机器学习数据科学基础——神经网络基础实验
Posted 云曦智划
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习数据科学基础——神经网络基础实验相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【机器学习】数据科学基础——神经网络基础实验

活动地址:[CSDN21天学习挑战赛](https://marketing.csdn.net/p/bdabfb52c5d56532133df2adc1a728fd)
作者简介:在校大学生一枚,华为云享专家,阿里云星级博主,腾云先锋(TDP)成员,云曦智划项目总负责人,全国高等学校计算机教学与产业实践资源建设专家委员会(TIPCC)志愿者,以及编程爱好者,期待和大家一起学习,一起进步~
.
博客主页:ぃ灵彧が的学习日志
.
本文专栏:机器学习
.
专栏寄语:若你决定灿烂,山无遮,海无拦
.
文章目录
前言
什么是神经网络?
神经网络是一门重要的机器学习技术,它是目前人工智能领域内最为火热的研究方向——深度学习技术的基础。神经网络是一种模仿动物神经网络行为特征,进行分布式并行信息处理的算法数学模型,也是我们后续学习自然语言处理和视觉图像处理的基础
一、基于全连接神经网络实型房价预测
(一)、数据加载及预处理
- 导入相关包:
# import paddle.fluid as fluid
import paddle
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 设置paddle默认的全局数据类型为float64
#设置默认的全局dtype为float64
paddle.set_default_dtype("float64")
#下载数据
print('下载并加载训练数据')
train_dataset = paddle.text.datasets.UCIHousing(mode='train')
eval_dataset = paddle.text.datasets.UCIHousing(mode='test')
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
eval_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(eval_dataset, batch_size = 8, shuffle=False)
(二)、模型配置
线性回归本质上是一层不带激活函数的全连接层,因此本实验使用
paddle.nn.Linear(in_features,out_features,weight_attr=None,nias_attr=None,name=None)
来实现线性变换,其中,in_features为输入特征的维度,out_features为输出特征的维度,weight_attr指定权重参数的属性,表示使用默认的权值参数属性,将权重参数初始化为0,bias_attr指定偏置参数的属性,设置为False时,表示不会为该层添加偏置,name用于网络层输出的前缀标识,在自定义网络模型时,应当继承paddle.nn.Layer类,该类属于基于OOD实现的动态图,实现了训练模式与验证模式,训练模型会执行反向传播,而验证模式不包含反向传播,同时也为dropout等训练,验证时不同的操作提供了支持。在神经网络中,从输入到输出的过程称为网络的前向计算,在飞浆中,可用forward关键字标识,forward()函数定义函数从前到后的完整计算过程,是实现网络框架最重要的环节。
定义全连接网络:
# 定义全连接网络
class Regressor(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(Regressor, self).__init__()
# 定义一层全连接层,输出维度是1,激活函数为None,即不使用激活函数
self.linear = paddle.nn.Linear(13, 1, None)
# 网络的前向计算函数
def forward(self, inputs):
x = self.linear(inputs)
return x
(三)、模型训练
本实验中使用
paddle.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001,parameters=None,weight_decay=None,grad_clip=None,name=None)
进行优化,其中learning_rate为学习率,也就是参数梯度的更新步长,parameters指定优化器需要优化的参数,weight_decay为权重衰减系数,grad_clip为梯度裁减的策略,支持三种裁剪策略:paddle.nn.ClipGradByGlobalNorm、paddle.nn.ClipGradByNorm、paddle.nn.ClipGradByValue,梯度裁剪将梯度值阶段约束在一个范围内,防止使用深度网络时出现梯度爆炸的情况,默认值为None,此时将不进行梯度裁剪。定义好模型、损失函数和优化器之后,将数据分批送入模型中,并执行梯度反向传播更新参数(loss.backward()),达到训练目的,模型训练结束后,调用paddle.save()保存模型,后续进行预测时,只需要将训练好的模型参数加载到模型中,便可利用训练数据提取到的规律对测试数据进行预测。
代码如下:
Batch=0
Batchs=[]
all_train_accs=[]
def draw_train_acc(Batchs, train_accs):
title="training accs"
plt.title(title, fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("batch", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("acc", fontsize=14)
plt.plot(Batchs, train_accs, color='green', label='training accs')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
