Spring - 事件监听机制 源码解析
Posted 小小工匠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring - 事件监听机制 源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录

Pre

众所周知,Spring Framework在 BeanFactory的基础容器之上扩展为了ApplicationContext上下文。 ApplicationContext处理包含了BeanFactory的全部基础功能之外,还额外提供了大量的扩展功能。

今天我们就来看看 扩展的 事件监听接口
概述
我们都知道 实现事件监听机制至少四个组成部分:
- 事件
- 事件生产者
- 事件消费者
- 控制器 (管理生产者、消费者和事件之间的注册监听关系)
在Spring中,事件监听机制主要实现是通过事件、事件监听器、事件发布者和事件广播器来实现。
ApplicationEvent ------ 事件

public abstract class ApplicationContextEvent extends ApplicationEvent
/**
* Create a new ContextStartedEvent.
* @param source the @code ApplicationContext that the event is raised for
* (must not be @code null)
*/
public ApplicationContextEvent(ApplicationContext source)
super(source);
/**
* Get the @code ApplicationContext that the event was raised for.
*/
public final ApplicationContext getApplicationContext()
return (ApplicationContext) getSource();
抽象父类ApplicationEvent,它的子抽象类ApplicationContextEvent 包含有当前ApplicationContext的引用,这样就可以确认每个事件是从哪一个Spring容器中发生的。
ApplicationListener ------ 事件监听器
顶级接口ApplicationListener,只有一个void onApplicationEvent(E event); ,当该监听器所监听的事件发生时,就会执行该方法
ApplicationEventPublisher ------ 事件发布者
顶级接口ApplicationEventPublisher,只有一个方法 void publishEvent(Object event); ,调用该方法就可以发生spring中的事件
ApplicationEventMulticaster ------ 事件广播器
spring中的事件核心控制器叫做事件广播器,两个作用
-
将事件监听器注册到广播器中
这样广播器就知道了每个事件监听器分别监听什么事件,且知道了每个事件对应哪些事件监听器在监听。
-
将事件广播给事件监听器
当有事件发生时,需要通过广播器来广播给所有的事件监听器,因为生产者只需要关心事件的生产,而不需要关心该事件都被哪些监听器消费。
spring主要的内置事件
ContextRefreshedEvent
ApplicationContext 被初始化或刷新时,该事件被发布。
也可以在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中使用 refresh()方法来发生。
此处的初始化是指:所有的Bean被成功装载,后处理Bean被检测并激活,所有Singleton Bean 被预实例化,ApplicationContext容器已就绪可用。
ContextStartedEvent
当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 start() 方法启动 ApplicationContext时,该事件被发布。
可以在接受到这个事件后重启任何停止的应用程序。
ContextStoppedEvent
当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中的 stop()停止ApplicationContext 时,发布这个事件。
可以在接受到这个事件后做必要的清理的工作
ContextClosedEvent
当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中的 close()方法关闭 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布。一个已关闭的上下文到达生命周期末端;它不能被刷新或重启
RequestHandledEvent
这是一个 web-specific 事件,告诉所有 bean HTTP 请求已经被服务。只能应用于使用DispatcherServlet的Web应用。在使用Spring作为前端的MVC控制器时,当Spring处理用户请求结束后,系统会自动触发该事件
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener
/**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
/**
* Create a new @code ApplicationListener for the given payload consumer.
* @param consumer the event payload consumer
* @param <T> the type of the event payload
* @return a corresponding @code ApplicationListener instance
* @since 5.3
* @see PayloadApplicationEvent
*/
static <T> ApplicationListener<PayloadApplicationEvent<T>> forPayload(Consumer<T> consumer)
return event -> consumer.accept(event.getPayload());
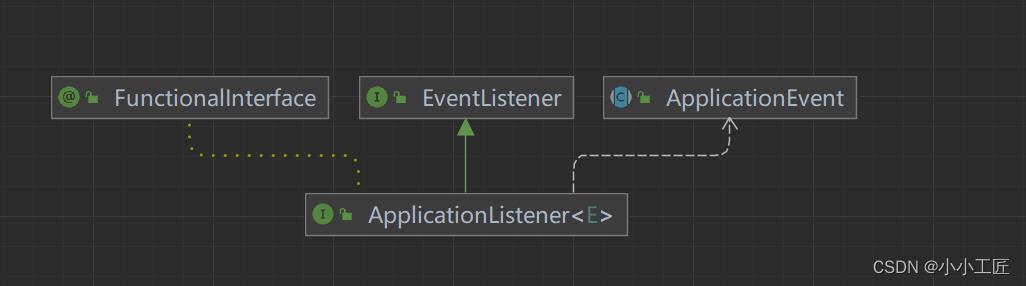
ApplicationListener可以监听某个事件的event,触发时机可以穿插在业务方法执行过程中,用户可以自定义某个业务事件。
源码分析
首先看看Spring在初始化的时候,有两个核心步骤和事件监听器有关,一个是初始化事件广播器,一个是注册所有的事件监听器
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
初始化事件广播器
/** Spring容器的事件广播器对象*/
private ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster;
/** 事件广播器对应的beanName*/
public static final String APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME = "applicationEventMulticaster";
/** 初始化事件广播器*/
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster()
//1.获取Spring容器BeanFactory对象
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
//2.从BeanFactory获取事件广播器的bean,如果存在说明是用户自定义的事件广播器
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME))
//2.1.给容器的事件广播器赋值
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
else
//3.如果没有自定义的,则初始化默认的事件广播器SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
//4.注册该bean
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
如果beanFactory中存在用于自定义的就使用自定义的,如果没有自定义的就创建新的默认的事件广播器SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象,然后赋值给applicationEventMulticaster对象。
注册事件监听器
/** 注册事件监听器*/
protected void registerListeners()
//1.遍历将通过编码方式创建的事件监听器加入到事件广播器中
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners())
//2.获取到当前事件广播器,添加事件监听器
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
//3.从BeanFactory中获取所有实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean,遍历加入到事件广播器中
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames)
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
//3.获取需要提前发布的事件
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null)
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess)
//5.遍历将提前发布的事件广播出去
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
从容器中找到所有的事件监听器,然后调用事件广播器的addApplicationListener方法将事件监听器添加到事件广播器中。

