YOLOV7学习记录之模型推理
Posted 彭祥.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了YOLOV7学习记录之模型推理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前面我们学习了YOLOV7的训练过程,今天我们学习其推理过程,即模型预测:其包含损失函数计算,输出值解码,非极大值抑制,mAP计算等过程。
同时还介绍原始图像上绘制目标框等功能。
我们从predict.py文件开始,这里博主将原本的单张图像预测修改为多张图像,只是加了个list循环而已。所用到的文件如下:
我们先来看一下predict的流程,其还是很容易理解的
生成模型:yolo = YOLO() yolo.py 此时只初始化并生成yolo模型
初始化参数 :模型权重文件目录等
检测图像:r_image = yolo.detect_image(image, crop = crop, count=count)
接下来便是在detect_image函数中层层调用
灰度转化:image = cvtColor(image)
图像大小调整:image_data = resize_image()
由于是预测过程,是不存在梯度变化的,故接下来的操作是在无梯度变化下进行的,即:with torch.no_grad():
将图像送入网络:outputs = self.net(images)
将输出解码:outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
非极大值抑制:results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression()
在图像中绘制预测框
将输出解码
输出解码是指将yolo三个预测头的输出转换为图片中目标的类型,位置参数(边框中心坐标和长宽),目标置信度等,其功能定义在util_box,py文件中。
首先是类的定义及初始化
class DecodeBox():
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, anchors_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]]):
super(DecodeBox, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.input_shape = input_shape
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 20x20的特征层对应的anchor是[142, 110],[192, 243],[459, 401]特征图感受野大,使用大的anchor
# 40x40的特征层对应的anchor是[36, 75],[76, 55],[72, 146]
# 80x80的特征层对应的anchor是[12, 16],[19, 36],[40, 28]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
self.anchors_mask = anchors_mask
执行解码过程:
def decode_box(self, inputs):
outputs = []
for i, input in enumerate(inputs):
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# batch_size = 1
# batch_size, 3 * (4 + 1 + 80), 20, 20
# batch_size, 255, 40, 40
# batch_size, 255, 80, 80
#-----------------------------------------------#
batch_size = input.size(0)
input_height = input.size(2)
input_width = input.size(3)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入为640x640时
# stride_h = stride_w = 32、16、8
#-----------------------------------------------#
stride_h = self.input_shape[0] / input_height
stride_w = self.input_shape[1] / input_width
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 此时获得的scaled_anchors大小是相对于特征层的
#-------------------------------------------------#
scaled_anchors = [(anchor_width / stride_w, anchor_height / stride_h) for anchor_width, anchor_height in self.anchors[self.anchors_mask[i]]]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# batch_size, 3, 20, 20, 85
# batch_size, 3, 40, 40, 85
# batch_size, 3, 80, 80, 85
#-----------------------------------------------#
prediction = input.view(batch_size, len(self.anchors_mask[i]),
self.bbox_attrs, input_height, input_width).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
w = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 2])
h = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 3])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得置信度,是否有物体
#-----------------------------------------------#
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 种类置信度
#-----------------------------------------------#
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:])
FloatTensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
LongTensor = torch.cuda.LongTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.LongTensor
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角
# batch_size,3,20,20
#----------------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, input_width - 1, input_width).repeat(input_height, 1).repeat(
batch_size * len(self.anchors_mask[i]), 1, 1).view(x.shape).type(FloatTensor)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, input_height - 1, input_height).repeat(input_width, 1).t().repeat(
batch_size * len(self.anchors_mask[i]), 1, 1).view(y.shape).type(FloatTensor)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 按照网格格式生成先验框的宽高
# batch_size,3,20,20
#----------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_w = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([0]))
anchor_h = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([1]))
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(h.shape)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用预测结果对先验框进行调整
# 首先调整先验框的中心,从先验框中心向右下角偏移
# 再调整先验框的宽高。
# x 0 ~ 1 => 0 ~ 2 => -0.5, 1.5 => 负责一定范围的目标的预测
# y 0 ~ 1 => 0 ~ 2 => -0.5, 1.5 => 负责一定范围的目标的预测
# w 0 ~ 1 => 0 ~ 2 => 0 ~ 4 => 先验框的宽高调节范围为0~4倍
# h 0 ~ 1 => 0 ~ 2 => 0 ~ 4 => 先验框的宽高调节范围为0~4倍
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes = FloatTensor(prediction[..., :4].shape)
pred_boxes[..., 0] = x.data * 2. - 0.5 + grid_x
pred_boxes[..., 1] = y.data * 2. - 0.5 + grid_y
pred_boxes[..., 2] = (w.data * 2) ** 2 * anchor_w
pred_boxes[..., 3] = (h.data * 2) ** 2 * anchor_h
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将输出结果归一化成小数的形式
#----------------------------------------------------------#
_scale = torch.Tensor([input_width, input_height, input_width, input_height]).type(FloatTensor)
output = torch.cat((pred_boxes.view(batch_size, -1, 4) / _scale,
conf.view(batch_size, -1, 1), pred_cls.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_classes)), -1)
