2018-1-23 7周2次课 iostat,free,ps,netstat,tcpdump
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2018-1-23 7周2次课 iostat,free,ps,netstat,tcpdump相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
10.6 监控io性能


iostat命令和sar属于同一个包,安装sysstat就可以
·查看磁盘使用情况iostat:(使用方法与vmstat一致)

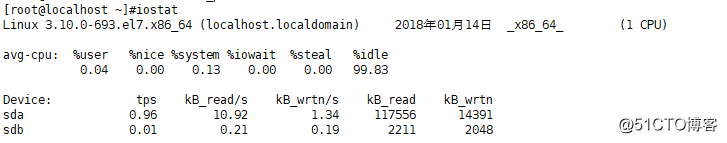
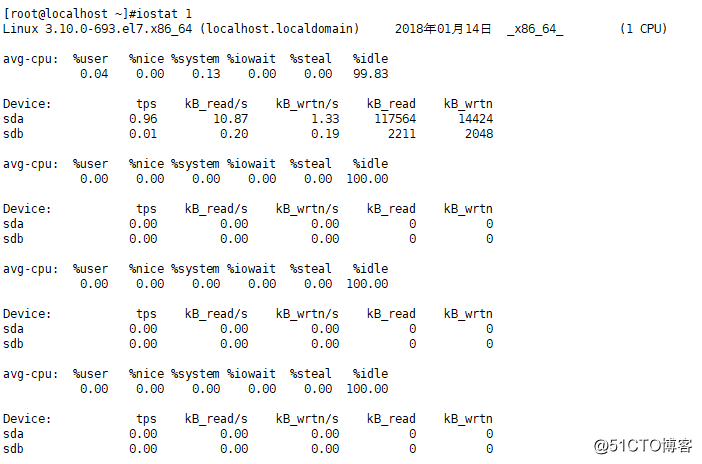
·每隔一秒查看一次磁盘使用情况

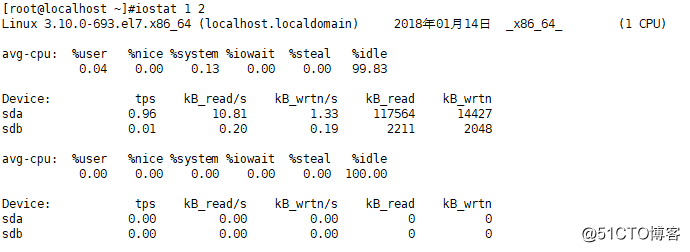
·每隔一秒查看磁盘情况一次,共查看两次

·iostat -x

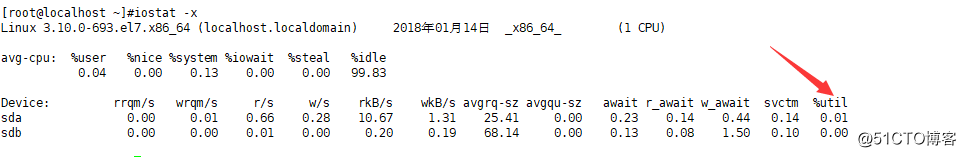
(%util表示一秒内IO操作所占的比例)
如果数字很大,那么磁盘读写也会很大;但是如果读写不大,而%util很大,那么磁盘可能存在故障
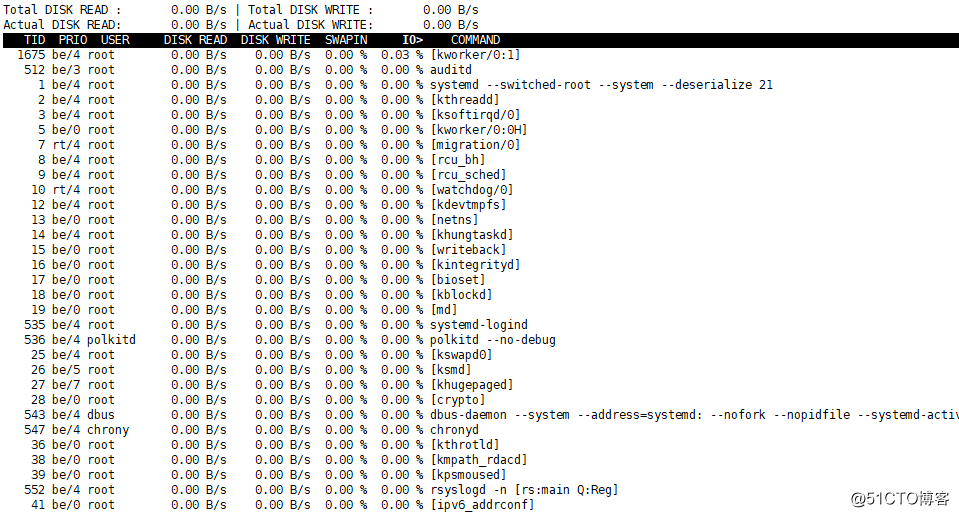
·iotop命令:
安装iotop命令:[[email protected] ~]#yum install -y iotop
iotop和top命令类似,都是动态显示

