线性表练习之Example046-使双链表中结点保持按访问频度非增(递减)的顺序排列,同时最近访问的结点排在频度相同的结点前面
Posted 二木成林
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线性表练习之Example046-使双链表中结点保持按访问频度非增(递减)的顺序排列,同时最近访问的结点排在频度相同的结点前面相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Example046
原文链接:Example046
题目
设头指针为 L 的带有表头结点的非循环双向链表,其每个结点中除有 pred(前驱指针)、data(数据)和 next(后继指针)域外,还有一个访问频度域 freq。在链表被启用前,其值均初始化为零。每当在链表中进行一次 Locate(L,x) 运算时,令元素值为 x 的结点中 freq 域的值增 1,并使此链表中结点保持按访问频度非增(递减)的顺序排列,同时最近访问的结点排在频度相同的结点前面,以便使频繁访问的结点总是靠近表头。试编写符合上述要求的 Locate(L,x) 运算的算法,该运算为函数过程,返回找到结点的地址,类型为指针型。
分析
本题考查的知识点:
- 双链表
- 双链表查找指定值结点
- 双链表删除节点
- 双链表插入节点
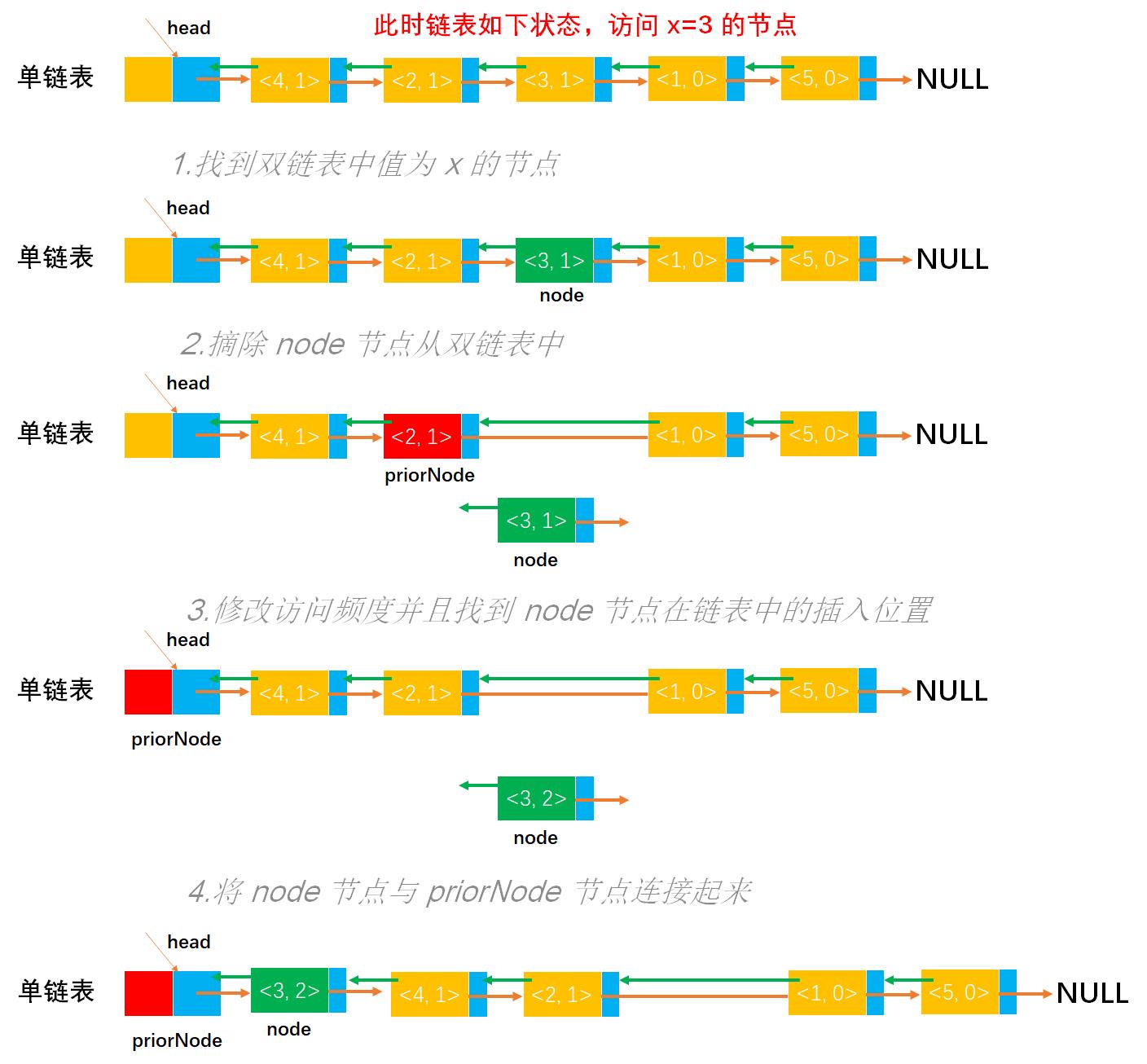
算法思想:首先在双链表中查找数据值等于 x 的节点 node,查到后,将该节点从链表上摘下(注意,恢复 node->prior 和 node->next 的连接),然后顺着节点的前驱链查找该节点的插入位置(按频度递减,且排在同频度的第一个,即向前找到第一个比它的频度大的节点,插入位置为该节点之后),最后插入到该位置。
图解
C实现
核心代码:
/**
* 按访问频度来修改指定值节点在链表中的位置
* @param list 双链表
* @param x 指定值
*/
DLNode *locate(DLNode **list, int x)
// 1.找到双链表中值为 x 的节点
// 变量,记录双链表节点用于扫描链表,初始为双链表的第一个节点
DLNode *node = (*list)->next;
// 从头到尾扫描双链表所有节点
while (node != NULL)
// 找到节点值等于 x 的节点
if (node->data == x)
break;
node = node->next;
// 2.摘除 node 节点从双链表中
// 变量,记录 node 节点的前驱节点
DLNode *priorNode = node->prior;
// 摘除 node 节点,将 pre 节点与 node 节点的后继节点连接起来
if (node->next != NULL)
node->next->prior = node->prior;
node->prior->next = node->next;
// 3.修改访问频度并且找到 node 节点在链表中的插入位置
// 将访问频度增加 1
node->freq = node->freq + 1;
// 找到 node 节点按访问频度应该在链表中的位置,即 node 节点应该插在 priorNode 节点的后面
while (priorNode->prior != NULL && priorNode->prior->freq <= node->freq) // 按访问频度,高频在前面,并且在同频的前面
priorNode = priorNode->prior;
// 4.将 node 节点与 priorNode 节点连接起来
node->next = priorNode->next;
priorNode->next->prior = node;
node->prior = priorNode;
priorNode->next = node;
return node;
完整代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
/**
* 双链表节点结构体
*/
typedef struct DLNode
/**
* 双链表节点数据域
*/
int data;
/**
* 访问频度数据域
*/
int freq;
/**
* 双链表节点的前驱节点,数据域
*/
struct DLNode *prior;
/**
* 双链表节点的后继节点,数据域
*/
struct DLNode *next;
DLNode;
/**
* 通过尾插法创建双链表
* @param list 双链表
* @param nums 会放入到双链表中的数据
* @param n 数组长度
* @return 创建成功的双链表
*/
DLNode *createByTail(DLNode **list, int nums[], int n)
// 1.初始化链表,即创建双链表的头结点,也可以直接调用 init 方法进行初始化
// 1.1 给双链表头结点分配空间
