自然语言处理(NLP)基于LSTM实现文字检测
Posted ぃ灵彧が
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自然语言处理(NLP)基于LSTM实现文字检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【自然语言处理(NLP)】基基于LSTM实现文字检测

作者简介:在校大学生一枚,华为云享专家,阿里云星级博主,腾云先锋(TDP)成员,云曦智划项目总负责人,全国高等学校计算机教学与产业实践资源建设专家委员会(TIPCC)志愿者,以及编程爱好者,期待和大家一起学习,一起进步~
.
博客主页:ぃ灵彧が的学习日志
.
本文专栏:人工智能
.
专栏寄语:若你决定灿烂,山无遮,海无拦
.
文章目录
任务描述
传统的谣言检测模型一般根据谣言的内容、用户属性、传播方式人工地构造特征,而人工构建特征存在考虑片面、浪费人力等现象。本次实践使用基于循环神经网络(RNN)的谣言检测模型,将文本中的谣言事件向量化,通过循环神经网络的学习训练来挖掘表示文本深层的特征,避免了特征构建的问题,并能发现那些不容易被人发现的特征,从而产生更好的效果。
数据集介绍:
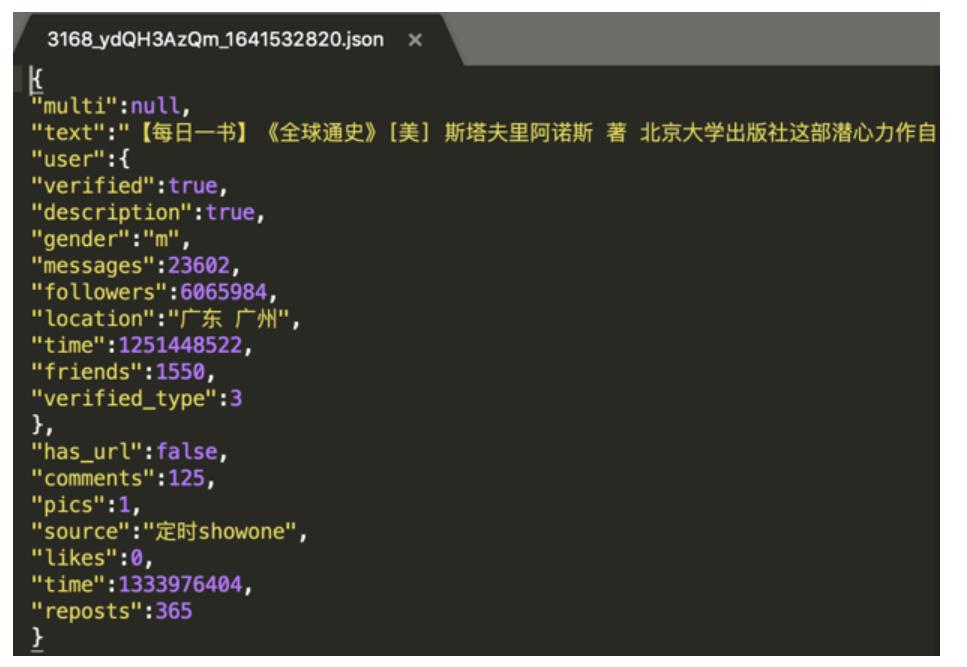
本次实践所使用的数据是从新浪微博不实信息举报平台抓取的中文谣言数据,数据集中共包含1538条谣言和1849条非谣言。如下图所示,每条数据均为json格式,其中text字段代表微博原文的文字内容。
更多数据集介绍请参考https://github.com/thunlp/Chinese_Rumor_Dataset。
一、环境设置
import paddle
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(paddle.__version__)
二、数据准备
(1)解压数据,读取并解析数据,生成all_data.txt
(2)生成数据字典,即dict.txt
(3)生成数据列表,并进行训练集与验证集的划分,train_list.txt 、eval_list.txt
(4)定义训练数据集提供器
(一)、解压数据
- 导入文件路径
import os, zipfile
src_path="data/data20519/Rumor_Dataset.zip"
target_path="/home/aistudio/data/Chinese_Rumor_Dataset-master"
if(not os.path.isdir(target_path)):
z = zipfile.ZipFile(src_path, 'r')
z.extractall(path=target_path)
z.close()
- 解析数据
import io
import random
import json
#谣言数据文件路径
rumor_class_dirs = os.listdir(target_path+"/Chinese_Rumor_Dataset-master/CED_Dataset/rumor-repost/")
#非谣言数据文件路径
non_rumor_class_dirs = os.listdir(target_path+"/Chinese_Rumor_Dataset-master/CED_Dataset/non-rumor-repost/")
original_microblog = target_path+"/Chinese_Rumor_Dataset-master/CED_Dataset/original-microblog/"
#谣言标签为0,非谣言标签为1
rumor_label="0"
non_rumor_label="1"
#分别统计谣言数据与非谣言数据的总数
rumor_num = 0
non_rumor_num = 0
all_rumor_list = []
all_non_rumor_list = []
#解析谣言数据
for rumor_class_dir in rumor_class_dirs:
if(rumor_class_dir != '.DS_Store'):
#遍历谣言数据,并解析
with open(original_microblog + rumor_class_dir, 'r') as f:
rumor_content = f.read()
rumor_dict = json.loads(rumor_content)
all_rumor_list.append(rumor_label+"\\t"+rumor_dict["text"]+"\\n")
rumor_num +=1
#解析非谣言数据
for non_rumor_class_dir in non_rumor_class_dirs:
if(non_rumor_class_dir != '.DS_Store'):
with open(original_microblog + non_rumor_class_dir, 'r') as f2:
non_rumor_content = f2.read()
non_rumor_dict = json.loads(non_rumor_content)
all_non_rumor_list.append(non_rumor_label+"\\t"+non_rumor_dict["text"]+"\\n")
non_rumor_num +=1
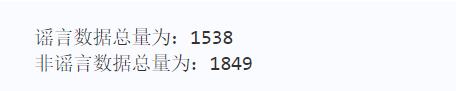
print("谣言数据总量为:"+str(rumor_num))
print("非谣言数据总量为:"+str(non_rumor_num))
