视觉高级篇23 # 如何模拟光照让3D场景更逼真?(上)
Posted 凯小默
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了视觉高级篇23 # 如何模拟光照让3D场景更逼真?(上)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
说明
【跟月影学可视化】学习笔记。
光照效果简介
物体的光照效果是由光源、介质(物体的材质)和反射类型决定的,而反射类型又由物体的材质特点决定。
在 3D 光照模型中,根据不同的光源特点分为四种:
环境光(Ambient Light):指物体所在的三维空间中天然的光,它充满整个空间,在每一处的光照强度都一样。- 特点1:在空间中均匀分布,在任何位置上环境光的颜色都相同
- 特点2:环境光没有方向,与物体的材质有关
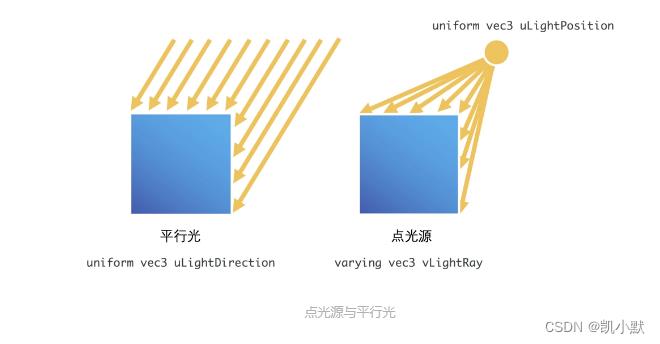
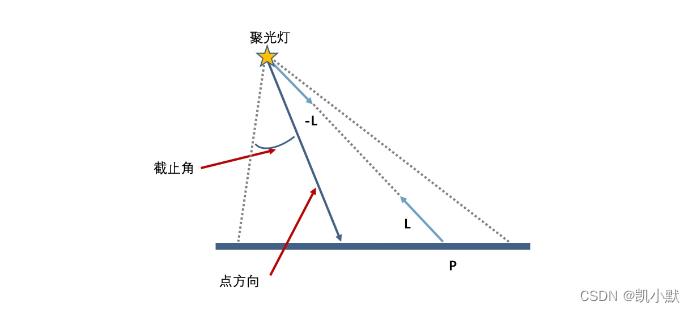
平行光(Directional Light):平行光是朝着某个方向照射的光,能够照亮几何体的一部分表面,它属于有向光。点光源(Positional Light):指空间中某一点发出的光,与方向光不同的是,点光源不仅有方向属性,还有位置属性。聚光灯(Spot Light):与点光源相比,聚光灯增加了方向以及角度范围,只有在这个范围内,光线才能照到。
点光源跟平行光的示意图:
聚光灯示意图:
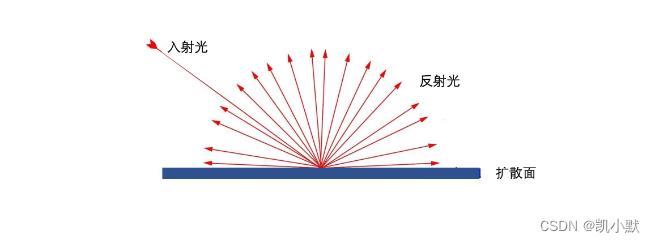
有向光在与物体发生作用的时候,根据物体的材质特性,会产生两种反射类型:
漫反射(Diffuse reflection)镜面反射(Specular reflection)
漫反射示意图:
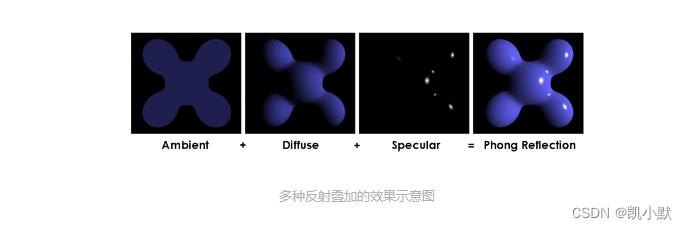
一个物体最终的光照效果,是漫反射、镜面反射以及环境光叠加在一起的效果,示意图如下:
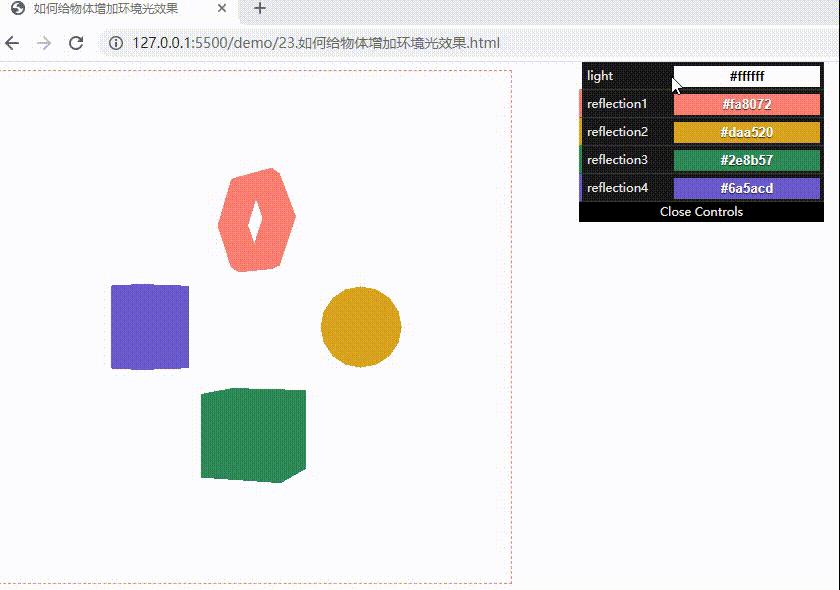
如何给物体增加环境光效果?
