JavaIo流总结
Posted 野生java研究僧
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaIo流总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
JavaIo流总结
1.学习javaIo流前置知识
1.先了解计算机存储单位的换算
8bit(只能存放1和0的单位,最小的存储单位)= 1Byte(字节)
Byte (B) = 8 bit
1 Kilo Byte (KB) = 1024 B
1 Mega Byte (MB) = 1024 KB
1 Giga Byte (GB)= 1024 MB
1 Tera Byte (TB)= 1024 GB
1 Peta Byte (PB) = 1024 TB
1 Exa Byte (EB) = 1024 PB
1 Zetta Byte (ZB) = 1024 EB
1 Yotta Byte (YB) = 1024 ZB
1 Bronto Byte (BB) = 1024 YB
1 Nona Byte (NB) =1024 BB
1 Dogga Byte (DB) =1024 NB
1 Corydon Byte (CB) = 1024 DB
1 Xero Byte (XB) = 1024 CB
2.io流的分类
1.按照功能来区分
- 字节流:节流操作的单元是数据单元是8位的字节
- 字符流:字符流操作的是数据单元为16位的字符
2.按照输出方向来区分
- 输入流:往内存中读叫做输入流,也就是将磁盘上的文件读取到内存中
- 输出流:将内存中的数据输出到磁盘上就叫做输出流
File类的常用方法
在java中,所有的文件路径和都被抽象为一个叫做File的类,这个类是用来操作我们电脑中的文件的。
public String getAbsolutePath() :返回此File的绝对路径名字符串。
注意:无论路径是绝对的还是相对的,getAbsolutePath方法返回的都是绝对路
public String getPath() :将此File转换为路径名字符串, 获取的构造方法中传递的路径
注意:将此File转换为路径名字符串。
public String getName() :返回由此File表示的文件或目录的名称。
public long length() :返回由此File表示的文件的长度。
注意:
文件夹是没有大小概念的,不能获取文件夹的大小
如果构造方法中给出的路径不存在,那么length方法返回0
public boolean exists() :此File表示的文件或目录是否实际存在。
public boolean isDirectory() :此File表示的是否为目录。(判断构造方法的路径是否以文件夹结尾)
public boolean isFile() :此File表示的是否为文件。(判断构造方法的路径是否以文件结尾)
public boolean createNewFile() :当且仅当具有该名称的文件尚不存在时,创建一个新的空文件。
public boolean delete() :删除由此File表示的文件或目录。(不走回收站,谨慎操作!)
public boolean mkdir() :创建由此File表示的目录。
public boolean mkdirs() :创建由此File表示的目录,包括任何必需但不存在的父目录。
public String[] list() :返回一个String数组,表示该File目录中的所有子文件或目录。
public File[] listFiles() :返回一个File数组,表示该File目录中的所有的子文件或目录。
File的案例实战:查询某个路径下的文件是否存在
/**
* 查询某个路径下的某个文件是否存在
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @param fileName 文件名称
* @return 如果存在 返回该文件的的绝对路径
*/
public static String fileIsExist(String filePath,String fileName)
if (!(fileName!=null && fileName.length()>0) || !(filePath!=null && filePath.length()>0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件名称或者文件路径不能为空");
File file = new File(filePath);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(files));
for (int i = 0; i<files.length; i++)
if (files[i].isFile() )
if (files[i].getName().equals(fileName))