输出结果如下图1所示:
- 全部数据进行乱序后写入all_data.txt
data_list_path="/home/aistudio/data/"
all_data_path=data_list_path + "all_data.txt"
all_data_list = all_rumor_list + all_non_rumor_list
random.shuffle(all_data_list)
#在生成all_data.txt之前,首先将其清空
with open(all_data_path, 'w') as f:
f.seek(0)
f.truncate()
with open(all_data_path, 'a') as f:
for data in all_data_list:
f.write(data)
(二)、生成数据字典
# 生成数据字典
def create_dict(data_path, dict_path):
with open(dict_path, 'w') as f:
f.seek(0)
f.truncate()
dict_set = set()
# 读取全部数据
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# 把数据生成一个元组
for line in lines:
content = line.split('\\t')[-1].replace('\\n', '')
for s in content:
dict_set.add(s)
# 把元组转换成字典,一个字对应一个数字
dict_list = []
i = 0
for s in dict_set:
dict_list.append([s, i])
i += 1
# 添加未知字符
dict_txt = dict(dict_list)
end_dict = "<unk>": i
dict_txt.update(end_dict)
end_dict = "<pad>": i+1
dict_txt.update(end_dict)
# 把这些字典保存到本地中
with open(dict_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(str(dict_txt))
print("数据字典生成完成!")
(三)、生成数据列表
- 创建序列化表示的数据,并按照一定比例划分训练数据train_list.txt与验证数据eval_list.txt
def create_data_list(data_list_path):
#在生成数据之前,首先将eval_list.txt和train_list.txt清空
with open(os.path.join(data_list_path, 'eval_list.txt'), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f_eval:
f_eval.seek(0)
f_eval.truncate()
with open(os.path.join(data_list_path, 'train_list.txt'), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f_train:
f_train.seek(0)
f_train.truncate()
with open(os.path.join(data_list_path, 'dict.txt'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_data:
dict_txt = eval(f_data.readlines()[0])
with open(os.path.join(data_list_path, 'all_data.txt'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_data:
lines = f_data.readlines()
i = 0
maxlen = 0
with open(os.path.join(data_list_path, 'eval_list.txt'), 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f_eval,open(os.path.join(data_list_path, 'train_list.txt'), 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f_train:
for line in lines:
words = line.split('\\t')[-1].replace('\\n', '')
maxlen = max(maxlen, len(words))
label = line.split('\\t')[0]
labs = ""
# 每8个 抽取一个数据用于验证
if i % 8 == 0:
for s in words:
lab = str(dict_txt[s])
labs = labs + lab + ','
labs = labs[:-1]
labs = labs + '\\t' + label + '\\n'
f_eval.write(labs)
else:
for s in words:
lab = str(dict_txt[s])
labs = labs + lab + ','
labs = labs[:-1]
labs = labs + '\\t' + label + '\\n'
f_train.write(labs)
i += 1
print("数据列表生成完成!")
