大家使用hibernate有没有碰到对于频繁的数据插入后p频繁查询速度很慢的问题..? 我现在使用mysql数据库
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了大家使用hibernate有没有碰到对于频繁的数据插入后p频繁查询速度很慢的问题..? 我现在使用mysql数据库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
系统a每隔秒往数据库中插入数据.系统b每隔3秒去查询数据库.
现在的问题是.时间一长.有些时候就查不到数据了.比如说.4个线程.开了一段时间后.刚开始都没有问题.都能查到数据.时间长了.有些线程就间隔性的查不到数据了.
这个是不是hibernate的原因.还是mysql的数据设置的问题.?求大虾指点方案..
你说的flush是在查询前把session给flush么..?
追答flush,或者clear下试试。不行再说。
追问现在问题是..我直接在navicat控制台跑sql..重复的执行sql..快的话.每隔10-17下之间就会出现空值..
我查的.是a表关联b表.
b表的数据查不到.
你看数据库中有值嘛?如果说一对多的话,让多的一方维护关联关系,多对一的话让一的一方维护。一对多,从多的一端保存数据比从一的一端保存数据要快,因为从一的一端保存数据时,会多更新多的一端的一个外键(是指定一的一端的。)你先查询b表的数据
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes = (Classes)session.load(Classes.class, 2);
System.out.println("classes.name=" + classes.getName());
Set students = classes.getStudents();
for (Iterator iter = students.iterator();iter.hasNext();)
Student student = iter.next();
System.out.println(student.getName());
tx.commit();
按照这种方式查询看看,首先你得确定数据库里有值才行啊。
你的session是每次都open一个吗?用getCurrentSession()
唉..大哥.我上面都说了..直接在工具里面跑sql..
不过问题解决了.
Hibernate 二级缓存配置
Hibernate之一级缓存和二级缓存
hibernate升级到4.3二级缓存cache配置改变了
原来是hibernate.cache.provider_class = org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
hibernate4.3的要改成:
hibernate.cache.provider_class =net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.EhCacheProvider
这还不够,还要加上下面这个,否则一样报错
hibernate.cache.region.factory_class=org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory
详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/Junsept/p/7324981.html
https://blog.csdn.net/feiyu1001/article/details/3173942
https://blog.csdn.net/culous/article/details/53355767
Hibernate的cache管理:
Cache就是缓存,它往往是提高系统性能的最重要手段,对数据起到一个蓄水池和缓冲的作用。Cache对于大量依赖数据读取操作的系统而言尤其重要。在大并发量的情况下,如果每次程序都需要向数据库直接做查询操作,它们所带来的性能开销是显而易见的,频繁的网络舆,数据库磁盘的读写操作都会大大降低系统的性能。此时如果能让数据库在本地内存中保留一个镜像,下次访问的时候只需要从内存中直接获取,那么显然可以带来不小的性能提升。引入Cache机制的难点是如何保证内存中数据的有效性,否则脏数据的出现将会给系统带来难以预知的严重后果。虽然一个设计得很好的应用程序不用Cache也可以表现出让人接受的性能,但毫无疑问,一些对读取操作要求比较高的应用程序可以通过Cache获得更高的性能。对于应用程序,Cache通过内存或磁盘保存了数据库中的当前有关数据状态,它是一个存储在本地的数据备份。Cache位于数据库和应用程序之间,从数据库更新数据,并给程序提供数据。
Hibernate实现了良好的Cache机制,可以借助Hibernate内部的Cache迅速提高系统的数据读取性能。Hibernate中的Cache可分为两层:一级Cache和二级Cache。
一级缓存:
Hibernate默认是开启一级缓存的,一级缓存存放在session上,属于事务级数据缓冲。
二级缓存:
二级缓存是在SessionFactory,所有的Session共享同一个二级Cache。二级Cache的内部如何实现并不重要,重要的是采用哪种正确的缓存策略,以及采用哪个Cache提供器。
在Hibernate中使用EhCache:
1)hibernate.cfg.xml 中增加对二级缓存的配置(maven项目放在resources文件夹下)
<?xml version=\'1.0\' encoding=\'utf-8\'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- Database connection settings --> <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=GBK</property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">admin</property> <!-- SQL dialect --> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<prop key="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</prop>
<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</property> <mapping resource="com/how2java/pojo/Product.hbm.xml" /> <mapping resource="com/how2java/pojo/Category.hbm.xml" /> <mapping resource="com/how2java/pojo/User.hbm.xml" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
说明一下:如果不设置“查询缓存”,那么hibernate只会缓存使用load()方法获得的单个持久化对象,如果想缓存使用findall()、list()、Iterator()、createCriteria()、createQuery()等方法获得的数据结果集的话,就需要设置hibernate.cache.use_query_cache true 才行
如果需要“查询缓存”,还需要在使用Query或Criteria()时设置其setCacheable(true);属性
hibernate升级到4.3二级缓存cache配置改变了
原来是hibernate.cache.provider_class = org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
hibernate4.3的要改成:
hibernate.cache.provider_class =net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.EhCacheProvider
这还不够,还要加上下面这个,否则一样报错
