callapplybind的应用和区别
Posted suwu150
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了callapplybind的应用和区别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
call、apply、bind的应用和区别
首先,要明白这三个函数的存在意义是什么?答案是改变函数执行时的上下文,再具体一点就是改变函数运行时的this指向。有了这个认识,接下来我们使用实例来看一下,怎么使用这三个函数。
let obj1 = name: 'tom';
let obj2 = name: 'jack';
function Child(name)
this.name = name;
Child.prototype =
constructor: Child,
showName: function()
console.log(this.name);
var child = new Child('thomas');
child.showName();
// call,apply,bind使用
child.showName.call(obj1);
child.showName.apply(obj2);
let bind = child.showName.bind(obj1); // 返回一个函数
bind();
首先大家来思考下,上面代码执行后打印的结果如何?
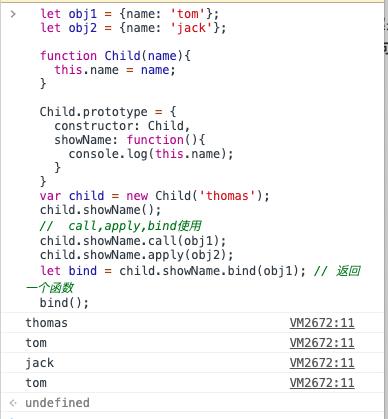
我们拿Child的showName方法,并通过执行call、apply、bind的方法动态改变其上下文帮自己输出了改变上下文之后的信息.
1.区别
bind方法是事先把fn的this改变为我们要想要执行的上下文的结果,并且把对应的参数值准备好,以后要用到了,直接的执行即可,也就是说bind同样可以改变this的指向,但和apply、call不同就是不会马上的执行
-
call、apply与bind的差别
call和apply改变了函数的this上下文后便执行该函数,而bind则是返回改变了上下文后的一个函数。 -
call、bind和apply的区别
call、bind和apply的第一个参数都是要改变上下文的对象,而call、bind从第二个参数开始以参数列表的形式展现. apply则是把除了改变上下文对象的参数放在一个数组里面作为它的第二个参数。
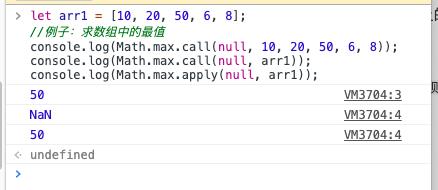
2.应用
- 将伪数组转化为数组(含有length属性的对象,dom节点, 函数的参数arguments)
javascript中的伪数组(例如通过document.getElementsByTagName获取的元素、含有length属性的对象)具有length属性,并且可以通过0、1、2…下标来访问其中的元素,但是没有Array中的push、pop等方法。就可以利用call,apply来转化成真正的数组,就可以使用数组的方法了
1.dom节点中类数组结构
<div class="div1">1</div>
<div class="div1">2</div>
<div class="div1">3</div>
let div = document.getElementsByTagName('div');
console.log(div); // htmlCollection(3) [div.div1, div.div1, div.div1] 里面包含length属性
let arr2 = Array.prototype.slice.call(div);
console.log(arr2); // 数组 [div.div1, div.div1, div.div1]
2.fn内的arguments
function fn10()
return Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
console.log(fn10(1,2,3,4,5)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
注意slice方法,在不传递任何参数的情况下,是会返回整个数组的
3.含有length属性的对象
let obj4 =
0: 1,
1: 'thomas',
2: 13,
length: 3 // 一定要有length属性
;
console.log(Array.prototype.slice.call(obj4)); // [1, "thomas", 13]
- 数组拼接,添加
let arr1 = [1,2,3];
let arr2 = [4,5,6];
//数组的concat方法:返回一个新的数组
let arr3 = arr1.concat(arr2);
console.log(arr3); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
console.log(arr1); // [1, 2, 3] 不变
console.log(arr2); // [4, 5, 6] 不变
// 用 apply方法
[].push.apply(arr1,arr2); // 给arr1添加arr2
console.log(arr1); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
console.log(arr2); // [4, 5, 6] 不变
- 判断变量类型
let arr1 = [1,2,3];
let str1 = 'string';
let obj1 = name: 'thomas';
//
function isArray(obj)
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Array]';
console.log(fn1(arr1)); // true
// 判断类型的方式,这个最常用语判断array和object,null(因为typeof null等于object)
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arr1)); // [object Array]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(str1)); // [object String]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(obj1)); // [object Object]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null)); // [object Null]
对于类型判断更多细节可参考这篇文章,总结了JavaScript中四种类型判断的方式:JavaScript中判断数据类型的四种方法
- 利用call和apply做继承
function Animal(name)
this.name = name;
this.showName = function()
console.log(this.name);
function Cat(name)
Animal.call(this, name);
// Animal.call(this) 的意思就是使用this对象代替Animal对象,那么
// Cat中不就有Animal的所有属性和方法了吗,Cat对象就能够直接调用Animal的方法以及属性了
var cat = new Cat("TONY");
cat.showName(); //TONY
- 多继承
function Class1(a,b)
this.showclass1 = function(a,b)
console.log(`class1: $a,$b`);
function Class2(a,b)
this.showclass2 = function(a,b)
console.log(`class2: $a,$b`);
function Class3(a,b,c)
Class1.call(this);
Class2.call(this);
let arr10 = [2,2];
let demo = new Class3();
demo.showclass1.call(this,1); // class1: 1,undefined
demo.showclass1.call(this,1,2); // class1: 1,2
demo.showclass2.apply(this,arr10); // class2: 2,2

以上是关于callapplybind的应用和区别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章