matlab求解单配送中心多车辆tsp路径优化问题mtspf_ga
Posted 张叔zhangshu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了matlab求解单配送中心多车辆tsp路径优化问题mtspf_ga相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
代码
function varargout = mtspf_ga(xy,dmat,salesmen,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,show_prog,show_res)
nargs = 8;
for k = nargin:nargs-1
switch k
case 0
% xy = 10*rand(40,2);
xy=[50,50;11,23;21,59;23,21;62,71;67,64;90,66;70,55;63,22;87,46;55,19;93,8;69,12;12,98;20,81;42,88;44,63;31,74];
case 1
N = size(xy,1);
a = meshgrid(1:N);
dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),N,N);
case 2
salesmen = 4;
case 3
min_tour = 2;
case 4
pop_size = 80;
case 5
num_iter = 5e3;
case 6
show_prog = 1;
case 7
show_res = 1;
otherwise
end
end
%%
% Verify Inputs
[N,dims] = size(xy);
[nr,nc] = size(dmat);
if N ~= nr || N ~= nc
error('Invalid XY or DMAT inputs!')
end
n = N - 1; % Separate Start/End City
% Sanity Checks
salesmen = max(1,min(n,round(real(salesmen(1)))));
min_tour = max(1,min(floor(n/salesmen),round(real(min_tour(1)))));
pop_size = max(8,8*ceil(pop_size(1)/8));
num_iter = max(1,round(real(num_iter(1))));
show_prog = logical(show_prog(1));
show_res = logical(show_res(1));
% Initializations for Route Break Point Selection
num_brks = salesmen-1;
dof = n - min_tour*salesmen; % degrees of freedom
addto = ones(1,dof+1);
for k = 2:num_brks
addto = cumsum(addto);
end
cum_prob = cumsum(addto)/sum(addto);
% Initialize the Populations
pop_rte = zeros(pop_size,n); % population of routes
pop_brk = zeros(pop_size,num_brks); % population of breaks
for k = 1:pop_size
pop_rte(k,:) = randperm(n)+1;
pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();
end
% Select the Colors for the Plotted Routes
clr = [1 0 0; 0 0 1; 0.67 0 1; 0 1 0; 1 0.5 0];
if salesmen > 5
clr = hsv(salesmen);
end
% Run the GA
global_min = Inf;
total_dist = zeros(1,pop_size);
dist_history = zeros(1,num_iter);
tmp_pop_rte = zeros(8,n);
tmp_pop_brk = zeros(8,num_brks);
new_pop_rte = zeros(pop_size,n);
new_pop_brk = zeros(pop_size,num_brks);
if show_prog
pfig = figure('Name','MTSPF_GA | Current Best Solution','Numbertitle','off');
end
for iter = 1:num_iter
% Evaluate Members of the Population
for p = 1:pop_size
d = 0;
p_rte = pop_rte(p,:);
p_brk = pop_brk(p,:);
rng = [[1 p_brk+1];[p_brk n]]';
for s = 1:salesmen
d = d + dmat(1,p_rte(rng(s,1))); % Add Start Distance
for k = rng(s,1):rng(s,2)-1
d = d + dmat(p_rte(k),p_rte(k+1));
end
d = d + dmat(p_rte(rng(s,2)),1); % Add End Distance
end
total_dist(p) = d;
end
% Find the Best Route in the Population
[min_dist,index] = min(total_dist);
dist_history(iter) = min_dist;
if min_dist < global_min
global_min = min_dist;
opt_rte = pop_rte(index,:);
opt_brk = pop_brk(index,:);
rng = [[1 opt_brk+1];[opt_brk n]]';
if show_prog
% Plot the Best Route
figure(pfig);
for s = 1:salesmen
rte = [1 opt_rte(rng(s,1):rng(s,2)) 1];
if dims == 3, plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:));
else plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); end
title(sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f, Iteration = %d',min_dist,iter));
hold on
end
if dims == 3, plot3(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),xy(1,3),'ko');
else plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'ko'); end
hold off
end
end
% Genetic Algorithm Operators
