OneFlow学习笔记:从OpExprInterpreter到OpKernel
Posted OneFlow深度学习框架
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OneFlow学习笔记:从OpExprInterpreter到OpKernel相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

撰文|月踏
更新|赵露阳
前文《OneFlow学习笔记:从Functor到OpExprInterpreter》讲了OpExprInterpreter的相关细节,再往下就是OneFlow中的虚拟机,它负责在eager模式下把指令(即op,在vm中称为指令)调度到具体的OpKernel上来执行。
1
Global简介
先看一个特殊的类Global,定义在oneflow/core/common/global.h,这个类很简单,但是对于整个系统来说很重要,主要的几个接口如下:
template<typename T, typename Kind = void>
class Global final
public:
// 获取创建过的对象
static T* Get() ...
// 创建对象
static void SetAllocated(T* val) ...
template<typename... Args>
static T* New(Args&&... args) ...
// 释放对象
static void Delete() ...
...
;这是一个可以根据指定顺序来创建全局单例对象的类,主要用在系统的初始化中,这样对于一些全局的对象在初始化的时候创建好,后续整个系统的各个模块就都可以使用了。
2
系统初始化过程
再继续看系统的初始化流程,首先在python/oneflow/__init__.py+217中可以找到下面这句话:
__oneflow_global_unique_env = env_util.GetEnv()GetEnv()方法在python/oneflow/framework/env_util.py中定义,其返回一个EnvHolder的Python对象,此对象初始化时,通过self._env_cxt = create_env()创建了OneFlow运行时所需要的环境上下文:
class EnvHolder(object):
def __init__(self):
if not HasAllMultiClientEnvVars():
SetDefaultMultiClientEnvVars()
self._env_cxt = create_env()
...
def create_env():
"""create environment
Returns:
Env: [description]
"""
global default_env_proto
assert len(default_env_proto.machine) > 0
CompleteEnvProto(default_env_proto)
if default_env_proto.ctrl_bootstrap_conf.world_size > 1:
check_non_localhost_proxy_and_print_warning()
return c_api_util.GetEnvContext(default_env_proto)create_env()中,首先会通过CompleteEnvProto创建默认的env_proto对象,然后根据此env proto对象创建oneflow所需要的环境上下文env_ctx。
这里面和初始化相关的主线是GetEnvContext,其定位位于python/oneflow/framework/c_api_util.py+45:
def GetEnvContext(env_proto):
assert type(env_proto) is env_pb2.EnvProto
env_proto_str = text_format.MessageToString(env_proto)
env_ctx = oneflow._oneflow_internal.EnvContext(env_proto_str)
return env_ctx这个EnvContext是oneflow内部导出的c api,其定义位于:oneflow/api/python/env/env.cpp:L46。
其作用即初始化一个单例——env作用域对象EnvGlobalObjectsScope,并在其构造之初,通过oneflow/core/job/env_global_objects_scope.cpp:L153的EnvGlobalObjectsScope::Init()方法初始化一些系统需要的其他全局单例对象/配置:
Maybe<void> EnvGlobalObjectsScope::Init(const EnvProto& env_proto)
...
Global<EnvDesc>::New(env_proto);
Global<ProcessCtx>::New();
...
#ifdef WITH_CUDA
Global<EagerNcclCommMgr>::New();
Global<CudnnConvAlgoCache>::New();
Global<embedding::EmbeddingManager>::New();
#endif
Global<vm::VirtualMachineScope>::New(Global<ResourceDesc, ForSession>::Get()->resource());
Global<EagerJobBuildAndInferCtxMgr>::New();
...