事件的发布和消费
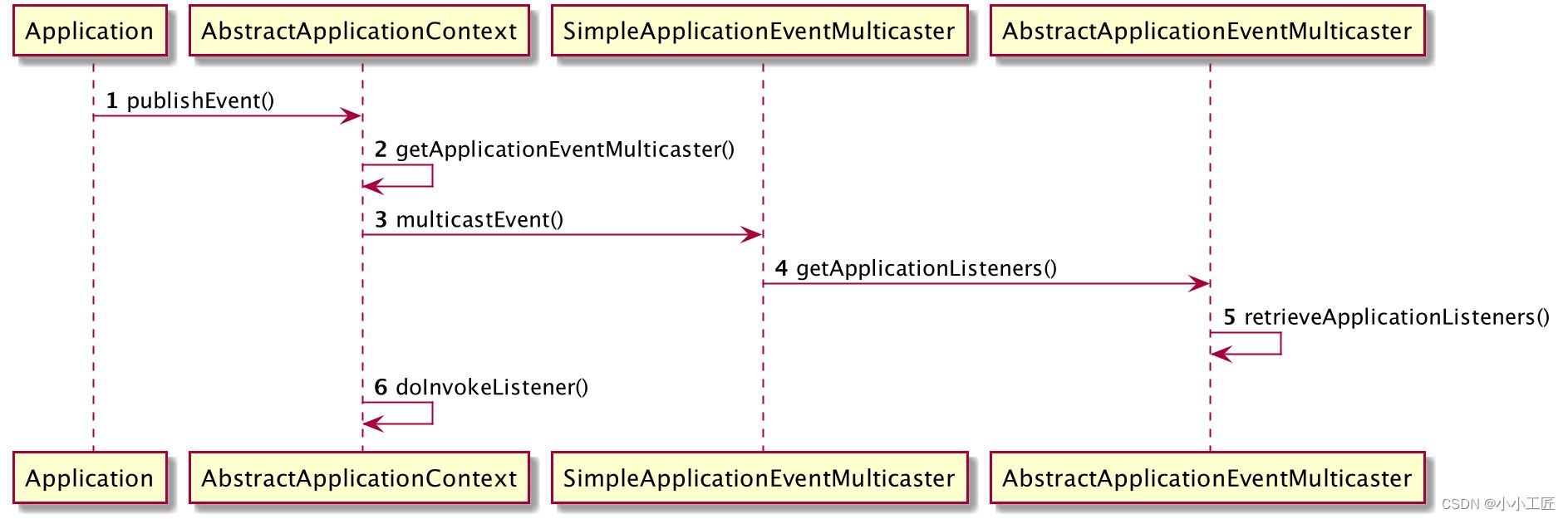
事件的发布是通过ApplicationEventPublisher的实现类实现的publishEvent方法实现的,ApplicationContext就实现了该接口,所以使用Spring时就可以直接使用ApplicationContext实例来调用publishEvent方法来发布事件
/** 发布事件
* @param event:事件对象
* */
@Override
public void publishEvent(Object event)
publishEvent(event, null);
/** 发布事件
* @param event:事件对象
* @param eventType:事件类型
* */
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType)
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
/** 1.将发布的事件封装成ApplicationEvent对象(因为传入的参数是Object类型,有可能没有继承ApplicationEvent) */
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent)
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
else
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null)
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null)
/** 2.1.如果需要提前发布的事件还没有发布完,则不是立即发布,而是将事件加入到待发布集合中*/
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
else
/** 2.2.获取当前的事件广播器,调用multicasterEvent方法广播事件*/
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
/** 3.如果当前applicationContext有父类,则再调用父类的publishEvent方法*/
if (this.parent != null)
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext)
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
else
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
首先是将发布的事件转化成ApplicationEvent对象,然后获取到事件广播器,调用事件广播器的multicastEvent方法来广播事件,所以核心逻辑又回到了事件广播器那里
/** 广播事件
* @param event:事件
* @param eventType:事件类型
* */
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType)
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor(); // (如果有Executor,则广播事件就是通过异步来处理的)
/**
* 1.根据事件和类型调用getApplicationListeners方法获取所有监听该事件的监听器
* */
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type))
if (executor != null)
/** 2. 异步遍历执行invokeListener方法来唤醒监听器处理事件 */
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
else
invokeListener(listener, event);
这里主要有两个核心步骤,
- 首先是根据事件和类型找到监听了该事件的所有事件监听器
- 然后遍历来执行监听器的处理逻辑.另外如果配置了执行器Executor,就会通过Executor来异步发布事件给监听器
根据事件获取事件监听器
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType)
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap...
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null)
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader))))
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex)
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null)
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
else
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
