Kubernetes入门至精通 | Kubernetes生命周期
Posted 一个热爱编程的通信人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kubernetes入门至精通 | Kubernetes生命周期相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Pod生命周期
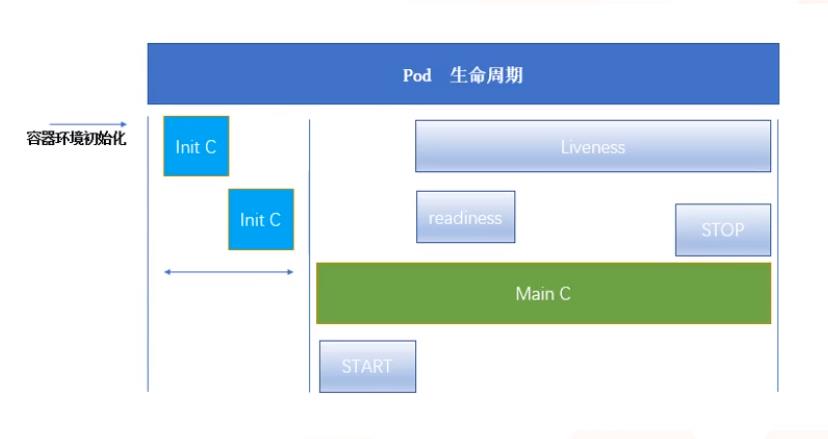
Pod能够具有多个容器,应用运行在容器里面,但是它也可能有一个或多个先于应用容器启动的Init容器
Init容器与普通的容器非常像,除了如下两点:
- Init容器总是运行到成功完成为止
- 每个Init容器都必须在下一个Init容器启动之前成功完成
如果Pod的Init容器失败,Kubernetes会不断地重启该Pod,直到Init容器成功为止。然而,如果Pod对应的restartPolicy为Never,它不会重新启动
因为Init容器具有与应用程序容器分离的单独镜像,所以它们的启动相关代码具有如下优势:
- 它们可以包含并运行实用工具,但是出于安全考虑,是不建议在应用程序容器镜像中包含这些实用工具的
- 应用程序镜像可以分离出创建和部署的角色,而没有必要联合它们构建一个单独的镜像
- Init容器使用Linux Namespace,所以相对应用程序容器来说具有不同的文件系统视图。因此,它们能够具有访问Secret的权限,而应用程序容器则不能
- 它们必须在应用程序容器启动之前运行完成,而应用程序容器是并行运行的,所以Init容器能够提供了一种简单的阻塞或延迟应用容器的启动的方法,直到满足了一组先决条件
特殊说明:
- 在Pod启动过程中,Init容器会按顺序在网络和数据卷初始化之后启动。每个容器必须在下一个容器启动之前成功退出
- 如果由于运行时或失败退出,将导致容器启动失败,它会根据Pod的restartPolicy指定的策略进行重试。然而,如果Pod的restartPolicy设置为Always,Init容器失败会使用RestartPolicy策略
- 在所有的Init容器没有成功之前,Pod将不会变成Ready状态。Init容器的端口将不会在Service中进行聚集。正在初始化中的Pod处于Pending状态,但应该会将Initializing状态设置为true
- 如果Pod重启,所有Init容器必须重新执行
- 对Init容器spec的修改被限制在容器image字段,修改其他字段都不会生效。更改Init容器的image字段,等价于重启该Pod
Init容器
init模板
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp-container
image: busybox:1.34.1
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo The app is running! && sleep 3600']
initContainers:
- name: init-myservice
image: busybox:1.34.1
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nslookup myservice; do echo waiting for myservice; sleep 2; done;']
- name: init-mydb
image: busybox:1.34.1
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nslookup mydb; do echo waiting for mydb; sleep 2; done;']kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: myservice
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 9376
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: mydb
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 9377Init容器具有应用容器的所有字段。除了readinessProbe,因为Init容器无法定义不同于完成(completion)的就绪(readiness)之外的其他状态。这会在验证过程中强制执行
在Pod中的每个app和Init容器的名称必须唯一;与任何其他容器共享同一个名称,会在验证时抛出错误
探针是由kubelet对容器执行的定期诊断。要执行诊断,kubelet调用由容器实现的Handler。有三种类型的处理程序:
- ExecAction:在容器内执行指定命令。如果命令退出时返回码为0则认为诊断成功。
- TCPSocketAction:对指定端口上的容器的IP地址进行TCP检查。如果端口打开,则诊断被认为是成功的。
- HTTPGetAction:对指定的端口和路径上的容器的IP地址执行HTTP Get请求。如果响应的状态码大于等于200且小于400,则诊断被认为是成功的
每次探测都将获得以下三种结果之一:
- 成功:容器通过了诊断
- 失败:容器未通过诊断
- 未知:诊断失败,因此不会采取任何行动
livenessProbe:指示容器是否正在运行。如果存活探测失败,则kubelet会杀死容器,并且容器将受到其重启策略的影响。如果容器不提供存活探针,则默认状态为Success
readinessProbe:指示容器是否准备好服务请求。如果就绪探测失败,端点控制器将从与Pod匹配的所有Service的端点中删除该Pod的IP地址。初始延迟之前的就绪状态默认为Failure。如果容器不提供就绪探针,则默认状态为Success
检测探针 - 就绪检测
readinessProbe-httpget
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: readiness-httpget-pod
namespace: default
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: readiness-httpget-container
image: wangyanglinux/myapp:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
port: 80
path: /index1.html
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3检测探针 - 存活探测
livenessProbe-exec
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: liveness-exec-pod
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-exec-container
image: busybox:1.34.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "touch /tmp/live; sleep 60; rm -rf /tmp/live; sleep 3600"]
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test", "-e", "/tmp/live"]
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3livenessProbe-httpget
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: liveness-httpget-pod
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-httpget-container
image: wangyanglinux/myapp:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
port: 80
path: /index.html
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
timeoutSeconds: 3livenessProbe-tcp
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: probe-tcp
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: wangyagnlinux/myapp:v1
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 1
tcpSocket:
port: 80Pod Hook(钩子)是由Kubernetes管理的kubelet发起的,当容器中的进程启动前或者容器中的进程终止之前运行,这是包含在容器的生命周期之中。可以同时为Pod中的所有容器都配置hook
Hook的类型包括两种:
- exec:执行一段命令
- HTTP:发送HTTP请求
启动、退出动作
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: lifecycle-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: lifecycle-demo-container
image: wangyanglinux/myapp:v1
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Hello from the postStart handler > /usr/share/message"]
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Hello from the poststop handler > /usr/share/message"]综合实例
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
name: test
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- image: wangyanglinux/myapp:v1
name: myapp
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
port: 80
path: /index1.html
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
timeoutSeconds: 3
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
port: 80
path: /index.html
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
timeoutSeconds: 3
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Hello from the postStart handler > /usr/share/message"]
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Hello from the poststop handler > /usr/share/message"]
- name: busybox-1
image: busybox:1.34.1
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "touch /tmp/live; sleep 60; rm -rf /tmp/live; sleep 3600"]
readinessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test", "-e", "/tmp/live"]
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test", "-e", "/tmp/live"]
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
initContainers:
- name: init-myservice
image: busybox:1.34.1
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nslookup myservice; do echo waiting for myservice; sleep 2; done;']
- name: init-mydb
image: busybox:1.34.1
command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nslookup mydb; do echo waiting for mydb; sleep 2; done;']
以上是关于Kubernetes入门至精通 | Kubernetes生命周期的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章