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
上面删去了很多代码,只展示了部分对象的创建,如:Global<vm::VirtualMachineScope>::New。
它会创建一个VirtualMachineScope的单例对象,这个类的构造函数因此会被执行一次,如下所示:
VirtualMachineScope::VirtualMachineScope(const Resource& resource)
Global<VirtualMachine>::New(resource, GlobalProcessCtx::Rank());
在这个构造函数里,又通过Global创建了一个VirtualMachine的单例对象,这是个很重要的单例对象,后面讲虚拟机时会用到它,所以先在这一节引出。
3
StreamType和InstructionType的注册
还需要再看一部分和后面虚拟机非常相关的内容作为准备,它们是StreamType和InstructionType的注册,先看下面这段代码,位于oneflow/core/eager/cpu_opkernel_instruction_type.cpp+34:
COMMAND(vm::RegisterInstructionType<CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType>("cpu.LocalCallOpKernel"));COMMAND是一个宏,位于oneflow/core/common/util.h+115,它的实现很巧妙,利用了匿名空间来保证在源文件定义的变量只在源文件可见,用CommandT和__LINE__在源文件中定义了一个唯一名字的struct,把注册语句放在它的构造函数中,然后再定义一个该struct的对象,其构造函数被自动执行的时候,注册语句也被执行:
#define COMMAND(...) \\
namespace \\
struct OF_PP_CAT(CommandT, __LINE__) \\
OF_PP_CAT(CommandT, __LINE__)() __VA_ARGS__; \\
; \\
OF_PP_CAT(CommandT, __LINE__) OF_PP_CAT(g_command_var, __LINE__); \\
再看实际的注册语句,它的模板参数是CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType,定义在oneflow/core/eager/cpu_opkernel_instruction_type.cpp+27,如下所示:
class CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType final : public LocalCallOpKernelInstructionType
public:
CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType() = default;
~CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType() override = default;
using stream_type = vm::CpuStreamType;
;这段代码中的stream_type在下面会很有用,这段代码其实是把CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType类和vm::CpuStreamType类建立了关联,再继续看COMMAND宏中的注册语句,单独摘出来如下所示:
vm::RegisterInstructionType<CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType>("cpu.LocalCallOpKernel")RegisterInstructionType是一个模板函数,定义位于oneflow/core/vm/instruction_type.h+80:
template<typename T>
void RegisterInstructionType(const std::string& instr_type_name)
RegisterInstrTypeId<T>(instr_type_name, StaticGlobalStreamType<typename T::stream_type>());
以这里COMMAND的示例中对CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType的注册为例,按行来看,注册函数RegisterInstructionType主要内容在:oneflow/core/vm/instruction_type.cpp+54:
void RegisterInstrTypeId(const std::string& instruction_name, const StreamType* stream_type,
const InstructionType* instruction_type)
InstrTypeId instr_type_id;
instr_type_id.__Init__(stream_type, instruction_type);
CHECK(InstrTypeId4InstructionName()->emplace(instruction_name, instr_type_id).second);
实际做了下面几件事(CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType的名字较长,为了方便表示,下面简称它为T):
-
初始化一个InstrTypeId对象,并调用其__Init__方法为其成员变量stream_type_和instruction_type_赋值,这里stream_type就是T::stream_type,即vm::CpuStreamType;instruction_type即指向T的指令类型的指针对象。
-
通过InstrTypeId4InstructionName()方法拿到一个静态HashMap<std::string, InstrTypeId> map对象的指针。
-
将instruction_name("cpu.LocalCallOpKernel")作为key,InstrTypeId对象instr_type_id作为value插入这个map中。
4
虚拟机调度过程1
前文《OneFlow学习笔记:从Functor到OpExprInterpreter》讲到了调用PhysicalRun之前的mirror mode和eager mode的大概流程,已经准备好了输入输出的EagerBlobObject以及一些context信息和相关的device信息,在调用PhysicalRun这个函数之后,就进入了虚拟机的部分。
4.1 放指令线程
PhysicalRun接受一个call-back function作为参数,这个call-back函数中会调用builder->LocalCallOpKernel这个函数,并且以前面准备好的输入、输出、ctx、device作为参数来执行,先来看PhysicalRun函数,它定义在oneflow/core/framework/instructions_builder.cpp+595:
Maybe<void> PhysicalRun(const std::function<Maybe<void>(InstructionsBuilder*)>& Build)
vm::InstructionMsgList instruction_list;
InstructionsBuilder instructions_builder(std::make_shared<vm::PhysicalIdGenerator>(),
&instruction_list);
JUST(Build(&instructions_builder));
JUST(vm::Run(instructions_builder.mut_instruction_list()));
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
这里的Build就是刚从传进来的call-back函数,整理出来再来加深一下印象:
[&](InstructionsBuilder* builder) -> Maybe<void>
return builder->LocalCallOpKernel(kernel, input_eager_blob_objects, output_eager_blob_objects, ctx, op_device);
在PhysicalRun中,以InstructionsBuilder对象为参数来调用这个call-back function,所以会执行InstructionsBuilder中的LocalCallOpKernel函数,这个函数位于oneflow/core/framework/instructions_builder.cpp+347:
Maybe<void> InstructionsBuilder::LocalCallOpKernel(...)