*list = (DLNode *) malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
// 1.2 将双链表的 prior 指针指向 null
(*list)->prior = NULL;
// 1.3 将双链表的 next 指针指向 null
(*list)->next = NULL;
// 使用尾插法,最重要的是知道链表的尾节点,初始时为链表的头结点
DLNode *tailNode = *list;
// 2.循环数组中元素,然后插入到链表的尾部
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// 2.1 创建新节点
// 2.1.1 为新节点分配空间
DLNode *newNode = (DLNode *) malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
// 2.1.2 指定新节点的数据域
newNode->data = nums[i];
// 2.1.3 将新节点的 prior 指针指向 null
newNode->prior = NULL;
// 2.1.4 将新节点的 next 指针指向 null
newNode->next = NULL;
// 2.1.5 将新节点的 freq 数据域初始为 0
newNode->freq = 0;
// 2.2 将新节点连接到链表中
// 2.2.1 将原尾节点的 next 指针指向新节点
tailNode->next = newNode;
// 2.2.2 将新节点的 prior 指针指向原尾节点,这时已经将新节点连接到链表的尾部了
newNode->prior = tailNode;
// 2.2.3 不要忘记更新尾节点,让新节点成为新的尾节点,才能进行下一次插入
tailNode = newNode;
return *list;
/**
* 按访问频度来修改指定值节点在链表中的位置
* @param list 双链表
* @param x 指定值
*/
DLNode *locate(DLNode **list, int x)
// 1.找到双链表中值为 x 的节点
// 变量,记录双链表节点用于扫描链表,初始为双链表的第一个节点
DLNode *node = (*list)->next;
// 从头到尾扫描双链表所有节点
while (node != NULL)
// 找到节点值等于 x 的节点
if (node->data == x)
break;
node = node->next;
// 2.摘除 node 节点从双链表中
// 变量,记录 node 节点的前驱节点
DLNode *priorNode = node->prior;
// 摘除 node 节点,将 pre 节点与 node 节点的后继节点连接起来
if (node->next != NULL)
node->next->prior = node->prior;
node->prior->next = node->next;
// 3.修改访问频度并且找到 node 节点在链表中的插入位置
// 将访问频度增加 1
node->freq = node->freq + 1;
// 找到 node 节点按访问频度应该在链表中的位置,即 node 节点应该插在 priorNode 节点的后面
while (priorNode->prior != NULL && priorNode->prior->freq <= node->freq) // 按访问频度,高频在前面,并且在同频的前面
priorNode = priorNode->prior;
// 4.将 node 节点与 priorNode 节点连接起来
node->next = priorNode->next;
priorNode->next->prior = node;
node->prior = priorNode;
priorNode->next = node;
return node;
/**
* 打印双链表中所有节点数据
* @param list 双链表
*/
void print(DLNode *list)
// 链表的第一个节点
DLNode *node = list->next;
// 循环遍历链表的所有节点
printf("[");
while (node != NULL)
printf("<%d,%d>", node->data, node->freq);
if (node->next != NULL)
printf(", ");
node = node->next;
printf("]\\n");
int main()
// 双链表
DLNode *list;
int nums[] = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5;
int n = 5;
createByTail(&list, nums, n);
print(list);
// 调用函数
