如何用VB做一个简单计算器 要求实现加减乘除乘方开方功能
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何用VB做一个简单计算器 要求实现加减乘除乘方开方功能相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
如何用VB做一个简单计算器 要求实现加减乘除乘方开方功能 用0~9按钮实现 类似WINDOWS系统自带的计算器 最好带图
最好有声明 代码太多 看着晃~
用记事本把这段代码复制过去,然后另存为.frm就可以了
VERSION 5.00
Begin VB.Form frmMain
Appearance = 0 'Flat
BackColor = &H80000005&
BorderStyle = 3 'Fixed Dialog
Caption = "简单计算器"
ClientHeight = 2430
ClientLeft = 45
ClientTop = 435
ClientWidth = 3150
KeyPreview = -1 'True
LinkTopic = "Form1"
MaxButton = 0 'False
MinButton = 0 'False
ScaleHeight = 2430
ScaleWidth = 3150
ShowInTaskbar = 0 'False
StartUpPosition = 3 '窗口缺省
Begin VB.CommandButton Command10
Caption = "^"
Height = 375
Left = 1920
TabIndex = 22
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.PictureBox picDisplay
Appearance = 0 'Flat
BackColor = &H80000005&
ForeColor = &H80000008&
Height = 255
Left = 120
ScaleHeight = 225
ScaleWidth = 2865
TabIndex = 19
Top = 120
Width = 2895
Begin VB.TextBox Text1
Alignment = 1 'Right Justify
BorderStyle = 0 'None
Height = 255
Left = 240
Locked = -1 'True
TabIndex = 20
Top = 0
Width = 2535
End
Begin VB.Label lblOperation
Appearance = 0 'Flat
BackColor = &H80000005&
ForeColor = &H80000008&
Height = 255
Left = 60
TabIndex = 21
Top = 0
Width = 255
End
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command9
Caption = "退格"
Height = 375
Left = 1920
TabIndex = 18
Top = 480
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command8
Caption = "清零"
Height = 375
Left = 2520
TabIndex = 17
Top = 480
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdDot
Caption = "."
Height = 375
Left = 120
TabIndex = 16
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command7
Caption = "Sqrt"
Height = 375
Left = 2520
TabIndex = 15
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command6
Caption = "="
Height = 375
Left = 1320
TabIndex = 14
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command5
Caption = "/"
Height = 375
Left = 2520
TabIndex = 13
Top = 1440
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command4
Caption = "*"
Height = 375
Left = 1920
TabIndex = 12
Top = 1440
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command3
Caption = "-"
Height = 375
Left = 2520
TabIndex = 11
Top = 960
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command2
Caption = "+"
Height = 375
Left = 1920
TabIndex = 10
Top = 960
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "9"
Height = 375
Index = 9
Left = 1320
TabIndex = 9
Top = 480
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "8"
Height = 375
Index = 8
Left = 720
TabIndex = 8
Top = 480
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "7"
Height = 375
Index = 7
Left = 120
TabIndex = 7
Top = 480
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "6"
Height = 375
Index = 6
Left = 1320
TabIndex = 6
Top = 960
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "5"
Height = 375
Index = 5
Left = 720
TabIndex = 5
Top = 960
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "4"
Height = 375
Index = 4
Left = 120
TabIndex = 4
Top = 960
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "3"
Height = 375
Index = 3
Left = 1320
TabIndex = 3
Top = 1440
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "2"
Height = 375
Index = 2
Left = 720
TabIndex = 2
Top = 1440
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "1"
Height = 375
Index = 1
Left = 120
TabIndex = 1
Top = 1440
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton Command1
Caption = "0"
Height = 375
Index = 0
Left = 720
TabIndex = 0
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
End
Attribute VB_Name = "frmmain"
Attribute VB_GlobalNameSpace = False
Attribute VB_Creatable = False
Attribute VB_PredeclaredId = True
Attribute VB_Exposed = False
Private Data As Double
Private lOperation As Long
Private fClear As Boolean
Private Sub cmdDot_Click()
If InStr(1, Text1.Text, ".") <= 0 Then Text1.Text = Text1.Text & "."
