不一样的视角来学习Spring源码之AOP---下
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了不一样的视角来学习Spring源码之AOP---下相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
不一样的视角来学习Spring源码之AOP---下
系列文章:
jdk 和 cglib 在 Spring 中的统一
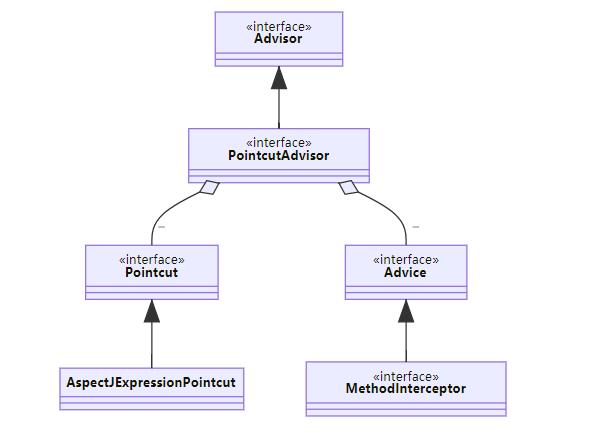
Spring 中对切点、通知、切面的抽象如下
- 切点:接口 Pointcut,典型实现 AspectJExpressionPointcut
- 通知:典型接口为 MethodInterceptor 代表环绕通知
- 切面:Advisor,包含一个 Advice 通知,PointcutAdvisor 包含一个 Advice 通知和一个 Pointcut
