100天精通Python(数据分析篇)——第71天:Pandas文本数据处理方法之str/object类型转换大小写转换文本对齐获取长度出现次数编码
Posted 无 羡ღ
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了100天精通Python(数据分析篇)——第71天:Pandas文本数据处理方法之str/object类型转换大小写转换文本对齐获取长度出现次数编码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

文章目录
1. 文本数据类型介绍
- Pandas文本数据类型有
object和string两种,如果一列数据中包含文本和数据,则会默认为object类型。- pandas1.0之前只有文本数据只有object类型,pandas1.01.0朝代之后有了string类型。
- 如果不特殊指定类型为string,文本类型一般为object
1)类型介绍
(1)一列数据中包含文本和数据,默认情况下为object类型:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(
'A': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'],
'B': ['ee', 'ff', 'gg', np.nan],
'C': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'D': [5, 6, 7, np.nan]
)
print(df)
print(df.dtypes)
运行结果:
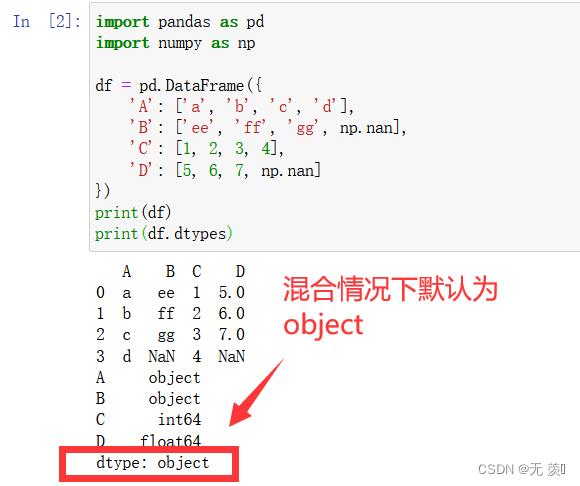
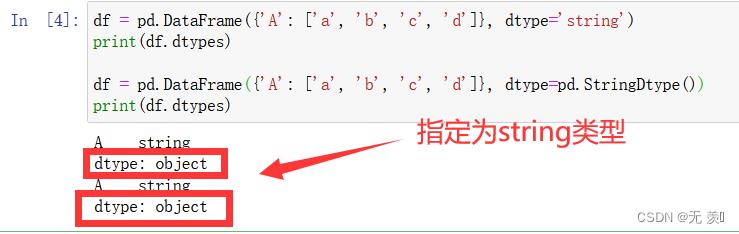
(2)string类型需要通过设置dtype参数进行指定:
# 方法1 :dtype='string'
df = pd.DataFrame('A': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='string')
print(df.dtypes)
# 方法2 : dtype=pd.StringDtype()
df = pd.DataFrame('A': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype=pd.StringDtype())
print(df.dtypes)
运行结果:
2)类型转换
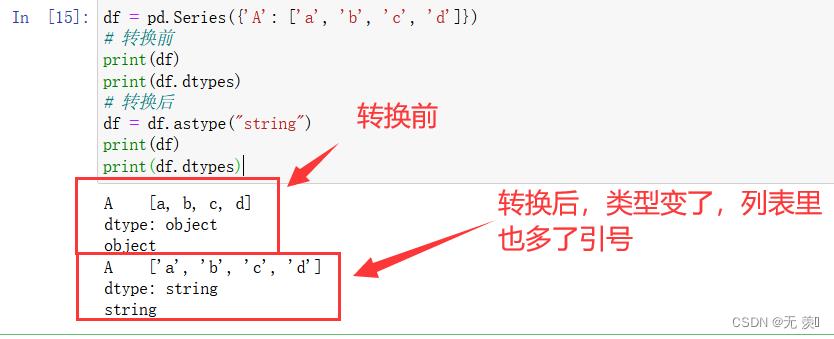
方法1:通过astype强制转换为string
