Opencv2.4.9源码分析——Stitching
Posted zhaocj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Opencv2.4.9源码分析——Stitching相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
5、曝光补偿
5.1 原理
即使通过几何投影,图像之间可以做到很好的拼接,但如果不同图像之间有不同的曝光程度,那么拼接图像中的重叠部分也会出现明显的边缘,这样就使图像看起来十分不自然。因此,我们还需要对每幅图像进行曝光补偿,来使所有图像具有相同的曝光程度。
目前,常用的曝光补偿方法有增益补偿和分块补偿这两种方法。增益补偿就是为每幅图像赋予一个增益系数,使重叠部分的图像强度相等或相似。它可以利用误差函数来实现:
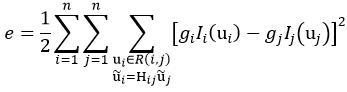 (83)
(83)
式中,gi和gj为图像i和图像j的增益系数,R(i,j)表示图像i和图像j的重叠部分,Ii(ui)表示图像i在重叠部分R(i,j)的强度平均值Iij:
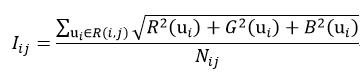 (84)
(84)
式中,R、G和B分别表示彩色图像的红、绿和蓝分量的强度值,Nij表示重叠部分R(i,j)的像素数量。
很显然,当g=0时,式83所表示的误差函数为零,也就是最优解,这明显不是我们想要的值;另外为了提高鲁棒性,增益补偿误差函数的经验公式为:
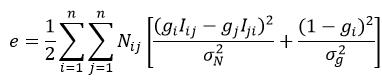 (85)
(85)
式中,σN和σg分别表示误差和增益的标准差,σN=10(如果强度范围为0~255),σg=0.1。
式85是增益系数g的一个二次目标函数,该函数可以通过使其导数为0得到闭合形式的解。式85对gi的导数为:
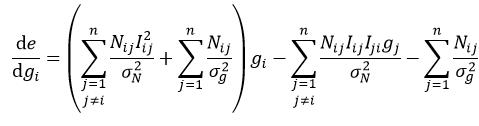 (86)
(86)
使该导数为0,并展开成以g1,g2,……,gn为变量的等式:
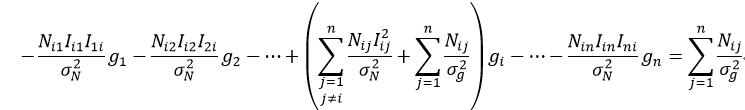 (87)
(87)
e对所有的g求导,这样就建立起了n个如式87一样的线性方程。求解该方程组,则最终得到了n幅图像的n个增益系数g。
第二种曝光补偿方法是分块补偿,它的原理是把图像分割成大小相同的不同块,这样以块为单位进行增益补偿,即每一块都有一个增益系数。该方法的补偿精度更好,并且还可以缓解增益补偿算法的复杂性。块的尺寸大小的经验值为32×32。分块补偿的结果会使拼接图像呈现“块”的形态,因此还需要对每一块的增益系数进行平滑滤波处理,具体来说,对同一幅图像的所有块的增益系数应用分割线性滤波的方法,分割滤波的核为[1/4, 1/2, 1/4]。
5.2 源码
曝光补偿的基类:
class CV_EXPORTS ExposureCompensator
public:
virtual ~ExposureCompensator()
enum NO, GAIN, GAIN_BLOCKS ;
static Ptr<ExposureCompensator> createDefault(int type);
void feed(const std::vector<Point> &corners, const std::vector<Mat> &images,
const std::vector<Mat> &masks);
virtual void feed(const std::vector<Point> &corners, const std::vector<Mat> &images,
const std::vector<std::pair<Mat,uchar> > &masks) = 0;
virtual void apply(int index, Point corner, Mat &image, const Mat &mask) = 0;
;
ExposureCompensator类中的createDefault函数表示创建曝光补偿器:
Ptr<ExposureCompensator> ExposureCompensator::createDefault(int type)
//type表示曝光补偿的方法
//该函数返回具体曝光补偿方法的函数指针
if (type == NO) //表示不进行曝光补偿
return new NoExposureCompensator(); //指向NoExposureCompensator类
if (type == GAIN) //表示应用增益补偿方法进行曝光补偿
return new GainCompensator(); //指向GainCompensator类
if (type == GAIN_BLOCKS) //表示应该分块补偿方法进行曝光补偿
return new BlocksGainCompensator(); //指向BlocksGainCompensator类
//没有其他的曝光补偿算法
CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "unsupported exposure compensation method");
return NULL;
ExposureCompensator类中有两个feed函数,其中的实函数为:
void ExposureCompensator::feed(const vector<Point> &corners, const vector<Mat> &images,
const vector<Mat> &masks)
//corners表示images在全景图像坐标系下的左上角坐标
//images表示投影变换后的各个图像
//masks表示上一步图像投影后的图像掩码
vector<pair<Mat,uchar> > level_masks; //表示为masks赋予一个等级系数
//为level_masks赋值
for (size_t i = 0; i < masks.size(); ++i)
level_masks.push_back(make_pair(masks[i], 255));
feed(corners, images, level_masks); //调用feed的虚函数
三种实现曝光补偿方法的类——NoExposureCompensator、GainCompensator和BlocksGainCompensator都是以ExposureCompensator类作为基类。NoExposureCompensator类表示不进行曝光补偿,其中的feed和apply函数都是空函数。GainCompensator类表示的是增益补偿方法,其中的feed函数表示计算增益系数:
void GainCompensator::feed(const vector<Point> &corners, const vector<Mat> &images,
const vector<pair<Mat,uchar> > &masks)
LOGLN("Exposure compensation..."); //终端输出