all_train_loss=[]
def draw_train_loss(Batchs, train_loss):
title="training loss"
plt.title(title, fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("batch", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("loss", fontsize=14)
plt.plot(Batchs, train_loss, color='red', label='training loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
model=Regressor() # 模型实例化
model.train() # 训练模式
mse_loss = paddle.nn.MSELoss()
opt=paddle.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.0005, parameters=model.parameters())
epochs_num=200 #迭代次数
for pass_num in range(epochs_num):
for batch_id,data in enumerate(train_loader()):
image = data[0]
label = data[1]
predict=model(image) #数据传入model
# print(predict)
# print(np.argmax(predict,axis=1))
loss=mse_loss(predict,label)
# acc=paddle.metric.accuracy(predict,label.reshape([-1,1]))#计算精度
# acc = np.mean(label==np.argmax(predict,axis=1))
if batch_id!=0 and batch_id%10==0:
Batch = Batch+10
Batchs.append(Batch)
all_train_loss.append(loss.numpy()[0])
# all_train_accs.append(acc.numpy()[0])
print("epoch:,step:,train_loss:".format(pass_num,batch_id,loss.numpy()[0]) )
loss.backward()
opt.step()
opt.clear_grad() #opt.clear_grad()来重置梯度
paddle.save(model.state_dict(),'Regressor')#保存模型
draw_train_loss(Batchs,all_train_loss)
模型训练过程中部分输出如下图1-1所示:

(四)、模型评估
- 模型训练结束后,根据保存的损失值的中间结果,绘制损失值随模型迭代次数的变化过程:
def draw_train_acc(Batchs,train_accs):
title="training accs"
plt.title(title,fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("batch",fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("acc",fontsize=14)
plt.plot(Batchs,train_accs,color='green',label='training accs')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
draw_train_loss(Batchs,all_train_loss)
模型损失值随迭代次数变化趋势如下图1-2所示:
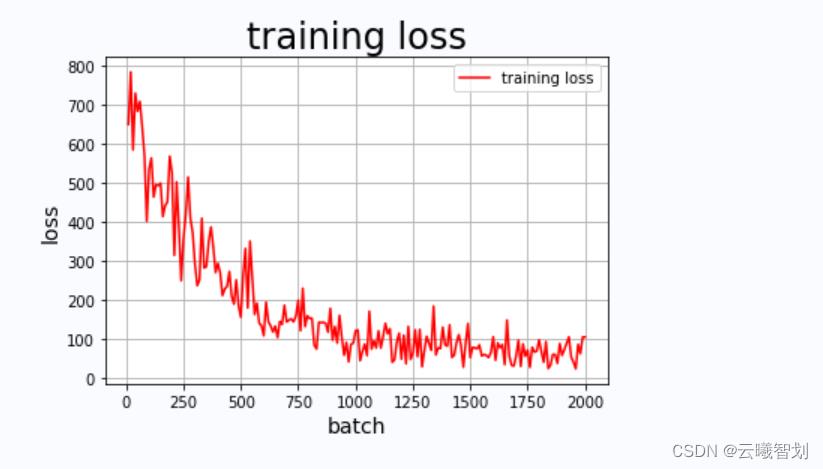
- 为了判断上述模型的性能,可在验证集上进行验证。首先将前面步骤保存的训练好的参数加载到新实例化的模型中,然后启动验证模型,将验证数据批量输入到网络中进行损失值计算,并输出模型在验证集上的损失值:
#模型评估
para_state_dict = paddle.load("Regressor")
model = Regressor()
model.set_state_dict(para_state_dict) #加载模型参数
model.eval() #验证模式
losses = []
infer_results=[]
groud_truths=[]
for batch_id,data in enumerate(eval_loader()):#测试集
image=data[0]
label=data[1]
groud_truths.extend(label.numpy())
predict=model(image)
infer_results.extend(predict.numpy())
loss=mse_loss(predict,label)
losses.append(loss.numpy()[0])
avg_loss = np.mean(losses)
print("当前模型在验证集上的损失值为:",avg_loss)
输出结果如下图1-3所示:
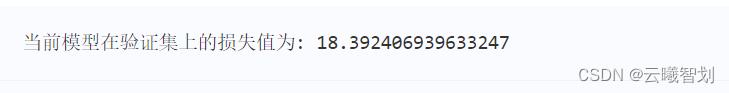
- 绘制模型预测结果与真实值之间的差异,当模型的预测值等于真实值时,模型的预测效果是最优的,但是这种情况几乎不可能出现,因此作为对照,可以观察预测值与真实值构成的坐标点位于y=x直线的位置,判断模型性能的好坏,代码实现及图示如下:
#绘制真实值和预测值对比图
def draw_infer_result(groud_truths,infer_results):
title='Boston'
plt.title(title, fontsize=24)
x = np.arange(1,20)
y = x
