所有过滤器的前面。而StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter过滤器可以让程序员在执行action之前写自己的Filter)
描述Struts流程:
网页产生HttpServletRequest请求->经过多个过滤器->到达ActionMaaper,判断是否是action请求(如果是)->通过StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter过滤器到达Actionproxy,一方面通过configuration Manager(配置管理器)读取struts.xml文档,另一方面创建一个实例,经过一系列的拦截器->执行到Action->返回result(对应了视图)->经过一系列的拦截器(逆序)->通过HttpServletResponse返回到用户实例。
二、三种访问servlet API的方法
struts2中没有提供任何一个servlet对象,不存在HttpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse对象。但是Struts2提供了三种方式间接的去访问Servlet API
1、ActionContext
通过ActionContext的getContext()静态方法获取ActionContext对象,通过ActionContext对象的一些getSession(),getApplication(),put()等方法,但是千万要注意的是,get获取到的对象都为Map键值对类型。com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext
1 public String execute() { 2 if ("ping".equals(username)) { 3 /* 4 * ActionContext可以获得Servlet对象 但是无法获得response响应对象获得 5 * 获得的request、session、Application 都是Map类型 6 */ 7 8 ActionContext.getContext().put("用户名", username); 9 Map session=ActionContext.getContext().getSession(); 10 Map application=ActionContext.getContext().getApplication(); 11 Map request=(Map)ActionContext.getContext().get(StrutsStatics.HTTP_REQUEST); 12 } else { 13 ActionContext.getContext().put("info", "信息"); 14 } 15 return SUCCESS; 16 }
2、ServletActionContext
通过调用ServletActionContext类的一些包括getResponse(),getRequest(),getServletContext()等在内的静态方法,这些静态方法的返回类型是和Servlet中的对象类型是一一对应的。其中getResponse()返回类型为HttpServletResponse,getRequest()返回类型为HttpServletRequest().
1 public String execute2() throws IOException { 2 if ("ping".equals(username)) { 3 HttpServletResponse response=ServletActionContext.getResponse(); 4 HttpServletRequest request=ServletActionContext.getRequest(); 5 HttpSession session=ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession(); 6 ServletContext application=ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); 7 } else { 8 9 } 10 System.out.println(username); 11 return SUCCESS; 12 }
3、实现xxxAware接口
(1)实现ServletRequestAware,ServletResponseAware,ServletSessionAware
1 public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware 2 3 4 private HttpServletRequest request; 5 //需实现方法 public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { this.request=request; } //response示例 6 public String execute1() throws IOException { 7 if ("ping".equals(username)) { 8 response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); 9 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); 10 out.print("<script type=\'text/javascript\'>alert(\'验证码输入错误!\')</script>"); 11 out.print("<script type=\'text/javascript\'>location.href=\'/index.jsp\'</script>"); 12 out.flush(); 13 out.close(); 14 } else { 15 response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); 16 PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); 17 out.print("<script type=\'text/javascript\'>alert(\'验证码输入错误!\')</script>"); 18 out.flush(); 19 out.close(); 20 } 21 System.out.println(username); 22 return SUCCESS; 23 }
(2)实现RequestWare、SessionWare、ApplicationWare等接口
public class LoginAction2 extends ActionSupport implements RequestAware,SessionAware, ApplicationAware { private Map<String, Object> request; private Map<String, Object> session; private Map<String, Object> application; //DI dependency injection //IoC inverse of control public String execute() { request.put("r1", "r1"); session.put("s1", "s1"); application.put("a1", "a1"); return SUCCESS; } @Override public void setRequest(Map<String, Object> request) { this.request = request; } @Override public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) { this.session = session; } @Override public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) { this.application = application; } }
三、struts三种接收参数方式
Struts有三种方式接收参数,且这三种方式都是自动完成赋值的setter方法。
1、使用Action的属性接收参数
