Quartz实战源码解析Quartz分布式集群实现
Posted Herman-Hong
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Quartz实战源码解析Quartz分布式集群实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、简介
之前的文章中已对quartz的使用有了一个初步的介绍【Quartz实战】quartz-2.2.3源码分析和【Quartz实战】Quartz与Spring的集成,本篇从源码角度解析Quartz分布式集群实现。
二、Quartz集群
Quartz集群是基于数据库锁实现的,一个Quartz集群中的每个节点是一个独立的Quartz应用,它又管理着其他的节点。这就意味着你必须对每个节点分别启动或停止。Quartz集群中,独立的Quartz节点并不与另一其的节点或是管理节点通信,而是通过相同的数据库表来感知到另一Quartz应用的。集群架构:
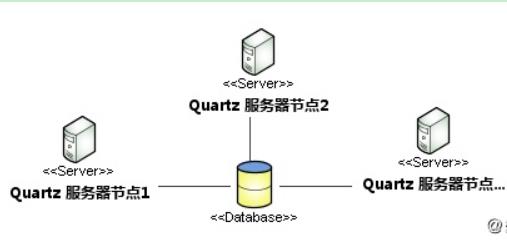
数据库表
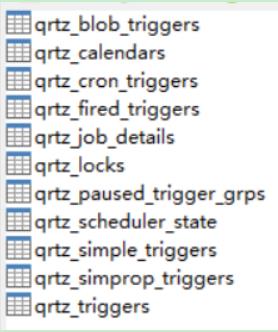
表信息介绍
qrtz_blob_triggers : 以Blob 类型存储的触发器。
qrtz_calendars存储Quartz的Calendar信息
qrtz_cron_triggers存储CronTrigger,包括Cron表达式和时区信息
qrtz_fired_triggers存储与已触发的Trigger相关的状态信息,以及相联Job的执行信息
qrtz_job_details存储每一个已配置的Job的详细信息
qrtz_locks存储程序的悲观锁的信息
qrtz_paused_trigger_grps存储已暂停的Trigger组的信息
qrtz_scheduler_state存储少量的有关Scheduler的状态信息,和别的Scheduler实例
qrtz_simple_triggers存储简单的Trigger,包括重复次数、间隔、以及已触的次数
qrtz_simprop_triggers 存储CalendarIntervalTrigger和DailyTimeIntervalTrigger两种类型的触发器
qrtz_triggers存储已配置的Trigger的信息
qrtz_locks就是Quartz集群实现同步机制的行锁表,包括以下几个锁:CALENDAR_ACCESS 、JOB_ACCESS、MISFIRE_ACCESS 、STATE_ACCESS 、TRIGGER_ACCESS
三、源码分析Quartz集群同步机制(数据库行锁表)
源码基于Quartz2.3.0。从执行任务调度QuartzSchedulerThread入手,看其run方法中获取触发器的过程
try
triggers = qsRsrcs.getJobStore().acquireNextTriggers(
now + idleWaitTime, Math.min(availThreadCount, qsRsrcs.getMaxBatchSize()), qsRsrcs.getBatchTimeWindow());
acquiresFailed = 0;
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("batch acquisition of " + (triggers == null ? 0 : triggers.size()) + " triggers");
catch (JobPersistenceException jpe)
if (acquiresFailed == 0)
qs.notifySchedulerListenersError(
"An error occurred while scanning for the next triggers to fire.",
jpe);
if (acquiresFailed < Integer.MAX_VALUE)
acquiresFailed++;
continue;
catch (RuntimeException e)
if (acquiresFailed == 0)
getLog().error("quartzSchedulerThreadLoop: RuntimeException "
+e.getMessage(), e);
if (acquiresFailed < Integer.MAX_VALUE)
acquiresFailed++;
continue;
JobStoreSupport.java
public List<OperableTrigger> acquireNextTriggers(final long noLaterThan, final int maxCount, final long timeWindow)
throws JobPersistenceException
String lockName;
if(isAcquireTriggersWithinLock() || maxCount > 1)
lockName = LOCK_TRIGGER_ACCESS;
else
lockName = null;
return executeInNonManagedTXLock(lockName,
new TransactionCallback<List<OperableTrigger>>()
public List<OperableTrigger> execute(Connection conn) throws JobPersistenceException
return acquireNextTrigger(conn, noLaterThan, maxCount, timeWindow);
,
new TransactionValidator<List<OperableTrigger>>()
public Boolean validate(Connection conn, List<OperableTrigger> result) throws JobPersistenceException
try
List<FiredTriggerRecord> acquired = getDelegate().selectInstancesFiredTriggerRecords(conn, getInstanceId());
Set<String> fireInstanceIds = new HashSet<String>();
for (FiredTriggerRecord ft : acquired)
fireInstanceIds.add(ft.getFireInstanceId());
for (OperableTrigger tr : result)
if (fireInstanceIds.contains(tr.getFireInstanceId()))
return true;
return false;
catch (SQLException e)
throw new JobPersistenceException("error validating trigger acquisition", e);
);
锁出现了,lockName
protected static final String LOCK_TRIGGER_ACCESS = "TRIGGER_ACCESS";
protected static final String LOCK_STATE_ACCESS = "STATE_ACCESS";接着看获取锁的过程
/**
* Execute the given callback having optionally acquired the given lock.