End Sub
Private Sub Command1_Click(Index As Integer)
If fClear = True Then Text1.Text = "": fClear = False
Text1.Text = Text1.Text & Index
End Sub
Private Sub Command10_Click()
If fClear = False Then
Select Case lOperation
Case 0
Case 1: Text1.Text = Data + Val(Text1.Text)
Case 2: Text1.Text = Data - Val(Text1.Text)
Case 3: Text1.Text = Data * Val(Text1.Text)
Case 4: If Val(Text1.Text) = 0 Then MsgBox "除数不等于0": Exit Sub Else Text1.Text = Data / Val(Text1.Text)
Case 5: Text1.Text = Data ^ Val(Text1.Text)
End Select
End If
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 5
lblOperation.Caption = "^"
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
If fClear = False Then
Select Case lOperation
Case 0
Case 1: Text1.Text = Data + Val(Text1.Text)
Case 2: Text1.Text = Data - Val(Text1.Text)
Case 3: Text1.Text = Data * Val(Text1.Text)
Case 4: If Val(Text1.Text) = 0 Then MsgBox "除数不等于0": Exit Sub Else Text1.Text = Data / Val(Text1.Text)
Case 5: Text1.Text = Data ^ Val(Text1.Text)
End Select
End If
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 1
lblOperation.Caption = "+"
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click()
If fClear = False Then
Select Case lOperation
Case 0
Case 1: Text1.Text = Data + Val(Text1.Text)
Case 2: Text1.Text = Data - Val(Text1.Text)
Case 3: Text1.Text = Data * Val(Text1.Text)
Case 4: If Val(Text1.Text) = 0 Then MsgBox "除数不等于0": Exit Sub Else Text1.Text = Data / Val(Text1.Text)
Case 5: Text1.Text = Data ^ Val(Text1.Text)
End Select
End If
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 2
lblOperation.Caption = "-"
End Sub
Private Sub Command4_Click()
If fClear = False Then
Select Case lOperation
Case 0
Case 1: Text1.Text = Data + Val(Text1.Text)
Case 2: Text1.Text = Data - Val(Text1.Text)
Case 3: Text1.Text = Data * Val(Text1.Text)
Case 4: If Val(Text1.Text) = 0 Then MsgBox "除数不等于0": Exit Sub Else Text1.Text = Data / Val(Text1.Text)
Case 5: Text1.Text = Data ^ Val(Text1.Text)
End Select
End If
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 3
lblOperation.Caption = "*"
End Sub
Private Sub Command5_Click()
If fClear = False Then
Select Case lOperation
Case 0
Case 1: Text1.Text = Data + Val(Text1.Text)
Case 2: Text1.Text = Data - Val(Text1.Text)
Case 3: Text1.Text = Data * Val(Text1.Text)
Case 4: If Val(Text1.Text) = 0 Then MsgBox "除数不等于0": Exit Sub Else Text1.Text = Data / Val(Text1.Text)
Case 5: Text1.Text = Data ^ Val(Text1.Text)
End Select
End If
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 4
lblOperation.Caption = "/"
End Sub
Private Sub Command6_Click()
If fClear = False Then
Select Case lOperation
Case 0
Case 1: Text1.Text = Data + Val(Text1.Text)
Case 2: Text1.Text = Data - Val(Text1.Text)
Case 3: Text1.Text = Data * Val(Text1.Text)
Case 4: If Val(Text1.Text) = 0 Then MsgBox "除数不等于0": Exit Sub Else Text1.Text = Data / Val(Text1.Text)
Case 5: Text1.Text = Data ^ Val(Text1.Text)
End Select
End If
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 0
lblOperation.Caption = ""
End Sub
Private Sub Command7_Click()
If Val(Text1.Text) <= 0 Then MsgBox "开方数大于等于0"
Text1.Text = Sqr(Val(Text1.Text))
Data = Val(Text1.Text)
fClear = True
lOperation = 0
lblOperation.Caption = ""
End Sub
Private Sub Command8_Click()
Text1.Text = ""
lOperation = 0
lblOperation.Caption = ""
End Sub
Private Sub Command9_Click()
If Len(Text1.Text) > 0 Then Text1.Text = Left(Text1.Text, Len(Text1.Text) - 1)
End Sub
Private Sub Form_KeyPress(KeyAscii As Integer)
Select Case KeyAscii
Case Asc("0"): Command1_Click 0
Case Asc("1"): Command1_Click 1
Case Asc("2"): Command1_Click 2
Case Asc("3"): Command1_Click 3
Case Asc("4"): Command1_Click 5
Case Asc("5"): Command1_Click 4
Case Asc("6"): Command1_Click 6
Case Asc("7"): Command1_Click 7
Case Asc("8"): Command1_Click 8
Case Asc("9"): Command1_Click 9
Case Asc("."): cmdDot_Click
Case Asc("+"): Command2_Click
Case Asc("-"): Command3_Click
Case Asc("*"): Command4_Click
Case Asc("/"): Command5_Click
Case Asc("^"): Command10_Click
Case Asc("s"): Command7_Click
Case Asc("S"): Command7_Click
Case vbKeyBack: Command9_Click
Case Asc("`"): Command8_Click
Case Asc("="): Command6_Click
Case 13: Command6_Click
End Select
KeyAscii = 0
End Sub
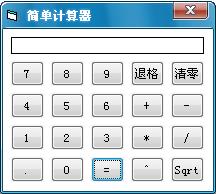
Text1 BackColor=&H00C0FFFF& Text=“0.”
Command1 Index 0――16
Index 0――9 Caption=“0”-“9” Index 10 Caption=“.”