print("样本最长长度:" + str(maxlen))
- 创建数据列表
# 把生成的数据列表都放在自己的总类别文件夹中
data_root_path = "/home/aistudio/data/"
data_path = os.path.join(data_root_path, 'all_data.txt')
dict_path = os.path.join(data_root_path, "dict.txt")
# 创建数据字典
create_dict(data_path, dict_path)
# 创建数据列表
create_data_list(data_root_path)
输出结果如下图2所示:

(四)、定义训练数据集提供器
- 数据预处理
def load_vocab(file_path):
fr = open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf8')
vocab = eval(fr.read()) #读取的str转换为字典
fr.close()
return vocab
- 打印前2条训练数据
vocab = load_vocab(os.path.join(data_root_path, 'dict.txt'))
def ids_to_str(ids):
words = []
for k in ids:
w = list(vocab.keys())[list(vocab.values()).index(int(k))]
words.append(w if isinstance(w, str) else w.decode('ASCII'))
return " ".join(words)
file_path = os.path.join(data_root_path, 'train_list.txt')
with io.open(file_path, "r", encoding='utf8') as fin:
i = 0
for line in fin:
i += 1
cols = line.strip().split("\\t")
if len(cols) != 2:
sys.stderr.write("[NOTICE] Error Format Line!")
continue
label = int(cols[1])
wids = cols[0].split(",")
print(str(i)+":")
print('sentence list id is:', wids)
print('sentence list is: ', ids_to_str(wids))
print('sentence label id is:', label)
print('---------------------------------')
if i == 2: break
输出结果如下图3所示:

- 定义训练数据集提供器
vocab = load_vocab(os.path.join(data_root_path, 'dict.txt'))
class RumorDataset(paddle.io.Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_dir):
self.data_dir = data_dir
self.all_data = []
with io.open(self.data_dir, "r", encoding='utf8') as fin:
for line in fin:
cols = line.strip().split("\\t")
if len(cols) != 2:
sys.stderr.write("[NOTICE] Error Format Line!")
continue
label = []
label.append(int(cols[1]))
wids = cols[0].split(",")
if len(wids)>=150:
wids = np.array(wids[:150]).astype('int64')
else:
wids = np.concatenate([wids, [vocab["<pad>"]]*(150-len(wids))]).astype('int64')
label = np.array(label).astype('int64')
self.all_data.append((wids, label))
def __getitem__(self, index):
data, label = self.all_data[index]
return data, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.all_data)
batch_size = 32
train_dataset = RumorDataset(os.path.join(data_root_path, 'train_list.txt'))
test_dataset = RumorDataset(os.path.join(data_root_path, 'eval_list.txt'))
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, places=paddle.CPUPlace(), return_list=True,
shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, drop_last=True)
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(test_dataset, places=paddle.CPUPlace(), return_list=True,
shuffle=True, batch_size=batch_size, drop_last=True)
#check
print('=============train_dataset =============')
for data, label in train_dataset:
print(data)
print(np.array(data).shape)
print(label)
break
print('=============test_dataset =============')
for data, label in test_dataset:
print(data)
print(np.array(data).shape)
print(label)
break
输出结果如下图4所示:

三、模型配置
import paddle
from paddle.nn import Conv2D, Linear, Embedding
from paddle import to_tensor
import paddle.nn.functional as F
class RNN(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.dict_dim = vocab["<pad>"]
self.emb_dim = 128
self.hid_dim = 128
self.class_dim = 2
self.embedding = Embedding(
self.dict_dim + 1, self.emb_dim,
sparse=False)
self._fc1 = Linear(self.emb_dim, self.hid_dim)
self.lstm = paddle.nn.LSTM(self.hid_dim, self.hid_dim)
self.fc2 = Linear(19200, self.class_dim)
def forward(self, inputs):
# [32, 150]
emb = self.embedding(inputs)
# [32, 150, 128]
fc_1 = self._fc1(emb)
# [32, 150, 128]
x = self.lstm(fc_1)
x = paddle.reshape(x[0], [0, -1])
x = self.fc2(x)
x = paddle.nn.functional.softmax(x)
return x
rnn = RNN()
paddle.summary(rnn,(32,150),"int64")
四、模型训练
- 实例化模型
def draw_process(title,color,iters,data,label):
plt.title(title, fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("iter", fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel(label, fontsize=20)
plt.plot(iters, data,color=color,label=label)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
- 模型训练
def train(model):
model.train()
opt = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.002, parameters=model.parameters())
steps = 0
Iters, total_loss, total_acc = []以上是关于自然语言处理(NLP)基于LSTM实现文字检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