df = pd.Series('A': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
# 转换前
print(df)
print(df.dtypes)
# 转换后
df = df.astype("string")
print(df)
print(df.dtypes)
运行结果:
方法2:通过df.convert_dtypes()进行智能数据类型选择
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(
'A': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'],
'B': ['ee', 'ff', 'gg', np.nan],
'C': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'D': [5, 6, 7, np.nan]
)
print('类型转换前')
print(df.dtypes)
df = df.convert_dtypes() # 智能数据类型选择
print('类型转换后')
print(df.dtypes)
运行结果:
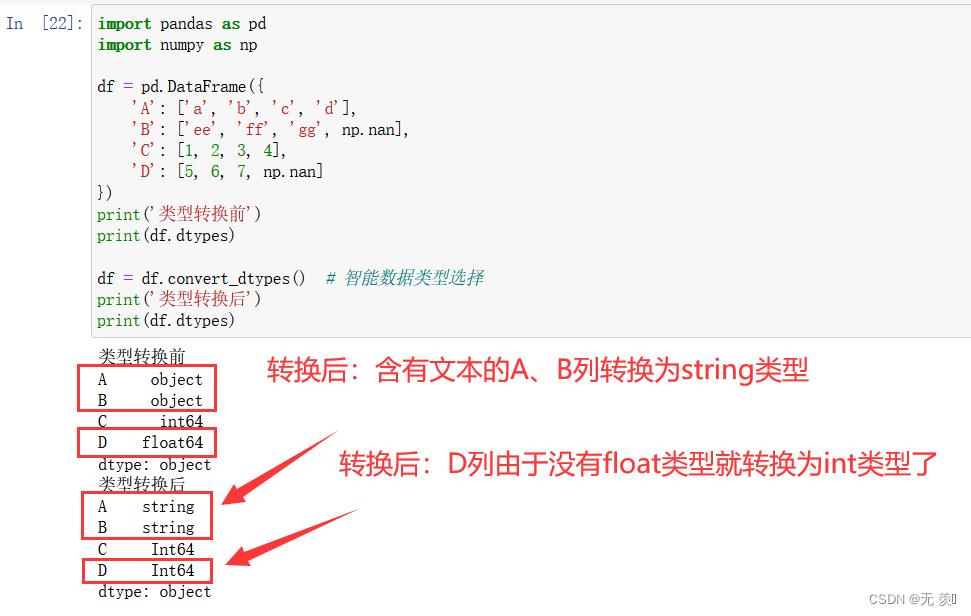
3)类型区别
string类型和object类型区别如下:
- sting来说,返回数字输出的字符串访问器方法将始终返回可为空的整数类型;对于object来说,是 int 或 float,具体取决于 NA 值的存在
- 对于string类型来说,返回布尔输出的方法将返回一个可为空的boolean布尔数据类型;而object类型还是object
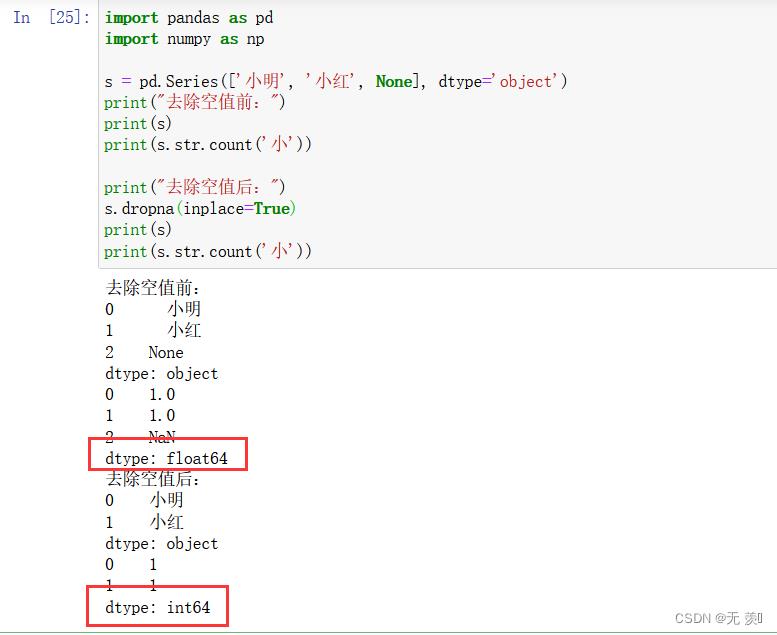
区别1:统计字符串时
统计字符串s.str.count()时:
- string类型的None返回NaN ,dtype为
Int64;通过dropna()去除缺失值后dtype也是Int64- object类型的None返回NaN,dtpye为
float64;通过dropna()去除缺失值后dtype是Int64
string类型:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(['小明', '小红', None], dtype='string')
print("去除空值前:")
print(s)
print(s.str.count('小'))
print("去除空值后:")
s.dropna(inplace=True)
print(s)
print(s.str.count('小'))
运行结果:

object类型:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(['小明', '小红', None], dtype='object')
print("去除空值前:")
print(s)
print(s.str.count('小'))
print("去除空值后:")
s.dropna(inplace=True)
print(s)
print(s.str.count('小'))
运行结果:
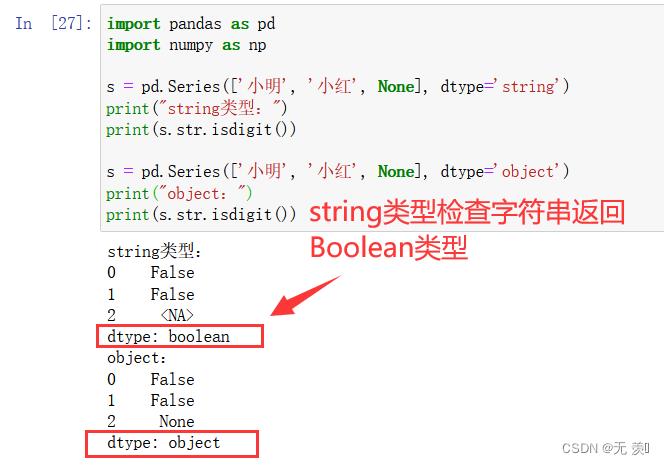
区别2:检查字符串时
通过str.isdigit ()检查字符串时:
- string类型,则返回布尔类型,dtype= boolean,缺失值为NA
- object类型,虽然返回是布尔类型,但是dtype= object, None返回 None
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(['小明', '小红', None], dtype='string')
print("string类型:")
print(s.str.isdigit())
s = pd.Series(['小明', '小红', None], dtype='object')
print("object:")
print(s.str.isdigit())
运行结果:
2. Python字符串内置方法
字符串是一种常见的数据类型,我们遇到的文本、json数据等都是属于字符串的范畴。Python内置了很多处理字符串的方法,这些方法为我们处理和清洗数据提供了很大的便利。本文将介绍大小写转换、文本对齐方法、
1) 大小写转换
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.lower() | 转换 string 中所有大写字符为小写 |
| string.upper() | 转换 string 中的小写字母为大写 |
| string.capitalize() | 把字符串的第一个字符大写 |
| string.title() | 把字符串的每个单词首字母大写 |
| string.swapcase() | 翻转 string 中的大小写 |
2) 文本对齐
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| string.ljust(width) | 返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
| string.rjust(width) | 返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
| string.center(width) | 返回一个原字符串居中,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
3)获取长度
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| len(string) | 返回字符串的长度。 |
4)获取出现次数
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| count(string) | 返回每个字符串元素出现的次数。 |
5)编码
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| encode(‘utf-8’) | 字符编码,传递字符串 |
3. Pandas怎么使用内置方法?
- 在日常进行数据清洗、数据分析的过程中,经常需要对字符串类型数据进行处理。而pandas其内置的基于
Series.str访问器的诸多针对字符串进行处理的方法,pandas特定的列经过str之后,就可以使用各种python常用的字符处理方法以及内置函数,可以帮助我们大大提升字符串型数据处理的效率。- Pandas通过
.str调用就可以在Series对象上使用字符串内置方法(pandas中的字符串处理函数以str开头),对数据框中的某一列进行操作,这种向量化的操作提高了处理效率。
1) 大小写转换
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| series_obj.str.lower() | 转换 string 中所有大写字符为小写 |
| series_obj.str.upper() | 转换 string 中的小写字母为大写 |
| series_obj.str.capitalize() | 把字符串的第一个字符大写 |
| series_obj.str.title() | 把字符串的每个单词首字母大写 |
| series_obj.str.swapcase() | 翻转 string 中的大小写 |
准备数据:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
series_obj = pd.Series(['A', 'b', 'ABC', 'Abc', 'abc', 'This is abc', np.nan], dtype='string')
print(df)
运行结果:

1、转换 string 中所有大写字符为小写:
series_obj.str.lower()
运行结果:

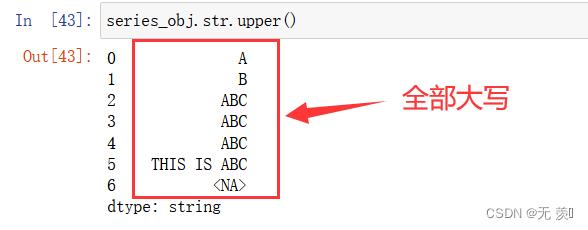
2、转换 string 中的小写字母为大写:
series_obj.str.upper()
运行结果:
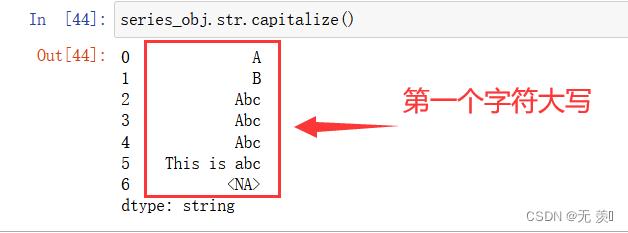
3、把字符串的第一个字符大写:
series_obj.str.capitalize()
运行结果:
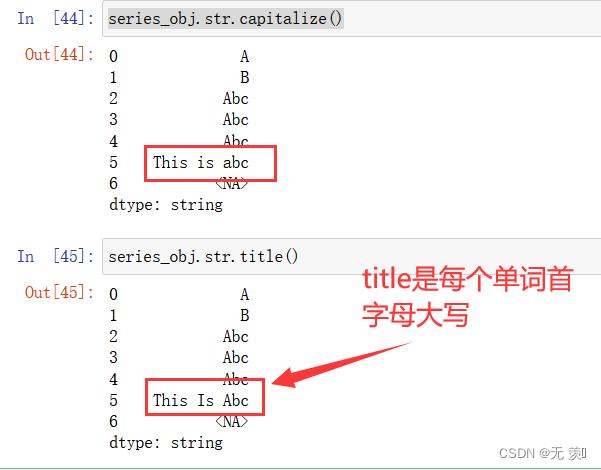
4、把字符串的每个单词首字母大写(注意和capitalize的区别):
series_obj.str.title()
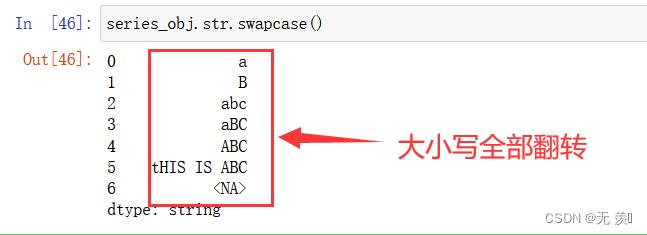
5、翻转 string 中的大小写:
series_obj.str.swapcase()
运行结果:
2) 文本对齐
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| series_obj.str.ljust(width) | 返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
| series_obj.str.rjust(width) | 返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
| series_obj.str.center(width) | 返回一个原字符串居中对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
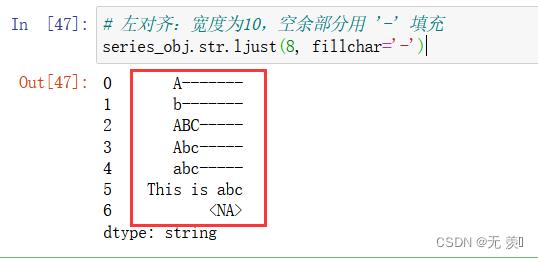
1、 返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串:
# 左对齐:宽度为10,空余部分用 '-' 填充
series_obj.str.ljust(8, fillchar='-')
运行结果:
2、返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串:
# 右对齐:宽度为10,空余部分用 '-' 填充
series_obj.str.rjust(8, fillchar='-')
运行结果:

3、返回一个原字符串居中对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串:
# 居中对齐:宽度为10,空余部分用 '-' 填充
series_obj.str.center(8, fillchar='-')
运行结果:

3)获取长度
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| series_obj.str.len(string) | 返回字符串的长度。 |
series_obj.str.len()
运行结果:

4)获取出现次数
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| series_obj.str.count(string) | 返回每个字符串元素出现的次数。 |
统计A出现了多少次,count会区分大小写的:
series_obj.str.count('A')
series_obj.str.count('a')
运行结果:

5)编码
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| series_obj.str.encode(‘utf-8’) | 字符编码,传递字符串 |
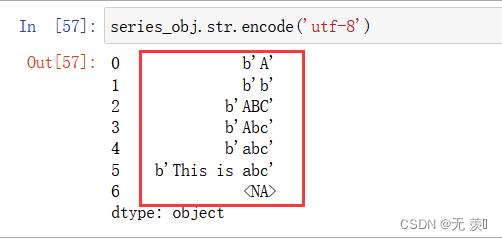
字符编码设置为utf8:
series_obj.str.encode('utf-8')
4. 注意事项
1、.str访问器只能对Series数据结构使用。 除了常规列变量df.col以外,也可以对索引类型df.Index和df.columns使用
2、确保访问的对象类型是字符串str类型。 如果不是需要先astype(str)转换类型,否则会报错
3、某些方法不能在上stringSeries使用,如: series_obj.str.decode(),因为Series存储的是字符串而不是字节:
series_obj.str.decode('utf-8')
运行结果:

4、访问器可以多个连接使用。 如series_obj.str.lower().str.title(),使用效果叠加:
# 先设置全部小写,然后设置首字母大写
series_obj.str.lower().str.title()
运行结果:

代理IP
python离不开爬虫,最近有些想学爬虫的小伙伴问我,代理IP哪里找,博主自己用的是高匿稳定爬虫代理IP:神龙HTTP代理(需要的可自行点击了解)
以上是关于100天精通Python(数据分析篇)——第71天:Pandas文本数据处理方法之str/object类型转换大小写转换文本对齐获取长度出现次数编码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章