...
auto phy_instr_operand = JUST(vm::LocalCallOpKernelPhyInstrOperand::New(
opkernel, input_eager_blob_objects, output_eager_blob_objects, consistent_tensor_infer_result,
ctx, *one::CurrentDevVmDepObjectConsumeMode()));
auto instruction = intrusive::make_shared<vm::InstructionMsg>(
Global<VirtualMachine>::Get()->mut_vm(), JUST(op_device->local_call_instruction_name()),
parallel_desc_sym, phy_instr_operand);
instruction_list_->EmplaceBack(std::move(instruction));
...
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
这个函数逻辑大概是把输入op相关的信息打包成一个vm::InstructionMsg对象,然后放到instruction_list_这个list中。
到这里前面的PhysicalRun中的Build部分就分析完了,继续看Build之后的逻辑vm::Run,它主要是调了oneflow/core/vm/vm_util.cpp+34中的Run方法:
Maybe<void> Run(vm::InstructionMsgList* instr_msg_list)
auto* virtual_machine = JUST(GlobalMaybe<VirtualMachine>());
JUST(virtual_machine->Receive(instr_msg_list));
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
这里通过GlobalMaybe来得到了在前面第一节OneFlow初始化中讲到的被创建好的VirtualMachine对象,这里调用了VirtualMachine中的Receive函数,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine.cpp+204:
Maybe<bool> VirtualMachineEngine::Receive(
intrusive::shared_ptr<InstructionMsg>&& compute_instr_msg)
InstructionMsgList instr_msg_list;
instr_msg_list.EmplaceBack(std::move(compute_instr_msg));
return Receive(&instr_msg_list);
这里的vm_变量类型是intrusive::shared_ptr<vm::VirtualMachineEngine>,在我们的示例中,会走到else分支,也就调用了VirtualMachineEngine的Receive函数,它位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+422,VirtualMachineEngine是一个很大很复杂的类,这里我们不关注它的其它功能,只关注当前的流程,下面是Receive函数的代码:
Maybe<bool> VirtualMachineEngine::Receive(InstructionMsgList* compute_instr_msg_list)
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_PUSH("vm:Receive");
INTRUSIVE_UNSAFE_FOR_EACH_PTR(compute_instr_msg, compute_instr_msg_list)
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_PUSH(compute_instr_msg->DebugName());
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_POP();
bool old_list_empty = mut_pending_msg_list()->MoveFrom(compute_instr_msg_list);
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_POP();
return old_list_empty;
Maybe<bool> VirtualMachineEngine::Receive(
intrusive::shared_ptr<InstructionMsg>&& compute_instr_msg)
InstructionMsgList instr_msg_list;
instr_msg_list.EmplaceBack(std::move(compute_instr_msg));
return Receive(&instr_msg_list);
从这里看到并没有指令被执行,唯一的一条线索是传进来的compute_instr_msg_list最终被放入了mut_pending_msg_list()中,当前的线程只负责往队列里放指令,另外有线程会从队列里往外取指令来执行,所以继续搜下mut_pending_msg_list()会在哪里被用到,可以搜到在oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+514的Schedule函数中被调用,Schedule又在oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine.cpp+291中的ScheduleLoop函数中被调用,这就引入了使用指令的线程。
4.2 用指令线程
直接看ScheduleLoop线程函数被启动的地方,它在VirtualMachine的构造函数中作为一个线程函数被创建和启动,VirtualMachine的构造函数位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine.cpp+114,如下所示:
VirtualMachine::VirtualMachine(const Resource& resource, int64_t this_machine_id)
: vm_threads_closed_(false)
...
std::function<void()> SchedulerInitializer;
GetSchedulerThreadInitializer(&SchedulerInitializer);
schedule_thread_ = std::thread(&VirtualMachine::ScheduleLoop, this, SchedulerInitializer);
从前面第一节讲的的OneFlow初始化流程中可知,在OneFlow初始化的时候创建一个VirtualMachine的全局对象,自然其构造函数会被调用,所以这个VirtualMachine::ScheduleLoop线程函数在那时就被启动了,继续看ScheduleLoop的内容,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine.cpp+291:
void VirtualMachine::ScheduleLoop(const std::function<void()>& Initializer)
...
while (pending_notifier_.WaitAndClearNotifiedCnt() == kNotifierStatusSuccess)
...
do
...
do
...
do vm->Schedule(schedule_ctx); while (!vm->ThreadUnsafeEmpty());
vm->MoveToGarbageMsgListAndNotifyGC(schedule_ctx);
while (++i < kNumSchedulingPerTimoutTest);
while (MicrosecondsFrom(start) < kWorkingMicroseconds);
...