核心方法是retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever)方法,源码如下:
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable ListenerRetriever retriever)
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
/** 初始化所有事件监听器,存入集合中*/
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex)
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
// Add programmatically registered listeners, including ones coming
// 遍历所有监听器,调用supportsEvent判断是否监听该事件
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners)
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType))
if (retriever != null)
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
/** 如果监听器监听当前事件,则加入到监听器集合中*/
allListeners.add(listener);
// Add listeners by bean name, potentially overlapping with programmatically
// registered listeners above - but here potentially with additional metadata.
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty())
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
//
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans)
try
if (supportsEvent(beanFactory, listenerBeanName, eventType))
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType))
if (retriever != null)
if (beanFactory.isSingleton(listenerBeanName))
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
else
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
allListeners.add(listener);
else
// Remove non-matching listeners that originally came from
// ApplicationListenerDetector, possibly ruled out by additional
// BeanDefinition metadata (e.g. factory method generics) above.
Object listener = beanFactory.getSingleton(listenerBeanName);
if (retriever != null)
retriever.applicationListeners.remove(listener);
allListeners.remove(listener);
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex)
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
/** 将所有监听器根据Order进行排序*/
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
if (retriever != null && retriever.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty())
retriever.applicationListeners.clear();
retriever.applicationListeners.addAll(allListeners);
return allListeners;
核心步骤:
-
1:获取事件广播器中所有的事件监听器
-
2:遍历事件监听器,判断该监听器是否监听当前事件
-
3:将所有监听当前事件的监听器进行排序
第二步判断监听器是否监听事件的判断,主要是通过反射获取该监听器实现的接口泛型类,如果包含当前事件的类则表示监听,否则就表示不监听
唤醒监听器处理事件
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?以上是关于Spring - 事件监听机制 源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章