Android Context使用详解
Posted 伟雪无痕
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Context使用详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.Context概述
1.Context是一个抽象类,其通用实现在ContextImpl类中。它的主要作用是一个访问application环境全局信息的接口,包括为Activities, Fragments, and Services提供访问resource files, images, themes/styles等相关的类,其具体结构类图如下:
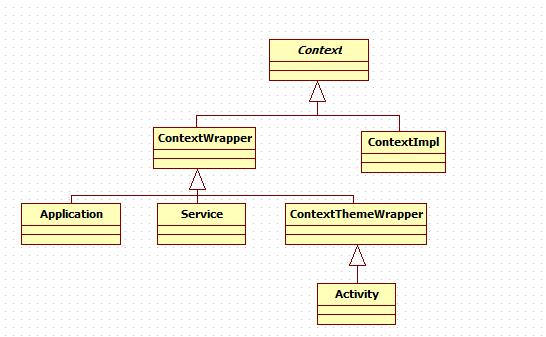
二.Context使用
1.启动Activity
1).java方式
Intent intent = new Intent(context, MyActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);2).kotlin方式
val intent = Intent(context, MyActivity::class.java)
startActivity(intent)2.创建View,
1).java方式
TextView textView = new TextView(context);2).kotlin方式
val textView = TextView(context)此外Contexts也包含view需要的一些信息,eg:
1‘. 将dp、sp 转换为像素的设备屏幕尺寸和维度
2'. styled属性
3'. activity onclick关联的属性
3.Inflating一个XML布局文件
1).java方式
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
inflater.inflate(R.layout.my_layout, parent);2).kotlin方式
val inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context)
inflater.inflate(R.layout.my_layout, parent)4.发送广播
1).java方式
Intent broadcastIntent = new Intent("action");
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(context).sendBroadcast(broadcastIntent);2).kotlin方式
val broadcastIntent = Intent("action")
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(context).sendBroadcast(broadcastIntent)5.获取系统Service,eg:发送通知,通知管理获取
1).java方式
NotificationManager notificationManager =
(NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
int notificationId = 1;
// Context is required to construct RemoteViews
Notification.Builder builder =
new Notification.Builder(context).setContentTitle("title");
notificationManager.notify(notificationId, builder.build());2).kotlin方式
val notificationManager = getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE) as NotificationManager
val notificationId = 1
// Context is required to construct RemoteViews
val builder = Notification.Builder(context).setContentTitle("title")
notificationManager.notify(notificationId, builder.build())6.Application和Activity Context对比
在传递Context参数的时候,如果是在Activity中,我们可以传递this(这里的this指的是Activity.this,是当前Activity的context)或者Activity.this。这个时候如果我们传入getApplicationContext(),我们会发现这样也是可以用的。可是大家有没有想过传入Activity.this和传入getApplicationContext()的区别呢?首先Activity.this和getApplicationContext()返回的不是同一个对象,一个是当前Activity的实例,一个是项目的Application的实例,这两者的生命周期是不同的,它们各自的使用场景不同,this.getApplicationContext()取的是这个应用程序的Context,它的生命周期伴随应用程序的存在而存在;而Activity.this取的是当前Activity的Context,它的生命周期则只能存活于当前Activity,这两者的生命周期是不同的。getApplicationContext() 生命周期是整个应用,当应用程序摧毁的时候,它才会摧毁;Activity.this的context是属于当前Activity的,当前Activity摧毁的时候,它才摧毁。
7.Context的应用场景
| Application | Activity | Service | ContentProvider | BroadcastReceiver | |
| New a Dialog | NO | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| Start Activity | NO1 | YES | NO1 | NO1 | NO1 |
| Inflation Layout | NO2 | YES | NO2 | NO2 | NO2 |
| Start Service | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Bind Service | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| Send Broadcast | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Register BroadcastReceiver | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO3 |
| Load Resource | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
大家注意看到有一些NO后面添加了一些数字,其实这些从能力上来说是YES,但是为什么说是NO呢?解释如下:
NO1:启动Activity在这些类中是可以的,但是需要创建一个新的task。一般情况不推荐。
NO2:在这些类中去layout inflate是合法的,但是会使用系统默认的主题样式,如果你自定义了某些样式可能不会被使用。
NO3:在receiver为null时允许,在4.2或以上的版本中,用于获取黏性广播的当前值。
8.Context的数量计算
Context个数=Activity数+Service数+1(Application)
三.Context内存泄露问题
1.单例模式导致内存泄漏
1).java demo
public class CustomManager
private static CustomManager sInstance;
public static CustomManager getInstance(Context context)
if (sInstance == null)
// This class will hold a reference to the context
// until it's unloaded. The context could be an Activity or Service.
sInstance = new CustomManager(context);
return sInstance;
private Context mContext;
private CustomManager(Context context)
mContext = context;
2).kotlin demo
class CustomManager private constructor(private val context: Context)
companion object
@Volatile
private var instance: CustomManager? = null
fun getInstance(context: Context): CustomManager
val i = instance
if (i != null)
return instance as CustomManager
return synchronized(this)
val i2 = instance
if (i2 != null)
i2
else
val created = CustomManager(context)
instance = created
created
上面demo有内存泄露的隐患,如果是在Activity中创建这个单例的话,传入的context为Activity的context,如果想要销毁Activity,但是单例的生命周期是整个应用,导致Activity的内存不能完全释放,
正确的方法是将application context存储在CustomManager.getInstance()中。 application context是一个单例,并且与应用程序进程的生命周期相关联,因此可以安全地存储对它的引用。
如果在组件的生命周期之外需要Context引用,或者它应该独立于传入的Context的生命周期,请使用application context。eg:
1).java方式
public static CustomManager getInstance(Context context)
if (sInstance == null)
sInstance = new CustomManager(context.getApplicationContext());
return sInstance;
2).kotlin方式
class CustomManager private constructor(private val context: Context)
companion object
fun getInstance(context: Context): CustomManager
val created = CustomManager(context.applicationContext)
以上是关于Android Context使用详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章