return files[i].getAbsolutePath();
else // 如果不是文件继续向下递归
fileIsExist(files[i].getAbsolutePath(),fileName);
return null;
2.io流的继承体系
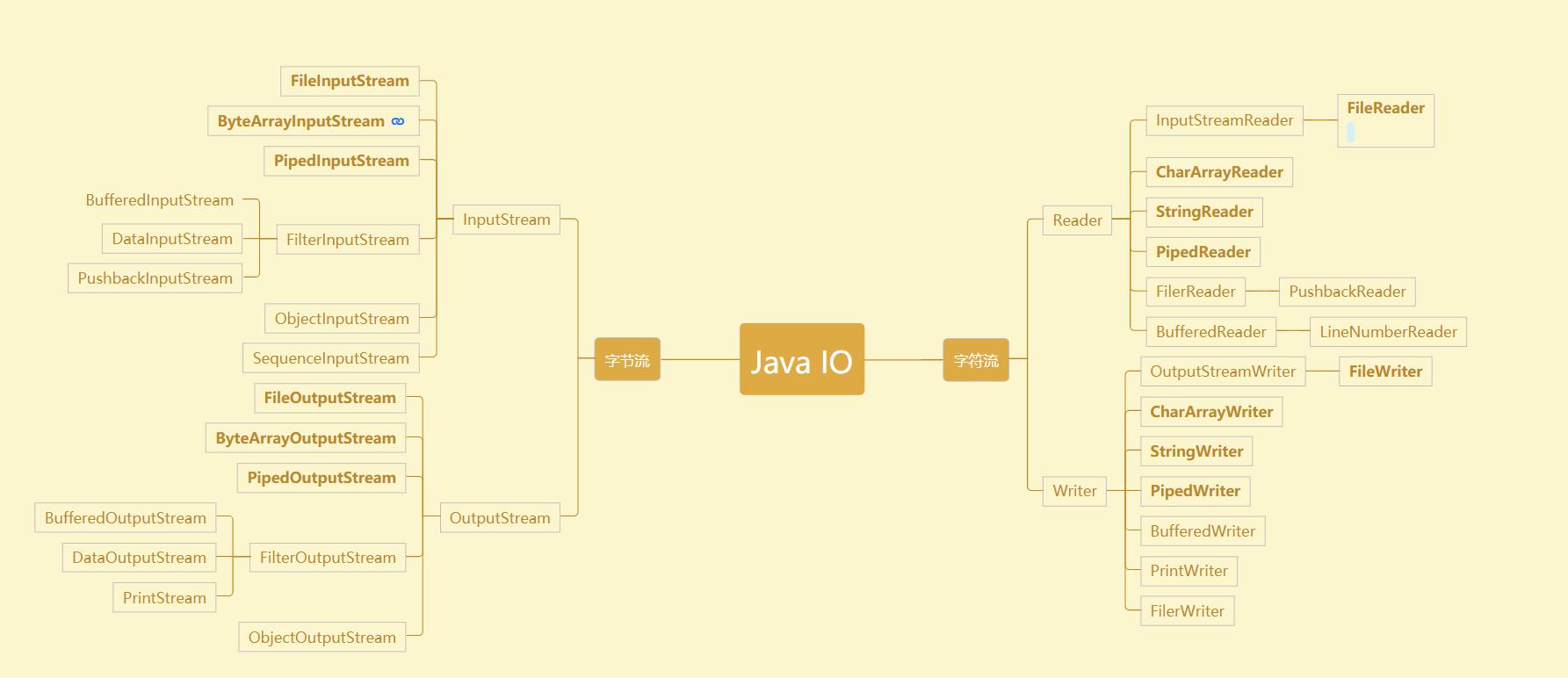 此图在我在网上找的,感谢这位网友的图。 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44411569
此图在我在网上找的,感谢这位网友的图。 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44411569
我们需要知道四个顶级的接口
字节流
- java.io.InputStream 字节输入流
- java.io.OutputStream 字节输出流
字符流
- java.io.Reader 字符输入流
- java.io.Writer 字符输出流
所有的流(输入输出)都实现了 java.io.Closeable接口,都是可关闭的,都有close()方法。
流毕竟是一个管道,这个是内存和硬盘之间的通道,用完之后一定要关闭,不然会耗费(占用)很多资源。养成好习惯,用完流一定要关闭。
所有的输出流都实现了 java.io.Flushable接口,都是可刷新的,都有flush()方法。
养成一个好习惯,输出流在最终输出之后,一定要记得flush()
刷新一下。这个刷新表示将通道/管道当中剩余未输出的数据
强行输出完(清空管道!)刷新的作用就是清空管道。
注意:如果没有flush()可能会导致丢失数据。
3.字节流
3.1 FileInputStrame
字节流是万能流,既可以读取文本,也可以读取二进制文件,比如视频,图片等文件。
他可以三种读取方式:
// (一次读一个byte数组,从什么位置开始读,读取的长度)
int read(byte b[], int off, int len)
// 一次读一个字节
int in.read();
// 一次读一个byte数组,byte数组有多大,就读取多少内容
int in.read(byte[] b);
案例:读取一个文件中的文本内容,并且输出到控制台
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStrameTest
public static void main(String[] args)
File file = new File("file/dengGao.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
FileInputStream in = null;
try
in = new FileInputStream(file);
// 每次读取的字节数,读取完的时候返回-1
int readCount = 0;
// 将每次读取到的内容放到这个字符串中
StringBuffer redContent = new StringBuffer();
// 循环读取文件中的内容,每次读取1KB,直到读取完毕为止
while ((readCount =in.read(bytes))!=-1)
redContent.append(new String(bytes,0,readCount));
System.out.println(redContent);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
in.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3.2 FileOutputStream
案例:将内存中的字符串写入到文本中
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamTest
public static void main(String[] args)
String wirteContent = " 长恨歌" +
"作者:白居易\\n" +
"汉皇重色思倾国,御宇多年求不得。\\n" +
"杨家有女初长成,养在深闺人未识。\\n" +
"天生丽质难自弃,一朝选在君王侧。\\n" +
"回眸一笑百媚生,六宫粉黛无颜色。\\n" +
"春寒赐浴华清池,温泉水滑洗凝脂。\\n" +
"侍儿扶起娇无力,始是新承恩泽时。\\n" +
"云鬓花颜金步摇,芙蓉帐暖度春宵。\\n" +
"春宵苦短日高起,从此君王不早朝。\\n" +
"承欢侍宴无闲暇,春从春游夜专夜。\\n" +
"后宫佳丽三千人,三千宠爱在一身。\\n" +
"金屋妆成娇侍夜,玉楼宴罢醉和春。\\n" +
"姊妹弟兄皆列土,可怜光彩生门户。\\n" +
"遂令天下父母心,不重生男重生女。\\n" +
"骊宫高处入青云,仙乐风飘处处闻。\\n" +