环境光没有方向,物体表面反射环境光的效果,只和环境光本身以及材质的反射率有关。
物体在环境光中呈现的颜色的公式如下:(环境光的颜色为 L,材质对光的反射率为 R。)
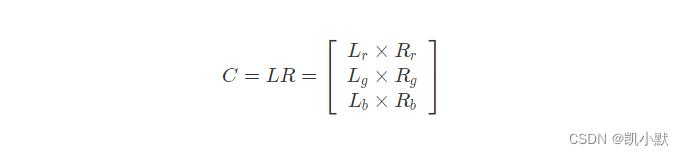
下面实现给物体增加环境光效果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>如何给物体增加环境光效果</title>
<style>
canvas
border: 1px dashed #fa8072;
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script type="module">
import Renderer, Camera, Transform, Sphere, Box, Cylinder, Torus, Orbit, Program, Mesh, Color from './common/lib/ogl/index.mjs';
// javascript Controller Library
import * as dat from './common/lib/dat.gui.js';
console.log(dat)
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const renderer = new Renderer(
canvas,
width: 512,
height: 512,
);
const gl = renderer.gl;
gl.clearColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
const camera = new Camera(gl, fov: 35);
camera.position.set(0, 0, 10);
camera.lookAt([0, 0, 0]);
const scene = new Transform();
const vertex = `
precision highp float;
attribute vec3 position;
attribute vec3 normal;
uniform mat4 modelViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 projectionMatrix;
uniform mat3 normalMatrix;
void main()
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(position, 1.0);
`;
// 传入环境光 ambientLight 和材质反射率 materialReflection
const fragment = `
precision highp float;
uniform vec3 ambientLight;
uniform vec3 materialReflection;
void main()
gl_FragColor.rgb = ambientLight * materialReflection;
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
`;
// 创建四个不同的几何体,初始化它们的环境光 ambientLight 以及材质反射率 materialReflection
const sphereGeometry = new Sphere(gl);
const cubeGeometry = new Box(gl);
const cylinderGeometry = new Cylinder(gl);
const torusGeometry = new Torus(gl);
const program1 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight: value: [1, 1, 1],
materialReflection: value: [250/255, 128/255, 114/255],
,
);
const program2 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight: value: [1, 1, 1],
materialReflection: value: [218/255, 165/255, 32/255],
,
);
const program3 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight: value: [1, 1, 1],
materialReflection: value: [46/255, 139/255, 87/255],
,
);
const program4 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight: value: [1, 1, 1],
materialReflection: value: [106/255, 90/255, 205/255],
,
);
const torus = new Mesh(gl, geometry: torusGeometry, program: program1);
torus.position.set(0, 1.3, 0);
torus.setParent(scene);
const sphere = new Mesh(gl, geometry: sphereGeometry, program: program2);
sphere.position.set(1.3, 0, 0);
sphere.setParent(scene);
const cube = new Mesh(gl, geometry: cubeGeometry, program: program3);
cube.position.set(0, -1.3, 0);
cube.setParent(scene);
const cylinder = new Mesh(gl, geometry: cylinderGeometry, program: program4);
cylinder.position.set(-1.3, 0, 0);
cylinder.setParent(scene);
const controls = new Orbit(camera);
// 添加动画
requestAnimationFrame(update);
function update()
requestAnimationFrame(update);
controls.update();
torus.rotation.y -= 0.02;
sphere.rotation.y -= 0.03;
cube.rotation.y -= 0.04;
cylinder.rotation.y -= 0.02;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
// 添加控制
const gui = new dat.GUI();
const palette =
light: '#FFFFFF',
reflection1: '#fa8072', // salmon rgb(250, 128, 114) [250/255, 128/255, 114/255, 1]
reflection2: '#daa520', // goldenrod rgb(218, 165, 32) [218/255, 165/255, 32/255, 1]
reflection3: '#2e8b57', // seagreen rgb(46, 139, 87) [46/255, 139/255, 87/255, 1]
reflection4: '#6a5acd', // slateblue rgb(106, 90, 205) [106/255, 90/255, 205/255, 1]
;
gui.addColor(palette, 'light').onChange((val) =>