Index 11 Caption=“=”
Index 12 Caption=“+”
Index 13 Caption=“-”
Index 14 Caption=“×”
Index 15 Caption=“÷”
Index 16 Caption=“清除”
如果想改变一些其他的属性,比如字体,可以自己定义一下Font属性,如果相对多个控件的共同属性进行改变,可以在窗体上按下鼠标,拖动,把多个控件一起选定,然后对它们的共同属性进行修改。
别看这个东西小,还费了近我两个小时呢,不觉大叹手生,里面也有些地方很绕弯子,我尽量解释清楚。
在编写程序之前,我们先来回顾一下计算器的使用。
按下数字键在液晶屏上会出现数字,这是最基本的功能。
第一次按下运算键,再按下数字键,将重新输入第二个数字,再次按下运算键,将算出前两个数的结果,然后按下数字键,将又重新输入新的数字。
输入数字后,按下“等于键”将仍输出原来的数字,输入运算符和第二个数字后在按下“等于”,将得到二者的结果。然后又重复第二、三步。
按下“清除”,数据被全部清除。
了解了这些,我们一步一步实现。 先实现数据的输入,请看代码。 与未创立组的控件相比,它的事件里多了Index参数,组里所有的对象都使用同一个事件。 先在General里声明窗体级全局变量:
Dim Num1, Num2 As Single
Dim StrNum1, StrNum2 As String
Dim FirstNum As Boolean '判断是否是数字开头
因为Text1里是存放字符串的,所以要把输入的数据进行运算,必须把字符型变量转变为实型变量,分别用Num1、Num2和StrNum1、StrNum2进行存放。 在Form_Load事件里给变量初赋值:
Num1 = 0
Num2 = 0
StrNum1 = ""
StrNum2 = ""
FirstNum = True
因为17个按钮使用的是同一事件,所以我们用一个Select Case语句区分各个按钮,双击任意按钮输入代码:
Private Sub Command1_Click(Index As Integer)
Select Case Index
Case 0 To 9
If FirstNum Then
StrNum1 = Str(Index)’实型转字符型
FirstNum = False’初赋值为假
Else’非初赋值
StrNum1 = StrNum1 + Str(Index)
End If
Text1.Text = StrNum1’显示
<还有其他语句,等待插入>
End Select
End Sub
运行程序的话已经可以输入数据,下面我们来处理小数点。 在General里声明新的变量:
Dim PointFlag As Boolean '判断是否已有小数点
我们知道小数点只能输入一次,一个数据中不能有多个小数点存在,所以需要一个布尔变量做判断。
在Form_Load里进行初赋值:
PointFlag = False
在Command的单击事件里接着上面输入新的代码:
Case 10
If Not PointFlag Then’如果没有小数点
If FirstNum Then’如果是第一个字符
StrNum1 = "0."
FirstNum = False
Else
StrNum1 = StrNum1 + "."
End If
Else’已有小数点
Exit Sub’则退出单击事件
End If
PointFlag = True
Text1.Text = StrNum1
下面会复杂一些,我们先跳过等号,而来处理四则运算:
先在General里声明新变量:
Dim Runsign As Integer '储存运算符号
Dim SignFlag As Boolean '判断是否已有运算符号
然后在Form_Load中进行初赋值:
Runsign = 0
SignFlag = False
在接下的Command1_Click中继续输入代码:
Case 12 To 15
FirstNum = True’使下一次可以输入新数据
PointFlag = False
'还原标记值
If SignFlag Then’前面已有运算符未运算
Call Run
Else
SignFlag = True
StrNum2 = StrNum1’把字符串1复制给字符串2
StrNum1 = ""’字符串1清空
End If
Runsign = Index - 11 ‘储存键入的运算符
里面运算的部分我用了一个过程,是因为在按下等号时还会调用到运算过程,这样可以减少代码的输入,也使程序便于浏览。建立过程(Procedure),可以在General部分直接输入,也可以通过菜单里的“Add Procedure”添加。Run的代码如下:
Sub Run()
Num1 = Val(StrNum2)
Num2 = Val(StrNum1)
Select Case Runsign
Case 1’加
equal = Num1 + Num2
Case 2’减
equal = Num1 - Num2
Case 3’乘
equal = Num1 * Num2
Case 4’除
equal = Num1 / Num2
End Select
StrNum2 = Str(equal)
StrNum1 = StrNum2
Text1.Text = StrNum2
End Sub
下面是其余的代码:(在Command1_Click事件里,接着写)
Case 11
If Not SignFlag Then
Text1.Text = StrNum1
equal = Val(StrNum1)
FirstNum = True
PointFlag = False
Else
Call Run
SignFlag = False
End If
Case Else’清除按钮
Call ClearData
里面又用到了一个ClearData过程,实际上就是Form_Load里的变量初赋值,代码如下:
Sub ClearData()
Num1 = 0
Num2 = 0
StrNum1 = ""
StrNum2 = ""
FirstNum = True
PointFlag = False
Runsign = 0
SignFlag = False
Text1.Text = "0."
End Sub
这样完整的程序就完成了,本章介绍了VB的第一个控件――按钮,并且举例,希望你继续看下一章――菜单。
下面给出完整的程序代码:
Dim Num1, Num2 As Single
Dim StrNum1, StrNum2 As String
Dim FirstNum As Boolean '判断是否是数字开头
Dim PointFlag As Boolean '判断是否已有小数点
Dim Runsign As Integer '储存运算符号
Dim SignFlag As Boolean '判断是否已有运算符号
Sub ClearData()
Num1 = 0
Num2 = 0
StrNum1 = ""
StrNum2 = ""
FirstNum = True
PointFlag = False
Runsign = 0
SignFlag = False
Text1.Text = "0."
