强化学习—— 离散与连续动作空间(随机策略梯度与确定策略梯度)
Posted CyrusMay
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了强化学习—— 离散与连续动作空间(随机策略梯度与确定策略梯度)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
强化学习—— 离散与连续动作空间(随机策略梯度与确定策略梯度)
1. 动作空间
1.1 离散动作空间
- 比如: l e f t , r i g h t , u p \\left,right,up\\ left,right,up
- DQN可以用于离散的动作空间(策略网络)

1.2 连续动作空间
- 比如:
A
=
[
0
∘
,
18
0
∘
]
∗
[
0
∘
,
36
0
∘
]
A=[0^\\circ ,180^\\circ ]*[0^\\circ ,360^\\circ ]
A=[0∘,180∘]∗[0∘,360∘]
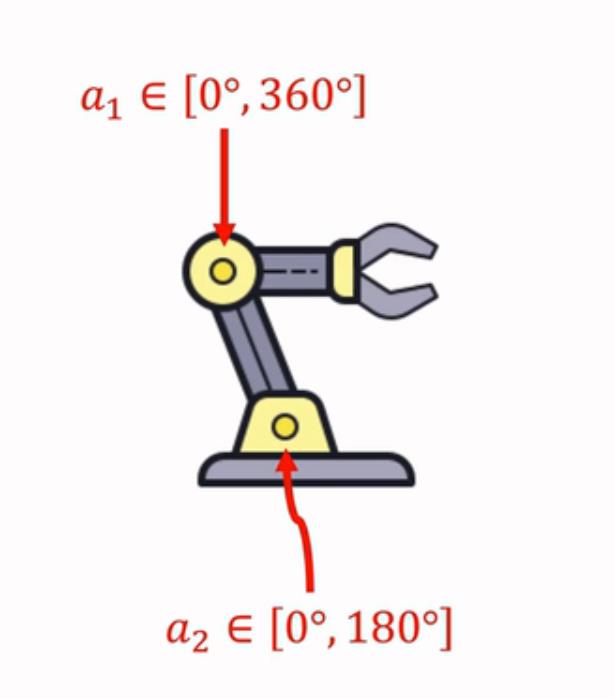
- 连续动作空间的两种处理方式:
- 离散化(discretization):比如机械臂进行二维网格划分。假设d为连续动作空间的自由度,动作离散化后的数量会随着d的增加呈现指数增长,从而造成维度灾难。
- 使用确定策略梯度。
- 使用随机策略梯度。
2. 确定策略梯度做连续控制
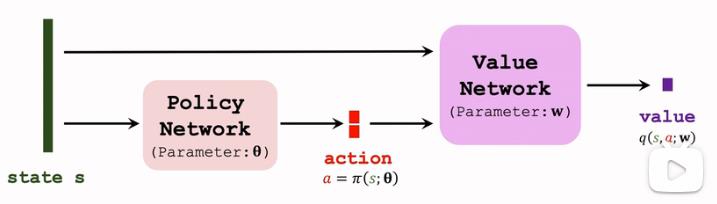
- 动作空间为 R d R^d Rd的一个子集
2.1 确定策略梯度推导
- 确定策略网络: a = π ( s ; θ ) a = \\pi(s;\\theta) a=π(s;θ)
- 价值网络(输出为一个标量):
q
(
s
,
a
;
W
)
q(s,a;W)
q(s,a;W)
网络学习过程为:
- 观测到一个transition: ( s t , a t , r t , s t + 1 ) (s_t,a_t,r_t,s_t+1) (st,at,rt,st+1)
- 计算t时刻价值网络的函数值: q t = q ( s t , a t ; W ) q_t = q(s_t,a_t;W) qt=q(st,at;W)
- 计算t+1时刻价值网络的函数值: a t + 1 − = π ( s t + 1 ; θ ) q t + 1 = q ( s t + 1 , a t + 1 − ; W ) a_t+1^-=\\pi(s_t+1;\\theta)\\\\q_t+1=q(s_t+1,a_t+1^-;W) at+1−=π(st+1;θ)qt+1=q(st+1,at+1−;W)
- TD Error为: δ t = q t − ( r t + γ ⋅ q t + 1 ) \\delta_t=q_t-(r_t+\\gamma\\cdot q_t+1) δt=qt−(rt+γ⋅qt+1)
- 更新价值网络: W ← W − α ⋅ ∂ q ( s t , a t ; W ) ∂ W W\\gets W-\\alpha\\cdot\\frac\\partial q(s_t,a_t;W)\\partial W W←W−α⋅∂W∂q(st,at;W)
- 更新策略网络所需的策略梯度推导: 策 略 网 络 的 目 标 为 通 过 策 略 网 络 a = π ( s ; θ ) 做 出 的 决 策 可 以 增 加 价 值 网 络 q = q ( s , a ; W ) 的 值 。 因 此 确 定 策 略 梯 度 ( d e t e r m i n i s t i c p o l i c y g r a d i e n t , D P G ) 为 : g = ∂ q ( s , π ( s ; θ ) ; W ) ∂ θ = ∂ q ( s . π ( s ; θ ) ; W ) ∂ π ( s ; θ ) ⋅ ∂ π ( s ; θ ) ∂ θ 策略网络的目标为通过策略网络a=\\pi(s;\\theta)\\\\做出的决策可以增加价值网络q=q(s,a;W)的值。\\\\ 因此确定策略梯度(deterministic policy gradient, DPG)为:\\\\ g=\\frac\\partial q(s,\\pi(s;\\theta);W)\\partial \\theta=\\frac\\partial q(s.\\pi(s;\\theta);W)\\partial \\pi(s;\\theta)\\cdot \\frac\\partial \\pi(s;\\theta)\\partial \\theta 策略网络的目标为通过策略网络a=π(s;θ)做出的决策可以增加价值网络q=q(s,a;W)的值。因此确定策略梯度(deterministicpolicygradient,DPG)为:g=∂θ∂q(s,π(s;θ);W)=∂π(s;θ)∂q(s.π(s;θ);W)⋅∂θ∂π(s;θ)
- 依据确定策略梯度进行策略网络参数更新: g = ∂ q ( s , π ( s ; θ ) ; W ) ∂ θ = ∂ q ( s . π ( s ; θ ) ; W ) ∂ π ( s ; θ ) ⋅ ∂ π ( s ; θ ) ∂ θ θ ← θ + β ⋅ g g=\\frac\\partial q(s,\\pi(s;\\theta);W)\\partial \\theta=\\frac\\partial q(s.\\pi(s;\\theta);W)\\partial \\pi(s;\\theta)\\cdot \\frac\\partial \\pi(s;\\theta)\\partial \\theta\\\\ \\theta\\gets \\theta+\\beta\\cdot g g=∂θ∂q(s,π(s;θ);W)=∂π(s;θ)∂q(s.π(s;θ);W)⋅∂θ∂π(s;θ)θ←θ+β⋅g
2.2 确定策略梯度网络的改进
2.2.1 使用Target网络
Bootstrapping现象:
- TD Target为: δ t = q t − ( r t + γ ⋅ q t − 1 ) \\delta_t =q_t-(r_t+\\gamma\\cdot q_t-1) δt=qt−以上是关于强化学习—— 离散与连续动作空间(随机策略梯度与确定策略梯度)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章