Linux基础Linux中的时区和时间
Posted jiangwei0512
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux基础Linux中的时区和时间相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基本概念
首先介绍Linux中会用到的时间概念:
UTC:Universal Time Coordinated,协调世界时,又称世界统一时间,世界标准时间,国际协调时间。它是一个与时区相关的时间,目前将世界时区分为24个。UTC跟GMT(Greenwich Mean Time,格林威治时间)一致,因为格林威治位于0时区,UTC时间即是0时区的时间。中国位于东八区,所以对应的时间是UTC时间加8小时,即UTC+8,也称为CST(China Standard Time)。UTC倾向于跟标准相关的时间。
RTC:Real Time Clock,实时时钟。RTC和UTC不是一个概念上的时间,RTC通常指的是硬件系统中的一个计时芯片,它将时间保存在CMOS(可以认为是一种非易失介质)中,而CMOS通过电池可以保持数据不丢失,因此在系统没有上电的情况下(RTC由电池供电)也还会正常更新时间。操作系统启动时会查看这个时间,也可以同步这个时间。RTC倾向于跟硬件相关的时间。
时间戳:指的是从当前时间到某个标准时间点经历的秒数,这里的标准时间点通常是指1970年1月1日0时0分0秒,这个时间点也被称为Epoch。时间戳是一个相对的时间值,倾向于跟软件相关。
Linux下查看时间
Linux可以通过命令查看上述的时间,下面是在Ubuntu18.04(本文后续所有内容都在该版本下做测试)中执行的结果:
- 首先是获取本地时间:
root@ubuntu:~# date
2023年 01月 07日 星期六 23:18:21 CST
这里的CST表示的就是前面提到的China Standard Time,就是东八区时间,也是我所在地的时间。
通过增加-u参数可以查看UTC时间:
root@ubuntu:~# date -u
2023年 01月 07日 星期六 15:19:28 UTC
可以看到这里的后缀已经从CST变成了UTC时间。因为UTC是标准时间,所以一般的Linux命令都可以获取到它。
另外date命令也可以查看时间戳:
root@ubuntu:~# date +%s
1673106588
注意时间戳是没有时区概念的,它只是从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒到当前时间的秒数。
- 之后查看RCT时间,它主要通过hwclcok命令来完成:
root@ubuntu:~# hwclock
2023-01-07 23:20:37.664556+0800
root@ubuntu:~# hwclock -l
2023-01-07 15:20:46.242465+0800
root@ubuntu:~# hwclock -u
2023-01-07 23:20:59.633316+0800
注意上述的3条命令,对比date命令中的-u参数,得到的结果可能会让人误解。因为hwclock以及加上-u参数,得到的都是本地时间,而加上-l(表示localtime)得到的才是真的RTC时间。
查看hwclock命令的参数说明:
Options:
-u, --utc the RTC timescale is UTC
-l, --localtime the RTC timescale is Local
实际上这里的-u表示的是假设RTC里面保存的是UTC时间,那么本地时间就应该要增加8个小时(因为我在东八区),而-l表示的是假设当前RTC时间就是本地时间,所以就直接显示出来了,这句话还隐含着一个意思就是RTC时间就是2023-01-07 15:20:46.242465+0800。这个可以通过增加--debug参数看到进一步的内容:
root@ubuntu:~# hwclock --debug
hwclock from util-linux 2.31.1
System Time: 1673105261.476314
Trying to open: /dev/rtc0
Using the rtc interface to the clock.
Assuming hardware clock is kept in UTC time. # 注意这里假设RTC中保存的是UTC时间
Waiting for clock tick...
...got clock tick
Time read from Hardware Clock: 2023/01/07 15:27:42
Hw clock time : 2023/01/07 15:27:42 = 1673105262 seconds since 1969
Time since last adjustment is 1673105262 seconds
Calculated Hardware Clock drift is 0.000000 seconds
2023-01-07 23:27:41.040147+0800
注意这里有一句Assuming hardware clock is kept in UTC time.,也就是前面说的假设RTC里面保存的是UTC时间。如果加上-l参数,显示的DEBUG信息是:
root@ubuntu:~# hwclock -l --debug
hwclock from util-linux 2.31.1
System Time: 1673106076.977518
Trying to open: /dev/rtc0
Using the rtc interface to the clock.