End Sub
Sub Run()
Num1 = Val(StrNum2)
Num2 = Val(StrNum1)
Select Case Runsign
Case 1
equal = Num1 + Num2
Case 2
equal = Num1 - Num2
Case 3
equal = Num1 * Num2
Case 4
equal = Num1 / Num2
End Select
StrNum2 = Str(equal)
StrNum1 = StrNum2
Text1.Text = StrNum2
End Sub
Private Sub about_Click()
MsgBox "Create by 周晓阳。1998/7/27", vbDefaultButton1, "VB教程第四章范例"
End Sub
Private Sub Command1_Click(Index As Integer)
Select Case Index
Case 0 To 9
If FirstNum Then
StrNum1 = Str(Index)
FirstNum = False
Else
StrNum1 = StrNum1 + Str(Index)
End If
Text1.Text = StrNum1
Case 10
If Not PointFlag Then
If FirstNum Then
StrNum1 = "0."
FirstNum = False
Else
StrNum1 = StrNum1 + "."
End If
Else
Exit Sub
End If
PointFlag = True
Text1.Text = StrNum1
Case 12 To 15
FirstNum = True
PointFlag = False
'还原标记值
If SignFlag Then
Call Run
Else
SignFlag = True
StrNum2 = StrNum1
StrNum1 = ""
End If
Runsign = Index - 11
Case 11
If Not SignFlag Then
Text1.Text = StrNum1
equal = Val(StrNum1)
FirstNum = True
PointFlag = False
Else
Call Run
SignFlag = False
End If
Case Else
Call ClearData
End Select
End Sub
Private Sub Form_Load()
Call ClearData
End Sub
按钮还有两个重要的属性Default(默认属性)和Cancel(取消属性),两个属性都以布尔赋值,把Default设为True,则在按下回车键时,不论焦点处于何处,都会触发该按钮的Click事件,而当Cancel属性被设为True,在按下ESC键时,该按钮的Click属性发生。下面举个例子:
建立一个新窗体和两个按钮,Name属性分别为cmdOK和cmdCancel,把前者的Default设为True,后者的Cancel设为True,Caption属性分别为OK和Cancel。
Private Sub cmdCancel_Click()
MsgBox "Cancel按钮被按下", vbDefaultButton1, "提示"
End Sub
Private Sub cmdOK_Click()
MsgBox "OK按钮被按下", vbDefaultButton1, "提示"
End Sub
快捷键大家一定都知道,在VB如何实现呢。其实很简单,在刚才的例子里在建立一个按钮Command1,把它的Caption属性设为Click &ME,如图4-11,在M的下面有一条下划线,运行程序,当你按下Alt+M的时候就触发了Command1_Click事件:
Private Sub Command1_Click()
MsgBox "Click ME 按钮被按下", vbDefaultButton1, "提示"
End Sub
你要是看不懂进这个网站,下半部分就是讲造计算器的:http://www.bianceng.cn/VBjc/vbrm/rm5.htm 参考技术B '这个很简单的了,你用记事本把这段代码复制过去,然后另存为.frm就可以了
'然后用vb打开。看看效果。
'以下保存为 任务名称.frm
VERSION 5.00
Begin VB.Form Form1
Caption = "计算机"
ClientHeight = 4230
ClientLeft = 60
ClientTop = 750
ClientWidth = 3165
LinkTopic = "Form1"
MaxButton = 0 'False
MinButton = 0 'False
ScaleHeight = 4230
ScaleWidth = 3165
StartUpPosition = 2 '屏幕中心
Begin VB.Frame Frame1
Height = 3495
Left = 120
TabIndex = 1
Top = 600
Width = 2895
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdResult
Caption = "="
BeginProperty Font
Name = "宋体"
Size = 12
Charset = 134
Weight = 400
Underline = 0 'False
Italic = 0 'False
Strikethrough = 0 'False
EndProperty
Height = 375
Left = 1080
TabIndex = 20
Top = 3000
Width = 1695
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdOff
Caption = "OFF"
Height = 375
Left = 1560
TabIndex = 19
Top = 240
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdCE
Caption = "CE"
Height = 375
Left = 2280
TabIndex = 18
Top = 240
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdchu
Caption = "/"
Height = 375
Left = 2280
TabIndex = 17
Top = 2520
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdjia
Caption = "+"
Height = 375
Left = 2280
TabIndex = 16
Top = 720
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd0
Caption = "0"
Height = 375
Left = 840
TabIndex = 15
Top = 2520
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd6
Caption = "6"
Height = 375
Left = 1560
TabIndex = 14
Top = 1320
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd8
Caption = "8"
Height = 375
Left = 840
TabIndex = 13
Top = 720
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd4
Caption = "4"
Height = 375
Left = 120
TabIndex = 12
Top = 1320
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd9
Caption = "9"
Height = 375
Left = 1560
TabIndex = 11
Top = 720
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd2
Caption = "2"
Height = 375
Left = 840
TabIndex = 10
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdjian
Caption = "-"
Height = 375
Left = 2280
TabIndex = 9
Top = 1320
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdPoint
Caption = "."
BeginProperty Font
Name = "宋体"
Size = 12
Charset = 134
Weight = 400
Underline = 0 'False
Italic = 0 'False
Strikethrough = 0 'False
EndProperty
Height = 375
Left = 1560
TabIndex = 8
Top = 2520
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdcheng
Caption = "*"
Height = 375
Left = 2280
TabIndex = 7
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd5
Caption = "5"
Height = 375
Left = 840
TabIndex = 6
Top = 1320
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd3
Caption = "3"
Height = 375
Left = 1560
TabIndex = 5
Top = 1905
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd1
Caption = "1"
Height = 375
Left = 120
TabIndex = 4
Top = 1920
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmd7
Caption = "7"
Height = 375
Left = 120
TabIndex = 3
Top = 720
Width = 495
End
Begin VB.CommandButton cmdChange
Caption = "+/-"
Height = 375
Left = 120
TabIndex = 2
Top = 2520
Width = 495
End
End
Begin VB.TextBox txt
Alignment = 1 'Right Justify
Enabled = 0 'False
BeginProperty Font
Name = "宋体"
Size = 10.5
Charset = 134
Weight = 400
Underline = 0 'False
Italic = 0 'False
Strikethrough = 0 'False
EndProperty
Height = 375
Left = 120
Locked = -1 'True
TabIndex = 0
Top = 120
Width = 2895
End
Begin VB.Menu meuFile
Caption = "文件(&F)"
Begin VB.Menu meuExit
Caption = "退出(&X)"
Shortcut = ^X
End
End
End
Attribute VB_Name = "Form1"
Attribute VB_GlobalNameSpace = False
Attribute VB_Creatable = False
Attribute VB_PredeclaredId = True
Attribute VB_Exposed = False
Dim XiaoShu As Boolean
'在窗体变量中声明一个布尔值来判断是否按下了小数点键,防止txt中出现多个小数。如果已经输入了小数点则Xiaoshu为True,否则为False
Dim FuHao As Byte
'声明一个Byte来记录我们按下了什么符号,1为"+",2为"-",3为"*",4为"/"
Dim FirstNumber As Double
'声明一个变量来记录操作数的第一个数,如A+B,那么FirstNumber来记下A的值。
Dim DengHao As Boolean
'声明一个变量来记录是否按下了=号,如果按下了则为True
Private Sub cmd0_Click()
If txt.Text <> "" Then txt.Text = txt.Text + "0" '防止多个0在文本中出现
End Sub
Private Sub cmd1_Click() '按下1时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "1"
Else
txt.Text = "1" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd2_Click() '按下2时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "2"
Else
txt.Text = "2" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd3_click() '按下3时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "3"
Else
txt.Text = "3" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd4_Click() '按下4时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "4"
Else
txt.Text = "4" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd5_Click() '按下5时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "5"
Else
txt.Text = "5" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd6_Click() '按下6时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "6"
Else
txt.Text = "6" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd7_Click() '按下7时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "7"
Else
txt.Text = "7" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd8_Click() '按下8时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "8"
Else
txt.Text = "8" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmd9_Click() '按下9时
If Not DengHao Then '没按下等号
txt.Text = txt.Text + "9"
Else
txt.Text = "9" '按下了等号
DengHao = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmdCE_Click()
txt.Text = ""
XiaoShu = False
End Sub
Private Sub cmdChange_Click()
If (Sgn(Val(txt.Text))) = 1 Then txt.Text = "-" + txt.Text: Exit Sub '用Sgn来判断txt文本框内的值的符号。大于0的话就在前面加上"-"
If (Sgn(Val(txt.Text))) = -1 Then txt.Text = Abs(Val(txt.Text)) 'txt文本框的文本为大于0的数txt前面的"-"去掉。
End Sub
Private Sub cmdcheng_Click()
FirstNumber = Val(txt.Text)
FuHao = 3
txt.Text = ""
XiaoShu = False
End Sub
Private Sub cmdchu_Click()
FirstNumber = Val(txt.Text)
FuHao = 4
txt.Text = ""
XiaoShu = False
End Sub
Private Sub cmdjia_Click()
FirstNumber = Val(txt.Text)
FuHao = 1
txt.Text = ""
XiaoShu = False
End Sub
Private Sub cmdjian_Click()
FirstNumber = Val(txt.Text)
FuHao = 2
txt.Text = ""
XiaoShu = False
End Sub
Private Sub cmdOff_Click()
End
End Sub
Private Sub cmdPoint_Click()
If txt.Text = "" Then txt.Text = "0"
If Not XiaoShu Then '当我们以前没有按下小数点键时在txt中加上小数点
txt.Text = txt.Text + "."
XiaoShu = True
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cmdResult_Click()
If FuHao = 1 Then '按下了+号
txt.Text = FirstNumber + Val(txt.Text)
End If
If FuHao = 2 Then '按下了-号
txt.Text = FirstNumber - Val(txt.Text)
End If
If FuHao = 3 Then '按下了*号
txt.Text = FirstNumber * Val(txt.Text)
End If
If FuHao = 4 Then '按下了、号
txt.Text = FirstNumber / Val(txt.Text)
End If
DengHao = True '记录下按了=号
XiaoShu = False
End Sub
Private Sub meuExit_Click()
End
End Sub 参考技术C Dim num1 As Single
Dim num2 As Single
Dim flag As Boolean
Dim op As String
Dim result As Single
Dim expr As String
Private Sub Command1_Click(Index As Integer)
Label1.Caption = Label1.Caption & Command1(Index).Caption
If flag <> True Then
num1 = Val(Label1.Caption)
Else
num2 = Val(Label1.Caption)
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
Select Case op
Case "+"
result = num1 + num2
Case "-"
result = num1 - num2
Case "*"
result = num1 * num2
Case "/"
result = num1 / num2
End Select
Label1.Caption = result
num1 = result
num2 = 0
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click(Index As Integer)
expr = Label1.Caption
If Label1.Caption <> "" Then
op = Command3(Index).Caption
Label1.Caption = ""
flag = True
Else
MsgBox ("请输入数字")
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Command4_Click()
num1 = 0
num2 = 0
op = ""
result = 0
Label1.Caption = ""
flag = False
expr = ""
End Sub 参考技术D 开平方还可以,若是你要求的是开N次方就比较难哦
如何用记事本编程
?
那里有下简单的编程程序,和代码资源
用VB做一个记事本实在不很复杂,我们完全可以通过向导来很方便地做出来。但本文只打算讨论用手动方法制作记事本,旨在向VB初学者展示:学VB原来是如此容易!
通过阅读、研究本文并按本文所述进行尝试,初学者将学到很多东西,如怎样使用RichText控件来打开和保存文件,怎样制作菜单、工具栏和状态栏以及如何对其编写代码等。
第一章 让我们的记事本马上运行
急于求成是初学者共有的心愿。那好,请按如下三个步骤做,我们的愿望立即就可以实现!
步骤一:绘制界面。
新建一个标准EXE工程,将其Caption属性改为“超级记事本”,点击Icon属性给它找个合适的Icon图标。单击菜单“工程”-“部件”,在弹出的“部件”对话框里找到Microsoft
RichText Box 6.0和公共对话框Microsoft Common Dialog 6.0并选中它们,单击“确定”按钮。这时左边的工具栏上出现了我们刚才新添的两个控件了。在窗体上绘制RichText
Box和Commn Dialog,其中RichText Box的大小和位置可不用理睬,我们将在代码中处理它,当然,有必要把它的ScrollBar属性设为2-rtfVertical,这样在打开和编辑文件时垂直滚动条才可用。
步骤二:编辑菜单。
按Ctrl+E调出菜单编辑器,我们来做如下几个菜单:
一.文件菜单:
文件(第一层) mnuFile
新建(第二层) mnuNew
打开(第二层) mnuOpen
保存(第二层) mnuSave
- (第二层) mnuFileSep (分隔线)
退出(第二层) mnuExit
二.编辑菜单:
编辑(第一层) mnuEdit
复制(第二层) mnuCopy
剪切(第二层) mnuCut
粘贴(第二层) mnuPaste
- (第二层) mnuEditSep (分隔线)
全选(第二层) mnuSelecAll
三.搜索菜单:
搜索(第一层) mnuSearch
查找(第二层) mnuFind
查找下一个(第二层) mnuFindOn
四.帮助菜单:
帮助(第一层) mnuHelp
使用说明(第二层) mnuUsage
关于(第二层) mnuAbout
(注:各菜单项的快捷键请自行设置)
好了,其它的菜单项以后再根据需要添加。现在进入:
步骤三:编写代码。
'声明查找变量
Dim sFind As String
'声明文件类型
Dim FileType, FiType As String
'初始化程序
Private Sub Form_Load()
'设置程序启动时的大小
Me.Height = 6000
Me.Width = 9000
End Sub
'设置编辑框的位置和大小
Private Sub Form_Resize()
On Error Resume Next '出错处理
RichTextBox1.Top=20
RichTextBox1.Left=20
RichTextBox1.Height = ScaleHeight-40
RichTextBox1.Width = ScaleWidth-40
End Sub
'新建文件
Private Sub mnuNew_Click()
RichTextBox1.Text = "" '清空文本框
FileName = "未命名"
Me.Caption = FileName
End Sub
'打开文件
Private Sub mnuOpen_Click()