locate(&list, 3);
print(list);
locate(&list, 2);
print(list);
locate(&list, 4);
print(list);
locate(&list, 3);
print(list);
执行结果:
[<1,0>, <2,0>, <3,0>, <4,0>, <5,0>]
[<3,1>, <1,0>, <2,0>, <4,0>, <5,0>]
[<2,1>, <3,1>, <1,0>, <4,0>, <5,0>]
[<4,1>, <2,1>, <3,1>, <1,0>, <5,0>]
[<3,2>, <4,1>, <2,1>, <1,0>, <5,0>]
Java实现
核心代码:
/**
* 按访问频度来修改指定值节点在链表中的位置
*
* @param x 指定值
*/
public DLNode locate(int x)
// 1.找到双链表中值为 x 的节点
// 变量,记录双链表节点用于扫描链表,初始为双链表的第一个节点
DLNode node = list.next;
// 从头到尾扫描双链表所有节点
while (node != null)
// 找到节点值等于 x 的节点
if (node.data == x)
break;
node = node.next;
// 2.摘除 node 节点从双链表中
// 变量,记录 node 节点的前驱节点
DLNode priorNode = node.prior;
// 摘除 node 节点,将 pre 节点与 node 节点的后继节点连接起来
if (node.next != null)
node.next.prior = node.prior;
node.prior.next = node.next;
// 3.修改访问频度并且找到 node 节点在链表中的插入位置
// 将访问频度增加 1
node.freq = node.freq + 1;
// 找到 node 节点按访问频度应该在链表中的位置,即 node 节点应该插在 priorNode 节点的后面
while (priorNode.prior != null && priorNode.prior.freq <= node.freq) // 按访问频度,高频在前面,并且在同频的前面
priorNode = priorNode.prior;
// 4.将 node 节点与 priorNode 节点连接起来
node.next = priorNode.next;
priorNode.next.prior = node;
node.prior = priorNode;
priorNode.next = node;
return node;
完整代码:
public class DoubleLinkedList
DLNode list;
/**
* 通过尾插法创建双链表
*
* @param nums 会放入到双链表中的数据
* @return 创建成功的双链表
*/
public DLNode createByTail(int... nums)
// 1.初始化链表,即创建双链表的头结点,也可以直接调用 init 方法进行初始化
// 1.1 给双链表头结点分配空间
list = new DLNode();
// 1.2 将双链表的 prior 指针指向 null
list.prior = null;
// 1.3 将双链表的 next 指针指向 null
list.next = null;
// 使用尾插法,最重要的是知道链表的尾节点,初始时为链表的头结点
DLNode tailNode = list;
// 2.循环数组中元素,然后插入到链表的尾部
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
// 2.1 创建新节点
// 2.1.1 为新节点分配空间
DLNode newNode = new DLNode();
// 2.1.2 指定新节点的数据域
newNode.data = nums[i];
// 2.1.3 将新节点的 prior 指针指向 null
newNode.prior = null;
// 2.1.4 将新节点的 next 指针指向 null
newNode.next = null;
// 2.1.5 将新节点的 freq 频度置为 0
newNode.freq = 0;
// 2.2 将新节点连接到链表中
// 2.2.1 将原尾节点的 next 指针指向新节点
tailNode.next = newNode;
// 2.2.2 将新节点的 prior 指针指向原尾节点,这时已经将新节点连接到链表的尾部了
newNode.prior = tailNode;
// 2.2.3 不要忘记更新尾节点,让新节点成为新的尾节点,才能进行下一次插入
tailNode = newNode;
return list;
/**
* 按访问频度来修改指定值节点在链表中的位置
*
* @param x 指定值
*/
public DLNode locate(int x)
