如何利用 nbconvert将 IPYNB文档转换 Markdown文档?
Posted 卓晴
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何利用 nbconvert将 IPYNB文档转换 Markdown文档?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简 介: IPYNB文件是现在基于IPython开发工程人员记录和分析处理算法和数据记录文档。将该文档转换成其它格式可以方便面进行思想共享,工作汇报等。利用 nbconvert可以很方便将ipynb的文档转换成 html, Markdown,PDF等。本文给出了一些应用实例。
关键词: IPYNB,Markdown,nbconvert
§00 背景介绍
在 Converting notebooks to other formats 给出了利用 ipython nbconvert软件将 Jupyter Notebook文档转换其它文档的方式。
一、基本命令
$ ipython nbconvert --to FORMAT notebook.ipynb
1、支持转换格式
-
–to html
-
–template full (default)
A full static HTML render of the notebook. This looks very similar to the interactive view. -
–template basic
Simplified HTML, useful for embedding in webpages, blogs, etc. This excludes HTML headers.
-
-
–to latex
Latex export. This generates NOTEBOOK_NAME.tex file, ready for export.-
–template article (default)
Latex article, derived from Sphinx’s howto template. -
–template report
Latex report, providing a table of contents and chapters. -
–template basic
Very basic latex output - mainly meant as a starting point for custom templates.
-
-
–to pdf
Generates a PDF via latex. Supports the same templates as --to latex. -
–to slides
This generates a Reveal.js HTML slideshow. It must be served by an HTTP server. The easiest way to do this is adding --post serve on the command-line. The serve post-processor proxies Reveal.js requests to a CDN if no local Reveal.js library is present. To make slides that don’t require an internet connection, just place the Reveal.js library in the same directory where your_talk.slides.html is located, or point to another directory using the --reveal-prefix alias. -
–to markdown
Simple markdown output. Markdown cells are unaffected, and code cells indented 4 spaces. -
