MicroPython RP2040读取DHT11温湿度传感器数据+ 0.96“I2C oled显示
Posted perseverance52
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MicroPython RP2040读取DHT11温湿度传感器数据+ 0.96“I2C oled显示相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【MicroPython RP2040】读取DHT11温湿度传感器数据+ oled显示
- ✨本示例基于
Thonny平台开发。

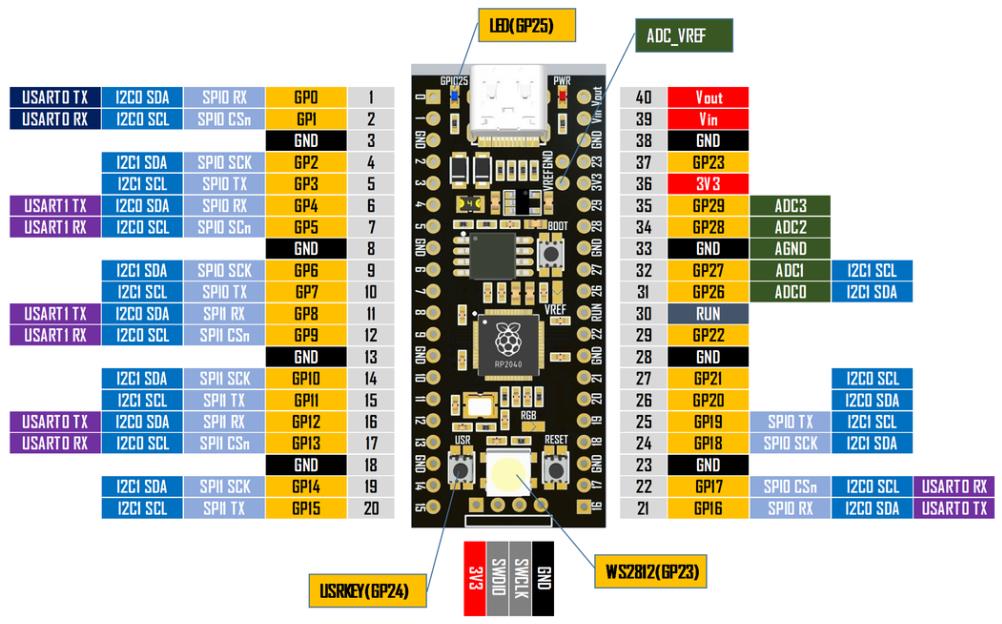
📒RP2040开发板

- 📘YD-RP2040开发板
🎄DHT11传感器

🎄ssd1306 I2C 0.96寸 OLED屏幕

📌注意事项
⛳在运行代码前,需要先将ssd1306 0.96寸 I2C OLED连接到RP2040开发板对应的引脚上,否则会报错,找不到I2C设备。
📔所需库模块
💎dht.py
import array
import micropython
import utime
from machine import Pin
from micropython import const
class InvalidChecksum(Exception):
pass
class InvalidPulseCount(Exception):
pass
MAX_UNCHANGED = const(100)
MIN_INTERVAL_US = const(200000)
HIGH_LEVEL = const(50)
EXPECTED_PULSES = const(84)
class DHT11:
_temperature: float
_humidity: float
def __init__(self, pin):
self._pin = pin
self._last_measure = utime.ticks_us()
self._temperature = -1
self._humidity = -1
def measure(self):
current_ticks = utime.ticks_us()
if utime.ticks_diff(current_ticks, self._last_measure) < MIN_INTERVAL_US and (
self._temperature > -1 or self._humidity > -1
):
# Less than a second since last read, which is too soon according
# to the datasheet
return
self._send_init_signal()
pulses = self._capture_pulses()
buffer = self._convert_pulses_to_buffer(pulses)
self._verify_checksum(buffer)
self._humidity = buffer[0] + buffer[1] / 10
self._temperature = buffer[2] + buffer[3] / 10
self._last_measure = utime.ticks_us()
@property
def humidity(self):
self.measure()
return self._humidity
@property
def temperature(self):
self.measure()
return self._temperature
def _send_init_signal(self):
self._pin.init(Pin.OUT, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
self._pin.value(1)
utime.sleep_ms(50)
self._pin.value(0)
utime.sleep_ms(18)
@micropython.native
def _capture_pulses(self):
pin = self._pin
pin.init(Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
val = 1
idx = 0
transitions = bytearray(EXPECTED_PULSES)
unchanged = 0
timestamp = utime.ticks_us()
while unchanged < MAX_UNCHANGED:
if val != pin.value():
if idx >= EXPECTED_PULSES:
raise InvalidPulseCount(
"Got more than pulses".format(EXPECTED_PULSES)
)
now = utime.ticks_us()
transitions[idx] = now - timestamp
timestamp = now
idx += 1
val = 1 - val
unchanged = 0
else:
unchanged += 1
pin.init(Pin.OUT, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
if idx != EXPECTED_PULSES:
raise InvalidPulseCount(
"Expected but got pulses".format(EXPECTED_PULSES, idx)
)
return transitions[4:]
def _convert_pulses_to_buffer(self, pulses):
"""Convert a list of 80 pulses into a 5 byte buffer
The resulting 5 bytes in the buffer will be:
0: Integral relative humidity data
1: Decimal relative humidity data
2: Integral temperature data
3: Decimal temperature data
4: Checksum
"""
# Convert the pulses to 40 bits
binary = 0
for idx in range(0, len(pulses), 2):
binary = binary << 1 | int(pulses[idx] > HIGH_LEVEL)
# Split into 5 bytes
buffer = array.array("B")
for shift in range(4, -1, -1):
buffer.append(binary >> shift * 8 & 0xFF)
return buffer
def _verify_checksum(self, buffer):
# Calculate checksum
checksum = 0
for buf in buffer[0:4]:
checksum += buf
if checksum & 0xFF != buffer[4]:
raise InvalidChecksum()
💎ssd1306.py
# MicroPython SSD1306 OLED driver, I2C and SPI interfaces
from micropython import const
import framebuf
# register definitions
SET_CONTRAST = const(0x81)
SET_ENTIRE_ON = const(0xA4)
SET_NORM_INV = const(0xA6)
SET_DISP = const(0xAE)
SET_MEM_ADDR = const(0x20)
SET_COL_ADDR = const(0x21)
SET_PAGE_ADDR = const(0x22)
SET_DISP_START_LINE = const(0x40)
SET_SEG_REMAP = const(0xA0)
SET_MUX_RATIO = const(0xA8)