10.7 free命令
·查看内存使用情况
[[email protected] ~]# free total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 999696 120152 621148 6820 258396 696728 Swap: 2097148 0 2097148
·指定单位为M
[[email protected] ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 976 117 605 6 253 680 Swap: 2047 0 2047
·可视化,方便查看
[[email protected] ~]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 976M 117M 605M 6.7M 253M 680M Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
cache缓存:磁盘——>内存(cache)——>CPU
buffer缓冲:CPU——>内存(buffer)——>磁盘
公式:
total = free + used + buff/cache
available = free + buff/cache的剩余部分
关注点:available
10.8 ps命令
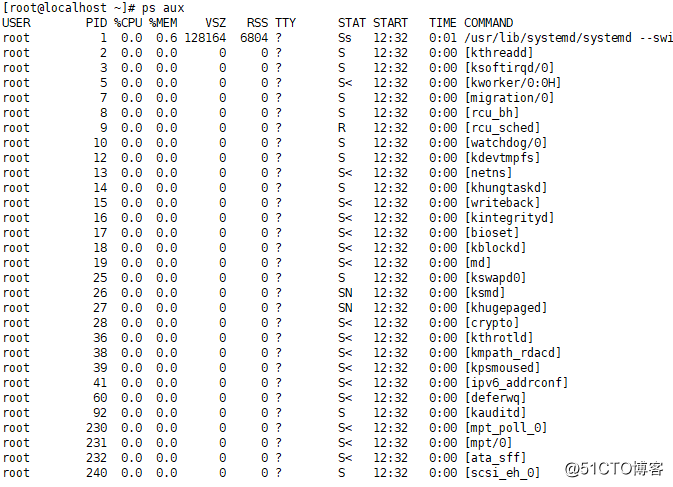
·查看系统进程
[[email protected] ~]# ps aux
·查看某个进程是否在运行:ps aux |grep 关键字
[[email protected] ~]# ps aux |grep mysql root 1812 0.0 0.0 112676 980 pts/0 S+ 16:48 0:00 grep --color=auto mysql
·查看系统所有进程,除了ps aux还可以使用ps -elf
[[email protected] ~]# ps -elf

