Informatica常用组件使用方法
Posted Jan丶X
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Informatica常用组件使用方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
表1中列出的是informatica中的所有组件。不会在本文档中出现的会在组件名后标出。
表1
Lookup
1.1 概要描述
获得一个关联的值。例如:源里包含employee ID,但你还需要employee name。
用于计算的植。例如:只是汇率或者个人所得税之类的固定数值,不是计算得出来的数据。
Update slowly changing dimension tables。主要是根据条件查出原表,若查出了,就把自己添加的标志位设为真,否则就设置为假。
1.2 Connected or unconnected
Connected 和 unconnected 的transformations的输入和输出是不同的,不同点如表2列出的。
表2
Connected
下面是Integration Service处理connected Lookup transformation的过程:
1. 一个connected Lookup transformation通过pipeline从其他的transformation获得输入值。
2. 为每个输入行,Integration Service会通过lookup ports 和 condition从源或者缓存中查询。
3. 如果组件没有使用缓存或者使用的静态缓存,Integration Service会使用lookup query来返回值。
4. 如果组件使用的动态缓存,当Integration Service在缓存找不到这行,它会把这行插入到缓存中。当Integration Service找到这行,它会修改这行在缓存中或者什么都不做。它标记这行是插入、修改或者是不做变动。
5. Integration Service从查询中返回值到下一个transformation。
如果transformation使用动态缓存,你可以把这行通过Filter 或者 Router transformation来过滤后在到目标中。
unconnected
l 你可以在一个mapping中调用这个Lookup transformation多次。
l 下面的步骤描述了Integration Service处理一个unconnected Lookup transformation的过程:
1. 一个unconnected Lookup transformation从另一个transformation的一个:LKP表达式的结果中获得输入值,例如一个Update Strategy transformation。
2. Integration Service通过transformation 中的lookup ports 和 condition来查询。
3. Integration Service返回一个值到Lookup transformation 的return port 中。
4. Integration Service把值返回到:LKP表达式中。
l 步骤
1. 添加input ports。
2. 添加查询条件。
3. 指定返回值。
4. 从其他的组件中调用该lookup。
l 用途
unconnected lookups多数用于:
1. 在一个表达式测试一个lookup的值。
2. 在查询的基础上过滤。
3. 标记行基于查询的结果,例如:updating slowly changing dimension tables。
4. 调用同一个查找多次在一个mapping中。
1.3 Relational or flat file lookup
当你在建立一个Lookup transformation时,你可以选择查询flat file或者relational table。
Relational
你可以通过SQL的来override默认的SQL,这样可以你可以加where或者查询多个表。
flat file
使用下面选项在使用flat file时:
1. 指定源是indirect files的。
2. 使用sorted输入。
Tips
l 使用这些技巧在你配置一个Lookup transformation的时候:
l 给被用于查询条件的列加一个索引。
l 把=号放在条件的第一位。
l 查询的时候,完全加载小的表。
l 在数据库中Join tables比使用查询要高校的多。
l 为静态cache设置固定的大小。
l 使用:LKP来调用unconnected Lookup transformations。
1.4 Cached or uncached
有时,你可以在使用lookup组件查询表的时候,把组件设置成Cached 的来提高session的速度。如果你选择了Cached ,你可以选择使用动态的还是静态的。默认的是使用静态的。
Cached
我们可以在一个lookup组件中为要查询的表配置cache。当第一行数据进入lookup组件的时候,Integration Service会在内存为它建立一个cache。它分配内存基于你在组件或者session的属性中配置的数量。Integration Service把条件值保存索引cache,把output值保存在数据cache。Integration Service会为每一条进入这个组件的行查询cache。
