Linux 时间同步 ntpd&chrony 内网
Posted 青冬
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux 时间同步 ntpd&chrony 内网相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Linux 时间同步 ntpd&chrony
在任何服务器集群中,为了更好的协同工作,除了一些互信机制外,需要的就是时间同步功能,如果时间不同步,就好比让在中国的同事与美国的同事进行沟通,会造成各种奇奇怪怪的时间相关的问题。而且很多资源访问都是有时效性的,如果时间不同步可能永远无法访问,对此我们需要进行时间同步的功能。
Linux 时间系统
在 windows 系统中,我们设置时间的时候一般都是通过右下角进入时间的设置界面进行设置,在设置过程中都是页面化,而且在我们关机、重启后都没有问题。系统时间会自动保存在 Bios 时钟中,这样电脑启动也会从 BIOS 中获取硬件的时间,以保证时间的不间断。
但在 linux 中,系统时间和硬件时间并不会自动同步,他们是互不干扰的。硬件使用 BIOS 电池维持;系统时间使用 CPU Tick 维持,启动时获取 BIOS 时间。
Linux 系统时间设置
在 Linux 中我们可以通过 date 命令进行设置:
# 查看当前时间
date
# 更改系统时间
date -s "19970118 20:00:00"
# 再次查看系统时间
date

Linux 硬件时间设置
硬件时间的设置可以使用 clock 或者 hwclock 命名,推荐使用第一个。
# 打印当前硬件时间
clock
# 设置当前硬件时间
clock --set --date "19970118 20:00:00"
# 再次打印硬件时间
clock
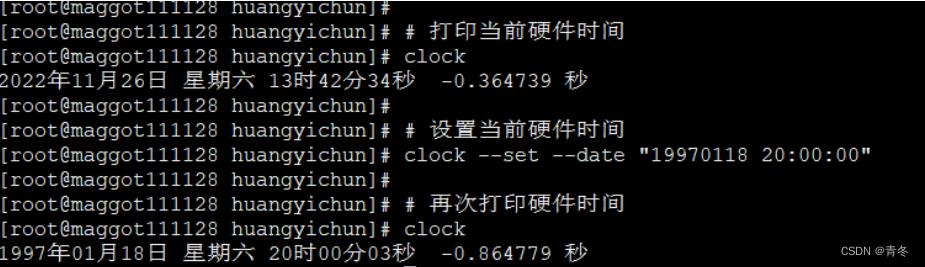
这时候我们可以查看这个文件 /etc/adjtime,如果我们更改了硬件时间,那么这个文件会记录两次时间的调整差异,后续如果再次使用 --set 或 --systohc 命令,会自动计算出差异平均值,进行硬件时钟的调整:
Linux 系统和硬件时间同步
现在我们将两个时间都定位到了 1997 年,现在我们需要进行一些同步,将时间矫正回来。(请确保有外网)
安装 ntpdate 服务
ntpdate 会在本文后面进行对应讲解,现在我们单台进行 ntpdate 服务器安装。
yum install ntpdate ntp
同步 ntp 时间
ntpdate -u cn.pool.ntp.org
# 也可以使用
# 上海的 NTP 服务器: ntp.api.bz
# 中国ntp服务器:cn.pool.ntp.org
# 上海交通大学网络中心NTP服务器:ntp.sjtu.edu.cn
# 阿里: ntp1.aliyun.com
查看系统时间
date
clock

可以看到我们的系统时间已经同步完成,但是硬件时间还停留在 1997 年。那么我们可以将系统时间同步到硬件时间:
# 将系统时间赋予硬件时间
clock -w
clock

集群时间同步
刚刚我们了解了 Linux 的时间系统,也完成了单服务器的同步到国家时间的流程,那如果我们需要自己搭建集群,也需要保证集群的时间同步,但没有外网环境。那么我们需要自己搭建时间基准,并通过这个基准,进行整个集群的时间同步。
现在一般有两种同步方法: ntpdate 和 chrony。更推荐 chrony,下面会讲解两个的使用方法。
ntpd 服务
NTP 其实就是 Network Time Protocol 网络时间协议,可以使计算机时间同步化的一种协议,可以使计算机对服务器或者时钟源进行同步。
前面我们已经安装过 ntpdate 了,现在快速回忆单台同步外网 ntp 服务器:
yum install ntpdate ntp
ntpdate -u ntp1.aliyun.com
集群时间主服务器
可以看到,如 ntp1.aliyun.com 其实就是一台外网可以访问的时间服务器,所以在我们需要搭建的集群中,也需要有这样一台时间服务器。这里我们选择 maggot111128.huangyichun.com 作为主服务器,其他在这台服务器上进行时间同步。

参考官网:
开启 ntpd 服务
systemctl status ntpd # 查看服务状态
systemctl start ntpd # 启动服务
systemctl enable ntpd # 设置开机启动
systemctl status ntpd # 再次查看

