C++ (operator overloading, friend functions) 矩阵 求大神~ 需要显示同例图样 满意加分~
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++ (operator overloading, friend functions) 矩阵 求大神~ 需要显示同例图样 满意加分~相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
定义并执行class Matrix(模拟一2x2输入整数的矩阵. Matrix class:
class Matrix
public:
Matrix(int a1, int b1, int c1, int d1);
private:
int a, b, c, d;
;
Matrix::Matrix(int a1, int b1, int c1, int d1)
a = a1;
b = b1;
c = c1;
d = d1;
1.以公共成员函数重载以下操作: +=, -=, and *=.
Left operand is the calling object.以下操作应只包括right operand, return the left operand by reference by returning *this,the dereferenced this pointer which points to the calling object.
2.以非成员友元函数重载以下操作: <<, >>, +, -, *, ==,!=.用上步定义的+=, -=, *=重载+, -, * Create a local Matrix variable called temp which is a copy of the left Matrix object r,have temp use +=(e.g.)with the other Matrix s as the right operand,and then return the resulting Matrix temp by value.
3.重载指数算子^(友元函数).The left operand is a const Matrix& r (pass in by reference).The right operand is a const int n, which represents the power to which to raise the Matrix r. r^2 should return a copy of the matrix r*r(e.g.) Here is how it works:
1)n负,output an error message using the error output stream cerr which works like cout,then use the statement exit(1);terminates the program.The argument 1 indicates that an error forced program termination.
2)n为0,return an identity Matrix [a=1 b=0 c=0 d=1] by value.
3)否则,create a Matrix called temp which is a local copy of the parameter Matrix r passed in. Then create a loop that keeps multiplying temp by r and storing the result in temp until temp reaches the desired power of r. Then return temp by value.
4)Stream insertion << and extraction >> operators.Return the stream object at the end of each definition so that the operator can be chained like in the following statement: cout << m << n;
源代码顺序: Matrix的类定义,成员函数定义,友元函数定义,及以下定义将测试class:
int main()
Matrix m(1, 2, 3, 4);
Matrix n(-1, 2, -3, 4);
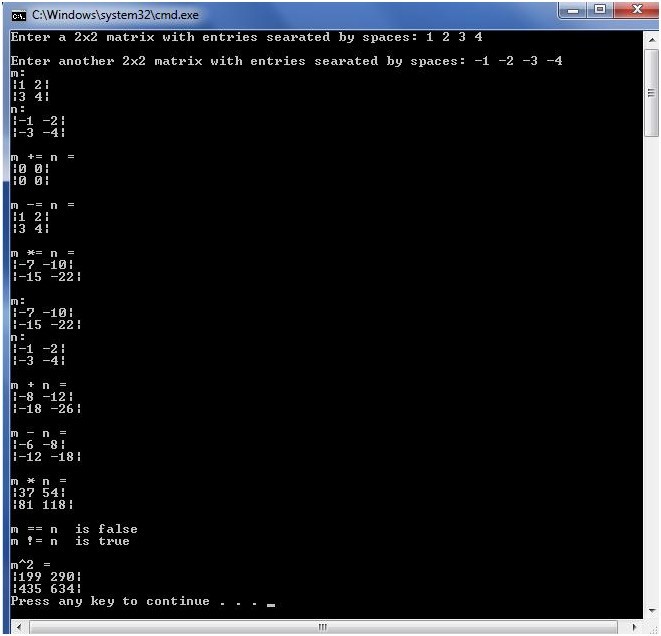
cout << "Enter a 2x2 matrix with entries separated by spaces: ";
cin >> m;
cout << endl;
cout << "Enter another 2x2 matrix with entries separated by spaces: ";
cin >> n;
cout << "m: " << m << endl << "n: " << n << endl << endl;
cout << "m += n" << " = ";
m += n;
cout << m << endl << endl;
cout << "m -= n" << " = ";
m -= n;
cout << m << endl << endl;
cout << "m *= n" << " = ";
m *= n;
cout << m << endl << endl;
cout << "m: " << m << endl << "n: " << n << endl << endl;
cout << "m + n = "<< (m+n) << endl << endl;
cout << "m - n = "<< (m-n) << endl << endl;
cout << "m * n = "<< (m*n) << endl << endl;
cout << "m == n " << " is " << (m==n? "true": "false") << endl;
cout << "m != n " << " is " << (m!=n? "true": "false") << endl << endl;
cout << "m^2 = " << (m^2) << endl;
return 0;
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
class Matrix
public:
Matrix(int a1, int b1, int c1, int d1);
private:
int a, b, c, d;
public:
Matrix& operator +=(Matrix const& rhs);
Matrix& operator -=(Matrix const& rhs);
Matrix& operator *=(Matrix const& rhs);
friend Matrix operator +(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs);
friend Matrix operator -(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs);