const color = new Color(val);
program1.uniforms.ambientLight.value = color;
program2.uniforms.ambientLight.value = color;
program3.uniforms.ambientLight.value = color;
program4.uniforms.ambientLight.value = color;
);
gui.addColor(palette, 'reflection1').onChange((val) =>
program1.uniforms.materialReflection.value = new Color(val);
);
gui.addColor(palette, 'reflection2').onChange((val) =>
program2.uniforms.materialReflection.value = new Color(val);
);
gui.addColor(palette, 'reflection3').onChange((val) =>
program3.uniforms.materialReflection.value = new Color(val);
);
gui.addColor(palette, 'reflection4').onChange((val) =>
program4.uniforms.materialReflection.value = new Color(val);
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
如何给物体增加平行光效果?
有向光的漫反射在各个方向上的反射光均匀分布,反射强度与光的射入方向与法线的夹角的余弦成正比。
下面实现给物体增加平行光效果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>如何给物体增加平行光效果</title>
<style>
canvas
border: 1px dashed #fa8072;
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script type="module">
import Renderer, Camera, Transform, Sphere, Box, Cylinder, Torus, Orbit, Program, Mesh, Color from './common/lib/ogl/index.mjs';
// JavaScript Controller Library
import * as dat from './common/lib/dat.gui.js';
console.log(dat)
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const renderer = new Renderer(
canvas,
width: 512,
height: 512,
);
const gl = renderer.gl;
gl.clearColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
const camera = new Camera(gl, fov: 35);
camera.position.set(0, 0, 10);
camera.lookAt([0, 0, 0]);
const scene = new Transform();
// 在顶点着色器中计算光线的方向的运算次数少
const vertex = `
precision highp float;
attribute vec3 position;
attribute vec3 normal;
uniform mat4 modelViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 projectionMatrix;
uniform mat4 viewMatrix;
uniform mat3 normalMatrix;
// 添加一道平行光
uniform vec3 directionalLight;
varying vec3 vNormal;
varying vec3 vDir;
void main()
// 计算光线方向
vec4 invDirectional = viewMatrix * vec4(directionalLight, 0.0);
vDir = -invDirectional.xyz;
// 计算法向量
vNormal = normalize(normalMatrix * normal);
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(position, 1.0);
`;
// 传入环境光 ambientLight 和材质反射率 materialReflection
// 在片元着色器里,计算光线方向与法向量夹角的余弦,计算出漫反射光。
const fragment = `
precision highp float;
uniform vec3 ambientLight;
uniform vec3 materialReflection;
uniform vec3 directionalLightColor;
varying vec3 vNormal;
varying vec3 vDir;
void main()
// 求光线与法线夹角的余弦
float cos = max(dot(normalize(vDir), vNormal), 0.0);
// 计算漫反射
vec3 diffuse = cos * directionalLightColor;
// 合成颜色
gl_FragColor.rgb = (ambientLight + diffuse) * materialReflection;
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
`;
// 创建四个不同的几何体,初始化它们的环境光 ambientLight 以及材质反射率 materialReflection
const sphereGeometry = new Sphere(gl);
const cubeGeometry = new Box(gl);
const cylinderGeometry = new Cylinder(gl);
const torusGeometry = new Torus(gl);
// 添加一个水平向右的白色平行光
const ambientLight = value: [1, 1, 1] ;
const directional =
directionalLight:
value: [1, 0, 0]
,
directionalLightColor:
value: [1, 1, 1]
;
const program1 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight,
materialReflection: value: [250/255, 128/255, 114/255],
...directional
,
);
const program2 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight,
materialReflection: value: [218/255, 165/255, 32/255],
...directional
,
);
const program3 = new Program(gl,
vertex,
fragment,
uniforms:
ambientLight,
materialReflection: value: [46/255, 139/255, 87/255],
...directional
,
);
const program4 = new Program(gl,