hibernate.cache.region.factory_class=org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory
2)ehcache.xml用户EhCache配置(maven项目放在resources文件夹下)
<ehcache> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" /> </ehcache>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" <!-- 缓存最大数目 --> eternal="false" <!-- 缓存是否持久 --> overflowToDisk="true" <!-- 是否保存到磁盘,当系统当机时--> timeToIdleSeconds="300" <!-- 当缓存闲置n秒后销毁 --> timeToLiveSeconds="180" <!-- 当缓存存活n秒后销毁--> diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds= "120"/> </ehcache>
Ehcache的配置说明 <ehcache> <!-- 磁盘存储配置: 用来指定缓存在磁盘上的存储位置。可以使用JavaVM环境变量(user.home, user.dir, java.io.tmpdir) --> <diskStore path = "/var/apps/cache/" /> <!-- 指定CacheManagerEventListenerFactory,这个对象在缓存添加的时候会得到相应的通知 CacheManagerEventListenerFactory的属性 *class - CacheManagerEventListenerFactory的一个实现类 *properties - CacheManagerEventListenerFactory的属性值,以逗号(,)分割多个属性 如果没有实现类被指定,则系统不创建CacheManager的监听器,没有默认值 --> <cacheManagerEventListenerFactory class="" properties="" /> <!-- 在进行分布式缓存的应用时候需要指定CacheManagerPeerProviderFactory, 用来生成CacheManagerPeerProvider的实例,以便和集群中的其他CacheManager通信。 *class -CacheManagerPeerProviderFactory的一个实现类 *properties - CacheManagerPeerProviderFactory的属性值,以逗号(,)分割多个属性 Ehcache内建了2种基于RMI分布系统的通信策略: *automatic - 使用多播组。在一个节点加入或者推出集群的时候自动感应 *manual - 硬编码方式 目前的awf中不考虑分布缓存 --> <cacheManagerPeerListenerFactory class="" properties="" /> <!-- 缓存配置。 以下属性是必须的: name - cache的标识符,在一个CacheManager中必须唯一 maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目 maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目 eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否有有效期。如果为true,timeouts属性被忽略 overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上 以下属性是可选的: timeToIdleSeconds - 缓存element在过期前的空闲时间。默认为0,表示可空闲无限时间. (如果指定了这个时间,是否在被hit的前超过了这个时间就会被remove?在内存缓存数目超限之前不会被remove) timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期。这个类似于timeouts,默认为0,不过期 (是否通常情况下应该大于等于timeToIdleSeconds,小于会如何?idle时间也会减小和这个数值一样) diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否持久化磁盘缓存,默认是false。 (测试一下true的情况?重载vm的时候会从磁盘进行序列化到对象) diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒. (测试一下0的时候会如何) memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU,可选的有LFU和FIFO 可对缓存中的element配置诸如监听器和加载器。Ehcahe内建了一些 *cacheEventListenerFactory - 监听缓存中element的put, remove, update和expire事件 *bootstrapCacheLoaderFactory - 启动时加载缓存的element 每个用来做分布式缓存都必须设定element的事件监听器,用来在各个CacheManager节点复制消息。 Ehcache内建了基于RMI的实现 - RMICacheReplicatorFactory <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronouly=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdateViaCopy=true, replicateRemovals=true" /> --> <cache .... /> <!-- 默认的Cache配置。用来实现CacheManager.add(String cacheName)创建的缓存 --> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" maxElementsOnDisk="1000000" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" /> </ehcache>
3)设置hbm
对于要进行二级缓存的实体类,进行配置,增加
1:事务(Transaction)仅在受管理的环境中可用。它保证可重读的事务隔离级别,可以对读/写比例高,很少更新的数据采用该策略。
2:读写(read-write)使用时间戳机制维护读写提交事务隔离级别。可以对读/写比例高,很少更新的数据采用该策略。
3:非严格读写(notstrict-read-write)不保证Cache和数据库之间的数据库的一致性。使用此策略时,应该设置足够的缓存过期时间,否则可能从缓存中读出脏数据。当一些数据极少改变,并且当这些数据和数据库有一部份不量影响不大时,可以使用此策略。
4:只读(read-only)当确保数据永不改变时,可以使用此策略。
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.domain"> <class name="Category" table="category"> <cache usage="read-write" /><!-- 二级缓存配置 --> <id name="id" column="id"> <generator class="native"> </generator> </id> <property name="name" column="name"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<class name="Videos" table="TEST" lazy="false"> <cache usage="read-write" region="ehcache.xml中的name的属性值"/>注意:这一句需要紧跟在class标签下面,其他位置无效。 hbm文件查找cache方法名的策略:如果不指定hbm文件中的region="ehcache.xml中的name的属性值",则使用name名为com.ouou.model.Videos的cache, 如果不存在与类名匹配的cache名称,则用defaultCache。 如果Videos包含set集合,则需要另行指定其cache 例如Videos包含Tags集合,则需要 添加如下配置到ehcache.xml中 <cache name="com.ouou.model.Tags" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="false" /> 另,针对查询缓存的配置如下: <cache name="org.hibernate.cache.UpdateTimestampsCache" maxElementsInMemory="5000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true"/> <cache name="org.hibernate.cache.StandardQueryCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true"/>