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('ground truth', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('infer result', fontsize=14)
plt.scatter(groud_truths, infer_results,color='green',label='training cost')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
draw_infer_result(groud_truths,infer_results)
真实值和预测值对比图如下图1-4所示:
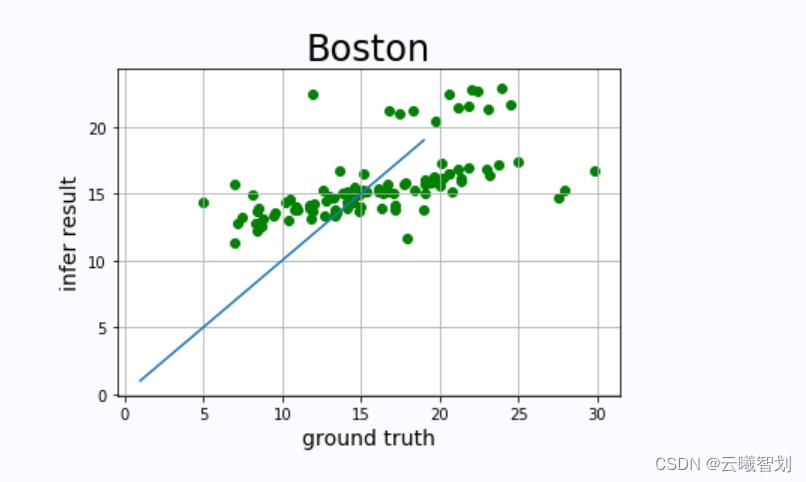
小结
上述方法获得模型的拟合能力并没有达到最优,仍然具有很大的优化空间。线性回归算法只能处理线性可分的数据,对于线性不可分数据,在传统机器学习算法中,需要使用对数线性回归、广义线性回归或者其它回归算法,但是在神经网络中,可以通过添加激活函数、加深网络深度,实现任意函数的拟合。
二、基于全连接神经网络实现宝石分类
(一)、数据加载及预处理
- 加载必要的包:
import os
import zipfile
import random
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import paddle
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from paddle.io import Dataset
- 参数配置:
'''
参数配置
'''
train_parameters =
"input_size": [3, 224, 224], #输入图片的shape
"class_dim": 25, #分类数
"src_path":"data/data55032/archive_train.zip", #原始数据集路径
"target_path":"/home/aistudio/data/dataset", #要解压的路径
"train_list_path": "./train.txt", #train_data.txt路径
"eval_list_path": "./eval.txt", #eval_data.txt路径
"label_dict":, #标签字典
"readme_path": "/home/aistudio/data/readme.json", #readme.json路径
"num_epochs": 40, #训练轮数
"train_batch_size": 32, #批次的大小
"learning_strategy": #优化函数相关的配置
"lr": 0.0001 #超参数学习率
- 定义解压函数,解压数据集:
def unzip_data(src_path,target_path):
'''
解压原始数据集,将src_path路径下的zip包解压至data/dataset目录下
'''
if(not os.path.isdir(target_path)):
z = zipfile.ZipFile(src_path, 'r')
z.extractall(path=target_path)
z.close()
else:
print("文件已解压")
- 生成数据列表:读取每个文件夹下的图片,将绝对路径统一保存于文件中:
def get_data_list(target_path,train_list_path,eval_list_path):
'''
生成数据列表
'''
#存放所有类别的信息
class_detail = []
#获取所有类别保存的文件夹名称
data_list_path=target_path
class_dirs = os.listdir(data_list_path)
if '__MACOSX' in class_dirs:
class_dirs.remove('__MACOSX')
# #总的图像数量
all_class_images = 0
# #存放类别标签
class_label=0
# #存放类别数目
class_dim = 0
# #存储要写进eval.txt和train.txt中的内容
trainer_list=[]
eval_list=[]
#读取每个类别
for class_dir in class_dirs:
if class_dir != ".DS_Store":
class_dim += 1
#每个类别的信息
class_detail_list =
eval_sum = 0
trainer_sum = 0
#统计每个类别有多少张图片
class_sum = 0
#获取类别路径
path = os.path.join(data_list_path,class_dir)
# 获取所有图片
img_paths = os.listdir(path)
for img_path in img_paths: # 遍历文件夹下的每个图片
if img_path =='.DS_Store':
continue
name_path = os.path.join(path,img_path) # 每张图片的路径
if class_sum % 15 == 0: # 每10张图片取一个做验证数据
eval_sum += 1 # eval_sum为测试数据的数目
eval_list.append(name_path + "\\t%d" % class_label + "\\n")
else:
trainer_sum += 1
trainer_list.append(name_path + "\\t%d" % class_label + "\\n")#trainer_sum测试数据的数目
class_sum += 1 #每类图片的数目
all_class_images += 1 #所有类图片的数目
# 说明的json文件的class_detail数据
class_detail_list['class_name'] = class_dir #类别名称
class_detail_list['class_label'] = class_label #类别标签
class_detail_list['class_eval_images'] = eval_sum #该类数据的测试集数目
