计算机视觉领域必读的9篇论文
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了计算机视觉领域必读的9篇论文相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 推荐下计算机视觉这个领域,依据学术范标准评价体系得出的近年来最重要的9篇论文吧:(对于英语阅读有困难的同学,访问后可以使用翻译功能)
一、Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
摘要:Deeper neural networks are more difficult to train. We present a residual learning framework to ease the training of networks that are substantially deeper than those used previously. We explicitly reformulate the layers as learning residual functions with reference to the layer inputs, instead of learning unreferenced functions. We provide comprehensive empirical evidence showing that these residual networks are easier to optimize, and can gain accuracy from considerably increased depth. On the ImageNet dataset we evaluate residual nets with a depth of up to 152 layers—8× deeper than VGG nets [40] but still having lower complexity. An ensemble of these residual nets achieves 3.57% error on the ImageNet test set. This result won the 1st place on the ILSVRC 2015 classification task. We also present analysis on CIFAR-10 with 100 and 1000 layers. The depth of representations is of central importance for many visual recognition tasks. Solely due to our extremely deep representations, we obtain a 28% relative improvement on the COCO object detection dataset. Deep residual nets are foundations of our submissions to ILSVRC & COCO 2015 competitions1, where we also won the 1st places on the tasks of ImageNet detection, ImageNet localization, COCO detection, and COCO segmentation.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
二、Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition
摘要:In this work we investigate the effect of the convolutional network depth on its accuracy in the large-scale image recognition setting. Our main contribution is a thorough evaluation of networks of increasing depth using an architecture with very small (3x3) convolution filters, which shows that a significant improvement on the prior-art configurations can be achieved by pushing the depth to 16-19 weight layers. These findings were the basis of our ImageNet Challenge 2014 submission, where our team secured the first and the second places in the localisation and classification tracks respectively. We also show that our representations generalise well to other datasets, where they achieve state-of-the-art results. We have made our two best-performing ConvNet models publicly available to facilitate further research on the use of deep visual representations in computer vision.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
三、U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
摘要:There is large consent that successful training of deep networks requires many thousand annotated training samples. In this paper, we present a network and training strategy that relies on the strong use of data augmentation to use the available annotated samples more efficiently. The architecture consists of a contracting path to capture context and a symmetric expanding path that enables precise localization. We show that such a network can be trained end-to-end from very few images and outperforms the prior best method (a sliding-window convolutional network) on the ISBI challenge for segmentation of neuronal structures in electron microscopic stacks. Using the same network trained on transmitted light microscopy images (phase contrast and DIC) we won the ISBI cell tracking challenge 2015 in these categories by a large margin. Moreover, the network is fast. Segmentation of a 512x512 image takes less than a second on a recent GPU. The full implementation (based on Caffe) and the trained networks are available at http://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/people/ronneber/u-net.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
四、Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context