Integration Service也同样会建立cache files用$PMCacheDir(相对路径,在consol中可以配置)中默认的。如果数据不适合内存cache时,Integration Service把超出的数据保存到cache files中。当seesion结束,Integration Service会释放cache记忆和删除cache files,除非你配置组件使用持久化的cache。
如果你使用flat file lookup,Integration Service总是会把它放在cache中。如果你配置flat file lookup为sorted input,Integration Service不会把它放入cache,如果条件类不是分组的。如果这些列是分组的,但是没有sorted,Integration Service会处理这个查询的方式和没有配置sorted input一样。
当你配置了lookup cache,你可以配置如下cache选项:
Building caches:你可以配置session建立多个cache用串行或者并行。当你建立串行的cache时,Integration Service会按照源行进入的顺序建立cache。当你建立并行的cache时,Integration Service不会等第一行进入Lookup transformation,就会建立cache。代替的是建立多个并行的cache。
Persistent cache:你可以保存lookup cache files并重用他们在Integration Service调用一个配置使用该cache的Lookup transformation。
Integration Service 对Persistent Caches的处理:
Recache from source:当持久化的cache不是同步的时候,你可以配置Lookup transformation重新建立新的cache。
Static cache:你可以为所有的lookup source配置一个静态,或者只读的cache。默认的,Integration Service建立静态的cache。它为所有进入组件的lookup file或者 table 以及 looks up values建立cache。当条件为真的时候,Integration Service从cache中返回一个值。
Dynamic cache:为一个target table或者flat file source建立cache,并且向cache中插入新的行或者修改现有的行,当使用动态cache。在cache中,Integration Service动态的插入或者修改数据并且把数据传到目标中。
Shared cache:你可以共享cache在多个组件之间。你可以共享一个匿名的cache在一张mapping中。你可以共享一个有名的cache在同一个或者不同的mapping中。
当你没有为Lookup transformation配置cache,Integration Service为每一个输入行查询查询表。结果和处理过程是同样的,不论你是否设置cache。然而,使用cache可以改善session的性能。当被查询的表很大的时候可以使用cache最大的优化性能。
Cache Comparison
uncached lookup, static cache, dynamic cache的区别:
Aggregator Transformation
Transformation type: Active 、Connected
功能概述:
可以使用该组件可以进行汇总计算,如平均值和求和等。Aggregator transformation和Expression transformation不一样,在Aggregator transformation中执行计算是要分组的。Expression transformation只允许你执行计算在row-by-row的基础上的。
当你使用transformation建立汇总表达式的时候,使用条件语句来过滤行,比SQL语句要灵活的多。
Integration Service执行汇总计算,只读和储存必要的数据组和行数据在aggregate cache中的。
Ports in the Aggregator Transformation (Aggregator Transformation中的port)
配置Aggregator Transformation中的port,完成如下的任务:
输入表达式在任何output port,使用条件或者非汇总函数在该port中。
建立多行汇总的output port。
配置任何input, input/output, output, 或者variable port作为group port。
改进性能,为后来的组件只连接必要的input/output port,减少数据cache的大小。
使用变量port作为本地变量。
建立一个连接像一个表达式一样。
Components of the Aggregator Transformation(汇总组件的组成)
汇总组件是一个active的组件,改变pipeline中的行数。汇总组件拥有下面的构成和选项:
汇总表达式(Aggregate expression):在一个output port中输入。可以包括非汇总表达式和条件子句。
汇总函数(Aggregate Functions)
你可以把一个汇总函数嵌套在另一个汇总函数中。
Transformation语言包括如下的汇总函数:
l AVG
l COUNT
l FIRST
l LAST
l MAX
l MEDIAN
l MIN
l PERCENTILE
l STDDEV