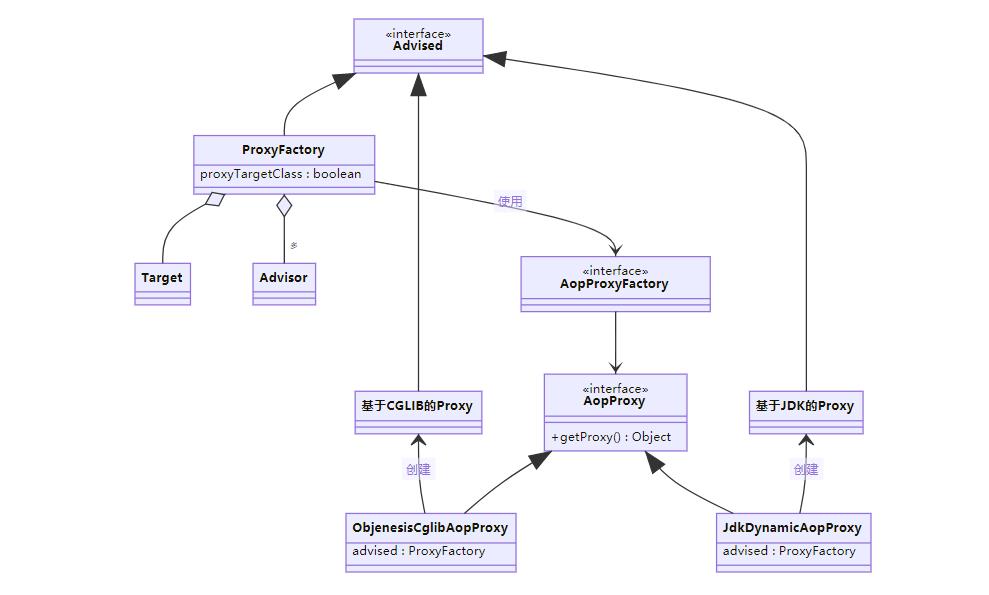
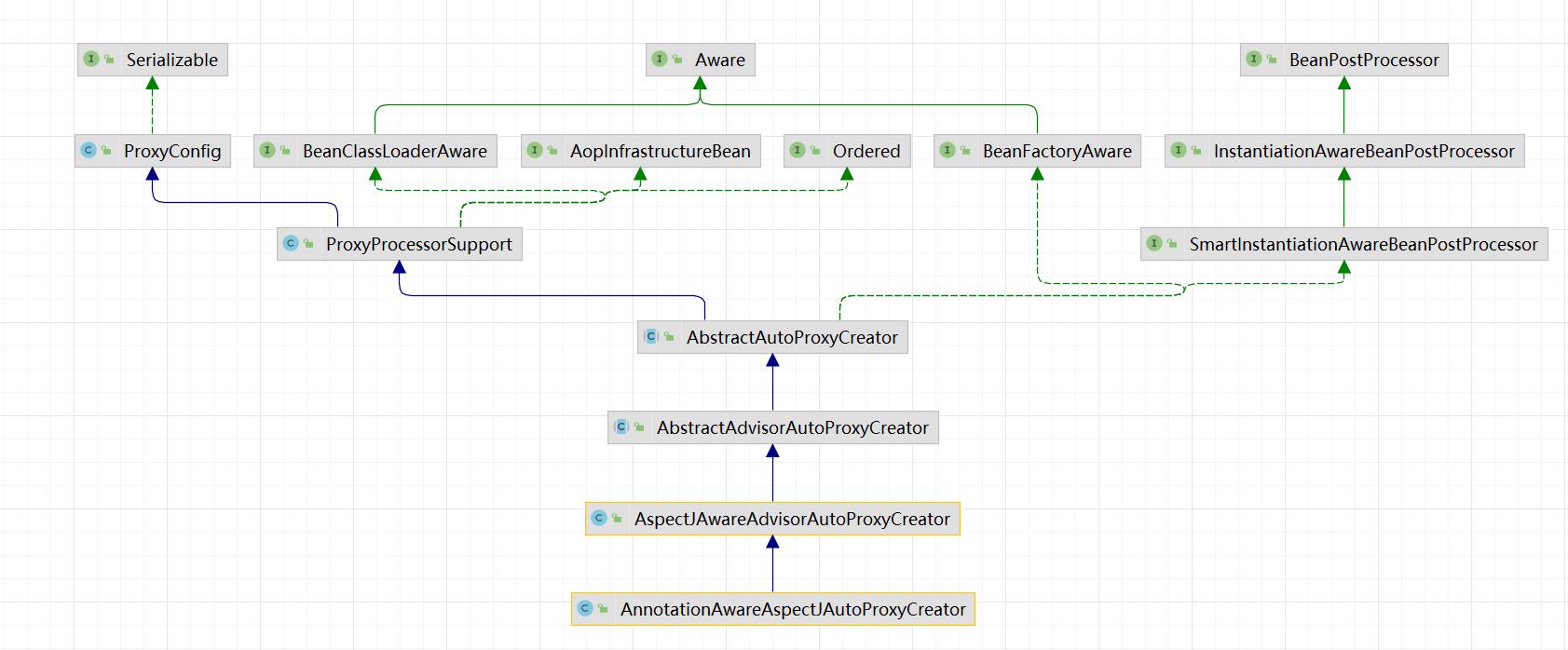
代理相关类图
- AopProxyFactory 根据 proxyTargetClass 等设置选择 AopProxy 实现
- AopProxy 通过 getProxy 创建代理对象
- 图中 Proxy 都实现了 Advised 接口,能够获得关联的切面集合与目标(其实是从 ProxyFactory 取得)
- 调用代理方法时,会借助 ProxyFactory 将通知统一转为环绕通知:MethodInterceptor
底层切点、通知、切面使用演示
public class A15
public static void main(String[] args)
/*
两个切面概念
aspect =
通知1(advice) + 切点1(pointcut)
通知2(advice) + 切点2(pointcut)
通知3(advice) + 切点3(pointcut)
...