Assuming hardware clock is kept in local time. # 注意这里假设RTC中保存的是本地时间
Waiting for clock tick...
...got clock tick
Time read from Hardware Clock: 2023/01/07 15:41:17
Hw clock time : 2023/01/07 15:41:17 = 1673077277 seconds since 1969
Time since last adjustment is 1673077277 seconds
Calculated Hardware Clock drift is 0.000000 seconds
2023-01-07 15:41:16.539634+0800
- 最后还有一个命令可以同时显示多个时间:
root@ubuntu:~# timedatectl
Local time: 六 2023-01-07 23:42:12 CST
Universal time: 六 2023-01-07 15:42:12 UTC
RTC time: 六 2023-01-07 15:42:11
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
System clock synchronized: yes
systemd-timesyncd.service active: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
这里可以看到本地时间,UTC时间,RTC时间还有时区等等内容。
本节主要介绍如何查看时间,后面会介绍具体的代码实现,比如RTC时间如何获取,如何转换成本地时间,等等。
时区
Linux中的时区主要通过一个文件来表示,这个文件是/etc/localtime,其中包含了Linux系统的时区信息:
root@ubuntu:~# ls -al /etc/localtime
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 33 1月 7 23:20 /etc/localtime -> /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
注意这里的/etc/localtime只是一个链接,查看被链接文件所在的目录:
root@ubuntu:~# ls /usr/share/zoneinfo/
Africa Cuba GMT0 Japan Pacific Turkey
America EET GMT-0 Kwajalein Poland UCT
Antarctica Egypt GMT+0 leap-seconds.list Portugal Universal
Arctic Eire Greenwich Libya posix US
Asia EST Hongkong localtime posixrules UTC
Atlantic EST5EDT HST MET PRC WET
Australia Etc Iceland Mexico PST8PDT W-SU
Brazil Europe Indian MST right zone1970.tab
Canada Factory Iran MST7MDT ROC zone.tab
CET GB iso3166.tab Navajo ROK Zulu
Chile GB-Eire Israel NZ Singapore
CST6CDT GMT Jamaica NZ-CHAT SystemV
这里包含了所有的时区相关的文件,这些文件被称为ztfile,可以在Linux查看:
TZFILE(5) Linux Programmer's Manual TZFILE(5)
