LeetCode刷题笔记-数据结构-day15
Posted ΘLLΘ
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode刷题笔记-数据结构-day15相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
LeetCode刷题笔记-数据结构-day15
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
1.题目描述
原题链接:108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
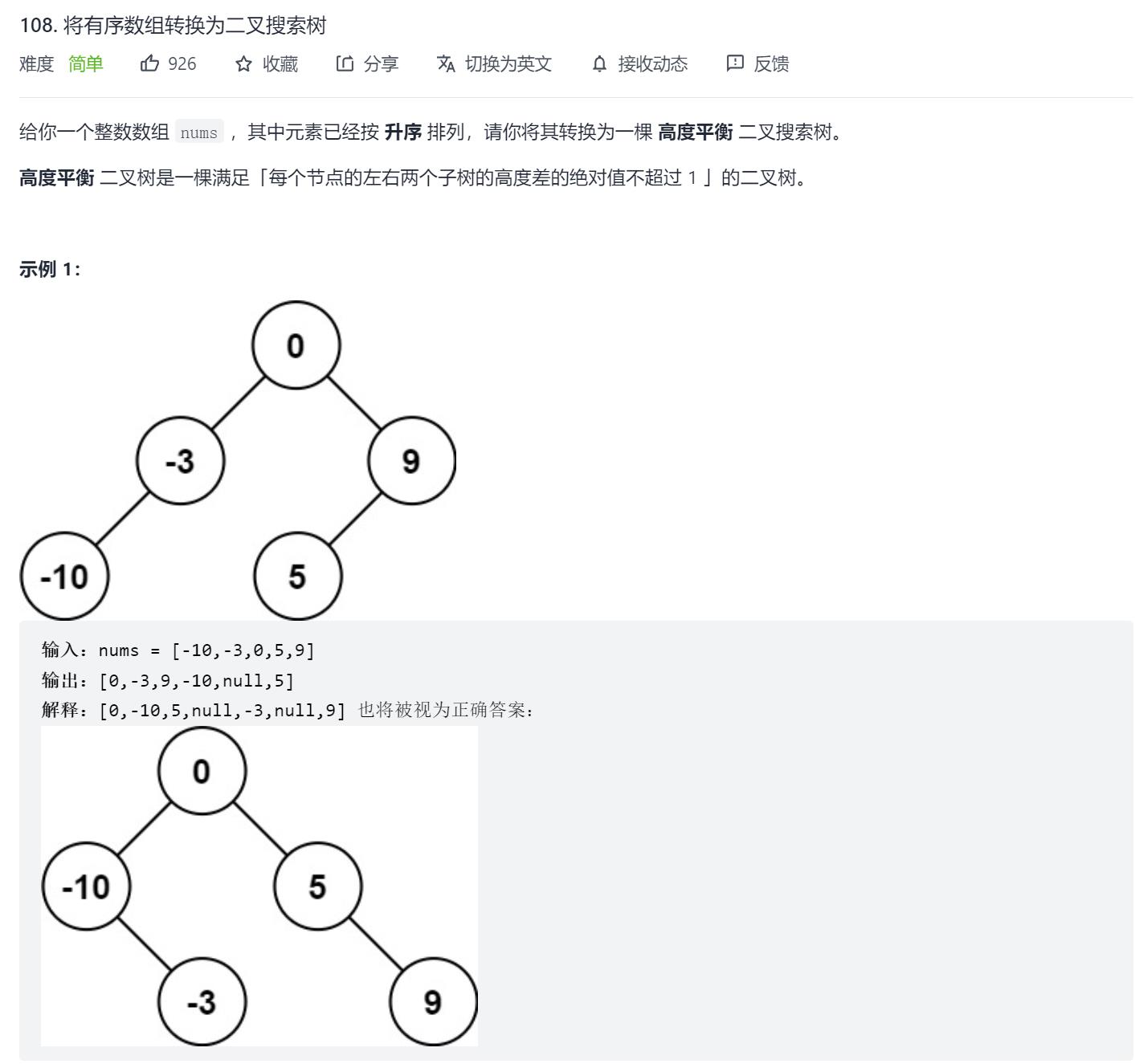
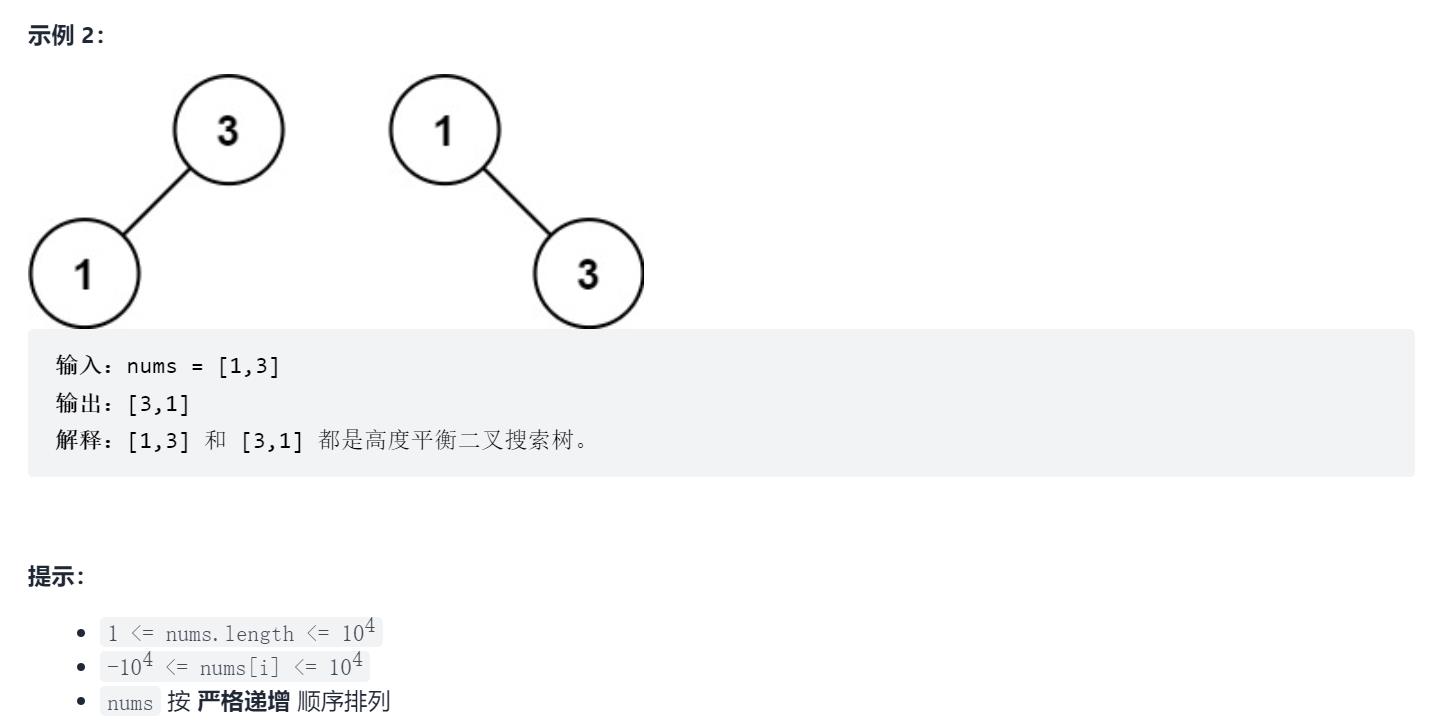
2.解题思路
题目要求:
- 二叉搜索树:对于所有节点的左子树的值全部小于它,右子树的值全部大于它
- 每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1
题目给出了一个升序的数组,我们可以直接从中间的位置dfs构建这个二叉树,每次以中点为根,左半部分为左子树,右半部分为右子树。分别递归建立左子树和右子树,根节点的指针指向这两颗子树。
3.代码
class Solution
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& a)
return dfs(a,0,a.size()-1);
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& a,int l,int r)
if(l>r) return NULL;
int t=l+r>>1;
TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(a[t]);