advisor = 更细粒度的切面,包含一个通知和切点
*/
// 1. 备好切点
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
// 2. 备好通知
MethodInterceptor advice = invocation ->
System.out.println("before...");
Object result = invocation.proceed(); // 调用目标
System.out.println("after...");
return result;
;
// 3. 备好切面----只包含一个pointcut和advice
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, advice);
/*
4. 创建代理
a. proxyTargetClass = false, 目标实现了接口, 用 jdk 实现
b. proxyTargetClass = false, 目标没有实现接口, 用 cglib 实现
c. proxyTargetClass = true, 总是使用 cglib 实现
*/
Target2 target = new Target2();
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory();
factory.setTarget(target);
factory.addAdvisor(advisor);
factory.setInterfaces(target.getClass().getInterfaces());
factory.setProxyTargetClass(false);
Target2 proxy = (Target2) factory.getProxy();
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
proxy.foo();
proxy.bar();
/*
学到了什么
a. Spring 的代理选择规则
b. 底层的切点实现
c. 底层的通知实现
d. ProxyFactory 是用来创建代理的核心实现, 用 AopProxyFactory 选择具体代理实现
- JdkDynamicAopProxy
- ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
*/
interface I1
void foo();
void bar();
static class Target1 implements I1
public void foo()
System.out.println("target1 foo");
public void bar()
System.out.println("target1 bar");
static class Target2
public void foo()
System.out.println("target2 foo");
public void bar()
System.out.println("target2 bar");

收获💡
- 底层的切点实现
- 底层的通知实现
- 底层的切面实现
- ProxyFactory 用来创建代理
- 如果指定了接口,且 proxyTargetClass = false,使用 JdkDynamicAopProxy
- 如果没有指定接口,或者 proxyTargetClass = true,使用 ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
- 例外:如果目标是接口类型或已经是 Jdk 代理,使用 JdkDynamicAopProxy
注意
- 要区分本章节提到的 MethodInterceptor,它与之前 cglib 中用的的 MethodInterceptor 是不同的接口
切点匹配
切点匹配演示
public class A16
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException
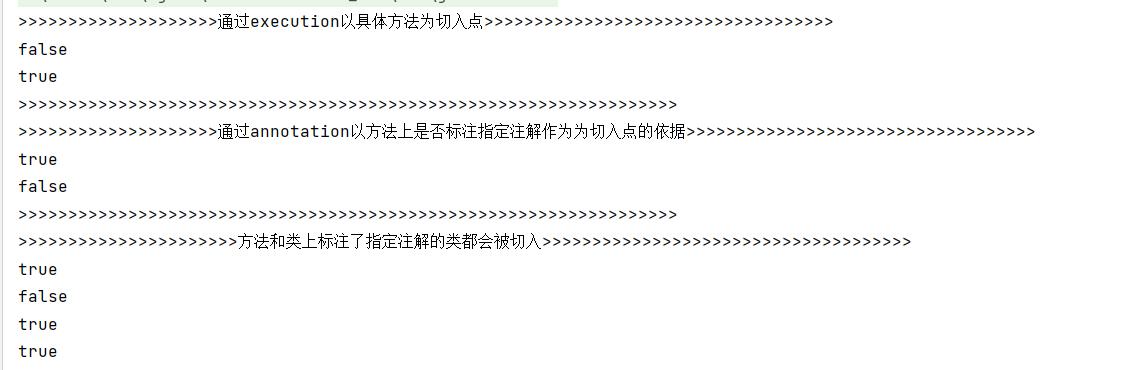
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>通过execution以具体方法为切入点>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
AspectJExpressionPointcut pt1 = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pt1.setExpression("execution(* bar())");
System.out.println(pt1.matches(T1.class.getMethod("foo"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt1.matches(T1.class.getMethod("bar"), T1.class));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>通过annotation以方法上是否标注指定注解作为为切入点的依据>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
AspectJExpressionPointcut pt2 = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pt2.setExpression("@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)");