l SUM
l VARIANCE
当你使用这些函数的时候,你必须在一个汇总组件的表达式中。
嵌套汇总函数(Nested Aggregate Functions):
你可以在一个汇总组件中的不同的output port中包括多个单层的函数(相对于嵌套函数)和嵌套的函数。但是你不能把他们放到一个汇总组件中。因此,如果一个汇总组件中的任何一个output port中包括一个单层函数,你不可以使用一个嵌套的函数在任何其他的port中在这个汇总组件中。当你在一个汇总组件中同时包括单层函数和嵌套函数,Designer会标记mapping或者mapplet为不正确的。如果你需要同时建立单层函数和嵌套函数,请建立在不同的汇总组件中。
条件子句(Conditional Clauses):
使用条件子句在汇总组件中,为了减少用在汇总的行数。条件子句可以是任何可以返回真或假的子句。
例如:你使用如下的表达式来计算出所有commissions大于QUOTA的员工总的commissions:
SUM( COMMISSION, COMMISSION > QUOTA )
非汇总函数(Non-Aggregate Functions)
你也可以使用非汇总函数在汇总表达式中。例如下面的表达式:
IIF( MAX( QUANTITY ) > 0, MAX( QUANTITY ), 0))
汇总函数中的Null值(Null Values in Aggregate Functions)
当你配置Integration Service时,你可以选择怎样处理NULL值在一个汇总函数中。你可以选择处理汇总函数中的NULL值,当作NULL或者零。默认的Integration Service处理在汇总函数的NULL值为NULL。
分组port(Group by port):指定如何建立组。这个port可以是任何类型的port,如:input, input/output, output, 或者 variable port。当数据分组后,汇总组件返回每组中最后一行,如果没有其他的指定。
汇总组件让你定义组汇总,性能比汇总所有输入的值好。例如:你查一个区域的总销售额比查询整个公司的要快。
为汇总表达式定义一个组,选择适当的input, input/output, output, 和 variable ports在汇总组件中。你可以选择多个port来建立一个新的唯一的联合的组。Integration Service会为定义的每个组进行汇总。
当你把数据分组了,Integration Service会为每一个组返回一个值。如果你没有,Integration Service会为所有输入的port输出一行。
当你在汇总组件中使用port分成多个组的时候,Integration Service使用port的序号来决定按照哪个组的顺序。例如:例如使用ITEM_ID 和 QUANTITY分组与使用QUANTITY 和 ITEM_ID是不同的。下面的汇总组件用STORE_ID 和 ITEM分组:
Integration Service 会执行如下的分组来执行汇总计算。
Integration Service会让每组最后一行返回,按照上面的汇总结果,可以得到如下:
使用默认值来代替分组中的null。中央Integration Service允许包括null的输入的汇总。
例如:如果你定义一个默认值为‘Misc’在物品列,Integration Service会把null用Misc代替。
排序后的输入(Sorted input):使用该种方法可以改善session的性能。使用Sorted input,你必须使数据通过组件的排序和分组的port相应,用升序或者降序。
条件(Conditions)
不要使用排序后的输入,如果以下两种情况任意一个为真:
汇总表达式中使用嵌套函数。
Session使用incremental汇总。
预先排序的数据(Pre-Sorting Data)
数据必须按照如下来排序:
在汇总分类使用的port,输入的数据要与它的顺序一致。
在session的配置中使用同一个顺序。如果数据不是严格按照session的排序的升序或者降序,Integration Service让这个session失败。例如:当你用French排序命令配置session,汇总组件也要用French排序命令。
对于关系和文件源,使用Sorter transformation排序在汇总组件之前。你可以放置这个Sorter transformation到任何地方,只要在连接到汇总组件之前没有其他组件改变他的排列顺序。汇总组件中的分组用的port的顺序必须要和Sorter transformation中出现的顺序一致。
如果session使用关系数据库作为源,你也可以使用Source Qualifier transformation的Number of Sorted Ports来进行排序。
例:使用ITEM_NAME来进行排序,
Sorter transformation排序后的结果如下:
汇总cache(Aggregate cache):Integration Service会把数据保存在汇总cache中直到汇总计算结束。它把组的值保存在索引cache中、把行数据保存在数据cache中。如果汇总的数据太大,cache中装不下,Integration Service保存多出的数据到cache files。你可以配置索引和数据cache在汇总组件中或者在session的属性中。或者你也可以在Integration Service决定cache大小在运行的时候。注意:在使用的数据是排序后的,Integration Service不使用cache的。
