c# 两个list的交集问题!
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了c# 两个list的交集问题!相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我写了个方法。
public void newList (List<object> a,List<object> b)
List<object> c= new List<object>();
for (int i = 0; i < a.Count; i++)
if(a[i].Equals(b[i]))
c.Add(a[i]);
我不知道是否有别的高效率的方法可以解决此问题,知道的分享下,谢谢!
public IEnumerable<T> newList (IEnumerable<T> a, IEnumerable<T> b)
foreach (T item in a)
if(b.Contains(item))
yield return item;
参考技术A public IEnumerable<T> newList<T> (IEnumerable<T> a, IEnumerable<T> b)
foreach (T item in a)
if(b.Contains(item))
yield return item;
参考技术B 回楼主,你写的这个方法是错的,当b的数量小于a数量的时候就会报错
C# Linq 交集并集差集去重
其实只要明白 LINQ查询操作符的Distinct、Union、Concat、Intersect、Except、Skip、Take、SkipWhile、TakeWhile、Single、SingleOrDefault、Reverse、SelectMany,Aggregate()的使用,一些简单的操作就可以了。
合并两个数组,并去掉重复元素,然后排序(C#)
List<int> numbers1 = new List<int>() { 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 12, 10 };
List<int> numbers2 = new List<int>() { 15, 14, 11, 13, 19, 18, 16, 17, 12, 10 };
var newQuerty = numbers1.Concat(
from n in numbers2
where !numbers1.Contains(n)
select n
).OrderBy(n => n);
string count = "";
foreach (int i in newQuerty)
{
count += i + ",";
}
MessageBox.Show(count);
在这简单的介绍几个关键字,Distinct、Union、Concat、Intersect、Except、Skip、Take
Distinct - 过滤集合中的相同项;
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
var newlist=list.Distinct();
得到的结果就是;1,2,3,4,5,6
Union - 连接不同集合,自动过滤相同项
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
List<int> list1= new List<int>() {5,6,6,7,8,9};
var newlist=list.Union (list1);
得到的结果就是;1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Concat - 连接不同集合,不会自动过滤相同项;
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
List<int> list1= new List<int>() {5,6,6,7,8,9};
var newlist=list.Union (list1);
得到的结果就是;1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6,5,6,6,7,8,9
Intersect - 获取不同集合的相同项(交集);
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
List<int> list1= new List<int>() {5,6,6,7,8,9};
var newlist=list.Intersect (list1);
得到的结果就是;5,6
Except - 从某集合中删除其与另一个集合中相同的项;其实这个说简单点就是某集合中独有的元素
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
List<int> list1= new List<int>() {5,6,6,7,8,9};
var newlist=list.Except (list1);
得到的结果就是;1,2,3,4
Skip - 跳过集合的前n个元素;
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
var newlist=list.Skip (3);
得到的结果就是;4,4,5,6,6
Take - 获取集合的前n个元素;延迟
List<int> list= new List<int>() {1,2,2,3,4,4,5,6,6 };
var newlist=list.Take (3);
得到的结果就是;1,2,2
List<string> ListA = new List<string>(); List<string> ListB = new List<string>(); List<string> ListResult = new List<string>(); ListResult = ListA.Distinct().ToList();//去重 ListResult = ListA.Except(ListB).ToList();//差集 ListResult= ListA.Union(ListB).ToList(); //并集 ListResult = ListA.Intersect(ListB).ToList();//交集
重写比较方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IList<Student> oneStudents = new List<Student>();
oneStudents.Add(new Student(1,false,"小新1","徐汇"));
oneStudents.Add(new Student(2,false,"小新2","闵行"));
oneStudents.Add(new Student(3, false, "小新3", "嘉定"));
oneStudents.Add(new Student(4, false, "小新4", "闸北"));
IList<Student> twoStudents = new List<Student>();
twoStudents.Add(new Student(5, false, "小新5", "贵州"));
twoStudents.Add(new Student(6, false, "小新6", "湖北"));
twoStudents.Add(new Student(7, false, "小新7", "山东"));
twoStudents.Add(new Student(8, false, "小新8", "西藏"));
IList<Student> threeStudents = new List<Student>();
threeStudents.Add(new Student(1, false, "小新1", "徐汇"));
threeStudents.Add(new Student(2, false, "小新2", "闵行"));
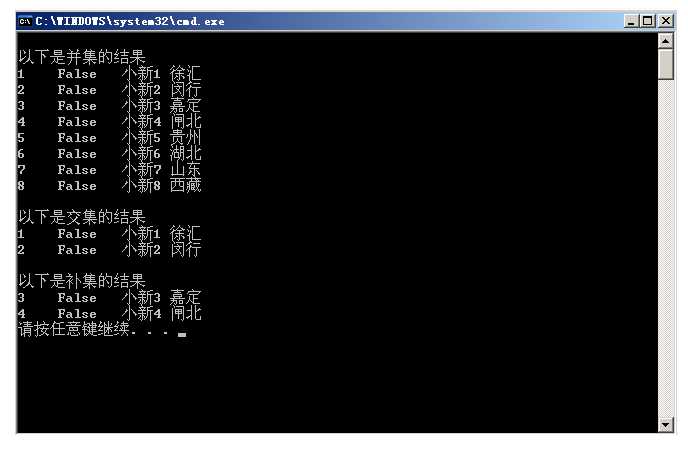
var bingji = oneStudents.Union(twoStudents, new StudentListEquality()).ToList();//并(全)集
var jiaoji = oneStudents.Intersect(threeStudents, new StudentListEquality()).ToList();//交集
var chaji = oneStudents.Except(threeStudents, new StudentListEquality()).ToList();//差集
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("以下是并集的结果");
bingji.ForEach(x =>
{
Console.WriteLine(x.StudentId.ToString() + " " + x.Sex.ToString() + " " + x.Name.ToString()+" "+x.Address.ToString());
});
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("以下是交集的结果");
jiaoji.ForEach(x =>
{
Console.WriteLine(x.StudentId.ToString() + " " + x.Sex.ToString() + " " + x.Name.ToString() + " " + x.Address.ToString());
});
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("以下是差集的结果");
chaji.ForEach(x =>
{
Console.WriteLine(x.StudentId.ToString() + " " + x.Sex.ToString() + " " + x.Name.ToString() + " " + x.Address.ToString());
});
}
}
public class Student
{
public Student(int studentId, bool sex, String name, String address)
{
this.StudentId = studentId;
this.Sex = sex;
this.Name = name;
this.Address = address;
}
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public bool Sex { get; set; }
public String Name { get; set; }
public String Address { get; set; }
}
public class StudentListEquality : IEqualityComparer<Student>
{
public bool Equals(Student x, Student y)
{
return x.StudentId == y.StudentId;
}
public int GetHashCode(Student obj)
{
if (obj == null)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return obj.ToString().GetHashCode();
}
}
}
}
以上是关于c# 两个list的交集问题!的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章