System.out.println(pt2.matches(T1.class.getMethod("foo"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt2.matches(T1.class.getMethod("bar"), T1.class));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>方法和类上标注了指定注解的类都会被切入>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
StaticMethodMatcherPointcut pt3 = new StaticMethodMatcherPointcut()
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass)
// 检查方法上是否加了 Transactional 注解
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(method);
if (annotations.isPresent(Transactional.class))
return true;
// 查看类上是否加了 Transactional 注解----到继承树上去寻找---本类---父类--接口上有也算
annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(targetClass, MergedAnnotations.SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY);
if (annotations.isPresent(Transactional.class))
return true;
return false;
;
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T1.class.getMethod("foo"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T1.class.getMethod("bar"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T2.class.getMethod("foo"), T2.class));
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T3.class.getMethod("foo"), T3.class));
/*
学到了什么
a. 底层切点实现是如何匹配的: 调用了 aspectj 的匹配方法
b. 比较关键的是它实现了 MethodMatcher 接口, 用来执行方法的匹配
*/
static class T1
@Transactional
public void foo()
public void bar()
@Transactional
static class T2
public void foo()
@Transactional
interface I3
void foo();
static class T3 implements I3
public void foo()
收获💡
- 常见 aspectj 切点用法
- aspectj 切点的局限性,实际的 @Transactional 切点实现
从 @Aspect 到 Advisor
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 9:17
*/
public class A17
public static void main(String[] args)
//不会自动注册相关后置处理器的干净的容器
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext=new GenericApplicationContext();
applicationContext.registerBean("aspectJ",AspectJ.class);
applicationContext.registerBean("config",Config.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(Target.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames())
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
Target bean = applicationContext.getBean(Target.class);
bean.foo();
static class Target
public void foo()
System.out.println("foo");
@Aspect//高级切面
static class AspectJ
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
System.out.println("aspect1 before");
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void after()
System.out.println("aspect1 after");
@Configuration
static class Config
@Bean//低级切面