CommonDialog1.Filter = "文本文档(*.txt)|*.txt|RTF文档(*.rtf)|*.rtf|所有文件(*.*)|*.*"
CommonDialog1.ShowOpen
RichTextBox1.Text = "" '清空文本框
FileName = CommonDialog1.FileName
RichTextBox1.LoadFile FileName
Me.Caption = "超级记事本:" & FileName
End Sub
'保存文件
Private Sub mnuSave_Click()
CommonDialog1.Filter = "文本文档(*.txt)|*.txt|RTF文档(*.rtf)|*.rtf|所有文件(*.*)|*.*"
CommonDialog1.ShowSave
FileType = CommonDialog1.FileTitle
FiType = LCase(Right(FileType, 3))
FileName = CommonDialog1.FileName
Select Case FiType
Case "txt"
RichTextBox1.SaveFile FileName, rtfText
Case "rtf"
RichTextBox1.SaveFile FileName, rtfRTF
Case "*.*"
RichTextBox1.SaveFile FileName
End Select
Me.Caption = "超级记事本:" & FileName
End Sub
'退出
Private Sub mnuExit_Click()
End
End Sub
'复制
Private Sub mnuCopy_Click()
Clipboard.Clear
Clipboard.SetText RichTextBox1.SelText
End Sub
'剪切
Private Sub mnuCut_Click()
Clipboard.Clear
Clipboard.SetText RichTextBox1.SelText
RichTextBox1.SelText = ""
End Sub
'全选
Private Sub mnuSelectAll_Click()
RichTextBox1.SelStart = 0
RichTextBox1.SelLength = Len(RichTextBox1.Text)
End Sub
'粘贴
Private Sub mnuPaste_Click()
RichTextBox1.SelText = Clipboard.GetText
End Sub
'查找
Private Sub mnuFind_Click()
sFind = InputBox("请输入要查找的字、词:", "查找内容",
sFind)
RichTextBox1.Find sFind
End Sub
'继续查找
Private Sub mnuFindOn_Click()
RichTextBox1.SelStart = RichTextBox1.SelStart + RichTextBox1.SelLength + 1
RichTextBox1.Find sFind, , Len(RichTextBox1)
End Sub
'使用说明
Private Sub mnuReadme_Click()
On Error GoTo handler
RichTextBox1.LoadFile "Readme.txt", rtfText '请写好Readme.txt文件并存入程序所在文件夹中
Me.Caption = "超级记事本:" & "使用说明"
Exit Sub
handler:
MsgBox "使用说明文档可能已经被移除,请与作者联系。",
vbOKOnly, " 错误信息"
End Sub
'关于
Private Sub mnuAbout_Click()
MsgBox "超级记事本 Ver1.0 版权所有(C) 2001 土人",vbOKOnly,"关于"
End Sub
'设置弹出式菜单(即在编辑框中单击鼠标右键时弹出的动态菜单)
Private Sub RichTextBox1_MouseDown(Button As Integer, Shift As Integer, X As
Single, Y As Single)
If Button = 2 Then
PopupMenu mnuEdit, vbPopupMenuLeftAlign
Else
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
'防止在切换输入法时字体自变(感谢王必成先生提供此方案)
Private Sub RichTextBox1_KeyUp(KeyCode As Integer, Shift As Integer)
If KeyCode = vbKeySpace Then
RichTextBox1.SelFontName = CommonDialog1.FontName
End If
End Sub
至此,我们的记事本可以编译使用了。点击菜单“文件”-“生成XXX.EXE”,回到桌面运行我们的记事本看看,是不是颇有成就感?
当然,这样的记事本还比较粗糙,我们还需要做些工作,请看下一章。
第二章 美化程序界面
多数字处理软件都有工具栏和状态栏。工具栏和状态栏除了能美化我们的程序使其更具有专业性质外,还给用户带来操作上的便利。现在我们就来做一做这两样东西。
一.工具栏
(一)制作工具栏
单击“工程”-“部件”,选中Microsoft Windows Common Control 6.0并确定。这时,我们要用到的控件就出现在左边的工具栏上了。
要做工具栏,首先需要一个叫ImageList的控件来装载图像。在程序界面上添加它,然后右键单击此控件,左键单击“属性”,弹出“属性页”对话框的“图像”,再单击“插入图片”就可以一次性装载图片了(如不满意,以后还可以添加)。图片可在C:Microsoft
Visual StudioCommonGraphicsBitmapsTlBr_W95下选择(这里假设你的VB安装在C盘下)。注意了:在插入图片时给每一张图片注明关键字,以便在引用图片时不至于混乱。如插入“新建”的图片,我们在“关键字”栏注明“New”。
图片有了,接下来在程序界面添加工具栏(ToolBar)。添加后工具栏就出现在菜单下面,右键单击它,选择“属性”,在弹出的“属性页”对话框中的“通用”项作些设置,主要如下两项:
1.“图像列表”:选择ImageList1
2.“样式”:根据喜爱选择1-trbStandard或者2-trbFlat