这里面最重要的是Schedule函数的调用,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+514,简化代码如下:
void VirtualMachineEngine::Schedule()
if (...) ReleaseFinishedInstructions();
if (...) TryRunBarrierInstruction();
if (...) HandleLocalPending();
if (...) DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructions();
这个函数里比较重要的两个函数是HandleLocalPending和DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructions,先看HandleLocalPending,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+62,它的精简代码如下:
void VirtualMachineEngine::HandlePending()
...
InstructionMsgList pending_instr_msgs;
INTRUSIVE_FOR_EACH_PTR(instr_msg, &pending_instr_msgs)
MakeInstructions(instr_msg, /*out*/ &new_instruction_list);
...
INTRUSIVE_FOR_EACH_PTR(instruction, &new_instruction_list)
ConsumeMirroredObjects(instruction);
if (likely(Dispatchable(instruction)))
mut_ready_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
new_instruction_list.Erase(instruction);
可见它的工作主要是通过MakeInstructions制作指令,然后把指令放入list,再看DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructions,它位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+320:
void VirtualMachineEngine::DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructions()
ReadyInstructionList tmp_ready_instruction_list;
mut_ready_instruction_list()->MoveTo(&tmp_ready_instruction_list);
INTRUSIVE_FOR_EACH(instruction, &tmp_ready_instruction_list)
...
DispatchInstruction(instruction.Mutable());
...
...
这个函数的主要工作是调用了DispatchInstruction,继续来看一下这个函数,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+344:
void VirtualMachineEngine::DispatchInstruction(Instruction* instruction,
const ScheduleCtx& schedule_ctx)
auto* stream = instruction->mut_stream();
stream->mut_running_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
if (stream->active_stream_hook().empty()) mut_active_stream_list()->PushBack(stream);
const auto& stream_type = stream->stream_type();
if (OnSchedulerThread(stream_type))
stream_type.Run(instruction);
else
stream->mut_thread_ctx()->mut_pending_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
schedule_ctx.OnWorkerLoadPending(stream->mut_thread_ctx());
从这个函数中可以看出,指令被stream_type.Run来执行了,这里打断一下,用下面一节内容来追一下这里的stream_type从哪来的。
5
指令中的stream
从上面第四节的最后一段代码中,可以看到stream_type来自于stream,stream来自于Instruction,本节来追一下Instruction中的stream是怎么来的。
以mirror mode为例,代码会首先进入4.1节讲过的LocalCallOpKernel函数执行,位于oneflow/core/framework/instructions_builder.cpp+347:
Maybe<void> InstructionsBuilder::LocalCallOpKernel(..., Symbol<Device> op_device)
...
const auto& instruction_name = JUST(StreamRoleSwitch<GetCallInstructionName>(
stream->stream_role(), stream->device()->enum_type()));
auto instruction = intrusive::make_shared<vm::InstructionMsg>(
Global<VirtualMachine>::Get()->mut_vm(), instruction_name, parallel_desc_sym,
phy_instr_operand);
instruction_list_->EmplaceBack(std::move(instruction));
...
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
这里主要是在创建指令instruction对象,创建完成后放入指令列表末尾。
这里先看一下instruction_name是怎么产生的,在GetCallInstructionName的结构体中维护着stream_role、stream type以及对应的指令名称instruction_name之间的映射关系,在StreamRoleSwitch模板中会转发至其Case方法,并最终返回instruction_name的字符串。
所以在我们的示例中会返回"cpu.LocalCallOpKernel",在第三节中的注册示例中,可以看到以这个字符串为key,注册了CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType这个类,它关联了vm::CpuStreamType类型,这些信息在后面都会用到。
再看InstructionMsg,它的定义位于oneflow/core/vm/instruction.h+39:
class InstructionMsg final : public intrusive::Base
...
InstrTypeId instr_type_id_;
std::string instr_type_name_;
...
Stream* phy_instr_stream_;
;InstructionMsg持有的InstrTypeId、Stream指针这两个成员和我们要追的stream的线索最相关,我们只需要关注这两个成员就好,在前面调用intrusive::make_shared<vm::InstructionMsg>(...)的时候,根据intrusive::make_shared的实现,会调用到InstructionMsg的下面这个__Init__函数,位于oneflow/core/vm/instruction.cpp+42:
void InstructionMsg::__Init__(VirtualMachineEngine* vm, const std::string& instr_type_name,
const std::shared_ptr<const ParallelDesc>& phy_instr_parallel_desc,
const std::shared_ptr<PhyInstrOperand>& phy_instr_operand)
__Init__();
if (likely(phy_instr_parallel_desc))
int device_id = phy_instr_parallel_desc->parallel_id2device_id().at(0);
vm->GetCachedInstrTypeIdAndPhyInstrStream(instr_type_name, device_id, mut_instr_type_id(),
&phy_instr_stream_);
...
instr_type_id_和phy_instr_stream_的赋值就是在上面代码中的GetCachedInstrTypeIdAndPhyInstrStream函数调用中完成的,定义位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+383:
void VirtualMachineEngine::GetCachedInstrTypeIdAndPhyInstrStream(const std::string& instr_type_name,
int device_id,
InstrTypeId* instr_type_id,
Stream** stream)
auto* cache = &instr_type_name2rt_instr_type_id_;
auto iter = cache->find(instr_type_name);
if (unlikely(iter == cache->end()))
const auto& instr_type_id_val = LookupInstrTypeId(instr_type_name);
const auto* stream_type = &instr_type_id_val.stream_type();
auto* stream_rt_desc = this->mut_stream_type2stream_rt_desc()->FindPtr(stream_type);
iter = cache->emplace(instr_type_name, RtInstrTypeId(instr_type_id_val, stream_rt_desc)).first;
instr_type_id->CopyFrom(iter->second.instr_type_id());
*stream = iter->second.GetStream(device_id);
这一段代码其实涉及的内容非常多,这里只能简单说一下,函数传进来的instr_type_name是"cpu.LocalCallOpKernel",先在VirtualMachineEngine的下面这个map成员查询这个key:
std::map<std::string, RtInstrTypeId> instr_type_name2rt_instr_type_id_;这个map的value type是RtInstrTypeId,从它可以得到InstrTypeId和相应的Stream指针,它定义位于oneflow/core/vm/runtime_instr_type_id.h+25:
class RtInstrTypeId final
public:
RtInstrTypeId(const RtInstrTypeId&) = default;
RtInstrTypeId(RtInstrTypeId&&) = default;
~RtInstrTypeId() = default;
RtInstrTypeId(const InstrTypeId& instr_type_id, StreamRtDesc* stream_rt_desc)
: instr_type_id_(instr_type_id), stream_rt_desc_(stream_rt_desc)
if (stream_rt_desc->stream_type().IsControlStreamType())
get_stream_ = &StreamRtDesc::GetSoleStream;
else
get_stream_ = &StreamRtDesc::GetDeviceStream;
const InstrTypeId& instr_type_id() const return instr_type_id_;
Stream* GetStream(int device_id) const return (stream_rt_desc_->*get_stream_)(device_id);
private:
const InstrTypeId instr_type_id_;
StreamRtDesc* stream_rt_desc_;
Stream* (StreamRtDesc::*get_stream_)(int device_id) const;
;如果没有从这个map中找到"cpu.LocalCallOpKernel"这个key,则会做下面操作:
if (unlikely(iter == cache->end()))
const auto& instr_type_id_val = LookupInstrTypeId(instr_type_name);
const auto* stream_type = &instr_type_id_val.stream_type();
auto* stream_rt_desc = this->mut_stream_type2stream_rt_desc()->FindPtr(stream_type);
iter = cache->emplace(instr_type_name, RtInstrTypeId(instr_type_id_val, stream_rt_desc)).first;
先通过LookupInstrTypeId查询第三节注册的数据结构C,从而找到"cpu.LocalCallOpKernel"相应的InstrTypeId,它里面包含相关的StreamTypeId信息,再使用这个StreamTypeId,通过调用mut_stream_type_id2stream_rt_desc()->FindPtr来找到对应的StreamRtDesc对象指针,然后根据instr_type_id_val和stream_rt_desc构造一个RtInstrTypeId对象作为value,维护到前面的map中,最后再从这个map得到InstrTypeId和相应的Stream指针返回。
顺便说一下mut_stream_type_id2stream_rt_desc()对应的数据结构,它在VirtualMachineEngine的__Init__函数中(构造的时候被调用)被初始化,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+358:
void VirtualMachineEngine::__Init__(const VmDesc& vm_desc)
...
INTRUSIVE_UNSAFE_FOR_EACH_PTR(stream_desc, &vm_desc.stream_type_id2desc())
if (stream_desc->num_threads() == 0) continue;
auto stream_rt_desc = intrusive::make_shared<StreamRtDesc>(stream_desc);
mut_stream_type_id2stream_rt_desc()->Insert(stream_rt_desc.Mutable());
...
这样就知道了构造好的InstructionMsg对象是怎么包含的Stream信息,继续看InstructionMsg是怎么转换为Instruction对象的,在前面4.2节中讲的HandleLocalPending函数,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+62:
void VirtualMachineEngine::HandlePending()
...
InstructionMsgList pending_instr_msgs;
INTRUSIVE_FOR_EACH_PTR(instr_msg, &pending_instr_msgs)
MakeInstructions(instr_msg, /*out*/ &new_instruction_list);
...
INTRUSIVE_FOR_EACH_PTR(instruction, &new_instruction_list)
ConsumeMirroredObjects(instruction);
if (likely(Dispatchable(instruction)))
mut_ready_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
new_instruction_list.Erase(instruction);
其中的MakeInstructions会做这个转换,它的定义位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+226,原来的Stream信息也会被维护到这个新的数据结构中:
void VirtualMachineEngine::MakeInstructions(InstructionMsg* instr_msg,
/*out*/ InstructionList* new_instruction_list)
const auto& instruction_type = instr_msg->instr_type_id().instruction_type();
bool is_barrier_instruction = instruction_type.IsFrontSequential();
Stream* stream = CHECK_NOTNULL(instr_msg->phy_instr_stream());
const auto& pd = instr_msg->phy_instr_parallel_desc();
intrusive::shared_ptr<Instruction> instr = stream->NewInstruction(instr_msg, pd);
LivelyInstructionListPushBack(instr.Mutable());
if (unlikely(is_barrier_instruction))
mut_barrier_instruction_list()->PushBack(instr.Mutable());
else
new_instruction_list->PushBack(instr.Mutable());
以上就是第四节末尾代码调用stream_type.Run()的时候,stream_type的由来,由前面的分析可知,它的实际类型就是和CpuLocalCallOpKernelInstructionType建立好关联的vm::CpuStreamType!下面继续看虚拟机的调度过程。
6
虚拟机调度过程2
再继续看第四节的最后一段代码,为方便阅读,重新贴一下主要内容,位于oneflow/core/vm/virtual_machine_engine.cpp+344:
void VirtualMachineEngine::DispatchInstruction(Instruction* instruction)
...
if (OnSchedulerThread(stream_type))
stream_type.Run(instruction);
else
stream->mut_thread_ctx()->mut_pending_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
schedule_ctx.OnWorkerLoadPending(stream->mut_thread_ctx());
...