root->left=dfs(a,l,t-1);
root->right=dfs(a,t+1,r);
return root;
;
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
1.题目描述
原题链接:105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
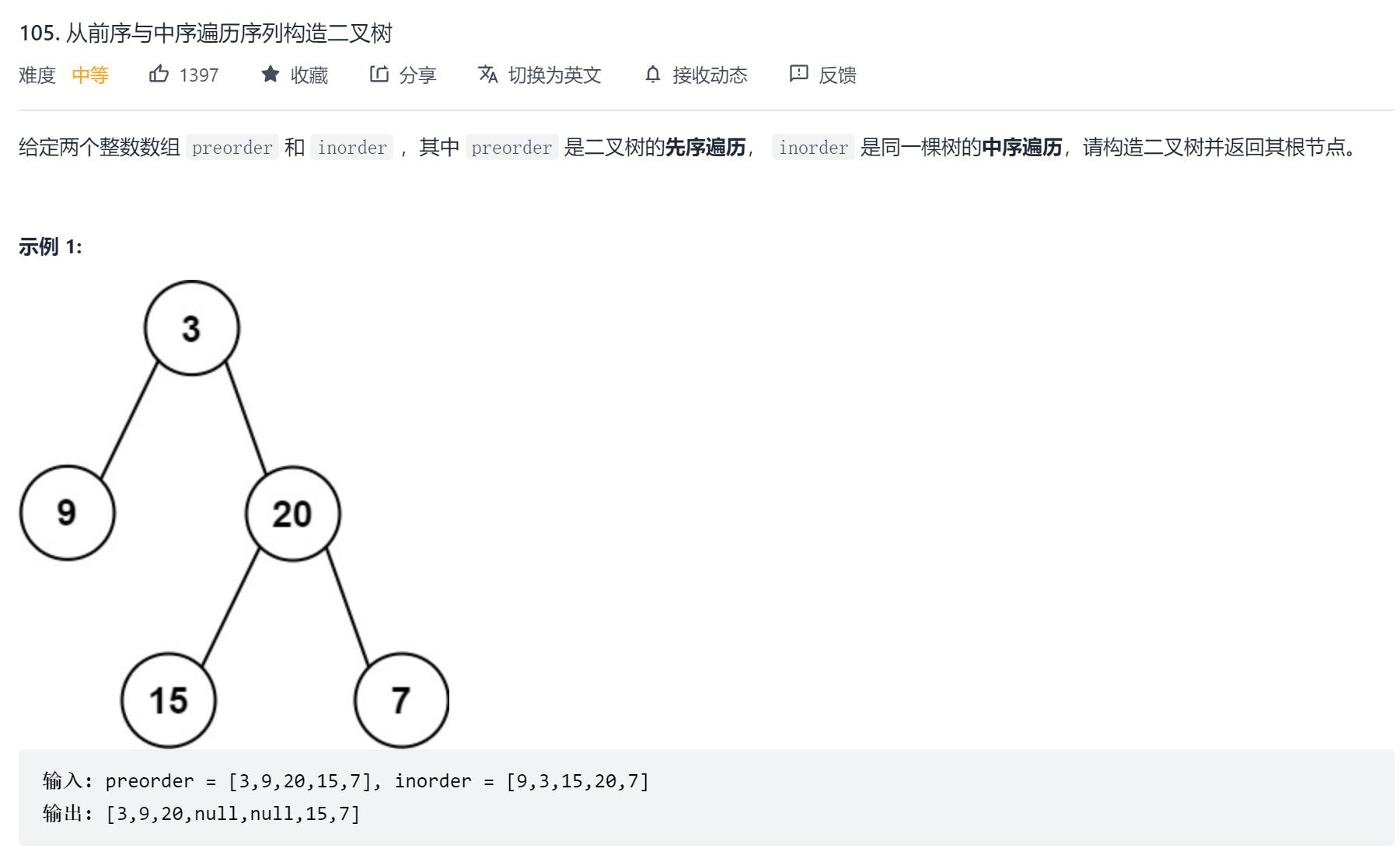

2.解题思路
算法:递归
具体实现:
- 使用一个
map存储中序遍历的每个值在中序遍历中的位置 - 利用前序遍历找到根节点的值,也就是前序遍历的第一个数
- 在中序遍历中根据
map找到对应根节点的位置t,则t左边的是左子树的中序遍历,t右边的是右子树的中序遍历 - 利用中序遍历及
t的值可以得到左子树遍历的长度k,则前序遍历根节点后面的k个数为左子树的前序遍历,剩余的为右子树的前序遍历 - 依照上面的过程递归创建左右子树即可
3.代码
class Solution
public:
map<int,int> hash;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& pre, vector<int>& ino)
int n=ino.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) hash[ino[i]]=i;
return dfs(pre,ino,0,n-1,0,n-1);
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& pre,vector<int>& ino,int pl,int pr,int il,int ir)
if(il>ir) return NULL;
TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(pre[pl]);
int t=hash[pre[pl]];
int k=t-il;
root->left=dfs(pre,ino,pl+1,pl+k,il,il+k-1);
root->right=dfs(pre,ino,pl+k+1,pr,il+k+1,ir);
return root;
;
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
1.题目描述
原题链接:103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历


2.解题思路
算法:队列+bfs
- 初始化一个队列存储每一层的节点,先加入根节点
root - 遍历队列,取出该层节点,并将其加入队列
v,表示这层的答案 - 取出节点时,需要从左到右将子节点入队
- 最后加入
v到最终答案res时,需要保证锯齿形层序遍历 - 我们这里用一个
bool变量f表示,初始值为true,每遍历一层f=!f - 如果为
f为false则将v翻转在加入
3.代码
class Solution
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root)
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
bool f=true;
while(q.size())
int k=q.size();
vector<int> v;
while(k--)
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
if(!f) reverse(v.begin(),v.end());
res.push_back(v);
f=!f;
return res;
;

以上是关于LeetCode刷题笔记-数据结构-day15的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章