继续点击“属性页”的“按钮”选项,插入若干按钮。按钮有多种样式,请根据需要设置。这里请一定注意:每一个与用户操作有关的按钮都必须注明关键字、装载图片,如“新建”按钮,在“关键字”项注明“新建”,在“图像”项键入“New”(即ImageList1中的图片关键字),需要的话还可以在“工具提示文本”项填入适当的提示语。
(二)编写工具栏的按钮代码
工具栏按钮的代码编辑很简单,可以按照下面的格式去编写:
Private Sub ToolBar1_ButtonClick(ByVal Button As MSComctlLib.Button)
On Error Resume Next '出错处理
Select Case Button.Key '按关键字选择
Case "新建"
mnuNew_Click '等于菜单项“新建”被单击
Case "打开" '等于菜单项“打开”被单击
mnuOpen_Click
'......(继续编写其它按钮的代码)
End Select
End Sub
完成后试运行一下我们的程序,我们发现,有了工具栏之后,程序变得漂亮多了,只是有一个问题:打开一个较长的文档后,编辑框的下拉滚动条向上的箭头不见了。原因是:工具条占用一定的空间。解决方法:将“设置编辑框的位置和大小”中的RichTextBox1.Top
= 20 和 RichTextBox1.Height = Me.ScaleHeight - 40分别改为RichTextBox1.Top =
380,RichTextBox1.Height = Me.ScaleHeight - 400即可。
二.状态栏
(一)制作状态栏
状态栏的英文名字叫StatusBar,在窗体上添加它后会默认出现在窗体的最下方。用鼠标右键点击它,调出“属性页”对话框,单击“窗格”项,插入一些窗格,可以将各个窗格的“样式”设置为:
0-sbrText 显示文本,需编写代码
1-sbrCaps 显示大小写状态,无需编程
2-sbrNum 显示NumLock键开关状态,无需编程
3-sbrIns 显示Insert键状态,无需编程
4-sbrScr1
5-sbrTime 显示时间,不编程时时间不会随系统时钟变化
6-sbrDate 显示日期,无需编程
注意:加进状态栏后需将Form_Resze中的RichTextBox1.Height =
Me.ScaleHeight - 400改为RichTextBox1.Height = Me.ScaleHeight - 600。
(二)状态栏根据其“样式”属性决定用不用编写代码(如上文所述)。下面举些例子,读者可以认真揣摩,从而达到举一反三的效果。
例一:用户选取了“新建”后,让第一个窗格显示:“目前状态:正在打开文件《……》”。请将下面代码写进“打开”菜单里面:
StatusBar1.Panels(1).Text = "目前状态:正在打开文件"
& "《" &CommonDialog1.FileTitle & "》"
例二:让第三个窗格显示时间并让时间跟随系统时钟变化。
首先,给程序加一个Timer控件,将其Interval属性设为1000。然后:
在Form_Load过程加入:StatusBar1.Panels(1).Text = Time;然后给Timer控件编写代码:
Private Sub Timer1_Timer()
If StatusBar1.Panels(3).Text <> CStr(Time) Then
StatusBar1.Panels(3).Text = Time
End If
End Sub
例三:当编辑框的文本发生变化时让第一个窗格显示:“正在编辑文档:文件名”。
Private Sub RichTextBox1_Chang()
StatusBar1.Panels(1).Text = "正在编辑文档:" &
CommonDialog1.FileName
End Sub
辛苦了那么久,我们现在已经拥有一个象模象样的记事本了。这个记事本由于用了RichText控件,理论上它能打开和编辑任意大的文档,使用起来的确比Windows自带的记事本方便得多。当然,还有一些其它的功能需要添加和完善,这就靠你慢慢去完成了。 参考技术A 别去考虑用“记事本编程”,个人理解,所谓的“记事本编程”,无非是指两方面的意思:
其一,指所写的程序非常简单、也很短。比如一些脚本代码、批处理代码等,没有很复杂的流程等,用记事本可以快速写就的一些程序或代码。
其二,说自己用“记事本编程”,显示一下自己对某门语言的精通,根本不需要助记环境就能写出来。
至于如何用记事本编程,很简单了,打开记事本,在里面写上几句程序(当然是指脚本程序,比如ASP等),保存并执行。
如:在记事本里写上这么一行:
----------
现在是:<%=now%>
----------
保存为test.asp,然后放到IIS目录下,从浏览器访问,就能得到现在的时间。
这就是所谓的记事本编程,没什么神秘。
事实上,没必要强调用记事本编程,每种语言都有各自最适合的开发编程环境,如VC/C++,VB等最合适的工具是VS6,.net最合适的工具是vs2005等。
对ASP、PHP等,因为语法不复杂,倒是经常用一些文本编辑器来写代码,比如EDITPLUS、ULTRAEDIT等,这些工具虽然没有助记功能,但编辑功能非常强大,而且运行快速方便,倒近似于记事本编程的说法,只不过也绝非简单的记事本。
呵呵~~~
胡谄这几句:) 参考技术B 用记事本只能编辑程序
构建(builde)或者编译(compile)的时候就必须要有编译器了。根据你编程语言不同,需要有不同的编译器
C++的编译器有很多种,windows环境下Borland C++ Builder和Microsoft Visual C++都有免费下载版本。
用记事本编辑后,把文件按编译器要求的后缀名保存到某个目录下,然后使用编译器对该文件进行编译,就可以了
具体步骤和命令,根据你使用的程序语言有所不同 参考技术C 关键问题是不要用中文码来代替英文码,例如双引号,分号等.编程语言,特别是起语法作用的词,应是英文,输出语句可能用中文.
存放,通常是ANSI txt. 混有中文时,如果是网页,存为unicode. 如果是c程序,混有中文时,存ANSI, 中文会丢失,只好试试unicode.
编c,最好用VC++带的Visual Studio. 用 word pad 也比notepad好. 参考技术D 在记事本里写下相应的代码(视具体语言而定)。然后将后缀名改成相关的后缀名,用命令编译即可。(因不同语言不一样,建议楼主说出要写什么语言的程序)
以上是关于如何用VB做一个简单计算器 要求实现加减乘除乘方开方功能的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章