LeetCode 0623.在二叉树中增加一行:DFS / BFS
Posted Tisfy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode 0623.在二叉树中增加一行:DFS / BFS相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【LetMeFly】623.在二叉树中增加一行:DFS / BFS
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-one-row-to-tree/
给定一个二叉树的根 root 和两个整数 val 和 depth ,在给定的深度 depth 处添加一个值为 val 的节点行。
注意,根节点 root 位于深度 1 。
加法规则如下:
- 给定整数
depth,对于深度为depth - 1的每个非空树节点cur,创建两个值为val的树节点作为cur的左子树根和右子树根。 cur原来的左子树应该是新的左子树根的左子树。cur原来的右子树应该是新的右子树根的右子树。- 如果
depth == 1意味着depth - 1根本没有深度,那么创建一个树节点,值val作为整个原始树的新根,而原始树就是新根的左子树。
示例 1:
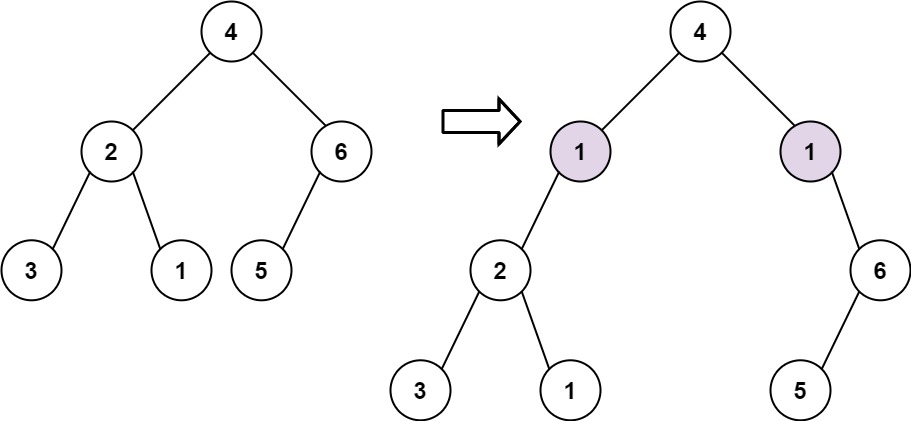
输入: root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2 输出: [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
示例 2:
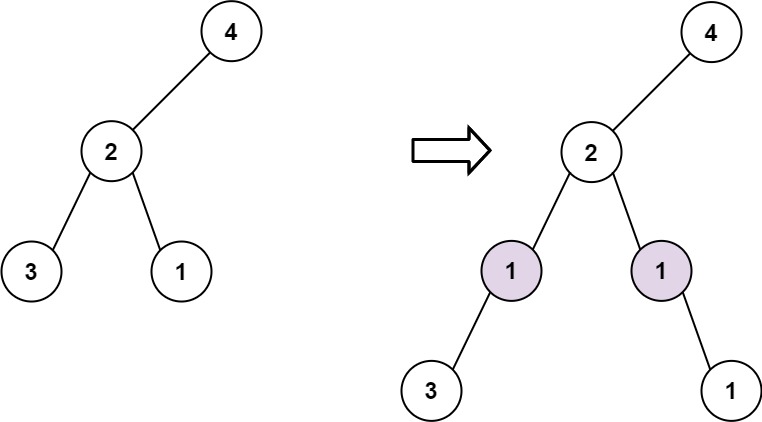
输入: root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3 输出: [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
提示:
- 节点数在
[1, 104]范围内 - 树的深度在
[1, 104]范围内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100-105 <= val <= 1051 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1
方法一.1:广度优先搜索
按照经典的 二叉树层次遍历的方法 对二叉树进行层次遍历,当遍历到对应的层的上一层时,为这一层的左右子都新建立一个值为val的新的子节点,并将新左子指向旧左子,新右子指向旧右子。
- 时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n是二叉树节点的个数
- 空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
AC代码
C++
class Solution
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth)
if (depth == 1)
TreeNode* newRoot = new TreeNode(val);
newRoot->left = root;
return newRoot;
int nowLayer = 1;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size())
int thisLayerNodesNum = q.size();
nowLayer++;
for (int i = 0; i < thisLayerNodesNum; i++)
TreeNode* thisNode = q.front();
q.pop();
if (nowLayer == depth)
TreeNode* leftNewNode = new TreeNode(val, thisNode->left, nullptr);
TreeNode* rightNewNode = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, thisNode->right);
thisNode->left = leftNewNode, thisNode->right = rightNewNode;
if (leftNewNode->left)
q.push(leftNewNode->left);
if (rightNewNode->right)
q.push(rightNewNode->right);
else
if (thisNode->left)
q.push(thisNode->left);
if (thisNode->right)
q.push(thisNode->right);
return root;
;
方法一.2:广度优先搜索 + 提前退出
在方法一.1的基础上,如果我们已经新建了节点,那么就已经没有必要再遍历下去了,因为层次遍历越往下层数越深,下面的节点不需要做出任何改变。
因此,方法一.2就是在方法一.1的基础上,插入新节点后,退出遍历。
- 时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n是二叉树节点的个数
- 空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
AC代码
C++
class Solution
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth)
if (depth == 1)
TreeNode* newRoot = new TreeNode(val);
newRoot->left = root;
return newRoot;
int nowLayer = 1;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size())
int thisLayerNodesNum = q.size();
nowLayer++;
for (int i = 0; i < thisLayerNodesNum; i++)
TreeNode* thisNode = q.front();
q.pop();
if (nowLayer == depth)
TreeNode* leftNewNode = new TreeNode(val, thisNode->left, nullptr);
TreeNode* rightNewNode = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, thisNode->right);
thisNode->left = leftNewNode, thisNode->right = rightNewNode;
// 相应地,这里也取消了入队操作 // -------------------
else
if (thisNode->left)
q.push(thisNode->left);
if (thisNode->right)
q.push(thisNode->right);
if (nowLayer == depth) // ------------------------
break; // 直接break掉即可
return root;
;
方法二:深度优先搜索
为什么先讲广度优先搜索再讲深度优先搜索?
因为深搜代码比广搜要简洁许多。
深搜时,如果depth > 2,就正常地递归即可
但是当depth = 2时,就说明这一层的下一层需要插入值为val的节点。那么就对这个节点新建两个值为val的新的子节点,(类似一.1)并将新左子指向旧左子,新右子指向旧右子。
建立新节点后,就不需要再继续递归了。
特别的,如果depth = 1(除非题目原始输入就是depth为1,否则不会遇到这种情况),就按题目要求新建值为val的节点,并将原始根节点赋值为新节点的左子节点,并返回新节点。
- 时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n是二叉树节点的个数
- 空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
AC代码
C++
class Solution // 递归的魅力
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth)
if (!root)
return nullptr;
if (depth == 1)
TreeNode* newRoot = new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
return newRoot;
if (depth == 2) // 不必再继续递归
root->left = new TreeNode(val, root->left, nullptr);
root->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, root->right);
else
addOneRow(root->left, val, depth - 1);
addOneRow(root->right, val, depth - 1);
return root;
;
同步发文于CSDN,原创不易,转载请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/126179967
以上是关于LeetCode 0623.在二叉树中增加一行:DFS / BFS的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Leetcode 623 在二叉树中增加一行 BFS与DFS