摘要:We present a new dataset with the goal of advancing the state-of-the-art in object recognition by placing the question of object recognition in the context of the broader question of scene understanding. This is achieved by gathering images of complex everyday scenes containing common objects in their natural context. Objects are labeled using per-instance segmentations to aid in precise object localization. Our dataset contains photos of 91 objects types that would be easily recognizable by a 4 year old. With a total of 2.5 million labeled instances in 328k images, the creation of our dataset drew upon extensive crowd worker involvement via novel user interfaces for category detection, instance spotting and instance segmentation. We present a detailed statistical analysis of the dataset in comparison to PASCAL, ImageNet, and SUN. Finally, we provide baseline performance analysis for bounding box and segmentation detection results using a Deformable Parts Model.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
五、Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision
摘要:Convolutional networks are at the core of most state of-the-art computer vision solutions for a wide variety of tasks. Since 2014 very deep convolutional networks started to become mainstream, yielding substantial gains in various benchmarks. Although increased model size and computational cost tend to translate to immediate quality gains for most tasks (as long as enough labeled data is provided for training), computational efficiency and low parameter count are still enabling factors for various use cases such as mobile vision and big-data scenarios. Here we are exploring ways to scale up networks in ways that aim at utilizing the added computation as efficiently as possible by suitably factorized convolutions and aggressive regularization. We benchmark our methods on the ILSVRC 2012 classification challenge validation set demonstrate substantial gains over the state of the art: 21:2% top-1 and 5:6% top-5 error for single frame evaluation using a network with a computational cost of 5 billion multiply-adds per inference and with using less than 25 million parameters. With an ensemble of 4 models and multi-crop evaluation, we report 3:5% top-5 error and 17:3% top-1 error on the validation set and 3:6% top-5 error on the official test set.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
六、Mask R-CNN
摘要:We present a conceptually simple, flexible, and general framework for object instance segmentation. Our approach efficiently detects objects in an image while simultaneously generating a high-quality segmentation mask for each instance. The method, called Mask R-CNN, extends Faster R-CNN by adding a branch for predicting an object mask in parallel with the existing branch for bounding box recognition. Mask R-CNN is simple to train and adds only a small overhead to Faster R-CNN, running at 5 fps. Moreover, Mask R-CNN is easy to generalize to other tasks, e.g., allowing us to estimate human poses in the same framework. We show top results in all three tracks of the COCO suite of challenges, including instance segmentation, bounding-box object detection, and person keypoint detection. Without tricks, Mask R-CNN outperforms all existing, single-model entries on every task, including the COCO 2016 challenge winners. We hope our simple and effective approach will serve as a solid baseline and help ease future research in instance-level recognition. Code will be made available.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
七、Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection
摘要:Feature pyramids are a basic component in recognition systems for detecting objects at different scales. But pyramid representations have been avoided in recent object detectors that are based on deep convolutional networks, partially because they are slow to compute and memory intensive. In this paper, we exploit the inherent multi-scale, pyramidal hierarchy of deep convolutional networks to construct feature pyramids with marginal extra cost. A top-down architecture with lateral connections is developed for building high-level semantic feature maps at all scales. This architecture, called a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN), shows significant improvement as a generic feature extractor in several applications. Using a basic Faster R-CNN system, our method achieves state-of-the-art single-model results on the COCO detection benchmark without bells and whistles, surpassing all existing single-model entries including those from the COCO 2016 challenge winners. In addition, our method can run at 5 FPS on a GPU and thus is a practical and accurate solution to multi-scale object detection. Code will be made publicly available.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