–to rst
Basic reStructuredText output. Useful as a starting point for embedding notebooks in Sphinx docs. -
–to script
Convert a notebook to an executable script. This is the simplest way to get a Python (or other language, depending on the kernel) script out of a notebook. If there were any magics in an IPython notebook, this may only be executable from an IPython session. -
–to notebook
§01 转换示例
一、转换成Markdown
下面是将 飞桨AI Studio - 人工智能学习与实训社区 中的 基于自监督学习的目标检测伪标签生成 文档转换成 Markdown格式文档。
转换命令如下:
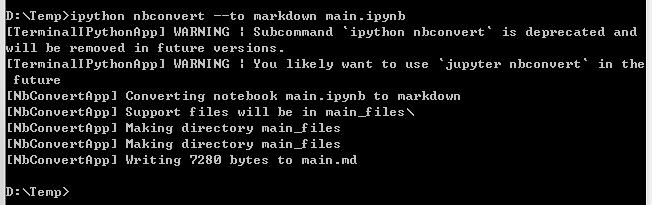
▲ 图1.1.1 转换命令
转换完之后,在本地生成 main.md 文档。下面将该文档导入 CSDN的编辑器。
1、转换结果
基于自监督学习的目标检测伪标签生成
手动标注数据是监督学习中必不可少的步骤,这是耗时,费力且有噪声的。与有监督的方法不一样,无监督的方法不依赖于人类给的标签。
本项目在视频流分割得到的掩码图上根据形状特征绘制最小外接矩形,以此做为目标检测的伪标签。
一、数据集简介
数据由场地内位置固定的摄像头采集而来,原始RGB图像如图1所示:
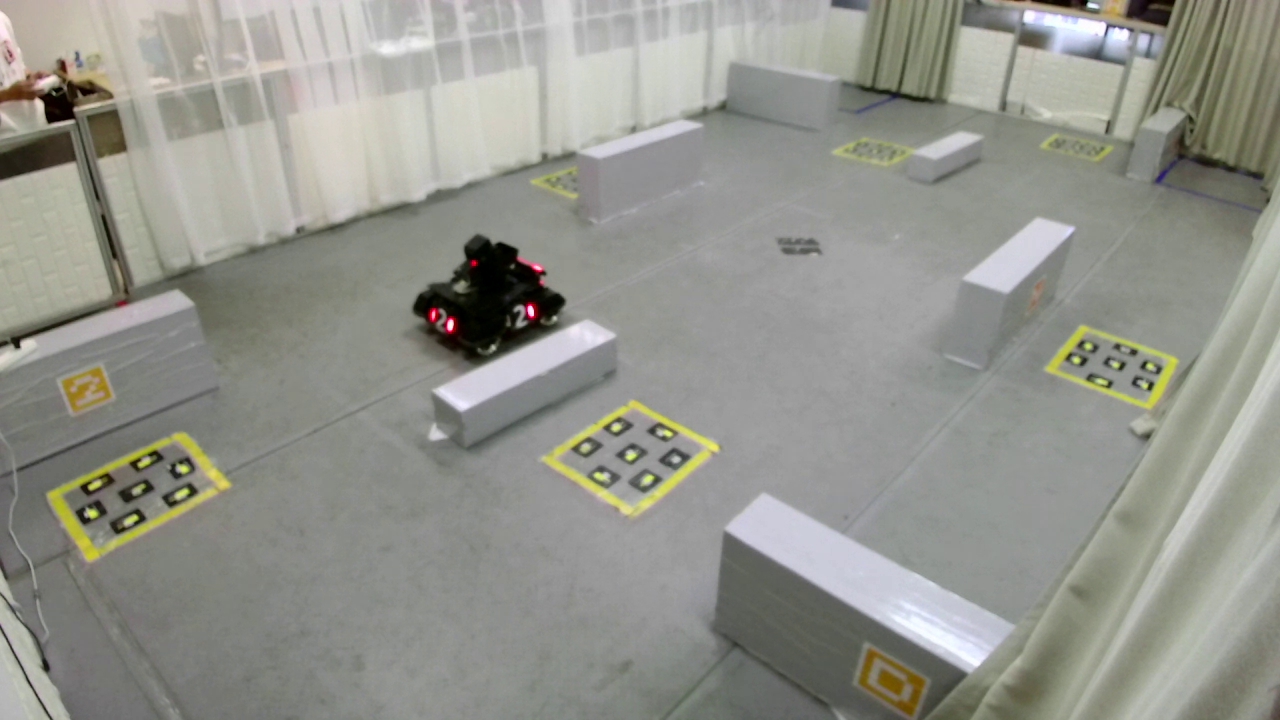
因为背景是固定的,且采集的数据是视频流,便可以根据当前帧与前后1帧、前后2帧的RGB图像将光流提取出来,提取出来的光流可以用掩码图表示,如图2所示:

光流的提取请参考:
二、外接矩形框的生成
本项目基于OpenCV画外接矩形框,可以分别画,也可以画成一个最大的。
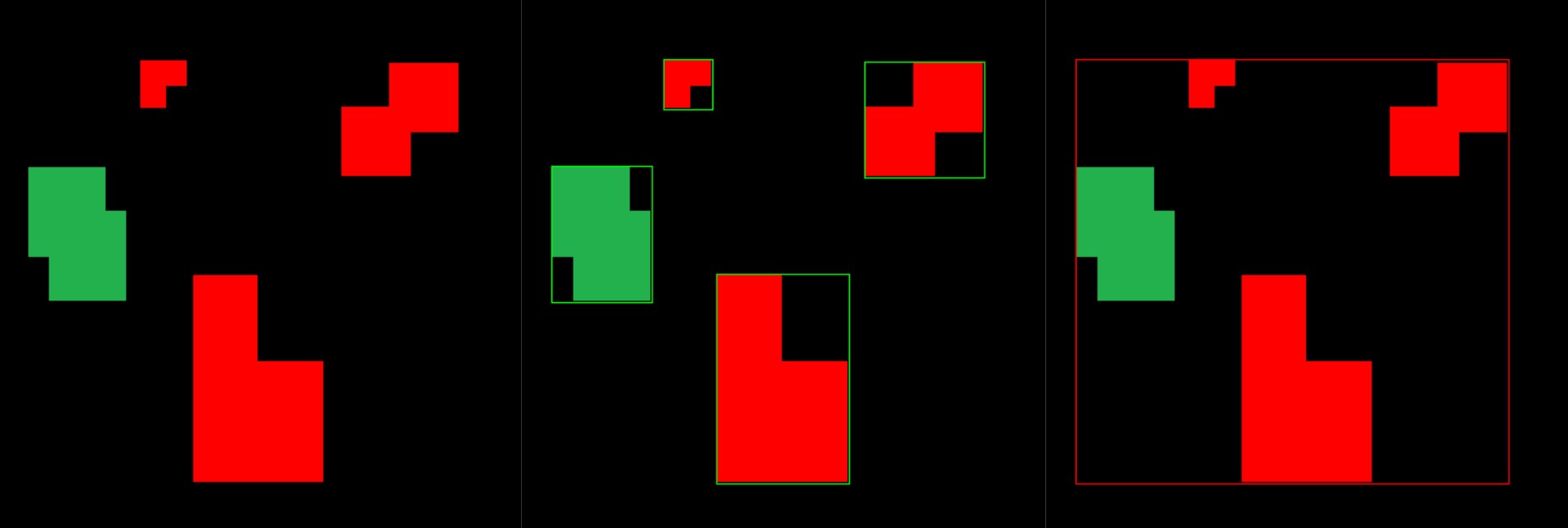
图片及参考资料源于:
# 运行下面的代码前请先在左侧文件系统里解压数据集
!unzip data/data125081/car.zip -d data/data125081
1.图像预处理
在正式的找到外接矩形框之前,为了提高准确率,需要先对掩码图做处理,进一步转化为二值图像。
以数据集的第一张图像为例,其图片路径为:
- data/data125081/car/000000.jpg
import cv2
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image = cv2.imread('data/data125081/car/000000.jpg')
print("image shape:".format(image.shape)) # (h, w, c)
# 图像转灰度图
img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 图像转二值图
thresh = 150
maxval = 255
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, thresh, maxval, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
plt.imshow(thresh)
plt.show()
image shape:(720, 1280, 3)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Xh4701lU-1642213975884)(main_files/main_5_1.png)]
如上面的输出所示,经过处理后,物体与背景就可以完全分离出来。如果效果不好可考虑调整thresh的数值。