SET_COM_OUT_DIR = const(0xC0)
SET_DISP_OFFSET = const(0xD3)
SET_COM_PIN_CFG = const(0xDA)
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV = const(0xD5)
SET_PRECHARGE = const(0xD9)
SET_VCOM_DESEL = const(0xDB)
SET_CHARGE_PUMP = const(0x8D)
# Subclassing FrameBuffer provides support for graphics primitives
# http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/pyboard/library/framebuf.html
class SSD1306(framebuf.FrameBuffer):
def __init__(self, width, height, external_vcc):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.external_vcc = external_vcc
self.pages = self.height // 8
self.buffer = bytearray(self.pages * self.width)
super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.MONO_VLSB)
self.init_display()
def init_display(self):
for cmd in (
SET_DISP | 0x00, # off
# address setting
SET_MEM_ADDR,
0x00, # horizontal
# resolution and layout
SET_DISP_START_LINE | 0x00,
SET_SEG_REMAP | 0x01, # column addr 127 mapped to SEG0
SET_MUX_RATIO,
self.height - 1,
SET_COM_OUT_DIR | 0x08, # scan from COM[N] to COM0
SET_DISP_OFFSET,
0x00,
SET_COM_PIN_CFG,
0x02 if self.width > 2 * self.height else 0x12,
# timing and driving scheme
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV,
0x80,
SET_PRECHARGE,
0x22 if self.external_vcc else 0xF1,
SET_VCOM_DESEL,
0x30, # 0.83*Vcc
# display
SET_CONTRAST,
0xFF, # maximum
SET_ENTIRE_ON, # output follows RAM contents
SET_NORM_INV, # not inverted
# charge pump
SET_CHARGE_PUMP,
0x10 if self.external_vcc else 0x14,
SET_DISP | 0x01,
): # on
self.write_cmd(cmd)
self.fill(0)
self.show()
def poweroff(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x00)
def poweron(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x01)
def contrast(self, contrast):
self.write_cmd(SET_CONTRAST)
self.write_cmd(contrast)
def invert(self, invert):
self.write_cmd(SET_NORM_INV | (invert & 1))
def show(self):
x0 = 0
x1 = self.width - 1
if self.width == 64:
# displays with width of 64 pixels are shifted by 32
x0 += 32
x1 += 32
self.write_cmd(SET_COL_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(x0)
self.write_cmd(x1)
self.write_cmd(SET_PAGE_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(0)
self.write_cmd(self.pages - 1)
self.write_data(self.buffer)
class SSD1306_I2C(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, i2c, addr=0x3C, external_vcc=False):
self.i2c = i2c
self.addr = addr
self.temp = bytearray(2)
self.write_list = [b"\\x40", None] # Co=0, D/C#=1
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.temp[0] = 0x80 # Co=1, D/C#=0
self.temp[1] = cmd
self.i2c.writeto(self.addr, self.temp)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.write_list[1] = buf
self.i2c.writevto(self.addr, self.write_list)
class SSD1306_SPI(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, spi, dc, res, cs, external_vcc=False):
self.rate = 10 * 1024 * 1024
dc.init(dc.OUT, value=0)
res.init(res.OUT, value=0)
cs.init(cs.OUT, value=1)
self.spi = spi
self.dc = dc
self.res = res
self.cs = cs
import time
self.res(1)
time.sleep_ms(1)
self.res(0)
time.sleep_ms(10)
self.res(1)
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.spi.init(baudrate=self.rate, polarity=0, phase=0)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(0)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(bytearray([cmd]))
self.cs(1)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.spi.init(baudrate=self.rate, polarity=0, phase=0)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(1)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(buf)
self.cs(1)
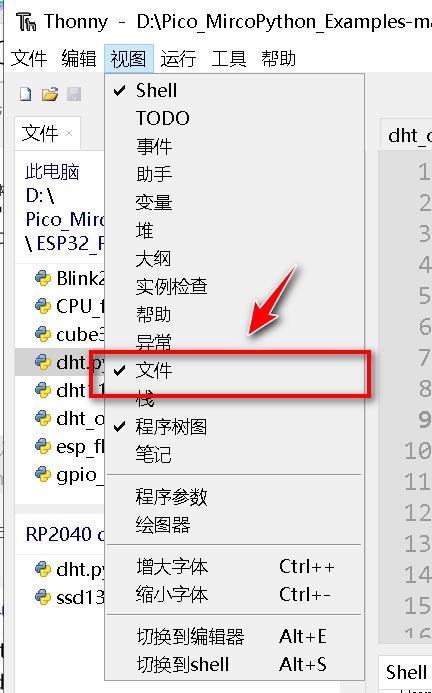
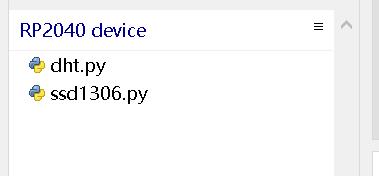
先将所需模块导入到micropython RP2040设备中