NAME
tzfile - timezone information
DESCRIPTION
The timezone information files used by tzset(3) are typically found
under a directory with a name like /usr/share/zoneinfo. These files
begin with a 44-byte header containing the following fields:
# 后面略
所以为了修改Linux系统的时区,只需要修改/etc/localtime链接的文件就可以了:
root@ubuntu:~# date
2023年 01月 07日 星期六 23:54:06 CST # 北京时间
root@ubuntu:~# ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Tokyo /etc/localtime # 链接到东京时间
root@ubuntu:~# date
2023年 01月 08日 星期日 00:54:43 JST # 时间发生了变化
除了直接修改链接,Ubuntu还提供了额外的配置方式,这需要使用dpkg-reconfigure工具,对应的命令:
root@ubuntu:~# dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
执行命令之后会显示一个图形界面:
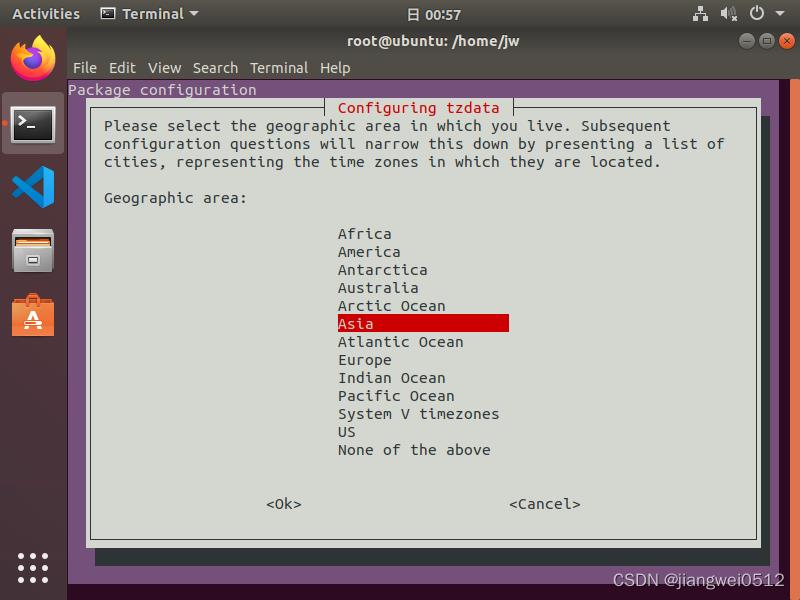
选择对应的时区所在地点之后会直接退出,并显示如下的内容:
root@ubuntu:~# dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Current default time zone: 'Asia/Shanghai'
Local time is now: 2023年 01月 07日 星期六 23:59:18 CST.
Universal Time is now: Sat Jan 7 15:59:18 UTC 2023.
表明修改已经成功,再次查看/etc/localtime:
root@ubuntu:~# ls -al /etc/localtime
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 33 1月 7 23:59 /etc/localtime -> /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
可以看到时区已经修改回去了。
当然如果使用的是Ubuntu的图形界面,显然可以直接在设置中修改:
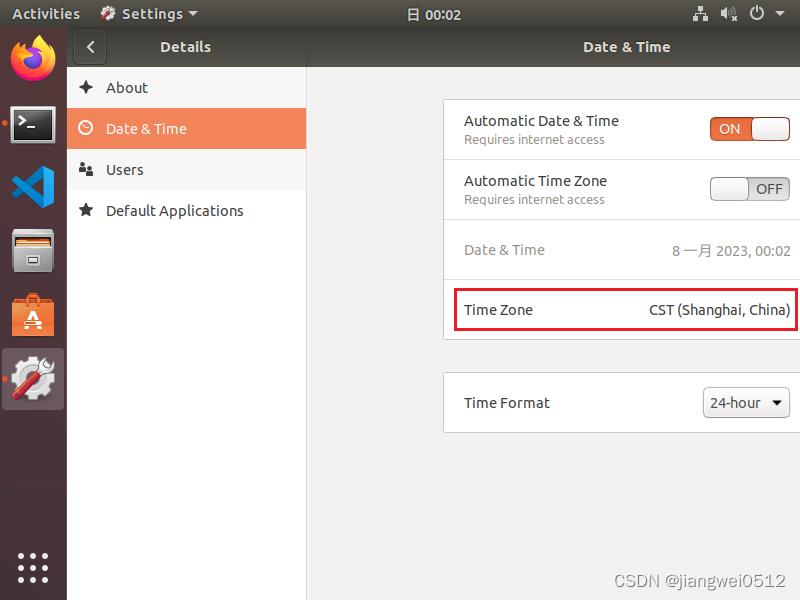
代码实现
代码下载
下面介绍Linux时间命令的具体实现,为此首先需要下载对应的代码,以hwclock为例(它的代码实现中已经包含了UTC、RTC、时间戳等相关的内容,而系统调用相关的代码将在时间相关的系统调用介绍),该命令属于util-linux 2.31.1的一部分:
root@ubuntu:~# hwclock -v
hwclock from util-linux 2.31.1
所以要下载util-linux的源码。在Ubuntu中下载源码,需要两步操作:
- 修改/etc/apt/sources.list文件,需要取消deb-src开头语句的注释,比如:
# deb cdrom:[Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS _Bionic Beaver_ - Release amd64 (20200203.1)]/ bionic main restricted