friend Matrix operator *(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs);
friend Matrix operator ^(Matrix const& lhs, int n);
friend bool operator ==(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs);
friend bool operator !=(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs);
friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, Matrix const& rhs);
friend istream& operator >>(istream& is, Matrix & rhs);
;
Matrix::Matrix(int a1, int b1, int c1, int d1)
a = a1;
b = b1;
c = c1;
d = d1;
Matrix& Matrix::operator +=(Matrix const& rhs)
this->a+=rhs.a;
this->b+=rhs.b;
this->c+=rhs.c;
this->d+=rhs.d;
return *this;
Matrix& Matrix::operator -=(Matrix const& rhs)
this->a -= rhs.a;
this->b -= rhs.b;
this->c -= rhs.c;
this->d -= rhs.d;
return *this;
Matrix& Matrix::operator *=(Matrix const& rhs)
int a, b, c, d;
a = rhs.a * this->a + rhs.c * this->b;
b = rhs.b * this->a + rhs.d * this->b;
c = rhs.a * this->c + rhs.c * this->d;
d = rhs.b * this->c + rhs.d * this->d;
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
this->c = c;
this->d = d;
return *this;
Matrix operator +(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs)
Matrix temp = lhs;
temp += rhs;
return temp;
Matrix operator -(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs)
Matrix temp = lhs;
temp -= rhs;
return temp;
Matrix operator *(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs)
Matrix temp = lhs;
temp *= rhs;
return temp;
Matrix operator ^(Matrix const& lhs, int n)
Matrix temp = lhs;
if ( n < 0 )
cerr << "ERROR: n < 0!" << endl;
exit(1);
else if ( n == 0 )
return Matrix(1,0,0,1);
else
while ( --n )
temp *= lhs;
return temp;
bool operator ==(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs)
return (lhs.a == rhs.a && lhs.b == rhs.b && lhs.c == rhs.c && lhs.d == rhs.d);
bool operator !=(Matrix const& lhs, Matrix const& rhs)
return !(lhs==rhs);
ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, Matrix const& rhs)
os << endl;
os << '|' << rhs.a << ' ' << rhs.b << '|' << endl;
os << '|' << rhs.c << ' ' << rhs.d << '|' << endl;
return os;
istream& operator >>(istream& is, Matrix & rhs)
is >> rhs.a >> rhs.b >> rhs.c >> rhs.d ;
return is;
int main()
Matrix m(1, 2, 3, 4);
Matrix n(-1, 2, -3, 4);
cout << "Enter a 2x2 matrix with entries separated by spaces: ";
cin >> m;
cout << endl;
cout << "Enter another 2x2 matrix with entries separated by spaces: ";
cin >> n;
cout << "m: " << m << endl << "n: " << n << endl << endl;
cout << "m += n" << " = ";
m += n;
cout << m << endl << endl;
cout << "m -= n" << " = ";
m -= n;
cout << m << endl << endl;
cout << "m *= n" << " = ";
m *= n;
cout << m << endl << endl;
cout << "m: " << m << endl << "n: " << n << endl << endl;
cout << "m + n = "<< (m+n) << endl << endl;
cout << "m - n = "<< (m-n) << endl << endl;
cout << "m * n = "<< (m*n) << endl << endl;
cout << "m == n " << " is " << (m==n? "true": "false") << endl;
cout << "m != n " << " is " << (m!=n? "true": "false") << endl << endl;
cout << "m^2 = " << (m^2) << endl;
return 0;
运行结果看这里http://ideone.com/yDZnn追问
能不能在大步骤的上方用//标一下步骤的目的挖,比如说//Matrix class definition, //overloaded operator+= delaration and definition. 刚学C++不大明白= = 3Q
追答代码太长这里没法贴了,我在ideone里面加了,你过去看吧
http://ideone.com/yDZnn
要是没法打开的话留个email我发给你
十个 C++ 运算符重载示例,看完不懂打我...