* This uses the non-managed transaction connection.
*
* @param lockName The name of the lock to acquire, for example
* "TRIGGER_ACCESS". If null, then no lock is acquired, but the
* lockCallback is still executed in a non-managed transaction.
*/
protected <T> T executeInNonManagedTXLock(
String lockName,
TransactionCallback<T> txCallback, final TransactionValidator<T> txValidator) throws JobPersistenceException
boolean transOwner = false;
Connection conn = null;
try
if (lockName != null)
// If we aren't using db locks, then delay getting DB connection
// until after acquiring the lock since it isn't needed.
if (getLockHandler().requiresConnection())
conn = getNonManagedTXConnection();
//获取锁
transOwner = getLockHandler().obtainLock(conn, lockName);
if (conn == null)
conn = getNonManagedTXConnection();
final T result = txCallback.execute(conn);
try
commitConnection(conn);
catch (JobPersistenceException e)
rollbackConnection(conn);
if (txValidator == null || !retryExecuteInNonManagedTXLock(lockName, new TransactionCallback<Boolean>()
@Override
public Boolean execute(Connection conn) throws JobPersistenceException
return txValidator.validate(conn, result);
))
throw e;
Long sigTime = clearAndGetSignalSchedulingChangeOnTxCompletion();
if(sigTime != null && sigTime >= 0)
signalSchedulingChangeImmediately(sigTime);
return result;
catch (JobPersistenceException e)
rollbackConnection(conn);
throw e;
catch (RuntimeException e)
rollbackConnection(conn);
throw new JobPersistenceException("Unexpected runtime exception: "
+ e.getMessage(), e);
finally
try
releaseLock(lockName, transOwner);
finally
cleanupConnection(conn);
/**
* Grants a lock on the identified resource to the calling thread (blocking
* until it is available).
*
* @return true if the lock was obtained.
*/
public boolean obtainLock(Connection conn, String lockName)
throws LockException
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(
"Lock '" + lockName + "' is desired by: "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
if (!isLockOwner(lockName))
//执行sql,获取锁操作
executeSQL(conn, lockName, expandedSQL, expandedInsertSQL);
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(
"Lock '" + lockName + "' given to: "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
getThreadLocks().add(lockName);
//getThreadLocksObtainer().put(lockName, new
// Exception("Obtainer..."));
else if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(
"Lock '" + lockName + "' Is already owned by: "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
return true;
org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.DBSemaphore
看下这两个的值
private String expandedSQL;
private String expandedInsertSQL;
private void setExpandedSQL()
if (getTablePrefix() != null && getSchedName() != null && sql != null && insertSql != null)
expandedSQL = Util.rtp(this.sql, getTablePrefix(), getSchedulerNameLiteral());
expandedInsertSQL = Util.rtp(this.insertSql, getTablePrefix(), getSchedulerNameLiteral());
先看下lockHandler的获取
private Semaphore lockHandler = null; // set in initialize() method...initialize方法
/**
* <p>
* Called by the QuartzScheduler before the <code>JobStore</code> is
* used, in order to give it a chance to initialize.