八、ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF
摘要:Feature matching is at the base of many computer vision problems, such as object recognition or structure from motion. Current methods rely on costly descriptors for detection and matching. In this paper, we propose a very fast binary descriptor based on BRIEF, called ORB, which is rotation invariant and resistant to noise. We demonstrate through experiments how ORB is at two orders of magnitude faster than SIFT, while performing as well in many situations. The efficiency is tested on several real-world applications, including object detection and patch-tracking on a smart phone.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
九、DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs
摘要:In this work we address the task of semantic image segmentation with Deep Learning and make three main contributions that are experimentally shown to have substantial practical merit. First , we highlight convolution with upsampled filters, or ‘atrous convolution’, as a powerful tool in dense prediction tasks. Atrous convolution allows us to explicitly control the resolution at which feature responses are computed within Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. It also allows us to effectively enlarge the field of view of filters to incorporate larger context without increasing the number of parameters or the amount of computation. Second , we propose atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) to robustly segment objects at multiple scales. ASPP probes an incoming convolutional feature layer with filters at multiple sampling rates and effective fields-of-views, thus capturing objects as well as image context at multiple scales. Third , we improve the localization of object boundaries by combining methods from DCNNs and probabilistic graphical models. The commonly deployed combination of max-pooling and downsampling in DCNNs achieves invariance but has a toll on localization accuracy. We overcome this by combining the responses at the final DCNN layer with a fully connected Conditional Random Field (CRF), which is shown both qualitatively and quantitatively to improve localization performance. Our proposed “DeepLab” system sets the new state-of-art at the PASCAL VOC-2012 semantic image segmentation task, reaching 79.7 percent mIOU in the test set, and advances the results on three other datasets: PASCAL-Context, PASCAL-Person-Part, and Cityscapes. All of our code is made publicly available online.
全文链接: 文献全文 - 学术范 (xueshufan.com)
希望对你有帮助!
ACM MM & ECCV 2022 | 美团视觉8篇论文揭秘内容领域的智能科技
人工智能技术正在成为内容领域的中台力量,其中视觉AI已经渗透到内容生产、内容审核、内容分发、用户互动、商业化变现等各个环节。美团视觉智能部以场景化的内容产品、智能化的内容工具助力产业,在内容的创作、内容分发等环节应用广泛。 前不久,美团视觉智能部的8篇论文被多媒体和计算机视觉领域顶会ACM MM 与ECCV收录,本文将快速带你了解这8篇论文的研究成果及其可在内容领域的落地应用。
内容生产
围绕素材解析、创意生成、展示自适应等内容生产链路,需要持续优化智能抠图、智能延拓、图像文案生成等核心功能模块。因此,在驱动视觉语义分割、跨模态生成等底层技术方向需要持续升级与创新。
ECCV | Adaptive Spatial-BCE Loss for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation(基于自适应空间二元交叉熵的弱监督语义分割)
论文作者:吴桐(北京理工大学&美团实习生),高广宇(北京理工大学),黄君实(美团),魏晓明(美团),魏晓林(美团),刘驰(北京理工大学)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:弱监督语义分割旨在解决全监督语义分割任务中所需的像素级标签人工成本和时间开销较大的缺点,通过引入较弱的监督信息来降低相关成本。其中本文所使用的图像级监督成本最低,但其较低的信息量也带来了更大的挑战。当前的通用流程是先通过分类网络生成分割伪标签,经过后处理细化后再用伪标签训练语义分割网络。先前方法主要有以下缺点:1)生成的伪标签物体轮廓不清晰;2)前背景的划分阈值需要人工调节,降低了泛用性;3)性能严重依赖后处理,训练复杂度较高。为了缓解这些缺点,我们提出了一个新的损失函数——空间二元交叉熵损失(Spatial-BCE),通过为前景和背景像素分配不同的优化方向来提高它们之间的特征差异性,进而实现更加清晰的伪标签物体轮廓,如下图1所示:
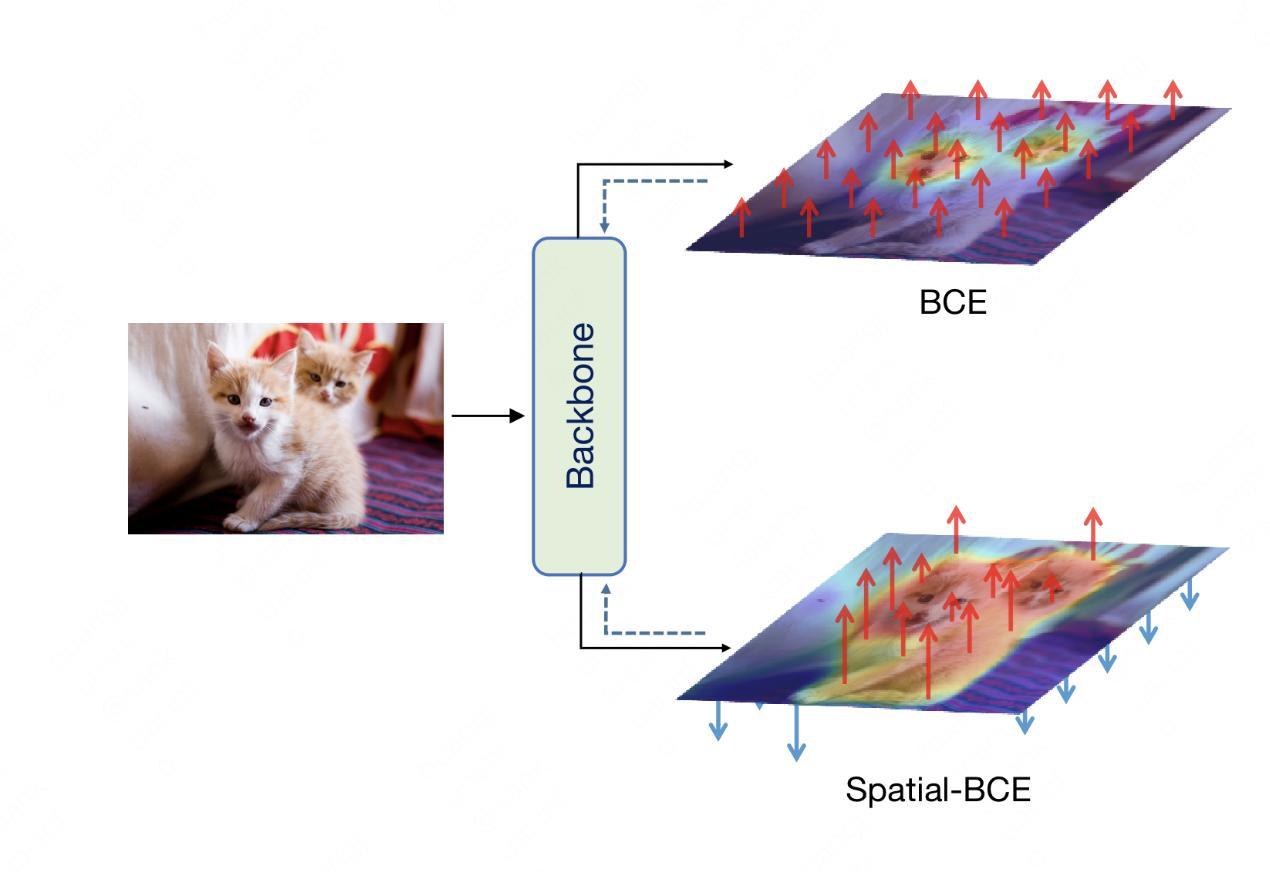
此外,我们还引入了自适应阈值,通过在训练中让损失函数自行划分前背景像素的比例,并在推理时可同样将划分阈值交由网络生成。最后,我们还设计了配套的迭代式训练方法,大幅提高了初始伪标签的准确率,即使不使用复杂的后处理方法,我们也可以实现当前的最优性能。大量实验表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS-COCO 2014数据集上在均可成为SoTA,如下图2所示:

该方法对于广告营销素材解析、商品白底图(如下图3)生产等任务,具有强大的提效作用。针对营销素材、商品主图等元素解析能力,传统的方法需要使用结构化PSD来实现各素材元素、商品主体的分离,这极大地限制了解析能力的使用场景。虽然,可以引入语义分割的能力来处理静态图片的素材解析,但是其标注成本高、主体定义繁杂等问题,一直困扰着设计和算法人员。为此,基于大量容易收集的图片级标签,可以通过本文的弱监督语义分割能力,高效地实现像素级的创意素材解析,进而为后续的创意重组和生成提供充足的供给。

ACM MM | Efficient Modeling of Future Context for Image Captioning(基于自适应空间二元交叉熵的弱监督语义分割)
论文作者:费政聪(美团),黄君实(美团),魏晓明(美团),魏晓林(美团)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:现有的图像描述(Image Caption)生成方法通常从左到右逐个生成单词,并受到局部信息(包括给定图像和历史单词)的约束。有许多研究的目标是在解码过程中尝试利用全局上下文进行优化,例如迭代解码,然而,如何有效和高效地结合未来上下文仍有待探索。
为了应对这个问题,受到非自回归图像描述(Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning, NAIC)可以利用修改掩码操作来理解双边关系的启发,我们旨在将这一进步移植到传统的自回归图像描述模型中,同时保持推理效率,不增加额外的时间成本,如下图4所示:

具体来说,自回归和非自回归图像描述模型首先通过共享视觉编码器进行联合训练,以强制视觉编码器包含有效的未来上下文;然后,迫使自回归图像描述模型对其不一致预测词的分布校准(类似于知识蒸馏),同时额外捕捉非自回归模型中跨层交换的因果变化。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在MS COCO基准的自动指标评估和人类评估方面明显超过了最先进的基准模型。
本文方法对于智能广告文案、商品介绍生成(如下图5)有重大价值,有助于提升营销、曝光点击率,减少人工设计成本。对于广告营销文案的生成,产品图片给用户的第一印象来自于外观,它对用户的决策有着重要的影响。因此,图像描述生成系统必须能够充分挖掘图片视觉信息,反映产品的外观特色,从而促成消费者的点击和下单转化。本文提出的高效未来信息建模方法,有助于更细粒度、更高质量的文本生成。

内容分发
高效的内容分发离不开对其结构化描述,包括图像视频的标签化、模态间(图-文、视频-文本)相关性等。近年来随着图文/短视频内容的广泛性、个性化及热点效应日趋显著,对新标签下的模型冷启动、更细粒度(包括空间上、语义上)的图文匹配、精细化的图像/视频-文本检索提出了更高的技术要求。
ACM MM | PPMN: Pixel-Phrase Matching Network for One-Stage Panoptic Narrative Grounding(针对单阶段全景指代分割的像素-短语匹配网络)
论文作者:丁子涵(北京航空航天大学&美团实习生),惠天瑞(中国科学院信息工程研究所),黄君实(美团),魏晓明(美团),魏晓林(美团),刘偲(北京航空航天大学)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:Panoptic Narrative Grounding (PNG) 是一项新兴任务,其目标是分割由静止图像的密集叙述字幕描述的things和stuff类别的视觉对象。之前的两阶段方法首先通过现有的全景分割模型提取分割候选区域,然后进行粗粒度的区域-短语匹配以得到每个名词短语对应的分割结果。
然而,两阶段方法通常有以下缺点:1)第一阶段低质量候选区域的性能限制;2)区域特征池化导致的空间细节损失;3)需为things和stuff类别分别设计的复杂策略。为了缓解这些缺点,我们提出了一种单阶段端到端像素短语匹配网络(PPMN)(如下图6),通过直接将每个短语与其对应的像素匹配并简单的组合输出全景分割。

因此,我们的模型可以从密集注释的像素-短语对而不是稀疏的区域-短语对的监督中利用足够和更精细的跨模态语义对应。此外,我们还提出了一种语言兼容像素聚合(LCPA)模块,通过多轮优化进一步增强短语特征的判别能力,该模块为每个短语选择最兼容的像素,以自适应地聚合相应的视觉上下文。大量的实验表明,我们的方法在 PNG 数据集上实现了最优的性能,该任务也为信息流场景下的像素级图像内容理解及图文对齐任务垫定了基础。
本文方法对于信息流场景下的用户评论标签挖掘有重大价值。评论数据作为用户对商家的多维度描述,承载了大量真实、多样的用户兴趣点。挖掘评论数据中的文本标签及图片定位信息,有助于我们从图文多模态角度深入理解用户兴趣,进而实现内容的精准投放。本文的方法弥补了以往粗粒度图文挖掘任务的不足,通过端到端的像素-语句级别对齐,实现了更为精准、细致的多模态内容理解能力。该能力可直接用于图像标签挖掘、跨模态以文搜图、图文多模态一致性判断等任务。
ACM MM | Concept Propagation via Attentional Knowledge Graph Reasoning for Video-Text Retrieval(基于注意力机制的知识图推理概念传播方法及其在视频文本检索任务中的应用)
论文作者:方晟(中国科学院计算技术研究所),王树徽(中国科学院计算技术研究所),卓君宝(中国科学院计算技术研究所&美团实习生),黄庆明(中国科学院计算技术研究所),马彬(美团),魏晓明(美团),魏晓林(美团)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:随着短视频平台的兴起,视频数量的急剧增长使得视频文本检索技术越发关键。这个任务的主要挑战在于如何找到视频和文本间细粒度的语义关联。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一个基于注意力的概念传播网络框架(Attentional Concept Propagation, ACP),如下图7所示:

本文考虑了概念层级的信息,在内容层面匹配的基础上引入了语义层面的匹配。在语义层面的匹配分支中,本文设计了概念传播机制来挖掘视频中的隐含语义。具体来说,在外部知识的指导下,本文的方法利用概念间的关联,扩展得到检测器之外的概念,以此来丰富视频的表征。通过这种方式,本文的方法实现了细粒度的视频文本的匹配,从而得到更准确的检索结果,并在多个不同的基准模型以及多个公开数据集上应用了该方法,均获得了稳定的性能提升,证明了本文方法的有效性和泛化性能。
该方法可以在短视频领域,用于扩展通用视频标签体系并为视频内容提供好的基础表征,进而在内容分发场景下,为用户呈现更加契合用户搜索意图与潜在兴趣的视频内容,改善用户体验。
ECCV | PromptDet: Towards Open-vocabulary Detection using Uncurated Images(使用未经处理的图像面向开放词汇的目标检测)
论文作者:冯承健(美团),钟毓杰(美团),揭泽群(美团),初祥祥(美团),任海兵(美团),魏晓林(美团),谢伟迪(上海交通大学),马林(美团)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:这项工作的目标是建立一个可扩展的目标检测器,使用零手动标注将目标检测器扩展到新的/未见过的类别,如下图8所示:

为了实现这一点,我们做出了以下四项贡献:
- 为了追求泛化性,我们提出了一个两阶段的开放词汇目标检测器,使用来自预训练视觉语言模型的文本编码器对类别无关的物体提议区域进行分类。
- 为了将RPN 提议区域的视觉潜在空间与预训练文本编码器的潜在空间配对,我们提出了区域提示(prompt)学习方法,以将文本嵌入空间与物体区域的视觉特征对齐。
- 为了扩大学习过程以检测更广泛的类别,我们通过一种新颖的自训练框架利用可用的在线资源,该框架允许在大量嘈杂的未经处理的网络图像上训练所提出的检测器。
- 为了评估我们提出的检测器,PromptDet,我们在具有挑战性的 LVIS 和MS-COCO数据集进行了广泛的实验。与现有方法相比,PromptDet使用更少的额外训练图像和零手动标注,表现出卓越的检测性能。
本文方法对于用户种草图片的理解和归类有重大价值,有助于向其他用户推荐相关商品和景点。用户在种草或评价时通常会分享一些图片,而在寻找好商品或好去处时通常使用文本来搜索,图片和文本之间没有直接的对应关系,从而不能根据用户的搜索文本推荐相关的种草商品和景点。通过本文提出的方法,可以根据自定义的文本(如商品名称)检测图片中的物体,对种草图片进行理解和归类。当用户使用文本搜索时,可以向用户推荐最相关的种草商品和景点,实现精准和多样化的种草内容推荐,提升种草转化率。
ACM MM | Synthesizing Counterfactual Samples for Effective Image-Text Matching(合成反事实样本以进行有效的图像-文本匹配)
论文作者:魏浩(中国科学院计算技术研究所),王树徽(中国科学院计算技术研究所),韩歆哲(中国科学院计算技术研究所),薛哲(北京邮电大学),马彬(美团),魏晓明(美团),魏晓林(美团)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:图像文本匹配(Image-Text Matching)是跨模态领域的一个基础研究问题,旨在度量图像和文本之间的语义相似性。最近的工作通常使用难负样本挖掘(Hard Negative Mining)来捕获图像和文本之间的多重对应关系。不幸的是,拥有丰富信息的负样本在训练数据中非常稀少,很难在随机采样的小批次中获得。受到因果推理的启发,本文通过类比难负样本挖掘和因果效应优化来解决这一问题。本文提出了反事实匹配(Counterfactual Matching, CFM)方法(如下图9),用于更加有效的匹配关系挖掘。

如上图,CFM包含三个主要部分,即用于自动因果因子识别的特征选择、用于保障因果因子完整性的自我探索和用于反事实样本合成的自我调整。与传统的难负样本挖掘相比,该方法缓解了过拟合现象,有效地捕获了图像和文本之间的细粒度匹配关联。本文将CFM与三种最先进的图像文本匹配模型结合起来进行评估。在两个公开数据集上进行的实验表明,本文提出的方法具有很强的通用性和有效性。
本文方法对于提升图像文本相关性建模效果具有重要价值,可进一步提升在图文相关性,图像细粒度理解,图像、视频检索等下游任务的效果(如下图10)。在内容展示中,对于提升信息流内容的图像-文本、视频封面-文本相关性,改善用户体验具有重要意义。