cv2.threshold会使图像中像素大于thresh的像素点全变成maxval,小于thresh的全变成了0。
2.轮廓检测
轮廓检测是图像处理中经常用到的。OpenCV-Python接口中使用cv2.findContours函数来查找物体的轮廓。
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
print("一共找到了个轮廓信息".format(len(contours)))
一共找到了24个轮廓信息
3.矩形边框
矩形边框(Bounding Rectangle)是用一个最小的矩形,把找到的形状包起来。
cv2.boundingRect的输入是上面输出的轮廓信息,输出是x,y,w,h,即矩形框左下角在图像里的坐标已经该矩形框的宽和高
# 找到第一个轮廓的边界坐标
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[0]) # 计算点集最外面的矩形边界
print(x, y, w, h)
764 171 1 1
cv2.findContours找到的轮廓信息通常不止一个,但这么多轮廓信息并不都是可以用的,需要把不满足需要的轮廓剔除,比如宽和高特别小的框应该要剔除。
x1 = []
y1 = []
x2 = []
y2 = []
for c in contours:
# 找到边界坐标
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 计算点集最外面的矩形边界
# 剔除不满足需求的框
if w < 50 or h < 50 or x < 50 or x > 1000 or y < 50 or w*h > 300*300:
continue
# 将(xywh)转换成(xyxy)
x1.append(x)
y1.append(y)
x2.append(x + w)
y2.append(y + h)
x11, y11, x22, y22 = min(x1), min(y1), max(x2), max(y2)
print(x11, y11, x22, y22)
755 119 892 209
经过筛选后,24个预选框里只剩下1个框。
4.矩形框可视化
cv2.rectangle可以将上面生成的矩形框可视化出来。
cv2.rectangle(image, (x11, y11), (x22, y22), (0, 255, 0), 4)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XtcHfzW1-1642213975884)(main_files/main_15_0.png)]
三、批量处理与保存
现实场景中可以采集到很多类似的数据,为了便于后续的模型训练,这里我们将生成的伪标签整理到一个.csv文件里。
1.数据表的写入
将数据存放在字典中,以便写入数据表文件
pip install xlsxwriter
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
Collecting xlsxwriter
[?25l Downloading https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/packages/cd/84/c239b08592a431f7ad8773f7869470255b5f1ad860d7b40a9e7ed3f01bde/XlsxWriter-3.0.2-py3-none-any.whl (149kB)
[K |████████████████████████████████| 153kB 9.8MB/s eta 0:00:01
[?25hInstalling collected packages: xlsxwriter
Successfully installed xlsxwriter-3.0.2
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