# See http://help.ubuntu.com/community/UpgradeNotes for how to upgrade to
# newer versions of the distribution.
deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted
deb-src http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted # 取消注释
## Major bug fix updates produced after the final release of the
## distribution.
deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted
deb-src http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted # 取消注释
修改之后执行apt update更新库。
- 通过如下的命令下载源码:
root@ubuntu:/home/jw/code# apt source util-linux
Reading package lists... Done
NOTICE: 'util-linux' packaging is maintained in the 'Git' version control system at:
https://salsa.debian.org/debian/util-linux.git
Please use:
git clone https://salsa.debian.org/debian/util-linux.git
to retrieve the latest (possibly unreleased) updates to the package.
Need to get 4,620 kB of source archives.
Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main util-linux 2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.7 (dsc) [4,122 B]
Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main util-linux 2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.7 (tar) [4,514 kB]
Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates/main util-linux 2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.7 (diff) [102 kB]
Fetched 4,620 kB in 4s (1,115 kB/s)
dpkg-source: info: extracting util-linux in util-linux-2.31.1
# 中间略
W: Download is performed unsandboxed as root as file 'util-linux_2.31.1-0.4ubuntu3.7.dsc' couldn't be accessed by user '_apt'. - pkgAcquire::Run (13: Permission denied)
这样源码就下载到了/home/jw/code/util-linux-2.31.1目录下(有报错但是不影响代码下载)。
hwclock
查看hwclock命令的实现,它位于sys-utils/hwclock.c,其主要的代码(仅以读操作为例):
if (!ctl.noadjfile && !(ctl.systz && (ctl.utc || ctl.local_opt)))
if ((rc = read_adjtime(&ctl, &adjtime)) != 0)
hwclock_exit(&ctl, rc);
else
/* Avoid writing adjtime file if we don't have to. */
adjtime.dirty = 0;
ctl.universal = hw_clock_is_utc(&ctl, adjtime);
rc = manipulate_clock(&ctl, set_time, startup_time, &adjtime);
函数流程主要是:
-
read_adjtime()函数默认获取/etc/adjtime文件,它用来获取时间调整信息,不过Ubuntu下没有这个文件。 -
hw_clock_is_utc()依赖于前面的read_adjtime()函数,不过由于不存在,所以传入的参数是默认的,其实现如下:
static int
hw_clock_is_utc(const struct hwclock_control *ctl,
const struct adjtime adjtime)
int ret;
if (ctl->utc) // 对应-u参数
ret = 1; /* --utc explicitly given on command line */
else if (ctl->local_opt) // 对应-l参数
ret = 0; /* --localtime explicitly given */
else
/* get info from adjtime file - default is UTC */
// 不带参数时,通过/etc/adjtime获取值,默认是UTC值为0,而LOCAL的值是1,所以最终ret=1
ret = (adjtime.local_utc != LOCAL);
if (ctl->debug)
printf(_("Assuming hardware clock is kept in %s time.\\n"),
ret ? _("UTC") : _("local"));
return ret;
从这里可以看出来,执行hwclock命令时,不带参数和带-u参数是相同的显示,这与前面执行命令的结果是一致的。该函数的返回值被赋值给如下的变量:
ctl.universal = hw_clock_is_utc(&ctl, adjtime);
这个变量在后面会使用到,而它的值,在当前的Ubuntu系统下,如果不带参数或者带了-u参数就是1,否则是0。
manipulate_clock()执行了最主要的时间操作,其执行代码如下:
read_hardware_clock()的实现可以参看RTC时间。mktime_tz()的实现如下:
static int
mktime_tz(const struct hwclock_control *ctl, struct tm tm,
time_t *systime_p)
int valid;
if (ctl->universal)
*systime_p = timegm(&tm);
else
*systime_p = mktime(&tm);
if (*systime_p == -1)
/*
* This apparently (not specified in mktime() documentation)
* means the 'tm' structure does not contain valid values
* (however, not containing valid values does _not_ imply
* mktime() returns -1).