#if ENABLE_LOG
int64 t = getTickCount(); //用于计时
#endif
//确保各个输入参数的数量的一致性
CV_Assert(corners.size() == images.size() && images.size() == masks.size());
const int num_images = static_cast<int>(images.size()); //表示待拼接的图像数量
//N表示两幅图像间重叠部分的像素数量,即式84中的Nij
Mat_<int> N(num_images, num_images); N.setTo(0);
//I表示两幅图像间重叠部分的第一个元素所代表的图像的强度,即式84的Iij
Mat_<double> I(num_images, num_images); I.setTo(0);
//Rect dst_roi = resultRoi(corners, images);
Mat subimg1, subimg2;
Mat_<uchar> submask1, submask2, intersect;
//遍历相交的图像对
for (int i = 0; i < num_images; ++i)
for (int j = i; j < num_images; ++j)
Rect roi; //表示图像i和图像j的相交部分
//判断图像i和图像j是否有相交部分
if (overlapRoi(corners[i], corners[j], images[i].size(), images[j].size(), roi))
//subimg1和subimg2分别表示图像i和图像j相交部分在各自图像上的子图像
subimg1 = images[i](Rect(roi.tl() - corners[i], roi.br() - corners[i]));
subimg2 = images[j](Rect(roi.tl() - corners[j], roi.br() - corners[j]));
//表示把subimg1和subimg2分别赋予submask1和submask2
submask1 = masks[i].first(Rect(roi.tl() - corners[i], roi.br() - corners[i]));
submask2 = masks[j].first(Rect(roi.tl() - corners[j], roi.br() - corners[j]));
//intersect表示掩码的相交部分
intersect = (submask1 == masks[i].second) & (submask2 == masks[j].second);
//得到Nij
N(i, j) = N(j, i) = max(1, countNonZero(intersect));
double Isum1 = 0, Isum2 = 0; //表示式84的分子部分
for (int y = 0; y < roi.height; ++y) //遍历重叠部分的行
//表示当前行的首地址
const Point3_<uchar>* r1 = subimg1.ptr<Point3_<uchar> >(y);
const Point3_<uchar>* r2 = subimg2.ptr<Point3_<uchar> >(y);
for (int x = 0; x < roi.width; ++x) //遍历当前行的每个像素
//计算相交重叠部分的强度,式(84)的分子部分
if (intersect(y, x))
Isum1 += sqrt(static_cast<double>(sqr(r1[x].x) + sqr(r1[x].y) + sqr(r1[x].z)));
Isum2 += sqrt(static_cast<double>(sqr(r2[x].x) + sqr(r2[x].y) + sqr(r2[x].z)));
I(i, j) = Isum1 / N(i, j); //式(84),得到Iij
I(j, i) = Isum2 / N(i, j); //式(84),得到Iji
double alpha = 0.01; //表示σN的平方的倒数
double beta = 100; //表示σg的平方的倒数
Mat_<double> A(num_images, num_images); A.setTo(0);
Mat_<double> b(num_images, 1); b.setTo(0);
//计算由式87组成的方程组的系数
for (int i = 0; i < num_images; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < num_images; ++j)
b(i, 0) += beta * N(i, j); //式87中等号右边的项
A(i, i) += beta * N(i, j); //式87中括号中的第二项
if (j == i) continue;
A(i, i) += 2 * alpha * I(i, j) * I(i, j) * N(i, j); //式87中gi前的系数
A(i, j) -= 2 * alpha * I(i, j) * I(j, i) * N(i, j); //式87中除gi以外的gj前的系数
//求解线性方程组,得到所有增益系数g的向量形式gains_
solve(A, b, gains_); //A × gains_ = b
//在终端显示运行时间
LOGLN("Exposure compensation, time: " << ((getTickCount() - t) / getTickFrequency()) << " sec");
在计算得到了增益系数g后,就可以利用apply函数进行曝光补偿:
void GainCompensator::apply(int index, Point /*corner*/, Mat &image, const Mat &/*mask*/)
//index表示待拼接的图像索引
//image表示补偿得到的图像
image *= gains_(index, 0); //增益系数乘以图像,就实现了曝光补偿
分块补偿方法的feed函数:
void BlocksGainCompensator::feed(const vector<Point> &corners, const vector<Mat> &images,
const vector<pair<Mat,uchar> > &masks)
//确保各个输入参数的数量的一致性
CV_Assert(corners.size() == images.size() && images.size() == masks.size());
const int num_images = static_cast<int>(images.size()); //表示待拼接的图像数量
vector<Size> bl_per_imgs(num_images); //表示每个图像的块数量