从这个函数中可以看出,指令被stream_type.Run来执行了,从前面第五节的分析可知,stream_type是vm::CpuStreamType类型,继承自StreamType类型,StreamType定义于oneflow/core/vm/stream_type.h,下面是它的主要接口:
class StreamType
public:
virtual ~StreamType() = default;
void Run(Instruction* instruction) const Compute(instruction);
virtual const char* stream_tag() const = 0;
virtual void InitDeviceCtx(std::unique_ptr<DeviceCtx>* device_ctx, Stream* stream) const = 0;
virtual void InitInstructionStatus(const Stream& stream,
InstructionStatusBuffer* status_buffer) const = 0;
virtual void DeleteInstructionStatus(const Stream& stream,
InstructionStatusBuffer* status_buffer) const = 0;
virtual bool QueryInstructionStatusDone(const Stream& stream,
const InstructionStatusBuffer& status_buffer) const = 0;
virtual void Compute(Instruction* instruction) const = 0;
virtual intrusive::shared_ptr<StreamDesc> MakeStreamDesc(const Resource& resource,
int64_t this_machine_id) const = 0;
virtual bool OnSchedulerThread() const = 0;
virtual bool SupportingTransportInstructions() const = 0;
virtual bool IsControlStreamType() const return false;
protected:
StreamType() = default;
;这里面含有前面代码中用到的Run接口(stream_type.Run),它的实现位于Compute函数中。从StreamType的定义可以知道,这是一个虚接口,StreamType有下面这些子类实现:
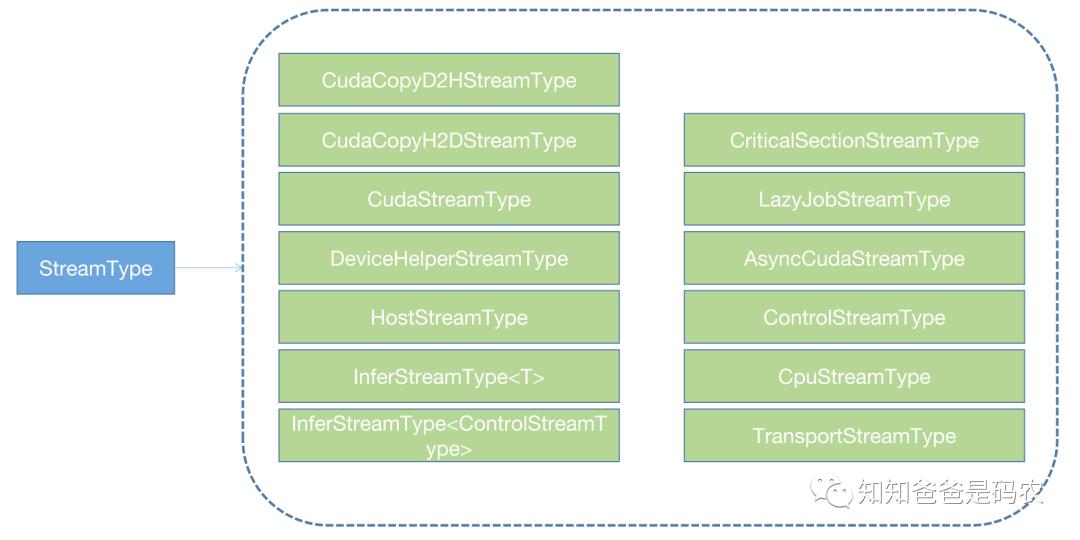
图1
我们这里使用的是CpuStreamType,定义位于oneflow/core/vm/cpu_stream_type.h,它的Compute函数位于oneflow/core/vm/cpu_stream_type.cpp+50,如下所示:
void CpuStreamType::Compute(Instruction* instruction) const
...
const auto& instr_type_id = instruction->mut_instr_msg()->instr_type_id();
instr_type_id.instruction_type().Compute(instruction);
auto* status_buffer = instruction->mut_status_buffer();
NaiveInstrStatusQuerier::MutCast(status_buffer->mut_buffer()->mut_data())->set_done();
...
可以看到这里又调用了instr_type_id.instruction_type().Compute()这个函数,这个Compute属于instruction_type()对应的类中,可以查到instruction_type()会返回一个InstructionType类型的const引用对象,所以关注InstructionType类即可,它的定义位于oneflow/core/vm/instruction_type.h,里面有Compute虚接口:
class InstructionType
...
virtual void Compute(Instruction* instruction) const = 0;
virtual void ComputeInFuseMode(InstructionMsg* instr_msg) const LOG(FATAL) << "UNIMPLEMENTED";
...