- 导入后,可以在设备信息文件栏看到。(如果
Thonny软件没有将文件勾选上将看不到。)
🎯主程序代码
from machine import Pin, I2C
from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C
import utime as time
from dht import DHT11, InvalidChecksum
WIDTH = 128 # oled display width
HEIGHT = 64 # oled display height
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(9), sda=Pin(8), freq=200000) # Init I2C using pins GP8 & GP9 (default I2C0 pins)
print("I2C Address : "+hex(i2c.scan()[0]).upper()) # Display device address
print("I2C Configuration: "+str(i2c)) # Display I2C config
oled = SSD1306_I2C(WIDTH, HEIGHT, i2c) # Init oled display
while True:
time.sleep(1)
pin = Pin(28, Pin.OUT, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
sensor = DHT11(pin)
t = (sensor.temperature)
h = (sensor.humidity)
print("Temperature: ".format(sensor.temperature))
print("Humidity: ".format(sensor.humidity))
# Clear the oled display in case it has junk on it.
oled.fill(0)
# Add some text
oled.text("Temp: ",10,16)
oled.text(str(sensor.temperature),50,16)
oled.text("*C",90,16)
oled.text("Humi: ",10,40)
oled.text(str(sensor.humidity),50,40)
oled.text("%",90,40)
time.sleep(1)
oled.show()
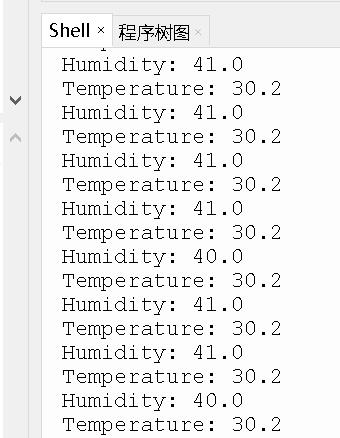
- Shell调试窗口输出dht传感器数据
以上是关于MicroPython RP2040读取DHT11温湿度传感器数据+ 0.96“I2C oled显示的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章