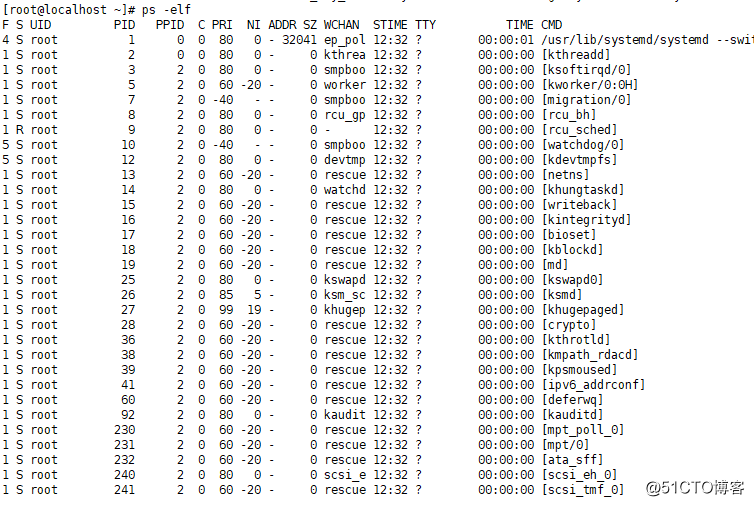
PID的用处:1,kill进程用 kill + 进程号
2,查看进程所在目录 ll /proc/数字
STAT部分说明:
D 不能中断的进程
R run状态的进程(某个时间段内在使用)
S sleep状态进程 (vmstat运行时间很短,运行一下就sleep,并不会消耗CPU资源)
T 暂停的进程
+ 前台进程
Z 僵尸进程(很少会有,但也会有)
< 高优先级进程
N 低优先级进程(不急)
L 内存中被锁了内存分页(不常见)
s 主进程
l 多线程进程(一个进程中有多个线程)
10.9 查看网络状态


·查看网络状态:netstat

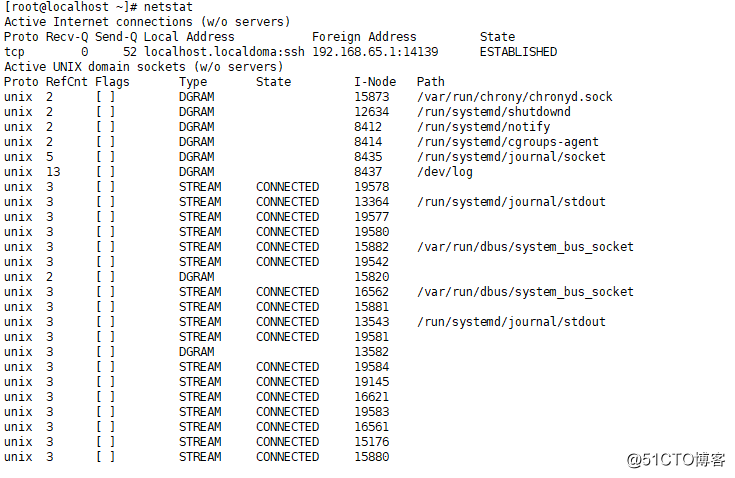
(不详细列举)
·查看监听端口
netstat -lnp (l=listen)