ACM MM | Zero-shot Video Classification with Appropriate Web and Task Knowledge Transfer(基于网络知识与任务知识迁移的零样本视频分类)
论文作者:卓君宝(中国科学院计算技术研究所&美团实习生),朱妍(中国科学院计算技术研究所&美团实习生),崔书豪(美团),王树徽(中国科学院计算技术研究所),黄庆明(中国科学院计算技术研究所),马彬(美团),魏晓明(美团),魏晓林(美团)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:零样本视频分类旨在识别在模型训练过程中从未见过的视频类别,一般通过构建视觉特征和语义嵌入之间的映射来实现。研究表明通过挖掘视频包含的物体作为属性并结合外部知识能有效提升模型的性能。但是,从可见类别挖掘的物体属性不能有效泛化到未见类,且外部知识中属性之间的关系与视频中出现的属性关系存在较大偏差。本文提出了基于网络知识的属性构建方法和属性-类别关系挖掘方法,如下图11所示:

根据视频类别名称在网络中搜集相关的图像,并应用预先训练的物体识别模型对收集的图像进行识别,提取频繁出现的物体作为该视频类别相关的属性,构建属性-类别关系。通过所挖掘的属性以及外部知识,采用图神经网络学习视觉特征到类别的映射,有效提升模型的泛化能力。此外,为解决现有方法过拟合到已见类别的问题,本文提出通过估计已见类和未知类之间的相似度来指导模型训练的方法。实验表明,所提方法取得了显著的性能提升。
本文方法可在需要新的类别标签时,快速实现样本冷启动,加速标签模型研发。对基于标签的短视频内容运营,媒资管理,内容分发等应用能起到重要支撑。可以通过少量示例样本快速构建视频分类模型,从存量内容池中自动挖掘高价值内容(如:“探店种草”)匹配大众点评App“发现好去处”的产品定位,在首页信息流中为用户提供丰富的信息参考,如下图12所示:

模型量化
ACM MM | Towards Accurate Post-Training Quantization for Vision Transformer(迈向Vision Transformer的高精度后量化算法)
论文作者:丁一芙(北京航空航天大学&美团实习生),秦浩桐(北京航空航天大学),闫青华(北京航空航天大学),柴振华(美团),刘俊杰(美团),魏晓林(美团),刘祥龙(北京航空航天大学)
论文下载:PDF
论文简介:后量化是CNN模型压缩中较为成熟的一个研究方向,然而如何在Vision Transformer上实现无损后量化在学界依然是一个没有解决的问题。通过引入高精度的后量化算法,可以解决Transformer结构在服务端部署效率不高、显存占用过大的落地痛点,同时也为Mobile Transformer在移动端设备的落地提供更多可能性。
现有的研究方法中比较代表的是华为诺亚方舟实验室的FQ-ViT,在极低比特的情况下对量化误差的评估与实际仍存在较大误差,同时对具有幂率分布的SoftMax层的处理方法有待有进一步优化。基于上述观察,我们提出了一种名为APQ-ViT(Accurate Post-training Quantization framework for Vision Transformer)的方法(如下图13):通过引入底部误差消除的逐块校准策略,基于块层面感知量化误差,减少量化对最终输出的影响,并设计了一种马太效应保持的Softmax后量化映射方法,可以达到在8 bit工业场景下基本性能无损的压缩效果,并且在更低比特(4/6 bit)下也能显著降低模型量化带来的精度损失。

本文方法可为内容场景中多媒体理解任务Transformer模型快速量化部署产生的性能损失问题提供优化方案,同时也为端侧Transformer的落地应用提供技术支撑,并进一步减少App的包体积。
本文介绍了美团视觉智能部围绕线上内容生产与分发,在跨模态匹配与生成、语义分割、物体检测、模型压缩等领域所做的一些科研工作,以及这些科研成果在实际场景中的应用,希望对大家有所帮助或启发。
阅读美团技术团队更多技术文章合集
前端 | 算法 | 后端 | 数据 | 安全 | 运维 | iOS | Android | 测试
| 在公众号菜单栏对话框回复【2021年货】、【2020年货】、【2019年货】、【2018年货】、【2017年货】等关键词,可查看美团技术团队历年技术文章合集。

| 本文系美团技术团队出品,著作权归属美团。欢迎出于分享和交流等非商业目的转载或使用本文内容,敬请注明“内容转载自美团技术团队”。本文未经许可,不得进行商业性转载或者使用。任何商用行为,请发送邮件至tech@meituan.com申请授权。
以上是关于计算机视觉领域必读的9篇论文的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
ACM MM & ECCV 2022 | 美团视觉8篇论文揭秘内容领域的智能科技