*/
valid = 0;
if (ctl->debug)
printf(_("Invalid values in hardware clock: "
"%4d/%.2d/%.2d %.2d:%.2d:%.2d\\n"),
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday,
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec);
else
valid = 1;
if (ctl->debug)
printf(_
("Hw clock time : %4d/%.2d/%.2d %.2d:%.2d:%.2d = "
"%ld seconds since 1969\\n"), tm.tm_year + 1900,
tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday, tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min,
tm.tm_sec, (long)*systime_p);
return valid;
这里关键是前面提到的ctl->universal,它的值来自hw_clock_is_utc()函数的返回值,根据不同的值会执行不同的分支函数:这里的mktime()是系统函数(参见mktime()),而timegm()的实现:
time_t timegm(struct tm *tm)
const char *zone = getenv("TZ");
time_t ret;
setenv("TZ", "", 1);
tzset();
ret = mktime(tm);
if (zone)
setenv("TZ", zone, 1);
else
unsetenv("TZ");
tzset();
return ret;
可以看到它其实也调用了mktime()函数,只不过在调用前后还会额外执行tzset()函数(它也是系统调用),来做时区相关的操作。
由于mktime()(参见tzset())受到TZ变量的影响,而将TZ变量设置为空实际上就是使用UTC时间,所以最终这里得到的时间戳是1970年1月1日0时0分0秒当UTC时间的秒数,而没有设置TZ(不同于设置为空),则得到的是1970年1月1日0时0分0秒到本地时间的秒数。这最终导致mktime_tz()得到不同的值,也是-l和-u参数的差异体现。
calculate_adjustment()函数也与/etc/adjtime文件有关,由于Ubuntu没有该文件,这里不做介绍。- 最后是
display_time()函数,该函数就是打印结果。
以上就是hwclcok命令显示时间的简单介绍,需要说明的是hwclcok不仅可以查看时间,还可以同步时间,不过这个不在本文的介绍范围中。
RTC时间
关于RTC时间的实现,可以直接参考hwclock命令的源代码util-linux-2.31.1,其实现在sys-utils\\hwclock-rtc.c:
static int read_hardware_clock_rtc(const struct hwclock_control *ctl,
struct tm *tm)
int rtc_fd, rc;
rtc_fd = open_rtc_or_exit(ctl);
/* Read the RTC time/date, return answer via tm */
rc = do_rtc_read_ioctl(rtc_fd, tm);
return rc;
open_rtc_or_exit()函数打开/dev/rtc0这个设备:
root@ubuntu:~# ll /dev/rtc0
crw------- 1 root root 249, 0 1月 7 23:17 /dev/rtc0
而do_rtc_read_ioctl()通过ioctl()函数来获取参数:
static int do_rtc_read_ioctl(int rtc_fd, struct tm *tm)
int rc = -1;
char *ioctlname;
ioctlname = "RTC_RD_TIME";
rc = ioctl(rtc_fd, RTC_RD_TIME, tm);
if (rc == -1)
warn(_("ioctl(%s) to %s to read the time failed"),
ioctlname, rtc_dev_name);
return -1;
tm->tm_isdst = -1; /* don't know whether it's dst */
return 0;
这样就得到了RTC时间,并存放在struct tm结构体变量中。
以下是自己写的一个示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <asm/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define RTC_DEV "/dev/rtc0"
#ifndef RTC_RD_TIME
#define RTC_RD_TIME _IOR('p', 0x09, struct linux_rtc_time)
#endif
struct linux_rtc_time
int tm_sec;
int tm_min;
int tm_hour;
int tm_mday;
int tm_mon;
int tm_year;
int tm_wday;
int tm_yday;
int tm_isdst;
;
int read_hardware_clock(struct tm *tm)
int rtc_fd;
int rc;
rtc_fd = open(RTC_DEV, O_RDONLY);
if (-1 == rtc_fd)
return -1;
rc = ioctl(rtc_fd, RTC_RD_TIME, tm)