// 1.找到双链表中值为 x 的节点
// 变量,记录双链表节点用于扫描链表,初始为双链表的第一个节点
DLNode node = list.next;
// 从头到尾扫描双链表所有节点
while (node != null)
// 找到节点值等于 x 的节点
if (node.data == x)
break;
node = node.next;
// 2.摘除 node 节点从双链表中
// 变量,记录 node 节点的前驱节点
DLNode priorNode = node.prior;
// 摘除 node 节点,将 pre 节点与 node 节点的后继节点连接起来
if (node.next != null)
node.next.prior = node.prior;
node.prior.next = node.next;
// 3.修改访问频度并且找到 node 节点在链表中的插入位置
// 将访问频度增加 1
node.freq = node.freq + 1;
// 找到 node 节点按访问频度应该在链表中的位置,即 node 节点应该插在 priorNode 节点的后面
while (priorNode.prior != null && priorNode.prior.freq <= node.freq) // 按访问频度,高频在前面,并且在同频的前面
priorNode = priorNode.prior;
// 4.将 node 节点与 priorNode 节点连接起来
node.next = priorNode.next;
priorNode.next.prior = node;
node.prior = priorNode;
priorNode.next = node;
return node;
/**
* 打印双链表中所有节点数据
*/
public void print()
// 链表的第一个节点
DLNode node = list.next;
// 循环遍历链表的所有节点
String str = "[";
while (node != null)
str += "<" + node.data + "," + node.freq + ">";
if (node.next != null)
str += ", ";
node = node.next;
str += "]";
// 打印结果
System.out.println(str);
/**
* 双链表节点,包括一个数据域和两个指针域(分别指向前驱节点和后继节点)
*/
class DLNode
/**
* 双链表节点的数据域
*/
int data;
/**
* 双链表节点的访问频度
*/
int freq;
/**
* 双链表节点的前驱节点
*/
DLNode prior;
/**
* 双链表节点的后继节点
*/
DLNode next;
测试代码:
public class DoubleLinkedListTest
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 双链表
DoubleLinkedList list = new DoubleLinkedList();
list.createByTail(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
list.print();
// 调用函数
list.locate(3);
list.print();
list.locate(2);
list.print();
list.locate(4);
list.print();
list.locate(3);
list.print();
执行结果:
[<1,0>, <2,0>, <3,0>, <4,0>, <5,0>]
[<3,1>, <1,0>, <2,0>, <4,0>, <5,0>]
[<2,1>, <3,1>, <1,0>, <4,0>, <5,0>]
[<4,1>, <2,1>, <3,1>, <1,0>, <5,0>]
[<3,2>, <4,1>, <2,1>, <1,0>, <5,0>]
以上是关于线性表练习之Example046-使双链表中结点保持按访问频度非增(递减)的顺序排列,同时最近访问的结点排在频度相同的结点前面的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
线性表练习之Example045-有一个带头结点的单链表 L,设计一个算法使其元素递增有序
线性表练习之Example037-判断带头节点的循环双链表是否对称
线性表练习之Example019-删除单链表中所有介于给定两个值之间的元素的元素
线性表练习之Example042-设计一个递归算法,删除不带头结点的单链表 L 中所有值为 x 的结点
线性表练习之Example015-求单链表倒数第 k 个节点
线性表练习之Example032-将一个带头结点的单链表 A 分解成两个单链表 A 和 B,其中 A 表只包含原表中序号为奇数的元素,B 表中只包含原表中序号为偶数的元素