outputs.append(output.data)
return outputs
对预测框进行筛选(置信度过滤和非极大值抑制)
一张640x640的图片输入到模型,会有8400个预测框(20X20+40X40+80X80),图片中不可能有那么目标,即便有,也无法绘制出来,我们需要对预测框进行筛选。筛选共分为两轮,第一轮是把置信度(目标置信度)低的预测框给过滤掉,第二轮是NMS,由于第一轮比较简单,并且两轮都需要遍历图片,所以我们把两轮写到同一个函数中。
简单来说,在一个图像中,每一个网格都会有一个预测框,它们都认为目标中心点在自己框内,那么我们就需要进行筛选,过程如下:
1、把置信度最高的一个boundingbox(bbox)作为目标,然后对比剩下bbox与目标bbox之间的交叉区域
2、如果交叉区域大于设定的阈值,则认为该框与我设定的最大框表示的是同一个目标,那么在剩下的bbox中去除该bbox(即使该bbox的置信度与目标bbox的置信度一样)—-这个操作就是抑制最大重叠区域
3、把第二置信度高的bbox作为目标,重复1、2
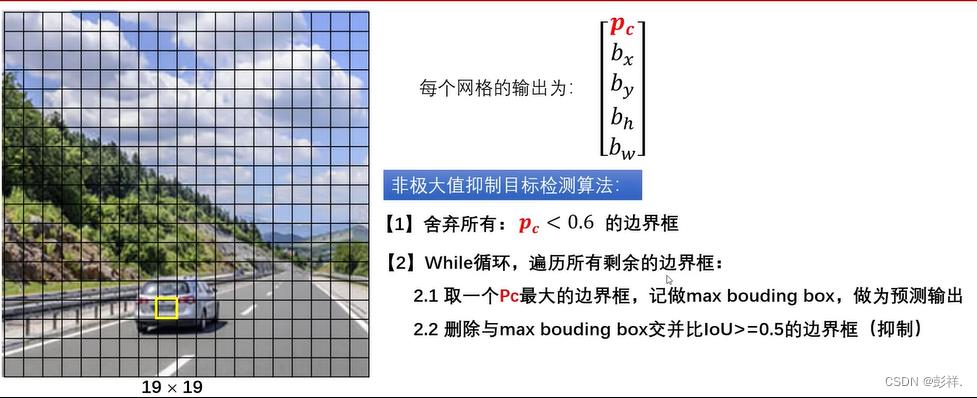
关于IOU,可以阅读博文:
def non_max_suppression(self, prediction, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果的格式转换成左上角右下角的格式。
# prediction [batch_size, num_anchors, 85]
#----------------------------------------------------------#
box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape)
box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4]
output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))]
for i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 对种类预测部分取max。
# class_conf [num_anchors, 1] 种类置信度
# class_pred [num_anchors, 1] 种类
#----------------------------------------------------------#
class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] * class_conf[:, 0] >= conf_thres).squeeze()
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 根据置信度进行预测结果的筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask]
class_conf = class_conf[conf_mask]
class_pred = class_pred[conf_mask]
if not image_pred.size(0):
continue
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# detections [num_anchors, 7]
# 7的内容为:x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1)
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测结果中包含的所有种类
#------------------------------------------#
unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique()
if prediction.is_cuda:
unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda()
detections = detections.cuda()
for c in unique_labels:
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得某一类得分筛选后全部的预测结果
#------------------------------------------#
detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c]
#------------------------------------------#
# 使用官方自带的非极大抑制会速度更快一些!
# 筛选出一定区域内,属于同一种类得分最大的框
#------------------------------------------#
keep = nms(
detections_class[:, :4],
detections_class[:, 4] * detections_class[:, 5],
nms_thres
)
max_detections = detections_class[keep]
# # 按照存在物体的置信度排序
# _, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4]*detections_class[:, 5], descending=True)
# detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index]
# # 进行非极大抑制
# max_detections = []
# while detections_class.size(0):
# # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉
# max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0))
# if len(detections_class) == 1:
# break
# ious = bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:])
# detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres]
# # 堆叠
# max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data
# Add max detections to outputs
output[i] = max_detections if output[i] is None else torch.cat((output[i], max_detections))
if output[i] is not None:
output[i] = output[i].cpu().numpy()
box_xy, box_wh = (output[i][:, 0:2] + output[i][:, 2:4])/2, output[i][:, 2:4] - output[i][:, 0:2]
output[i][:, :4] = self.yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image)
return output
其中使用了一个名为bbox_iou的函数,它是用来求边框之间的IOU,位于util.py中
在图像中绘制预测框
先前的实验中我们一直使用模拟数据,而在现实中我们使用真实数据时不见得会符合标准,如我们这里要求图像是正方形且为32的倍数,而下方的图像很明显不符合要求

对输入图片进行调整(letterbox及缩放)
这里调整到指定大小,不是直接暴力缩放,而是要高宽等比缩放,那么需要先使用letterbox算法,即在上下或者左右添加灰条,添加上灰条后再进行缩放。
def resize_image(image, size, letterbox_image):
iw, ih = image.size
w, h = size
if letterbox_image:
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', size, (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
else:
new_image = image.resize((w, h), Image.BICUBIC)
return new_image
将边框绘制在图片中
先将字体文件simhei.ttf和coco类名文件下载下来,复制到yolox_from_scratch/model_data中,结果如下:
下面这段代码是绘制边框的代码,其集成在了detect_image函数中了
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='model_data/simhei.ttf', size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = int(max((image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // np.mean(self.input_shape), 1))
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 计数
#---------------------------------------------------------#
if count:
print("top_label:", top_label)
classes_nums = np.zeros([self.num_classes])
for i in range(self.num_classes):
num = np.sum(top_label == i)
if num > 0:
print(self.class_names[i], " : ", num)
classes_nums[i] = num
print("classes_nums:", classes_nums)
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# 是否进行目标的裁剪
#---------------------------------------------------------#
if crop:
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_boxes)):
top, left, bottom, right = top_boxes[i]
top = max(0, np.floor(top).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right).astype('int32'))
dir_save_path = "img_crop"
以上是关于YOLOV7学习记录之模型推理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章