;这也是个继承体系,InstructionType有非常多的子类,下面是我找到的一部分示例,没有列完:
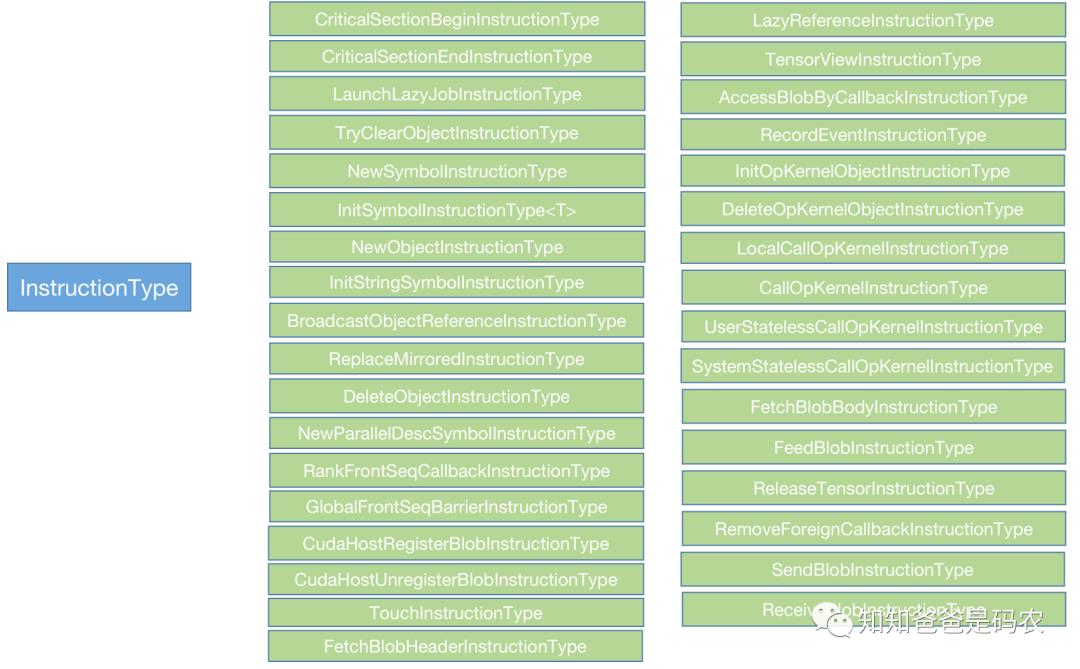
我们调用的Compute位于上图中的LocalCallOpKernelInstructionType,位于oneflow/core/eager/opkernel_instruction_type.cpp+150,它的Compute函数定义如下:
void LocalCallOpKernelInstructionType::Compute(vm::Instruction* instruction) const
CHECK_JUST(LocalCallOpKernelUtil::Compute(instruction));
可见又继续调用了LocalCallOpKernelUtil::Compute,继续追这个函数,它的定义位于oneflow/core/eager/opkernel_instruction_type.cpp+44:
struct LocalCallOpKernelUtil final
static inline Maybe<void> Compute(vm::Instruction* instruction)
...
OpKernelCompute(operand, device_ctx, state, cache);
...
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
...
;这里又继续调用了OpKernelCompute,在同一个类中:
struct LocalCallOpKernelUtil final
...
static inline void OpKernelCompute(LocalCallOpKernelPhyInstrOperand* operand,
DeviceCtx* device_ctx, user_op::OpKernelState* state,
const user_op::OpKernelCache* cache)
...
operand->user_opkernel()->Compute(compute_ctx, state, cache);
...
;其中user_opkernel()会返回一个user_op::OpKernel的指针,而这个OpKernel就是我们定义算子的时候必须要继承的一个基类,以我们的relu示例来说,relu的计算部分定义在oneflow/user/kernels/relu_kernel.cpp,精简代码如下:
class ReluKernel final : public user_op::OpKernel, public user_op::CudaGraphSupport
private:
void Compute(user_op::KernelComputeContext* ctx) const override
// do computing!
;至此,终于从上到下打通了一条执行路线!
Reference
本文主要梳理了OneFlow虚拟机的的作用和相关实现,主要参考的是OneFlow的官方代码和之前的一些相关文章,但限于篇幅和本人目前的认知,里面有很多地方还没有弄懂或者没有总结,比如指令边的部分,SkipList、SkipListHead、ListHookArray、ListHook、SkipListHook等基础数据结构的作用及实现细节等,需要继续学习的地方还有很多,继续加油~
下面是相关链接:
-
https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/oneflow
(本文参考代码:
https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/oneflow/commit/888ad73fe28e2a4509ce7e563f196011e88b817d)
特别感谢同事路强、俊丞、后江在我学习和理解这部分内容的过程中提供的帮助。
其他人都在看
欢迎下载体验OneFlow v0.7.0最新版本:
https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/oneflow/ https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/oneflow/
https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/oneflow/
以上是关于OneFlow学习笔记:从OpExprInterpreter到OpKernel的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Global Tensor和实习总结|OneFlow学习笔记
BBuf的CUDA笔记八,对比学习OneFlow 和 FasterTransformer 的 Softmax Cuda实现