import xlsxwriter as xw
def xw_toExcel(data, fileName): # xlsxwriter库储存数据到excel
workbook = xw.Workbook(fileName) # 创建工作簿
worksheet1 = workbook.add_worksheet("sheet1") # 创建子表
worksheet1.activate() # 激活表
title = ['img_name', 'label', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax'] # 设置表头
worksheet1.write_row('A1', title) # 从A1单元格开始写入表头
i = 2 # 从第二行开始写入数据
for j in range(len(data)):
insertData = [data[j]["img_name"], data[j]["label"], data[j]["xmin"], data[j]["ymin"], data[j]["xmax"], data[j]["ymax"]]
row = 'A' + str(i)
worksheet1.write_row(row, insertData)
i += 1
workbook.close() # 关闭表
2.批量生成标签
将本文第二部分的代码进行整理,并且从工程上优化代码。
def get_label(image, item):
# 图像转灰度图
img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 图像转二值图
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 200, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
x1 = []
y1 = []
x2 = []
y2 = []
for c in contours:
# 找到边界坐标
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 计算点集最外面的矩形边界
if w < 50 or h < 50 or x < 50 or y < 50 or x > 1000 or w*h > 300*300:
continue
# print(x, y, w, h)
# 因为这里面包含了,图像本身那个最大的框,所以用了if,来剔除那个图像本身的值。
if x != 0 and y != 0 and w != image.shape[1] and h != image.shape[0]:
x1.append(x)
y1.append(y)
x2.append(x + w)
y2.append(y + h)
# 数据集中可能存在个别图像找不到最小外接矩形的情况,因为图像是连续的,我们可以根据上一张图像的伪标签标定当前图像
if len(x1) < 1:
return None, None, None, None
else:
x11 = min(x1)
y11 = min(y1)
x22 = max(x2)
y22 = max(y2)
return x11, y11, x22, y22
3.生成伪标签并保存
数据集中可能存在个别图像找不到最小外接矩形的情况,因为图像是连续的,我们可以根据上一张图像的伪标签标定当前图像
class LastLabel():
def __init__(self):
self.xmin = None
self.ymin = None
self.xmax = None
self.ymax = None
def update(self, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax):
self.xmin, self.ymin, self.xmax, self.ymax = xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
