通过USB数据线实现Android端与PC端的通信
Posted PK_night
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了通过USB数据线实现Android端与PC端的通信相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android端与PC通信之 Socket
ONE Goal ,ONE Passion!
给浦发银行做的一个项目,其中最让人头疼的一点是,要求必须使用usb数据线进行数据的交互.这就遇到两个问题:
1.由于每个pc端的ip不同 然而 pad端ip="127.0.0.1",所以pad(android端)不能作为client端.要让pc作为client端主动发起请求连接.
2.使用模拟器时通信一切正常,可是使用了pad进行测试时根本无法通信,问了公司老大,查了一些资料终于找到了其中的解决办法.
使用虚拟机可以的原因也许是:虚拟机运行在pc电脑上,虚拟机内部做了一些处理. 可是使用真机时需要将pc上的端口转发来作为请求端口,这就需要是用adb命令进行转发操作
第一. pc端转发操作:
先做准备工作.将我们的adb路径配置到path中,否则的话会报错的.以为执行adb命令不是系统级别,是不能执行的一般我们的sdk中都有adb.exe文件.在sdk/platform-tools下.
提供adb下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/fengltxx/9305923
1,先执行adb命令 这些命令在cmd命令行也可以执行
//这句adb命令可以不用.执行下面两句也可以实现转发.只是为了避免重复开启service所以在转发端口前先stop一下
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("adb shell am broadcast -a NotifyServiceStop");
//转发的关键代码
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("adb forward tcp:5000 tcp:13000");
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("adb shell am broadcast -a NotifyServiceStart");2,接下来就和普通的socket通信没有什么区别了
try
final Socket client = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 5000);
// 得到socket管道中的输出流--------------像手机端写数据
final BufferedOutputStream out = new BufferedOutputStream(client
.getOutputStream());
// 得到socket管道中的输人流--------------读取手机端的数据
final BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(client
.getInputStream());
// 开启子线程去读去数据
new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
try
String readMsg = "";
while (true)
try
if (!client.isConnected())
break;
// 读到后台发送的消息 然后去处理
readMsg = readMsgFromSocket(in);
if (readMsg.length() == 0)
break;
// 将要返回的数据发送给pc
out.write((readMsg + "1").getBytes());
out.flush();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
in.close();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
.start();
catch (Exception e)
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
//一个读取输入流的方法
public static String readMsgFromSocket(InputStream in)
String msg = "";
byte[] tempbuffer = new byte[1024;
try
int numReadedBytes = in.read(tempbuffer, 0, tempbuffer.length);
msg = new String(tempbuffer, 0, numReadedBytes, "utf-8");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
return msg;
第二 android端关键代码:
android端其实就方便多了,作为服务端我们只需要监听端口就可以了.
关键代码如下:
class SocketServerThread extends Thread
@Override
public void run()
try
Log.d("fy", "等待连接");
System.out.println("---------socket 通信线程----等待连接");
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(13000);
while (true)
client = serverSocket.accept();
out = new BufferedOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
// 开启子线程去读去数据
new Thread(new SocketReadThread(new BufferedInputStream(client.getInputStream()))).start();//另外开启一个线程去读数据
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 暴露给外部调用写入流的方法 如:SocketServerThread.SendMsg(str)
public void SendMsg(String msg)
String msg_1 = msg; //回写给银行的数据
try
out.write(msg_1.getBytes("UTF-8"));
out.flush();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
class SocketReadThread implements Runnable
private BufferedInputStream in;
public SocketReadThread(BufferedInputStream inStream) throws IOException
this.in = inStream;
public void run()
try
String readMsg = "";
while (true)
try
if (!client.isConnected())
break;
// 读到后台发送的消息 然后去处理
currCMD = readMsgFromSocket(in);
// 处理读到的消息(主要是身份证信息),然后保存在sp中;
if (currCMD.length() == 0)
break;
if (readMsg .equals("0002"))
// 将要返回的数据发送给 pc
out.write((readMsg + "flag").getBytes());
out.flush();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
in.close();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
public String readMsgFromSocket(InputStream in)
int MAX_BUFFER_BYTES = 2048;
String msg = "";
byte[] tempbuffer = new byte[MAX_BUFFER_BYTES];
try
int numReadedBytes = in.read(tempbuffer, 0, tempbuffer.length);
msg = new String(tempbuffer, 0, numReadedBytes, "utf-8");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
return msg;
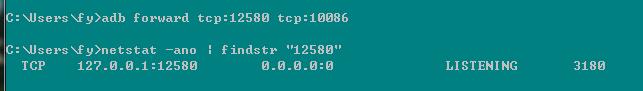
//有一些变量的声明没有给出来,很简单的东西不在写了.终于搞定了.把这快搞定浦发的项目基本就ok了.终于能歇歇了.哦!忘记一点.如果看端口有没有转发成功可以通过cmd命令行查看.
netstat -ano | findstr "80" (注80是你想要看查看的端口号)如图则恭喜我们转发成功
 创作打卡挑战赛
创作打卡挑战赛
 赢取流量/现金/CSDN周边激励大奖
赢取流量/现金/CSDN周边激励大奖
以上是关于通过USB数据线实现Android端与PC端的通信的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
使用 OTG USB 的 PC 到 Android USB 流数据 - 如何?
普通PC通过USB转485串口 ModBus-RTU通信协议控制伺服电机