rand_grouping = randperm(pop_size);
for p = 8:8:pop_size
rtes = pop_rte(rand_grouping(p-7:p),:);
brks = pop_brk(rand_grouping(p-7:p),:);
dists = total_dist(rand_grouping(p-7:p));
[ignore,idx] = min(dists);
best_of_8_rte = rtes(idx,:);
best_of_8_brk = brks(idx,:);
rte_ins_pts = sort(ceil(n*rand(1,2)));
I = rte_ins_pts(1);
J = rte_ins_pts(2);
for k = 1:8 % Generate New Solutions
tmp_pop_rte(k,:) = best_of_8_rte;
tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = best_of_8_brk;
switch k
case 2 % Flip
tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = fliplr(tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J));
case 3 % Swap
tmp_pop_rte(k,[I J]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[J I]);
case 4 % Slide
tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1:J I]);
case 5 % Modify Breaks
tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();
case 6 % Flip, Modify Breaks
tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = fliplr(tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J));
tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();
case 7 % Swap, Modify Breaks
tmp_pop_rte(k,[I J]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[J I]);
tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();
case 8 % Slide, Modify Breaks
tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1:J I]);
tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();
otherwise % Do Nothing
end
end
new_pop_rte(p-7:p,:) = tmp_pop_rte;
new_pop_brk(p-7:p,:) = tmp_pop_brk;
end
pop_rte = new_pop_rte;
pop_brk = new_pop_brk;
end
if show_res
% Plots
figure('Name','MTSPF_GA | Results','Numbertitle','off');
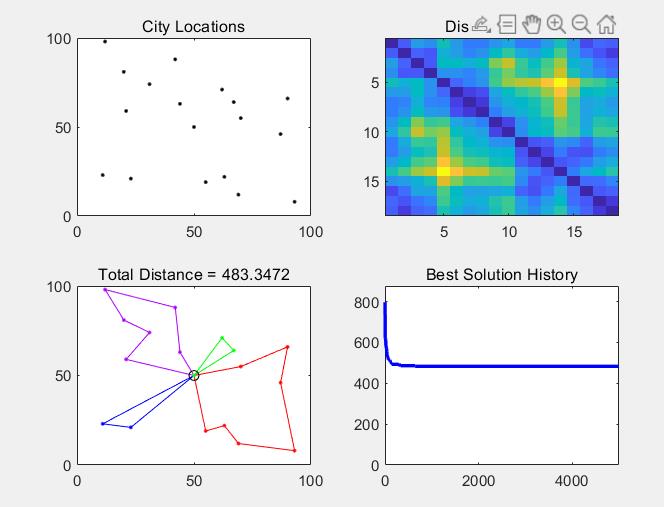
subplot(2,2,1);
if dims == 3, plot3(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),xy(:,3),'k.');
else plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'k.'); end
title('City Locations');
subplot(2,2,2);
imagesc(dmat([1 opt_rte],[1 opt_rte]));
title('Distance Matrix');
subplot(2,2,3);
rng = [[1 opt_brk+1];[opt_brk n]]';
for s = 1:salesmen
rte = [1 opt_rte(rng(s,1):rng(s,2)) 1];
if dims == 3, plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:));
else plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); end
title(sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f',min_dist));
hold on;
end
if dims == 3, plot3(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),xy(1,3),'ko');
else plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'ko'); end
subplot(2,2,4);
plot(dist_history,'b','LineWidth',2);
title('Best Solution History');
set(gca,'XLim',[0 num_iter+1],'YLim',[0 1.1*max([1 dist_history])]);
end
% Return Outputs
if nargout
varargout1 = opt_rte;
varargout2 = opt_brk;
varargout3 = min_dist;
end
% Generate Random Set of Break Points
function breaks = randbreaks()
if min_tour == 1 % No Constraints on Breaks
tmp_brks = randperm(n-1);
breaks = sort(tmp_brks(1:num_brks));
else % Force Breaks to be at Least the Minimum Tour Length
num_adjust = find(rand < cum_prob,1)-1;
spaces = ceil(num_brks*rand(1,num_adjust));
adjust = zeros(1,num_brks);
for kk = 1:num_brks
adjust(kk) = sum(spaces == kk);
end
breaks = min_tour*(1:num_brks) + cumsum(adjust);
end
end
end
如需帮忙VX:zzs1056600403
以上是关于matlab求解单配送中心多车辆tsp路径优化问题mtspf_ga的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章