"缓歌慢舞凝丝竹,尽日君王看不足。\\n" +
"渔阳鼙鼓动地来,惊破霓裳羽衣曲。\\n" +
"九重城阙烟尘生,千乘万骑西南行。\\n" +
"翠华摇摇行复止,西出都门百余里。\\n" +
"六军不发无奈何,宛转蛾眉马前死。\\n" +
"花钿委地无人收,翠翘金雀玉搔头。\\n" +
"君王掩面救不得,回看血泪相和流。\\n" +
"黄埃散漫风萧索,云栈萦纡登剑阁。\\n" +
"峨嵋山下少人行,旌旗无光日色薄。\\n" +
"蜀江水碧蜀山青,圣主朝朝暮暮情。\\n" +
"行宫见月伤心色,夜雨闻铃肠断声。\\n" +
"天旋日转回龙驭,到此踌躇不能去。\\n" +
"马嵬坡下泥土中,不见玉颜空死处。\\n" +
"君臣相顾尽沾衣,东望都门信马归。\\n" +
"归来池苑皆依旧,太液芙蓉未央柳。\\n" +
"芙蓉如面柳如眉,对此如何不泪垂。\\n" +
"春风桃李花开夜,秋雨梧桐叶落时。\\n" +
"西宫南苑多秋草,落叶满阶红不扫。\\n" +
"梨园弟子白发新,椒房阿监青娥老。\\n" +
"夕殿萤飞思悄然,孤灯挑尽未成眠。\\n" +
"迟迟钟鼓初长夜,耿耿星河欲曙天。\\n" +
"鸳鸯瓦冷霜华重,翡翠衾寒谁与共。\\n" +
"悠悠生死别经年,魂魄不曾来入梦。\\n" +
"临邛道士鸿都客,能以精诚致魂魄。\\n" +
"为感君王辗转思,遂教方士殷勤觅。\\n" +
"排空驭气奔如电,升天入地求之遍。\\n" +
"上穷碧落下黄泉,两处茫茫皆不见。\\n" +
"忽闻海上有仙山,山在虚无缥渺间。\\n" +
"楼阁玲珑五云起,其中绰约多仙子。\\n" +
"中有一人字太真,雪肤花貌参差是。\\n" +
"金阙西厢叩玉扃,转教小玉报双成。\\n" +
"闻道汉家天子使,九华帐里梦魂惊。\\n" +
"揽衣推枕起徘徊,珠箔银屏迤逦开。\\n" +
"云鬓半偏新睡觉,花冠不整下堂来。\\n" +
"风吹仙袂飘飖举,犹似霓裳羽衣舞。\\n" +
"玉容寂寞泪阑干,梨花一枝春带雨。\\n" +
"含情凝睇谢君王,一别音容两渺茫。\\n" +
"昭阳殿里恩爱绝,蓬莱宫中日月长。\\n" +
"回头下望人寰处,不见长安见尘雾。\\n" +
"惟将旧物表深情,钿合金钗寄将去。\\n" +
"钗留一股合一扇,钗擘黄金合分钿。\\n" +
"但令心似金钿坚,天上人间会相见。\\n" +
"临别殷勤重寄词,词中有誓两心知。\\n" +
"七月七日长生殿,夜半无人私语时。\\n" +
"在天愿作比翼鸟,在地愿为连理枝。\\n" +
"天长地久有时尽,此恨绵绵无绝期。\\n";
FileOutputStream os = null;
try
File file = new File("file/changHenGe");
os = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = wirteContent.getBytes("utf-8");
// 将一个byte数组的内容直接写入到磁盘
os.write(bytes);
// 写完后记得刷新管道
os.flush();
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
os.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3.3 使用FileInputStrame 和 FileOutputStream完成文件的复制
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileCopyStreamTest
public static void main(String[] args)
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
try
in = new FileInputStream("file/sources.txt");
os = new FileOutputStream("file/target.txt");
//一次最多读1字节
byte [] bytes = new byte[1024];
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = in.read(bytes)) != -1)
// write(byte数组,bytes中的起始偏移量,需要写入的字节数);
// 核心点在于每次读多少,就写入多少
os.write(bytes,0,readCount);
os.flush();
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
// 记住流用完一定要关闭,如果有多个流需要分开try,否则会影响其他流的关闭
try
in.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
try