提示(Tips )
使用下列的方法来优化汇总组件的性能。
使用排序后的输入来减少汇总cache的使用。
限制input/output或者output ports的连接数量。
在汇总之前过滤。
汇总组件问题解决(Troubleshooting Aggregator Transformations)
我使用排序后的输入,但是workflow使用的时间和以前一样。
你可能使用排序后的输入,以以下任意一种方式:
汇总表达式包括嵌套汇总函数。
Session使用增量汇总。
源数据是data driven。
一个session使用一个汇总组件造成性能低下。
workflow 期间,Integration Service可能过多的把内存分页拿到硬盘上。你可以使用提高transformation属性中的索引cache和数据cache的大小来提高session的性能。
我输入了一个覆盖的cache路径在汇总组件中,但是Integration Service保存session incremental aggregation files到其他某处。
你可以覆盖transformation cache directory在一个session级别。Integration Service会记录cache directory在session log中。你也可以检查session属性为一个cache directory。
Expression Transformation
Transformation type: Passive 、Connected
使用Expression transformation在一行中计算值,在你写入目标之前。例如,你需要校准员工的工资,连接first和last名字,或者把string转换为number。使用Expression transformation执行任何非汇总的计算。你也可以使用Expression transformation来测试条件语句在你输出结果到目标表或者其他transformations。
计算值:
使用Expression transformation为一行计算,你必须包括以下ports:
被使用在计算的port必须是Input 或者 input/output ports。例如:当为一个定单计算总价格时,等于被订的物品数量乘单价,这个port是input 或者input/output的。一个port是供给给单价的,另一个是供给给订的数量的。
Output port是给表达式的。你为output port输入表达式像配置一个选项一样。返回值需要和表达式的返回值式匹配的。如果想获得更多关于表达式的信息,请查看下节Working with Expressions。
加入多个计算:
在一个Expression transformation中,你可以输入多个表达式。只要为每一个output port输入一个表达式,你可以创建任意多的output port在这个transformation中。用这种方法,比分开建立多个transformations要好。
例如:你可能想从员工薪水中计算一些种类的代扣税,如:本地和联邦的个人所得税,社保和医保。所有的这些计算都需要员工的工资,税种,和/或者相应的税率,你可以建立一个Expression transformation,把工资和税种作为input/output ports,并且建立output port为每个需要的计算。
Working with Expressions (使用表达式)
你可以在一些transformations中使用表达式编辑器来输入表达式。建立表达式可以使用如下的函数:
Transformation language functions。类SQL 函数被设计用来操作普通的表达式。
用户自定义函数是你在PowerCenter中使用transformation language functions建立的。
订制函数是你使用订制函数API建立的。
Using the Expression Editor (使用表达式编辑器)
使用表达式编辑器来建立一个类SQL的语句。虽然你可以用手来建立表达式,但是你应该使用point-and-click方法来建立。选择函数,port,变量,和操作符从point-and-click界面,来减低你建立表达式时的错误率。
Entering Port Names into an Expression (输入一个port名到表达式)
对于一个连接的transformations,如果你使用port名在一个表达式里,Designer会修改表达式,当你在该transformation中修改该port名时。例如:你写了一个有效的表达式用来判断两个日期的不同,Date_Promised 和Date_Delivered。后来,你把Date_Promised port的名字改为Due_Date,Designer也会把表达式中的名字改为Due_Date。
你可以为一个表达式添加注释,来给这个表达式添加描述信息,或者指定一个URL到一个业务文档关于这个表达式的。
l 在表达式中使用--或者//来添加注释。
l 单击Comments按钮,在注释对话框中添加。
Validating Expressions (验证表达式)
使用Validate按钮来验证表达式。如果你不验证一个表达式,Designer会在你关闭它的时候来验证。如果表达式不合法的,Designer会发出警告。你可以保存错误的表达式或者改正它。你不能运行一个有错误表达式的mapping在session中。
Expression Editor Display (表达式编辑器的显示)