vector<Point> block_corners; //表示块的左上角在全景图像上的坐标
vector<Mat> block_images; //表示块图像
vector<pair<Mat,uchar> > block_masks; //表示块的掩码
// Construct blocks for gain compensator
for (int img_idx = 0; img_idx < num_images; ++img_idx) //遍历所有图像,建立块
//bl_per_img表示当前图像的块数量,其中全局变量bl_width_和bl_height_表示块的宽和高,它们都被初始化为32,也就是块的理论尺寸为32×32
Size bl_per_img((images[img_idx].cols + bl_width_ - 1) / bl_width_,
(images[img_idx].rows + bl_height_ - 1) / bl_height_);
//bl_width和bl_height表示当前图像的块尺寸的实际宽和高
int bl_width = (images[img_idx].cols + bl_per_img.width - 1) / bl_per_img.width;
int bl_height = (images[img_idx].rows + bl_per_img.height - 1) / bl_per_img.height;
bl_per_imgs[img_idx] = bl_per_img; //赋值
//遍历图像的每个块
for (int by = 0; by < bl_per_img.height; ++by)
for (int bx = 0; bx < bl_per_img.width; ++bx)
//bl_tl表示当前块的左上角坐标点
Point bl_tl(bx * bl_width, by * bl_height);
//bl_br表示当前块的右下角坐标点
Point bl_br(min(bl_tl.x + bl_width, images[img_idx].cols),
min(bl_tl.y + bl_height, images[img_idx].rows));
//block_corners矢量变量赋值
block_corners.push_back(corners[img_idx] + bl_tl);
//block_images矢量变量赋值
block_images.push_back(images[img_idx](Rect(bl_tl, bl_br)));
//block_masks矢量变量赋值
block_masks.push_back(make_pair(masks[img_idx].first(Rect(bl_tl, bl_br)),
masks[img_idx].second));
//实例化GainCompensator,每个块都应用增益补偿方法
GainCompensator compensator;
compensator.feed(block_corners, block_images, block_masks); //得到块补偿系数
vector<double> gains = compensator.gains(); //得到增益系数
//全局变量gain_maps_表示所有块的增益
gain_maps_.resize(num_images);
Mat_<float> ker(1, 3); //表示分割线性滤波的核
ker(0,0) = 0.25; ker(0,1) = 0.5; ker(0,2) = 0.25;
int bl_idx = 0;
for (int img_idx = 0; img_idx < num_images; ++img_idx) //遍历所有的图像
Size bl_per_img = bl_per_imgs[img_idx]; //提取出当前图像的块数量
gain_maps_[img_idx].create(bl_per_img); //创建当前图像的gain_maps_
//遍历当前图像的所有块,得到块的增益系数
for (int by = 0; by < bl_per_img.height; ++by)
for (int bx = 0; bx < bl_per_img.width; ++bx, ++bl_idx)
gain_maps_[img_idx](by, bx) = static_cast<float>(gains[bl_idx]);
//两次应用分割线性滤波,平滑同一图像的块增益系数
sepFilter2D(gain_maps_[img_idx], gain_maps_[img_idx], CV_32F, ker, ker);
sepFilter2D(gain_maps_[img_idx], gain_maps_[img_idx], CV_32F, ker, ker);
应用分块补偿,对图像进行曝光补偿的apply函数:
void BlocksGainCompensator::apply(int index, Point /*corner*/, Mat &image, const Mat &/*mask*/)
CV_Assert(image.type() == CV_8UC3); //确保image的正确
Mat_<float> gain_map;
//得到该图像的块增益系数
if (gain_maps_[index].size() == image.size())
gain_map = gain_maps_[index];
else
resize(gain_maps_[index], gain_map, image.size(), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
//对该图像的红、绿、蓝分量进行增益补偿
for (int y = 0; y < image.rows; ++y)
const float* gain_row = gain_map.ptr<float>(y);
Point3_<uchar>* row = image.ptr<Point3_<uchar> >(y);
for (int x = 0; x < image.cols; ++x)
row[x].x = saturate_cast<uchar>(row[x].x * gain_row[x]);
row[x].y = saturate_cast<uchar>(row[x].y * gain_row[x]);
row[x].z = saturate_cast<uchar>(row[x].z * gain_row[x]);
5.3 应用
下面我们曝光补偿的应用:
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "highgui.h"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/autocalib.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/blenders.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/camera.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/exposure_compensate.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/matchers.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/motion_estimators.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/seam_finders.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/util.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/warpers.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/warpers.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace detail;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
vector<Mat> imgs; //输入图像
Mat img = imread("1.jpg");
imgs.push_back(img);
img = imread("2.jpg");
imgs.push_back(img);
Ptr<FeaturesFinder> finder; //特征检测
finder = new SurfFeaturesFinder();
vector<ImageFeatures> features(2);
(*finder)(imgs[0], features[0]);
(*finder)(imgs[1], features[1]);
vector<MatchesInfo> pairwise_matches; //特征匹配
BestOf2NearestMatcher matcher(false, 0.3f, 6, 6);
matcher(features, pairwise_matches);
HomographyBasedEstimator estimator; //相机参数评估
vector<CameraParams> cameras;
estimator(features, pairwise_matches, cameras);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cameras.size(); ++i)
Mat R;
cameras[i].R.convertTo(R, CV_32F);
cameras[i].R = R;
Ptr<detail::BundleAdjusterBase> adjuster; //光束平差法,精确相机参数
adjuster = new detail::BundleAdjusterReproj();
adjuster->setConfThresh(1);
(*adjuster)(features, pairwise_matches, cameras);
vector<Mat> rmats;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cameras.size(); ++i)
rmats.push_back(cameras[i].R.clone());
waveCorrect(rmats, WAVE_CORRECT_HORIZ); //波形校正
for (size_t i = 0; i < cameras.size(); ++i)
cameras[i].R = rmats[i];
//图像映射变换
vector<Point> corners(2);
vector<Mat> masks_warped(2);
vector<Mat> images_warped(2);
vector<Mat> masks(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
masks[i].create(imgs[i].size(), CV_8U);
masks[i].setTo(Scalar::all(255));
Ptr<WarperCreator> warper_creator;
warper_creator = new cv::PlaneWarper(); //平面投影
Ptr<RotationWarper> warper = warper_creator->create(static_cast<float>(cameras[0].focal));
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
Mat_<float> K;
cameras[i].K().convertTo(K, CV_32F);
corners[i] = warper->warp(imgs[i], K, cameras[i].R, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_REFLECT, images_warped[i]);
warper->warp(masks[i], K, cameras[i].R, INTER_NEAREST, BORDER_CONSTANT, masks_warped[i]);
//创建曝光补偿器,应用增益补偿方法
Ptr<ExposureCompensator> compensator =
ExposureCompensator::createDefault(ExposureCompensator::GAIN);
compensator->feed(corners, images_warped, masks_warped); //得到曝光补偿器
for(int i=0;i<2;++i) //应用曝光补偿器,对图像进行曝光补偿
compensator->apply(i, corners[i], images_warped[i], masks_warped[i]);
imwrite("warped1.jpg", images_warped[0]); //存储图像
imwrite("warped2.jpg", images_warped[1]);
return 0;
我们对图11中的两幅图像进行曝光补偿。很明显,两幅图像的曝光程度是不同的,尤其是两者的重叠区域,左侧要比右侧暗一些。图12是曝光补偿后的图像,经过补偿后,左侧图像变亮了,而右侧图像却变暗了。


图11 原图


图12 曝光补偿的结果
以上是关于Opencv2.4.9源码分析——Stitching的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章