os.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3.4 BufferedInputStream
案例:使用BufferedInputStream读取磁盘上的文件
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedInputStreamTest
public static void main(String[] args)
try (
BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("copy/sources.txt"))
)
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = in.read(bytes)) !=-1)
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3.5 BufferedOutputStream
使用 BufferedOutputStream向文件中写入的内容
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedOutputStreamTest
public static void main(String[] args)
String content = " 登高\\n" +
" 作者:杜甫\\n" +
"风急天高猿啸哀,渚清沙白鸟飞回。\\n" +
"无边落木萧萧下,不尽长江滚滚来。\\n" +
"万里悲秋常作客,百年多病独登台。\\n" +
"艰难苦恨繁霜鬓,潦倒新停浊酒杯。";
try (BufferedOutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy/target.txt"));)
os.write(content.getBytes("utf-8"));
os.flush();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3.6 完成目录的深层拷贝
import java.io.*;
public class DirCopyTest
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
File srcFolder = new File("D:\\\\IDE2019\\\\code\\\\javase-io\\\\file");
File destFolder = new File("D:\\\\IDE2019\\\\code\\\\javase-io\\\\copy");
copyFolder(srcFolder, destFolder);
/**
* 复制多级文件夹
*
* @param srcFolder 源文件夹
* @param destFolder 目的文件夹
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void copyFolder(File srcFolder, File destFolder) throws IOException
// 判断路径是否存在
if (!destFolder.exists())
destFolder.mkdirs();
// 获取目的文件列表
File[] listFiles = srcFolder.listFiles();
// 遍历目的文件列表
for (File file : listFiles)
if (file.isDirectory())
copyFolder(file, new File(destFolder, file.getName()));
else
copyFile(file, new File(destFolder, file.getName()));
/**
* 复制文件
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param destFile 目的文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1)
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.close();
bis.close();
3.7 ByteArrayInputStream
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class ByteArrayInputStreamTest
public static void main(String[] args)
String content = "hello world";
// 如以上是关于JavaIo流总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章