表达式编辑器可以使用不同的颜色来标记表达式的语法,以便很好的阅读。如果你有最新的Rich Edit,riched20.dll,安装到了系统,表达式显示表达式函数为兰色,注释式灰色,引用的字符串式绿色。
你可以调整编辑器的大小。用拖拽边的方法来扩大对话框。Designer保存这个新的大小像客户机设置一样。
Adding Expressions to an Output Port (添加一个表达式到Output Port)
1. 在transformation中,选择port并打开表达式编辑器。
2. 输入表达式。
3. 添加注释。
4. 验证表达式。
Filter Transformation
Filter Transformation Overview
Transformation type: Active 、Connected
功能:根据条件过滤到不符合条件的行。
你可以使用SALARY > 30000来过滤掉SALARY小于等于3000的行。
过滤条件:过滤条件就是可以返回真或假的表达式。可以是一表达式,也可以是几个表达式,但表达式之间是与关系。如果你在条件中输入的是SALARY > 30000 和 SALARY < 100000,他们就等于SALARY > 30000 AND SALARY < 100000。
提示:
在mapping中,使用Filter transformation越早越好。
尽量使用Source Qualifier transformation来过滤数据。
Joiner Transformation
1.5 Transformation type:
Active 、Connected
1.6 功能:
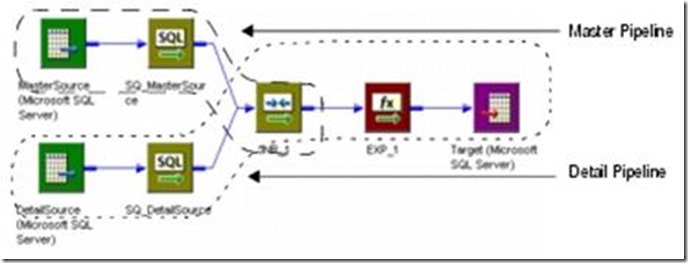
你可以使用本组件连接两个不同源的关系表或者file系统。当然你也可以连接来自同一个源的数据(一般使用Source Qualifier Transformation,在下面会介绍使用本组件连接来自同一个源的数据的情况)。本组件一次只能连接两个源,如果有多个源就使用多个该种组件,直到你把所有你想连接的源都连接了为止。影响连接结果的有,连接的条件,连接的类型和输入的源。
图1显示的是一张mapping 的一个 Joiner transformation的master 和 detail pipelines。
图1
1.7 不能使用Joiner transformation的两种情况:
l input pipeline中包括Update Strategy transformation情况下,你不能使用本组件。
l 你不能直接把Sequence Generator transformation连接到本组件。
1.8 如何让一个Joiner Transformation工作:
如果你想让Joiner Transformation工作,你需要以下步骤:
1. 配置组件属性。
2. 配置连接条件。
3. 配置连接条件。
4. 配置session为sorted 或者 unsorted input。
5. 配置transaction scope。
1.9 属性:
图2显示的是Joiner Transformation 的Properties Tab:
图2
表1是Joiner Transformation 的所有属性(Properties):
表1
1.10 怎样设置master 和 detail以最佳的性能:
在session运行中,Integration Service会使用master源的每一行来和detail源进行比较。为了达到最佳性能,对于无序的输入源,使用行数最少的作为master;对于有序的,使用duplicate key values最少的为master。默认的,Integration Service会把第一个被引入该组件的pipeline设置为detail。你可以在Ports tab 中的ports中的M column来更改。
1.11 定义条件:
你可以基于来自于两个输入源的port建立一个或者多个条件。例如:有两个输入源表EMPLOYEE_AGE和EMPLOYEE_POSITION,它们都包含一个字段employee ID是number型的,你就可以建立如下的连接条件:EMP_ID1 = EMP_ID2
1.12 连接类型:
Joiner transformation和SQL 的join很像,只是它的数据可以来自于不同类型的源。
下面介绍组件提供的几种连接类型:
Normal Join:
Integration Service会去掉所有master 和 detail中不符合条件的数据。
例如:你有两个源叫PARTS_SIZE 和 PARTS_COLOR,并且有如下的数据:
PARTS_SIZE (master source)
PARTS_COLOR (detail source)
连接条件如下:
PART_ID1 = PART_ID2
结果如下:
下面是等价的语句:
SELECT * FROM PARTS_SIZE, PARTS_COLOR WHERE PARTS_SIZE.PART_ID1 = PARTS_COLOR.PART_ID2
Master Outer Join
保留所有detail的行,并且和master进行匹配。它抛弃不匹配的master行。
以和上面同样的条件会得到如下的结果:
| 以上是关于Informatica常用组件使用方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章 Informatica PowerCenter 常用转换组件一览表 Informatica PowerCenter 常用转换组件一览表 |