class_detail_list['class_trainer_images'] = trainer_sum #该类数据的训练集数目
class_detail.append(class_detail_list)
#初始化标签列表
train_parameters['label_dict'][str(class_label)] = class_dir
class_label += 1
#初始化分类数
train_parameters['class_dim'] = class_dim
print(train_parameters)
#乱序
random.shuffle(eval_list)
with open(eval_list_path, 'a') as f:
for eval_image in eval_list:
f.write(eval_image)
#乱序
random.shuffle(trainer_list)
with open(train_list_path, 'a') as f2:
for train_image in trainer_list:
f2.write(train_image)
# 说明的json文件信息
readjson =
readjson['all_class_name'] = data_list_path #文件父目录
readjson['all_class_images'] = all_class_images
readjson['class_detail'] = class_detail
jsons = json.dumps(readjson, sort_keys=True, indent=4, separators=(',', ': '))
with open(train_parameters['readme_path'],'w') as f:
f.write(jsons)
print ('生成数据列表完成!')
- 调用前面的功能函数,生成数据列表,用于后面的训练与验证:
'''
参数初始化
'''
src_path=train_parameters['src_path']
target_path=train_parameters['target_path']
train_list_path=train_parameters['train_list_path']
eval_list_path=train_parameters['eval_list_path']
batch_size=train_parameters['train_batch_size']
'''
解压原始数据到指定路径
'''
unzip_data(src_path,target_path)
'''
划分训练集与验证集,乱序,生成数据列表
'''
#每次生成数据列表前,首先清空train.txt和eval.txt
with open(train_list_path, 'w') as f:
f.seek(0)
f.truncate()
with open(eval_list_path, 'w') as f:
f.seek(0)
f.truncate()
#生成数据列表
get_data_list(target_path,train_list_path,eval_list_path)
-
为训练模型,需要定义一个数据集类将数据进行封装,该类需要继承paddle.io.Dataset抽象类,Dataset抽象了数据集的方法和行为,须实现以下方法:
__ getitem__:根据给定索引获取数据集中指定样本,在paddle.io.DataLoader中需要使用此函数通过下标获取样本;
__ len__:返回数据集样本个数,paddle.io.BatchSampler中需要样本个数生成下标序列。
本实验中自定义Reader(命名可自定义)类继承Dataset,然后再使用paddle.io.DataLoader进行批量数据处理,获取可批量迭代的数据加载器:
class Reader(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_path, mode='train'):
"""
数据读取器
:param data_path: 数据集所在路径
:param mode: train or eval
"""
super().__init__()
self.data_path = data_path
self.img_paths = []
self.labels = []
if mode == 'train':
with open(os.path.join(self.data_path, "train.txt"), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
self.info = f.readlines()
for img_info in self.info:
img_path, label = img_info.strip().split('\\t')
self.img_paths.append(img_path)
self.labels.append(int(label))
else:
with open(os.path.join(self.data_path, "eval.txt"), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
self.info = f.readlines()
for img_info in self.info:
img_path, label = img_info.strip().split('\\t')
self.img_paths.append(img_path)
self.labels.append(int(label))
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
获取一组数据
:param index: 文件索引号
:return:
"""
# 第一步打开图像文件并获取label值
img_path = self.img_paths[index]
img = Image.open(img_path)
if img.mode != 'RGB':
img = img.convert('RGB')
img = img.resize((224,