**也可以用Hibernate注解配置缓存实体类**
**Java代码 @Entity @Table @Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE) public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -5121812640999313420L; private Integer id; private String name; ...... }**
4)测试效果
使用不同的session,都去获取id=1的category,只会访问一次数据库。因为第二次获取虽然没有从第二个session中拿到缓存,但是从sessionfactory中拿到了Category缓存对象。
log1
Hibernate: select category0_.id as id1_0_, category0_.name as name1_0_ from category category0_ where category0_.id=?
log2
log3
//一级缓存session System.out.println("log1"); Category c1 = (Category)session.get(Category.class, 1); System.out.println("log2"); Category c2 = (Category)session.get(Category.class, 1);//不会显示SQL语句 //提交事务 session.getTransaction().commit(); //二级缓存SessionFactory Session session2 = factory.openSession(); session2.beginTransaction(); System.out.println("log3"); Category p3 = (Category) session2.get(Category.class, 1);//不会显示 session2.getTransaction().commit();
5)注意事项
maven所需包,hibernate 3.0版本,hibernate-ehcache
<dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>3.6.10.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId> <version>3.6.7.Final</version> </dependency>
实际操作:
1.ehcache.xml(maven项目放在resources文件夹下):基本为默认配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" /> </ehcache>
2.实体类
@Entity @Table(name="device") @Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE) public class Device { }
3.maven依赖
<!--hibernate core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>4.3.11.Final</version> </dependency> <!--hibernate cache --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId> <version>4.3.11.Final</version> </dependency>
4.hibernate 配置
<prop key="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</prop> <prop key="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</prop> <prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.EhCacheProvider</prop> <prop key="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</prop>
5.测试实现类
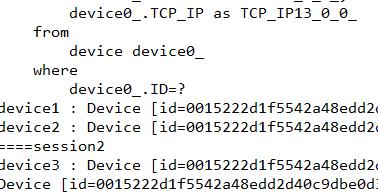
@Override public Device getDeviceFromSecondCache(String deviceId) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("====session1"); Session session1 = sessionFactory.openSession(); Transaction transaction1 = session1.getTransaction(); transaction1.begin(); Device device1 = (Device) session1.get(Device.class, deviceId); System.out.println("device1 : " + device1); Device device2 = (Device) session1.get(Device.class, deviceId);//不会显示sql System.out.println("device2 : " + device2); //提交事务 transaction1.commit(); System.out.println("====session2"); Session session2= sessionFactory.openSession(); Transaction transaction2 = session2.getTransaction(); transaction2.begin(); Device device3 = (Device) session1.get(Device.class, deviceId); //提交事务 System.out.println("device3 : " + device2); transaction2.commit(); return device2; }
@Test @Transactional public void testGet(){ //System.out.println(testDao.getDeviceById("0015222d1f5542a48edd2d40c9dbe0d3")); //testDao.saveDevice(null); testDao.getDeviceFromSecondCache("0015222d1f5542a48edd2d40c9dbe0d3"); }
运行结果只进行一次sql查询
以上是关于大家使用hibernate有没有碰到对于频繁的数据插入后p频繁查询速度很慢的问题..? 我现在使用mysql数据库的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章