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,advice);
@Bean
public MethodInterceptor advice()
return new MethodInterceptor()
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable
System.out.println("advice before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice after");
return proceed;
;
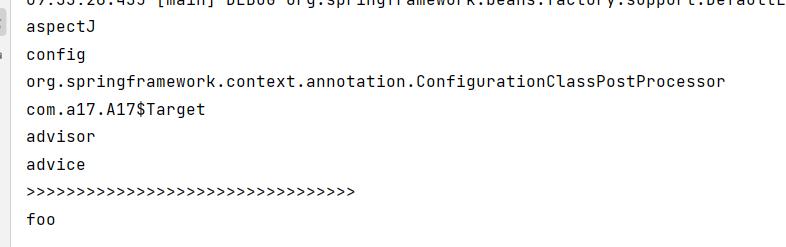
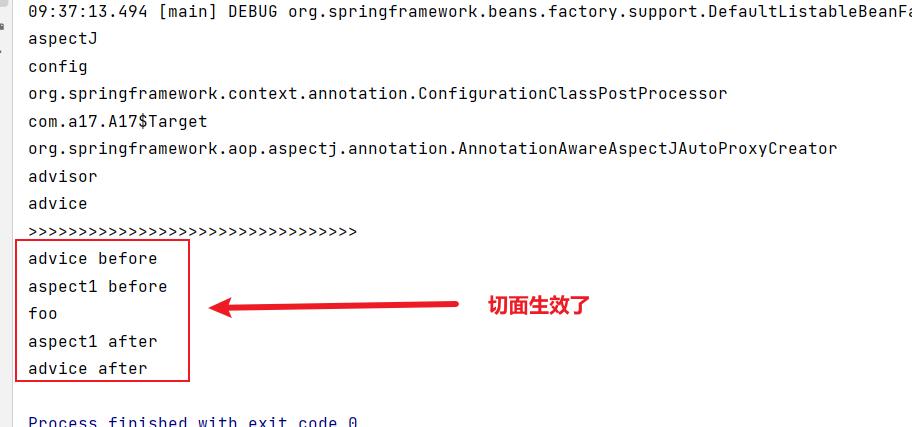
可以看到,我们注册了一个高级切面类AspectJ和低级切面Advisor到容器中,但是此时运行,发现目标对象方法没有被代理,说明光有切面没用,还少了点啥子,让切面能够运作起来
代理创建器
少了神魔呢?—》少了下面这个自动代理的后置处理器
//自动代理
applicationContext.registerBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
该后置处理器: 创建bean----> 上面的后置处理器干点事 ---->依赖注入----->初始化—>上面的后置处理器干点事
此时再进行测试:
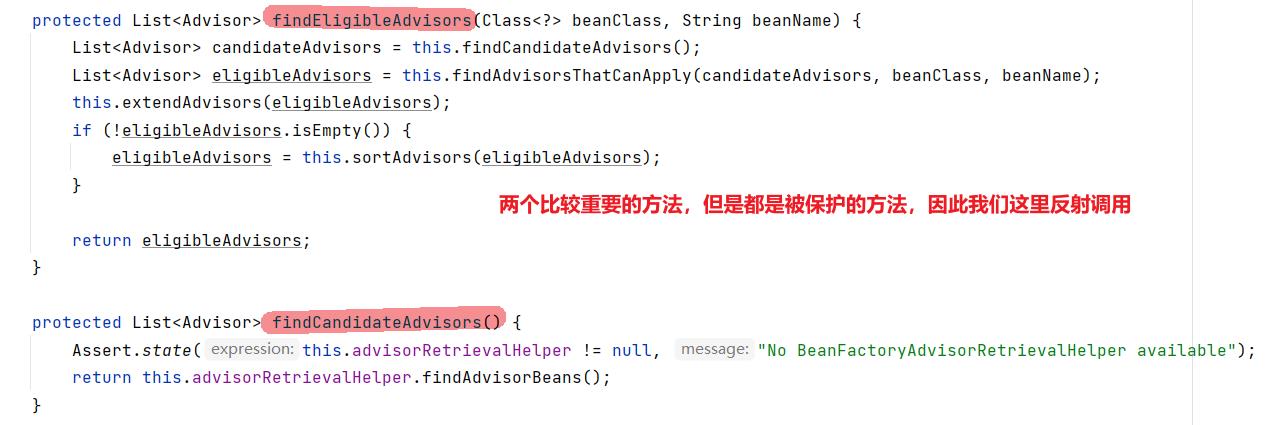
findEligibleAdvisors—找出符合当前目标对象的所有切面
这里不直接翻源码,而是通过调用该后置处理器中的方法来模拟一下源码中的思路:
这里因为是受保护的方法,所以除了反射调用之外,还可以把我们的测试类所在包名改为上面这个后置处理器包名相同,也可以直接调用
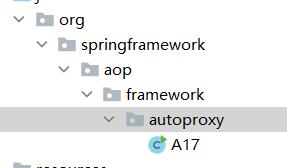
//包名改为这个即可
package org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy;
public class A17
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException
//不会自动注册相关后置处理器的干净的容器
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext=new GenericApplicationContext();
applicationContext.registerBean("aspectJ",AspectJ.class);
applicationContext.registerBean("config",Config.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(Target.class);
//自动代理
applicationContext.registerBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames())
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
System.out.println("- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ");
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator = applicationContext.getBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
List<Advisor> advisors = annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors(Target.class, "target");
System.out.println("符合当前传入目标对象的低级切面有:");
advisors.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
static class Target
public void foo()
System.out.println("foo");
@Aspect//高级切面
static class AspectJ
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
System.out.println("aspect1 before");
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void after()
System.out.println("aspect1 after");
@Configuration
static class Config
@Bean//低级切面
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,advice);
@Bean
public MethodInterceptor advice()
return new MethodInterceptor()
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable
System.out.println("advice before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed(