YOLO目标检测之IOU计算及其衍变体
Posted 彭祥.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了YOLO目标检测之IOU计算及其衍变体相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
IOU损失函数目前主要应用于目标检测的领域,其演变的过程如下:IOU --> GIOU --> DIOU -->CIOU损失函数,每一种损失函数都较上一种损失函数有所提升。下面来具体介绍这几种损失函数。
IOU(Intersection over Union)
IoU就是我们所说的交并比,是目标检测中最常用的指标,在anchor-based的方法中,他的作用不仅用来确定正样本和负样本,还可以用来评价输出框(predict box)和ground-truth的距离。
IOU计算公式

优点
其有以下两个优点:
1.它可以反映预测检测框与真实检测框的检测效果。
2.尺度不变性,也就是对尺度不敏感(scale invariant), 在regression任务中,判断predict box和gt的距离最直接的指标就是IoU。(满足非负性;同一性;对称性;三角不等性)
其计算的是两个box的交并比:如下图所示

a,b分别表示两个框,其中1,2表示每个框的左上角坐标与右下角坐标
但其也存在以下三种情况:

这时我们就要进行判断了
公式原理
先计算交集部分(即公式分子部分):
相交部分左上角坐标为:

相交部分右下角坐标为:

那么相交部分的面积计算公式就是为:

这里,都+1的目的,我个人认为是为了排除两个框之间重叠的像素对面积的影响,取max(*,0)的目的是为了避免出现负数的情况
再来计算一下两个框的并集部分:
两个框的面积为:
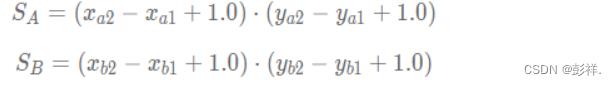
计算相比部分面积:

所以,最终的iou计算公式为:

代码实现
def compute_IOU(rec1,rec2):
"""
计算两个矩形框的交并比。
:param rec1: (x0,y0,x1,y1) (x0,y0)代表矩形左上的顶点,(x1,y1)代表矩形右下的顶点。下同。
:param rec2: (x0,y0,x1,y1)
:return: 交并比IOU.
"""
left_column_max = max(rec1[0],rec2[0])
right_column_min = min(rec1[2],rec2[2])
up_row_max = max(rec1[1],rec2[1])
down_row_min = min(rec1[3],rec2[3])
#两矩形无相交区域的情况
if left_column_max>=right_column_min or down_row_min<=up_row_max:
return 0
# 两矩形有相交区域的情况
else:
S1 = (rec1[2]-rec1[0])*(rec1[3]-rec1[1])
S2 = (rec2[2]-rec2[0])*(rec2[3]-rec2[1])
S_cross = (down_row_min-up_row_max)*(right_column_min-left_column_max)
return S_cross/(S1+S2-S_cross)
#测试样例1
r1=(2,3,10,12)
r2=(12,5,20,24)
IOU = compute_IOU(r1,r2)
print("测试样例1,IOU:%f"%IOU)
#测试样例2
r1=(2,2,4,4)
r2=(3,3,5,5)
IOU = compute_IOU(r1,r2)
print("测试样例2,IOU:%f"%IOU)

IOU作为损失函数会出现的问题(缺点)
1.如果两个框没有相交,根据定义,IoU=0,不能反映两者的距离大小(重合度)。同时因为loss=0,没有梯度回传,无法进行学习训练。
2.IoU无法精确的反映两者的重合度大小。如下图所示,三种情况IoU都相等,但看得出来他们的重合度是不一样的,左边的图回归的效果最好,右边的最差。

为了解决以上问题,提出了GIOU
GIOU(Generalized Intersection over Union)
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.09630

上面公式的意思是:先计算两个框的最小闭包区域面积 Ac (通俗理解:同时包含了预测框和真实框的最小框的面积),再计算出IoU,再计算闭包区域中不属于两个框的区域占闭包区域的比重,最后用IoU减去这个比重得到GIoU
特性优势
1.与IoU相似,GIoU也是一种距离度量,作为损失函数的话,LGIOU=1-GIOU ,满足损失函数的基本要求
2.GIoU对scale不敏感
3.GIoU是IoU的下界,在两个框无限重合的情况下,IoU=GIoU=1
IoU取值[0,1],但GIoU有对称区间,取值范围[-1,1]。在两者重合的时候取最大值1,在两者无交集且无限远的时候取最小值-1,因此GIoU是一个非常好的距离度量指标。
.与IoU只关注重叠区域不同,GIoU不仅关注重叠区域,还关注其他的非重合区域,能更好的反映两者的重合度。
def Giou(rec1,rec2):
#分别是第一个矩形左右上下的坐标
x1,x2,y1,y2 = rec1
x3,x4,y3,y4 = rec2
iou = Iou(rec1,rec2)
area_C = (max(x1,x2,x3,x4)-min(x1,x2,x3,x4))*(max(y1,y2,y3,y4)-min(y1,y2,y3,y4))
area_1 = (x2-x1)*(y1-y2)
area_2 = (x4-x3)*(y3-y4)
sum_area = area_1 + area_2
w1 = x2 - x1 #第一个矩形的宽
w2 = x4 - x3 #第二个矩形的宽
h1 = y1 - y2
h2 = y3 - y4
W = min(x1,x2,x3,x4)+w1+w2-max(x1,x2,x3,x4) #交叉部分的宽
H = min(y1,y2,y3,y4)+h1+h2-max(y1,y2,y3,y4) #交叉部分的高
Area = W*H #交叉的面积
add_area = sum_area - Area #两矩形并集的面积
end_area = (area_C - add_area)/area_C #闭包区域中不属于两个框的区域占闭包区域的比重
giou = iou - end_area
return giou
DIoU(Distance-IoU)
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08287.pdf
DIoU要比GIou更加符合目标框回归的机制,将目标与anchor之间的距离,重叠率以及尺度都考虑进去,使得目标框回归变得更加稳定,不会像IoU和GIoU一样出现训练过程中发散等问题。
基于IoU和GIoU存在的问题,作者提出了两个问题:
- 直接最小化anchor框与目标框之间的归一化距离是否可行,以达到更快的收敛速度?
- 如何使回归在与目标框有重叠甚至包含时更准确、更快?

其中,b ,bgt 分别代表了预测框和真实框的中心点,且 p 代表的是计算两个中心点间的欧式距离。c 代表的是能够同时包含预测框和真实框的最小闭包区域的对角线距离。

与GIoU loss类似,DIoU loss( LDIOU=1-DIOU )在与目标框不重叠时,仍然可以为边界框提供移动方向。
DIoU loss可以直接最小化两个目标框的距离,因此比GIoU loss收敛快得多。
对于包含两个框在水平方向和垂直方向上这种情况,DIoU损失可以使回归非常快,而GIoU损失几乎退化为IoU损失。
DIoU还可以替换普通的IoU评价策略,应用于NMS中,使得NMS得到的结果更加合理和有效。
def Diou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
dious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:#
return dious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
dious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
# #xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax->[:,0],[:,1],[:,2],[:,3]
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
dious = inter_area / union - (inter_diag) / outer_diag
dious = torch.clamp(dious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
dious = dious.T
return dious
CIoU(Complete-IoU)
论文考虑到bbox回归三要素中的长宽比还没被考虑到计算中,因此,进一步在DIoU的基础上提出了CIoU。其惩罚项如下面公式:

def bbox_overlaps_ciou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
cious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:
return cious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
cious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
u = (inter_diag) / outer_diag
iou = inter_area / union
with torch.no_grad():
arctan = torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)), 2)
S = 1 - iou
alpha = v / (S + v)
w_temp = 2 * w1
ar = (8 / (math.pi ** 2)) * arctan * ((w1 - w_temp) * h1)
cious = iou - (u + alpha * ar)
cious = torch.clamp(cious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
cious = cious.T
return cious
YOLOV7中的应用
在YOLOv7的pytorch版本中,以上四种方式都有实现以供选择。
def bbox_iou(self, box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7):#计算IOU,GIOU,DIOU
box2 = box2.T
if x1y1x2y2:
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else:
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \\
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
iou = inter / union
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 +
(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center distance squared
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi 以上是关于YOLO目标检测之IOU计算及其衍变体的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章