* </p>
*/
public void initialize(ClassLoadHelper loadHelper,
SchedulerSignaler signaler) throws SchedulerConfigException
if (dsName == null)
throw new SchedulerConfigException("DataSource name not set.");
classLoadHelper = loadHelper;
if(isThreadsInheritInitializersClassLoadContext())
log.info("JDBCJobStore threads will inherit ContextClassLoader of thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
initializersLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
this.schedSignaler = signaler;
// If the user hasn't specified an explicit lock handler, then
// choose one based on CMT/Clustered/UseDBLocks.
if (getLockHandler() == null)
// If the user hasn't specified an explicit lock handler,
// then we *must* use DB locks with clustering
if (isClustered())
setUseDBLocks(true);
if (getUseDBLocks())
if(getDriverDelegateClass() != null && getDriverDelegateClass().equals(MSSQLDelegate.class.getName()))
if(getSelectWithLockSQL() == null)
String msSqlDflt = "SELECT * FROM 0LOCKS WITH (UPDLOCK,ROWLOCK) WHERE " + COL_SCHEDULER_NAME + " = 1 AND LOCK_NAME = ?";
getLog().info("Detected usage of MSSQLDelegate class - defaulting 'selectWithLockSQL' to '" + msSqlDflt + "'.");
setSelectWithLockSQL(msSqlDflt);
getLog().info("Using db table-based data access locking (synchronization).");
setLockHandler(new StdRowLockSemaphore(getTablePrefix(), getInstanceName(), getSelectWithLockSQL())); //handler赋值
else
getLog().info(
"Using thread monitor-based data access locking (synchronization).");
setLockHandler(new SimpleSemaphore());
仿佛看到了sql以及lockHandler的赋值
new StdRowLockSemaphore(getTablePrefix(), getInstanceName(), getSelectWithLockSQL())
// MISC CONSTANTS
String DEFAULT_TABLE_PREFIX = "QRTZ_";
getInstanceName() //配置文件中的实例名
getSelectWithLockSQL() //这里为null,由于采用的不是mssql;
public StdRowLockSemaphore(String tablePrefix, String schedName, String selectWithLockSQL)
super(tablePrefix, schedName, selectWithLockSQL != null ? selectWithLockSQL : SELECT_FOR_LOCK, INSERT_LOCK);
public static final String SELECT_FOR_LOCK = "SELECT * FROM "
+ TABLE_PREFIX_SUBST + TABLE_LOCKS + " WHERE " + COL_SCHEDULER_NAME + " = " + SCHED_NAME_SUBST
+ " AND " + COL_LOCK_NAME + " = ? FOR UPDATE";
public static final String INSERT_LOCK = "INSERT INTO "
+ TABLE_PREFIX_SUBST + TABLE_LOCKS + "(" + COL_SCHEDULER_NAME + ", " + COL_LOCK_NAME + ") VALUES ("
+ SCHED_NAME_SUBST + ", ?)";
public DBSemaphore(String tablePrefix, String schedName, String defaultSQL, String defaultInsertSQL)
this.tablePrefix = tablePrefix;
this.schedName = schedName;
setSQL(defaultSQL);
setInsertSQL(defaultInsertSQL);
其中有两个sql,两个锁名称
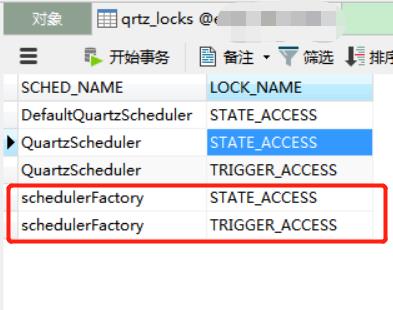
可以看出采用了Quartz集群采用了悲观锁的方式对triggers表进行行加锁, 以保证任务同步的正确性。当线程使用上述的SQL对表中的数据执行操作时,数据库对该行进行行加锁; 于此同时, 另一个线程对该行数据执行操作前需要获取锁, 而此时已被占用, 那么这个线程就只能等待, 直到该行锁被释放。
回到
private String expandedSQL;
//SELECT * FROM QRTZ_LOCKS WHERE SCHED_NAME = 'schedulerFactory' AND LOCK_NAME = ? FOR UPDATE
private String expandedInsertSQL;
//INSERT INTO QRTZ_LOCKS (SCHED_NAME, LOCK_NAME) VALUES ('schedulerFactory', ?);
private void setExpandedSQL()
if (getTablePrefix() != null && getSchedName() != null && sql != null && insertSql != null)
expandedSQL = Util.rtp(this.sql, getTablePrefix(), getSchedulerNameLiteral());
expandedInsertSQL = Util.rtp(this.insertSql, getTablePrefix(), getSchedulerNameLiteral());
两个的值就可以确定了,看下获取锁的过程,这里lockName为"TRIGGER_ACCESS"
org.quartz.impl.jdbcjobstore.StdRowLockSemaphore#executeSQL
/**
* Execute the SQL select for update that will lock the proper database row.