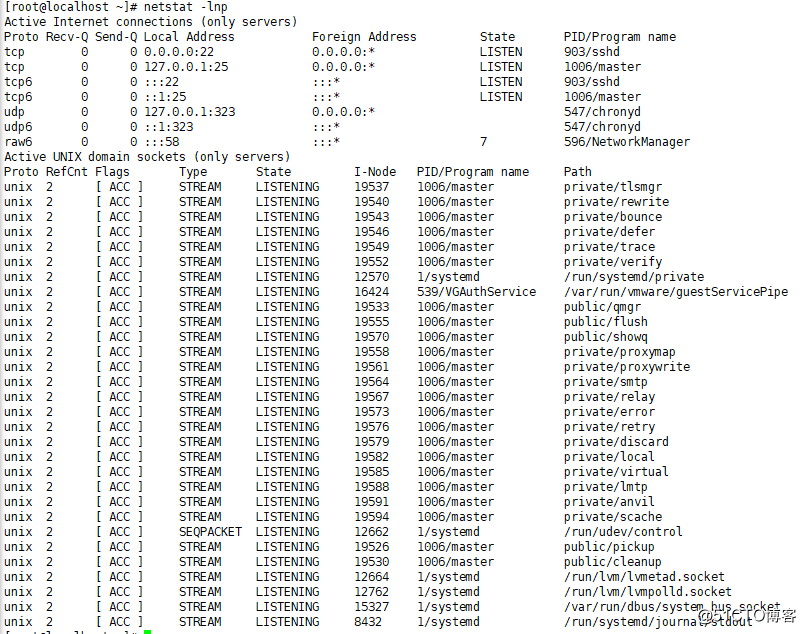
·查看所有连接状态:netstat -an

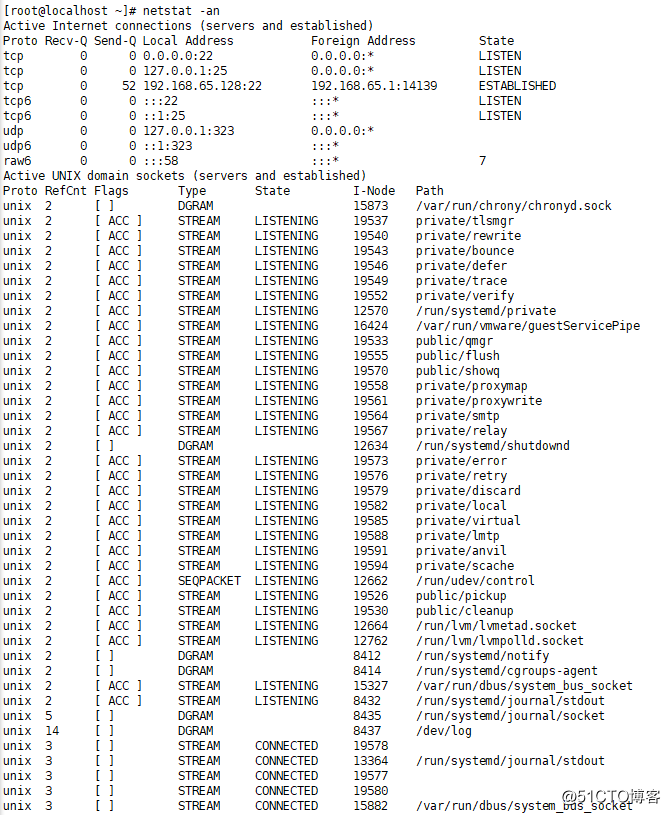
(不详细列举)
·只看tcp的,不包含socket:netstat -lntp
[[email protected] ~]# netstat -lntp Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 903/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1006/master tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 903/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1006/master
·只看tcp和udp的:netstat -luntp
[[email protected] netstat -luntp Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 903/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1006/master tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 903/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1006/master udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:* 547/chronyd udp6 0 0 ::1:323 :::* 547/chronyd
·ss -an 和 netstat异曲同工(缺点是不显示进程的名字)
[[email protected] ~]# ss -an |grep -i listen u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/tlsmgr 19537 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/rewrite 19540 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/bounce 19543 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/defer 19546 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/trace 19549 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/verify 19552 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 128 /run/systemd/private 12570 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 32 /var/run/vmware/guestServicePipe 16424 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 public/qmgr 19533 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 public/flush 19555 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 public/showq 19570 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/proxymap 19558 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/proxywrite 19561 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/smtp 19564 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/relay 19567 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/error 19573 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/retry 19576 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/discard 19579 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/local 19582 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/virtual 19585 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/lmtp 19588 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/anvil 19591 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 private/scache 19594 * 0 u_seq LISTEN 0 128 /run/udev/control 12662 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 public/pickup 19526 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 100 public/cleanup 19530 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 128 /run/lvm/lvmetad.socket 12664 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 128 /run/lvm/lvmpolld.socket 12762 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 128 /var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket 15327 * 0 u_str LISTEN 0 128 /run/systemd/journal/stdout 8432 * 0 tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* tcp LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* tcp LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* tcp LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::*
netstat -an | awk '/^tcp/ {++sta[$NF]} END {for(key in sta) print key,"\t",sta[key]}'
[[email protected] ~]# netstat -an | awk '/^tcp/ {++sta[$NF]} END {for(key in sta) print key,"\t",sta[key]}' LISTEN 4 ESTABLISHED 1
(关注ESTABLISHED,数字越大,越忙)
10.10 Linux下抓包
抓包工具:tcpdump
安装tcpdump:yum install -y tcpdump
·使用方法:tcpdump -nn
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -nn tcpdump: packet printing is not supported for link type NFLOG: use -w
(因为网卡名比较特殊,默认时eth0,所以无法使用,需要指定)
·指定网卡抓包:tcpdump -nn -i 网卡名

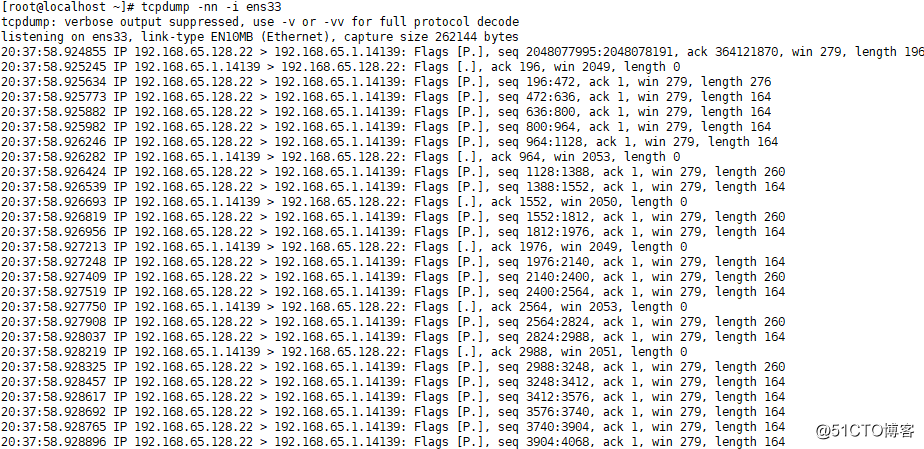
(内容过多,中间省略)

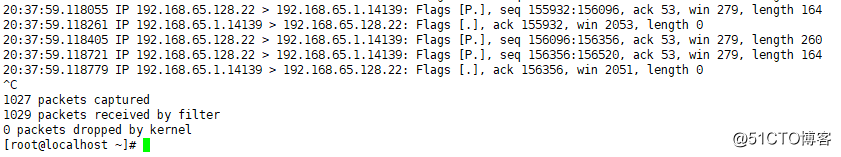
-nn的第一个n表示IP用数字显示出来,如果不加n,则会显示主机名

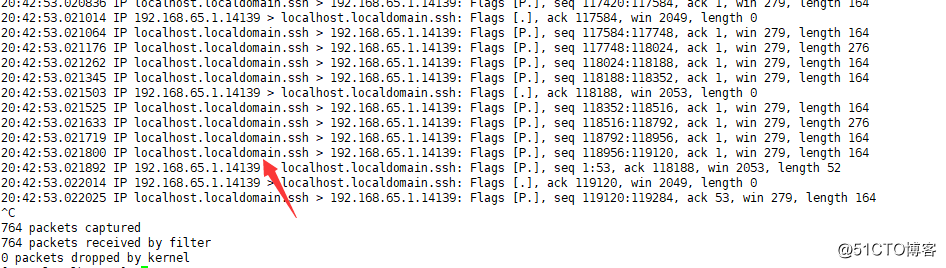
-nn用数字显示,比较直观
(关注点:数据流向,length)
·指定端口:tcpdump -nn port 端口号
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -nn -i ens33 port 22
·指定不要的端口:tcpdump -nn not port 端口号
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -nn -i ens33 not port 22
·同时指定不要的端口和指定IP的包:tcpdump -nn not port 端口号 and host 指定IP地址
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -nn -i ens33 not port 22 and host 192.168.65.1
·指定数据包个数:tcpdump -nn -c 个数
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -nn -i ens33 -c 20 ##抓20个包