Data = []
lastLabel = LastLabel()
for item in range(1300):
path = "data/data125081/car/:0=6.jpg".format(item)
image = cv2.imread(path)
RGB_path = "RGB/:0=6.jpg".format(item)
RGB = cv2.imread(RGB_path)
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = get_label(image, item)
if xmin == None:
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = lastLabel.xmin, lastLabel.ymin, lastLabel.xmax, lastLabel.ymax
else:
lastLabel.update(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
cv2.rectangle(RGB, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (0, 255, 0), 4)
# 伪标签可视化
cv2.imwrite("RGB_view/:0=6.jpg".format(item), RGB)
label = "img_name": ":0=6.jpg".format(item), "label":0 , "xmin": xmin, "ymin": ymin, "xmax": xmax, "ymax": ymax
Data.append(label)
fileName = 'gaplabel.xlsx'
xw_toExcel(Data, fileName)
4.检查生成的伪标签
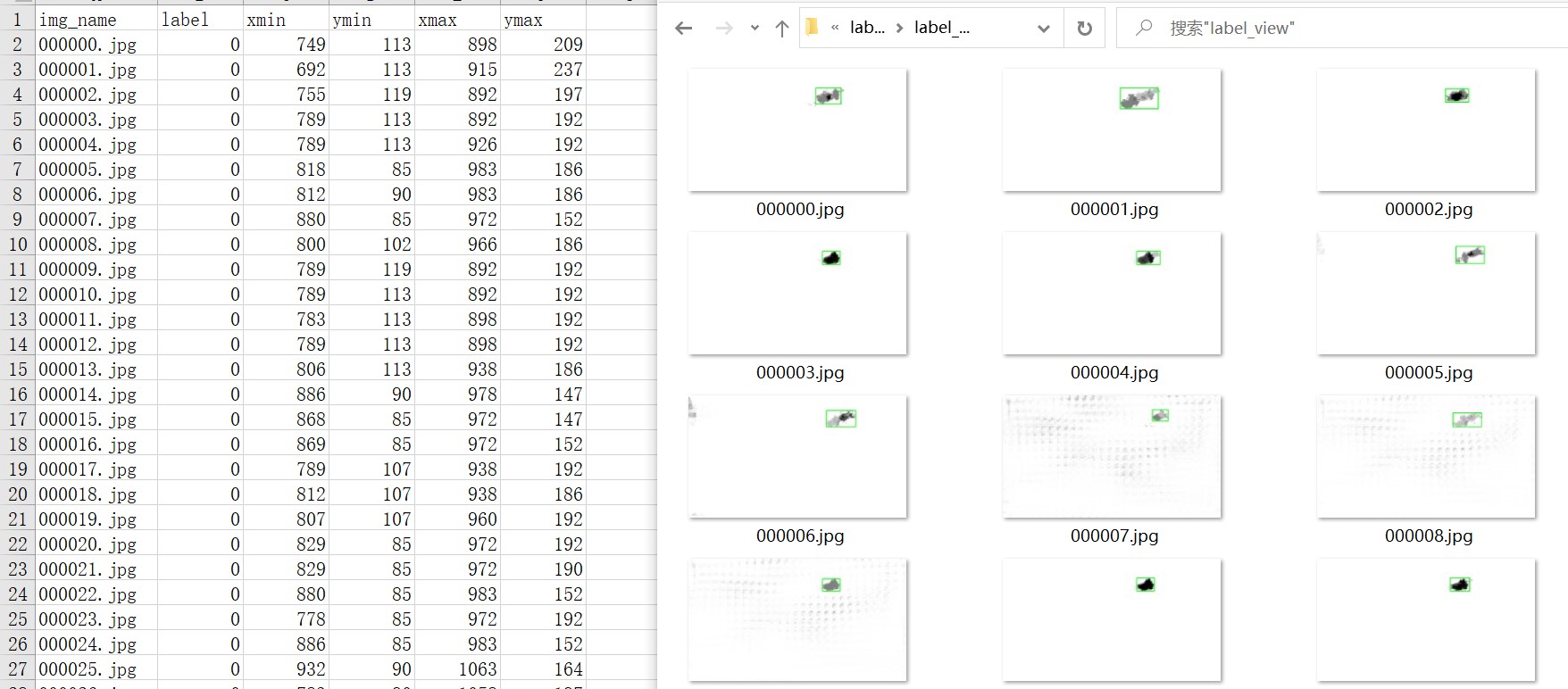
生成的伪标签保存在了数据表文件里,如下图所示:
四、总结与升华
1. 本文介绍了如何基于光流的掩码图获取目标检测需要的标签,因为标签的生成是全自动的,所以这也属于自监督学习的范畴,可以用生成的伪标签做目标检测任务
2. 数据预处理的好坏往往决定了伪标签的好坏,因此这也是一个难点,另外,我们还需要通过一些工程上的方法(根据特征筛选伪标签)提高伪标签的准确率
作者简介
北京联合大学 机器人学院 自动化专业 2018级 本科生 郑博培
中国科学院自动化研究所复杂系统管理与控制国家重点实验室实习生
百度飞桨开发者技术专家 PPDE
百度飞桨北京领航团团长
百度飞桨官方帮帮团、答疑团成员
深圳柴火创客空间 认证会员
百度大脑 智能对话训练师
阿里云人工智能、DevOps助理工程师
我在AI Studio上获得至尊等级,点亮10个徽章,来互关呀!!!
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/personalcenter/thirdview/147378

学院自动化研究所复杂系统管理与控制国家重点实验室实习生
百度飞桨开发者技术专家 PPDE
百度飞桨北京领航团团长
百度飞桨官方帮帮团、答疑团成员
深圳柴火创客空间 认证会员
百度大脑 智能对话训练师
阿里云人工智能、DevOps助理工程师
我在AI Studio上获得至尊等级,点亮10个徽章,来互关呀!!!
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/personalcenter/thirdview/147378
[外链图片转存中…(img-8lZGnRjv-1642213975885)]
二、转换成PDF
使用下
以上是关于如何利用 nbconvert将 IPYNB文档转换 Markdown文档?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章