*/
@Override
protected void executeSQL(Connection conn, final String lockName, final String expandedSQL, final String expandedInsertSQL) throws LockException
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
SQLException initCause = null;
// attempt lock two times (to work-around possible race conditions in inserting the lock row the first time running)
int count = 0;
do
count++;
try
ps = conn.prepareStatement(expandedSQL);
ps.setString(1, lockName);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled())
getLog().debug(
"Lock '" + lockName + "' is being obtained: " +
Thread.currentThread().getName());
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (!rs.next())
getLog().debug(
"Inserting new lock row for lock: '" + lockName + "' being obtained by thread: " +
Thread.currentThread().getName());
rs.close();
rs = null;
ps.close();
ps = null;
ps = conn.prepareStatement(expandedInsertSQL);
ps.setString(1, lockName);
int res = ps.executeUpdate();
if(res != 1)
if(count < 3)
// pause a bit to give another thread some time to commit the insert of the new lock row
try
Thread.sleep(1000L);
catch (InterruptedException ignore)
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
// try again ...
continue;
throw new SQLException(Util.rtp(
"No row exists, and one could not be inserted in table " + TABLE_PREFIX_SUBST + TABLE_LOCKS +
" for lock named: " + lockName, getTablePrefix(), getSchedulerNameLiteral()));
return; // obtained lock, go
catch (SQLException sqle)
//Exception src =
// (Exception)getThreadLocksObtainer().get(lockName);
//if(src != null)
// src.printStackTrace();
//else
// System.err.println("--- ***************** NO OBTAINER!");
if(initCause == null)
initCause = sqle;
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled())
getLog().debug(
"Lock '" + lockName + "' was not obtained by: " +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + (count < 3 ? " - will try again." : ""));
if(count < 3)
// pause a bit to give another thread some time to commit the insert of the new lock row
try
Thread.sleep(1000L);
catch (InterruptedException ignore)
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
// try again ...
continue;
throw new LockException("Failure obtaining db row lock: "
+ sqle.getMessage(), sqle);
finally
if (rs != null)
try
rs.close();
catch (Exception ignore)
if (ps != null)
try
ps.close();
catch (Exception ignore)
while(count < 4);
throw new LockException("Failure obtaining db row lock, reached maximum number of attempts. Initial exception (if any) attached as root cause.", initCause);
获取锁的过程也值得细细品味。获取行锁的方式,insert是保证获取锁,因为select for update失败也可能没有这条数据。
如果已经有lockName代表的行,直接加锁,如果没有插入。但是在加锁时或插入时有可能失败,失败则重试,重试如果超过一定次数就会直接抛出异常。

0.调度器线程run()
1.获取待触发trigger
1.1数据库LOCKS表TRIGGER_ACCESS行加锁
1.2读取JobDetail信息
1.3读取trigger表中触发器信息并标记为"已获取"
1.4commit事务,释放锁
2.触发trigger
2.1数据库LOCKS表STATE_ACCESS行加锁
2.2确认trigger的状态
2.3读取trigger的JobDetail信息
2.4读取trigger的Calendar信息
2.3更新trigger信息
2.3commit事务,释放锁
3实例化并执行Job
3.1从线程池获取线程执行JobRunShell的run方法
四、总结
一个调度器实例在执行涉及到分布式问题的数据库操作前,首先要获取QUARTZ2_LOCKS表中对应当前调度器的行级锁,获取锁后即可执行其他表中的数据库操作,随着操作事务的提交,行级锁被释放,供其他调度器实例获取。
以上是关于Quartz实战源码解析Quartz分布式集群实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章