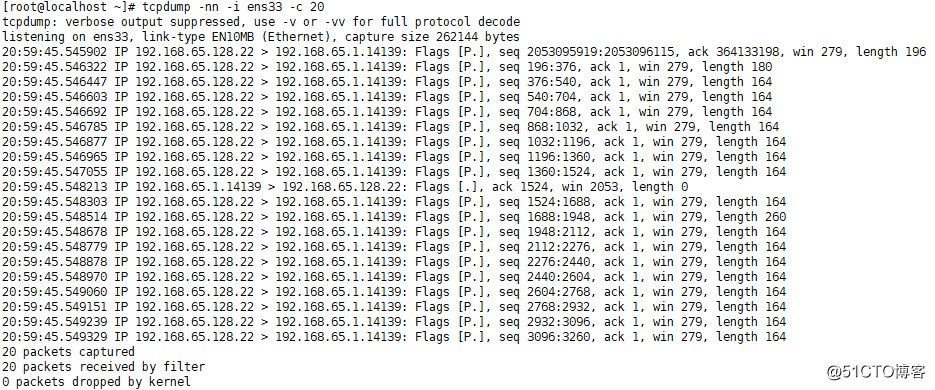
·将指定个数抓的包存到指定文件中:tcpdump -nn -c 个数 -w 绝对路径
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -nn -i ens33 -c 100 -w /tmp/1.cap tcpdump: listening on ens33, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 100 packets captured 100 packets received by filter 0 packets dropped by kernel
(1.cap是无法cat的)
·查看.cap文件:tcpdump -r 目标文件
[[email protected] ~]# tcpdump -r /tmp/1.cap

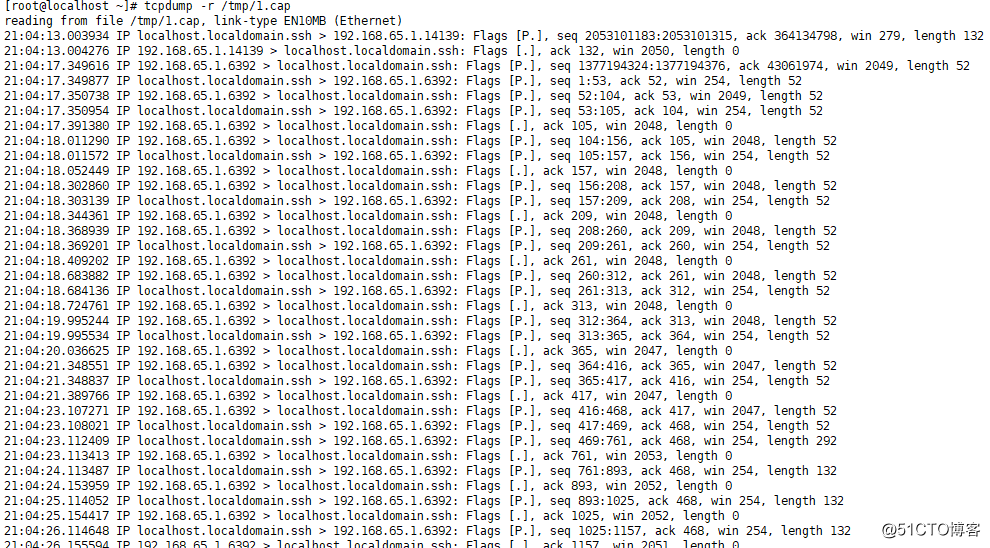
·tshark命令
安装:yum install -y wireshark
查看指定网卡80端口web访问情况:
[[email protected] ~]# tshark -n -t a -R http.request -T fields -e "frame.time" -e "ip.src" -e "http.host" -e "http.request.method" -e "http.request.uri"
(类似于访问日志,可以查看什么IP访问什么链接)
以上是关于2018-1-23 7周2次课 iostat,free,ps,netstat,tcpdump的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章