下面是一些 C++ 运算符重载示例,包括算术运算符、赋值运算符、逻辑运算符、成员运算符、关系运算符等等,这些都是使用频率较高的几个运算符重载案例。
⭐️ 所有示例代码均存放于 GitHub: getiot/cpp-courses/operator_overloading 。
示例 1:一元运算符重载
一元运算符即只对一个操作数进行操作的运算符,例如:!obj、-obj、++obj 、obj++ 或 obj-- 等等。
下面示例将对负号(-)进行重载:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Distance
private:
int feet; // 0 到无穷
int inches; // 0 到 12
public:
// 构造函数
Distance()
feet = 0;
inches = 0;
Distance(int f, int i)
feet = f;
inches = i;
// 显示距离
void displayDistance()
cout << "F: " << feet << ", I: " << inches << endl;
// 重载负运算符 ( - )
Distance operator- ()
feet = -feet;
inches = -inches;
return Distance(feet, inches);
;
int main(void)
Distance d1(1, 10), d2(-5, 110);
-d1; // 取相反数
d1.displayDistance(); // 距离 D1
-d2; // 取相反数
d2.displayDistance(); // 距离 D2
return 0;
编译并运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
F: -1, I: -10
F: 5, I: -110
示例 2:二元运算符重载
二元运算符即需要两个参数的运算符,例如:加运算符(+)、减运算符(-)、乘运算符(*)、除运算符(/)。
下面示例将重载加运算符(+):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
double length; // 长度
double width; // 宽度
double height; // 高度
public:
Box ()
length = 0.0;
width = 0.0;
height = 0.0;
Box (double a, double b ,double c)
length = a;
width = b;
height = c;
double getVolume(void)
return length * width * height;
// 重载 + 运算符,用于把两个 Box 对象相加
Box operator+(const Box& b)
Box box;
box.length = this->length + b.length;
box.width = this->width + b.width;
box.height = this->height + b.height;
return box;
;
int main(void)
Box b1(5.0, 4.0, 3.0);
Box b2(6.0, 5.0, 4.0);
Box b3;
cout << "Volume of b1 : " << b1.getVolume() << endl;
cout << "Volume of b2 : " << b2.getVolume() << endl;
// 把两个对象相加,得到 Box3
b3 = b1 + b2;
// Box3 的体积
cout << "Volume of b3 : " << b3.getVolume() << endl;
return 0;
使用 g++ main.cpp && ./a.out 命令编译运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
Volume of b1 : 60
Volume of b2 : 120
Volume of b3 : 693
示例 3:关系运算符重载
C++ 允许重载任何一个关系运算符(例如 < 、 > 、 <= 、 >= 、 == 等),重载后的关系运算符可用于比较类的对象。许多 C++ 内置的数据类型也都支持各种关系运算符。
下面示例将重载小于符(<):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect
private:
double width;
double height;
public:
Rect(double a, double b)
width = a;
height = b;
double area()
return width * height;
// 重载小于运算符 ( < ), 按照面积比大小
bool operator<(Rect& that)
return this->area() < that.area();
;
int main()
Rect r1(3.0, 5.0), r2(3.5, 4.5);
cout << "Area of r1 = " << r1.area() << endl;
cout << "Area of r2 = " << r2.area() << endl;
if ( r1 < r2 )
cout << "r1 is less than r2" << endl;
else
cout << "r1 is large than r2" << endl;
return 0;
编译运行以上代码,输出结果如下:
Area of r1 = 15
Area of r2 = 15.75
r1 is less than r2
示例 4:输入/输出运算符重载
C++ 使用流提取运算符(>>)和流插入运算符(<<)来输入和输出内置的数据类型,同时也允许重载 >> 和 << 来操作对象等用户自定义的数据类型。
可以把运算符重载函数声明为类的友元函数,这样就可以不用创建对象而直接调用函数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect
public:
double width;
double height;
Rect()
width = 0;
height = 0;
Rect(double a, double b )
width = a;
height = b;
double area()
return width * height;
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &output, Rect &r)
output << "width: " << r.width << ", ";
output << "height: " << r.height << ", ";
output << "area: " << r.area();
return output;
friend std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &input, Rect &r)
input >> r.width >> r.height;
return input;
;
int main()
Rect r1(3.0, 4.0), r2(6.0, 8.0), r3;
cout << "Enter the value of object: \\n";
cin >> r3;
cout << "r1: " << r1 << endl;
cout << "r2: " << r2 << endl;
cout << "r3: " << r3 << endl;
return 0;
编译和运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
Enter the value of object:
2 3
r1: width: 3, height: 4, area: 12
r2: width: 6, height: 8, area: 48
r3: width: 2, height: 3, area: 6
示例 5:++ 和 – 运算符重载
递增运算符(++)和递减运算符(--)是 C++ 语言中两个重要的一元运算符,包括前缀和后缀两种用法。
下面示例将演示如何重载前缀自增(++obj)和后缀自减运算符(obj--):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Time
private:
int minute;
int second;
public:
Time ()
minute = 0;
second = 0;
Time (int m, int s)
minute = m;
second = s;
void display()
cout << minute << " : " << second << endl;
// 重载前缀递增运算符 ( ++ )
Time operator++()
second++;
if (second >= 60)
minute++;
second = 0;
return Time(minute, second);
// 重载后缀递增运算符( ++ )
Time operator++(int)
Time t(minute, second); // 保存原始值
second++; // 对象加 1
if (second >= 60)
minute++;
second = 0;
return t; // 返回旧的原始值
;
int main()
Time t1(12, 58), t2(0,45);
t1.display();
(++t1).display();
(++t1).display();
t2.display();
(t2++).display();
(t2++).display();
return 0;
编译运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
12 : 58
12 : 59
13 : 0
0 : 45
0 : 45
0 : 46
示例 6:赋值运算符重载
C++ 允许重载赋值运算符(=),用于创建一个对象,比如拷贝构造函数。
下面示例重载 Rect 中的赋值运算符,并在每次拷贝的时候就把长度和宽度数值各加 1。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect
private:
double width;
double height;
public:
Rect()
width = 0;
height = 0;
Rect(double a, double b)
width = a;
height = b;
void display()
cout << " width: " << width;
cout << " height: " << height;
void operator= (const Rect &r)
width = r.width + 1;
height = r.height + 1;
;
int main()
Rect r1(3.0, 4.0), r2;
r2 = r1;
cout << "r1: ";
r1.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "r2: ";
r2.display();
cout << endl;
return 0;
编译和运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
r1: width: 3 height: 4
r2: width: 4 height: 5
示例 7:函数调用运算符重载
C++ 允许重载函数调用运算符(即 () 符号)。重载 () 的目的不是为了创造一种新的调用函数的方式,而是创建一个可以传递任意个参数的运算符函数。其实就是创建一个可调用的对象。
下面示例将演示重载函数调用运算符的妙用:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect
private:
int width;
int height;
public:
Rect()
width = 0;
height = 0;
Rect(int a ,int b)
width = a;
height = b;
void operator()()
cout << "Area of myself is:" << width * height << endl;
;
int main()
Rect r1(3, 4), r2(6, 8);
cout << "r1: ";
r1();
cout << "r2: ";
r2();
return 0;
编译和运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
r1: Area of myself is:12
r2: Area of myself is:48
示例 8:下标运算符重载
下标操作符([])通常用于访问数组元素。C++ 允许重载下标运算符用于增强操作 C++ 数组的功能,重载下标运算符最重要的作用就是设置一个哨兵,防止数组访问越界。
下面示例演示重载下标运算符:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 10;
class Fibo
private:
// 偷懒,防止把 SIZE 设置的过小
int arr[SIZE+3];
public:
Fibo()
arr[0] = 0;
arr[1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i<SIZE; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i-2] + arr[i-1];
int& operator[](unsigned int i)
if (i >= SIZE)
std::cout << "(索引超过最大值) ";
return arr[0]; // 返回第一个元素
return arr[i];
;
int main()
Fibo fb;
for (int i=0; i<SIZE+1; i++)
cout << fb[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
编译和运行以上示例,输出结果如下:
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 (索引超过最大值) 0
示例 9:类成员访问运算符重载
C++ 允许重载类成员访问运算符(->),用于为一个类赋予 “指针” 行为。重载 -> 运算符时需要注意以下几点:
- 运算符
->必须是一个成员函数; - 如果使用了
->运算符,返回类型必须是指针或者是类的对象; - 运算符
->通常与指针引用运算符*结合使用,用于实现智能指针的功能; - 这些指针是行为与正常指针相似的对象,唯一不同的是,通过指针访问对象时,它们会执行其它的任务(比如,当指针销毁时,或者当指针指向另一个对象时,会自动删除对象)。
间接引用运算符 -> 可被定义为一个一元后缀运算符,比如:
class Ptr
//...
X * operator->();
;
类 Ptr 的对象可用于访问类 X 的成员,使用方式与指针的用法十分相似,如下:
void f(Ptr p )
p->m = 10 ; // (p.operator->())->m = 10
语句 p->m 被解释为 (p.operator->())->m。通过下面示例加深理解:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 假设一个实际的类
class Obj
static int i, j;
public:
void f() const cout << i++ << endl;
void g() const cout << j++ << endl;
;
// 静态成员定义
int Obj::i = 10;
int Obj::j = 12;
// 为上面的类实现一个容器
class ObjContainer
std::vector<Obj*> a;
public:
void add(Obj* obj)
a.push_back(obj); // 调用向量的标准方法
friend class SmartPointer;
;
// 实现智能指针,用于访问类 Obj 的成员
class SmartPointer
ObjContainer oc;
int index;
public:
SmartPointer(ObjContainer& objc)
oc = objc;
index = 0;
// 前缀版本
// 返回值表示列表结束
bool operator++()
if(index >= oc.a.size())
return false;
if(oc.a[++index] == 0)
return false;
return true;
// 后缀版本
bool operator++(int)
return operator++();
// 重载运算符 ->
Obj