使用循环神经网络做手写数字识别
Posted 卡尔曼和玻尔兹曼谁曼
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用循环神经网络做手写数字识别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明原文出处!
写作时间:2019-03-02 21:36:12
使用循环神经网络做手写数字识别
思路分析
做图像识别的使用卷积神经网络CNN是最好的选择,但是其实我们也可以使用循环神经网络RNN做,只是大部分时候没有卷积网络效果好!下面分析一下如何使用RNN做手写数字的识别。
- 数据的下载我们可以直接使用PyTorch中的
torchvision.datasets提供的数据接口 - 对于每一张图像(28$\\times$28)我们可以将图像的每一行看做一个样本,然后所有行排列起来做成一个有序序列。对于这个序列,我们就可以使用RNN做识别训练了。
- 下面的实现中使用一个LSTM+Linear层组合实现(不要使用经典RNN,效果不好),损失函数使用CrossEntropyLoss。
- 在实践中设置
batch_first=True可以减少一些额外的维度变换和尺寸转换的代码,推荐使用
PyTorch实现
import torch
from torch import nn
import torchvision.datasets as datasets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
torch.manual_seed(2019)
# 超参设置
EPOCH = 1 # 训练EPOCH次,这里为了测试方便只跑一次
BATCH_SIZE = 32
TIME_STEP = 28 # RNN时间跨度(图片高度)
INPUT_SIZE = 28 # RNN输入尺寸(图片宽度)
INIT_LR = 0.01 # 初始学习率
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True # 设置是否需要下载数据集
# 使用DataLoader加载训练数据,为了演示方便,对于测试数据只取出2000个样本进行测试
train_data = datasets.MNIST(root='mnist', train=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor(), download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
test_data = datasets.MNIST(root='mnist', train=False)
test_x = test_data.test_data.type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000] / 255.
test_y = test_data.test_labels.numpy()[:2000]
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(
input_size=INPUT_SIZE,
hidden_size=64,
num_layers=1,
batch_first=True
)
self.out = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# x shape (batch_size, time_step, input_size)
# r_out shape (batch_size, time_step, output_size)
# h_n shape (n_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
# h_c shape (n_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
r_out, (h_n, h_c) = self.rnn(x)
# 取出最后一次循环的r_out传递到全连接层
out = self.out(r_out[:, -1, :])
return out
rnn = RNN()
print(rnn)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=INIT_LR)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# RNN训练
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader):
# 数据的输入为(batch_size, time_step, input_size)
b_x = b_x.view(-1, TIME_STEP, INPUT_SIZE)
output = rnn(b_x)
loss = loss_func(output, b_y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step % 50 == 0:
prediction = rnn(test_x) # 输出为(2000, 10)
pred_y = torch.max(prediction, 1)[1].data.numpy()
accuracy = (pred_y == test_y).sum() / float(test_y.size)
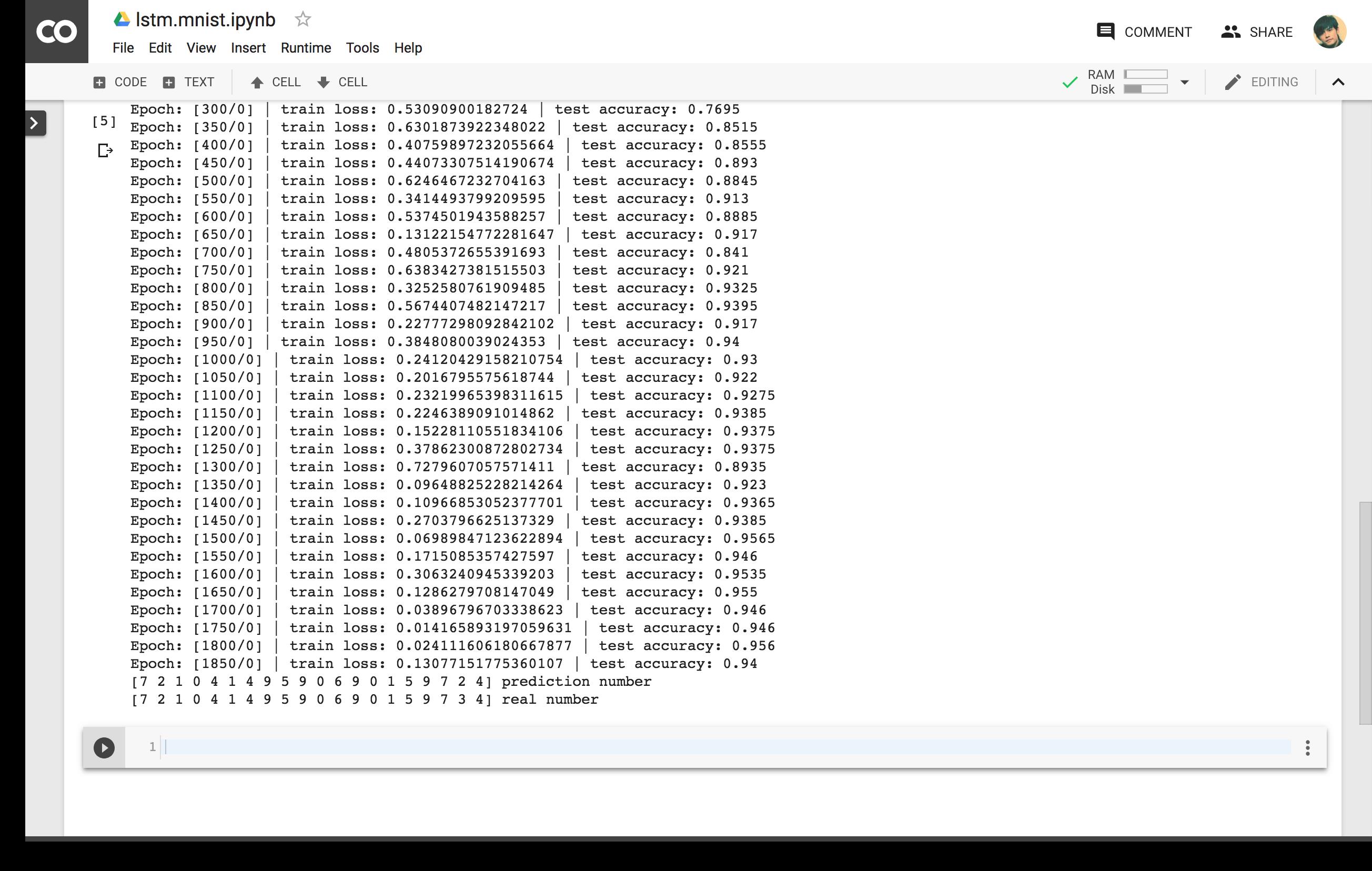
print(f'Epoch: [step/epoch]', f'| train loss: loss.item()', f'| test accuracy: accuracy')
# 打印测试数据集中的后20个结果
prediction = rnn(test_x[:20].view(-1, 28, 28))
pred_y = torch.max(prediction, 1)[1].data.numpy()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:20], 'real number')
下面是训练结果的截图,可以看到效果还不错!
以上是关于使用循环神经网络做手写数字识别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章