代码:
struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="LoginAction" method="login" class="com.third.LoginAction1"> <result>/loginSuccess.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
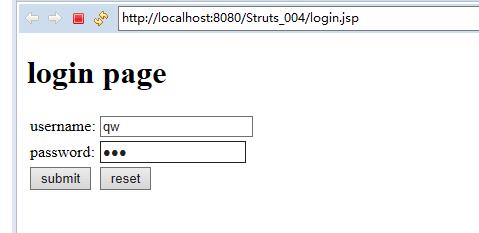
login.jsp(登陆提示页面)
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h1>login page</h1> <form action="LoginAction.action" method="post"> <table> <tr> <td>username:</td> <td><input type="text" name="username"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>password:</td> <td><input type="password" name="password"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td><input type="submit" value="submit"></td> <td><input type="reset" value="reset"></td> </tr> </table> </form> </body> </html>
loginSuccess.jsp(登陆成功提示界面)
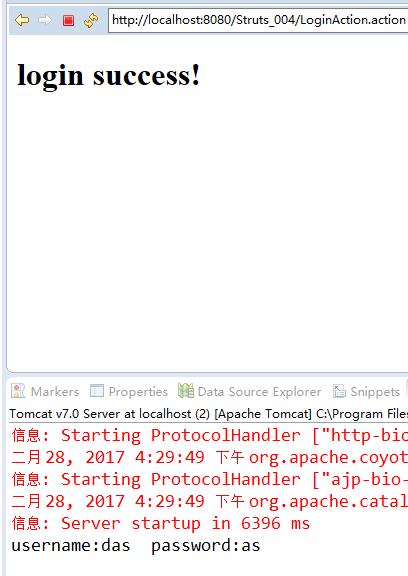
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>login success!</title> </head> <body> <h1>login success!</h1> </body> </html>
LoginAction.java
1 package com.third; 2 3 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; 4 5 public class LoginAction1 extends ActionSupport { 6 7 private String username; 8 private String password; 9 10 public String login(){
//这里能够打印出来传入的值,则说明能够自动调用setter方法完成赋值 11 System.out.println("username:"+username+" password:"+password); 12 return SUCCESS; 13 } 14 15 public String getUsername() { 16 return username; 17 } 18 19 public void setUsername(String username) { 20 this.username = username; 21 } 22 23 public String getPassword() { 24 return password; 25 } 26 27 public void setPassword(String password) { 28 this.password = password; 29 } 30 31 }
运行结果截图:
2、使用DomainModel接收参数
注:这里在表单传值是,必须指明这个属性值,到底穿个action中的那个引用,例如user.username.
代码:
struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.1//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.1.dtd"> <struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="LoginAction" method="login" class="com.third.LoginAction"> <result>/loginSuccess.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
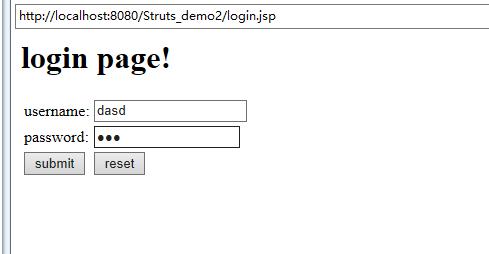
login.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP \'login.jsp\' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> <h1>login page!</h1> <form action="LoginAction.action" method="post"> <table> <tr> <td>username:</td> <td><input type="text" name="user.username"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>password:</td> <td><input type="password" name="user.password"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td><input type="submit" value="submit"></td> <td><input type="reset" value="reset"></td> </tr> </table> </form> </body> </html>
loginSuccess.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP \'loginSuccess.jsp\' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> <h1>login success!</h1> </body> </html>
User.java
package com.third; public class User { private String username; private String password; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
LoginAction.java
1 package com.third; 2 3 import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; 4 5 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; 6 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; 7 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Context; 8 9 public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport { 10 11 private User user; 12 public User getUser() { 13 return user; 14 } 15 16 public void setUser(User user) { 17 this.user = user; 18 } 19 public String login(){
//这里可以打印出传入的值的话,Action完成了自动调用setter方法赋值 20 System.out.println("username:"+user.getUsername()+" password:"+this.getUser().getPassword()); 21 return SUCCESS; 22 } 23 24 }
运行结果截图:
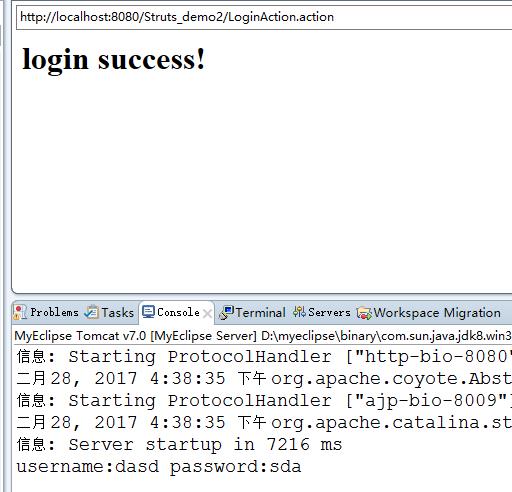
3、使用ModelDriven接受参数
struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!学好正则表达式需要注意的几点