在安装了 ntp 后,相关的配置在 /etc/ntp.conf 中。我们需要进行一些配置 vim /etc/ntp.conf:
- 提供服务器网段扩大
# 在 acccess 中添加
# Permit all access over the loopback interface. This could
# be tightened as well, but to do so would effect some of
# the administrative functions.
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
restrict 192.168.0.0 # 可以对 192.168.0.0网段提供服务
# or
# restrict 192.168.111.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
- 该节点更改为只与自己同步
# 注释掉server 开头的行,取消同步其他服务器
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 127.127.1.0 # 添加自己为时间同步服务器
127.127.1.0 stratum 8 # 并设置自己的层级(最多16层)
- 重启 ntpd 服务
systemctl restart ntpd
集群客户端服务器
集群中的其他服务器要与这台服务器进行时间同步,也需要 ntp 服务,在安装完后进行 /etc/ntp.conf 的配置:
yum install ntp ntpd
vim /etc/ntp.conf
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server maggot111128.huangyichun.com # 添加需要同步的服务器
server maggot111128 # 添加需要同步的服务器
然后启动 ntpd 服务:
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl enable ntpd
systemctl status ntpd
使用 ntpstat 查看同步状态: 
当前处于未同步状态,如果需要手动同步:
ntpdate -d maggot111128
如果出现类似于 no server suitable for synchronization found,请查看主服务器的防火墙设置:

防火墙设置参考:
firewall-cmd --stat # 查看防火墙是否开启
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports # 在开启情况下,打开了哪些通道
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=123/tcp --permanent # 开启123/tcp通道
# or
# 直接关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
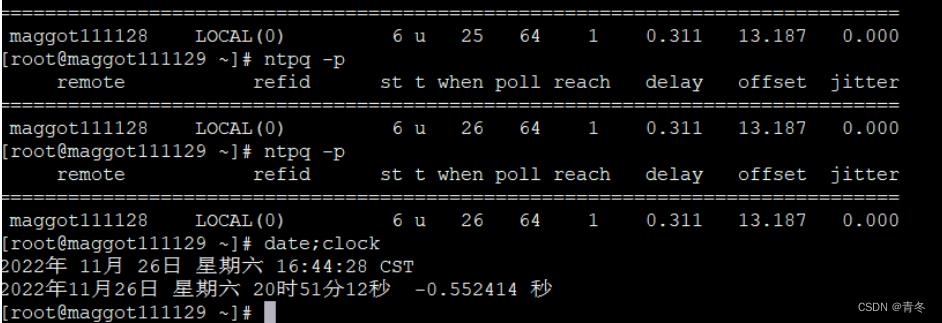
注意,仅仅这样并不会让硬件时间进行同步,需要更改 /etc/sysconfig/ntpd 文件:
SYNC_HWCLOCK=yes
下图为更改前:
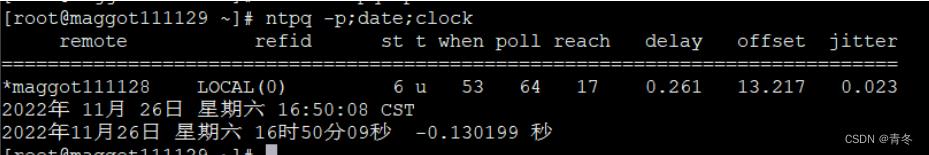
更改后(记得重启 ntpd):
chrony 服务
Chrony 是开源的时间同步服务,是 centos7 的默认时间同步工具。能够与时间服务器进行时间同步,并始终让时间保持同步,比 NTP 更快、配置更简单、依赖更简单。
- 更快的同步只需要数分钟而非数小时时间,从而最大程度的减少时间和频率误差,这对于并非全天运行的台式计算机或系统而言非常有用。
- 能够更好的响应时间频率的快速变化,这对于具备不稳定时钟的虚拟机或导致时钟频率发生变化的节能技术而言非常有用。
- 在初始同步后,它并不会停止时钟,以防对需要系统时间保持单调的程序造成影响。
- 在应对临时非对称延迟时,(例如,大规模下载造成链接饱和时)提供了更好的稳定性。
- 无需对服务器进行定期轮询,因此具备间歇性网络连接的系统仍然可以快速同步时钟。
注意进行 chrony 安装之前,我们需要停止 ntpd 相关服务。
# 所有节点均停止 ntpd 服务
systemctl status ntpd
systemctl stop ntpd
systemctl disable ntpd
systemctl status ntpd
# 查看 ntpd 默认端口123 是否被占用
netstat -tunlpa |grep 123

chrony 时间源
跟 ntpd 服务器一样,我们需要搭建 chrony 的事件源服务器,首先安装 chrony 服务(如果是 centos 7 应该是默认安装)
yum install chrony
使用 /etc/chrony.conf 进行 chrony 相关配置
vim /etc/chrony.conf
# 与 ntpd 一致,将自己设置为 server 节点
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 127.0.0.1 iburst
# 如果有外网,建议添加
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst
# 如果是私网必须添加
local stratum 10
# 打开允许同步的网段
# Allow NTP client access from local network.
#allow 192.168.0.0/16
allow 192.168.0.0/16
然后重启 chrony 服务,并查看服务状态
systemctl restart chronyd.service
systemctl enable chronyd.service # 开机启动
# 查看服务状态
systemctl status chronyd -l
chronyc sources -v
# 查看端口同步
netstat -tunlpa |grep 123
# 检查是否同步
<strong>chronyc tracking</strong>
# 需要注意 最后一行 Leap Status
chrony 客户端
安装 chrony
yum install chrony
更改配置文件
vim /etc/chrony.conf
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server maggot111128.huangyichun.com
重启 chronyd 服务
systemctl restart chronyd.service
使用 chronyc sources 命令进行同步查看,如果出现 ^* 则为获取时间成功,正在同步中,错位时间看 Last:
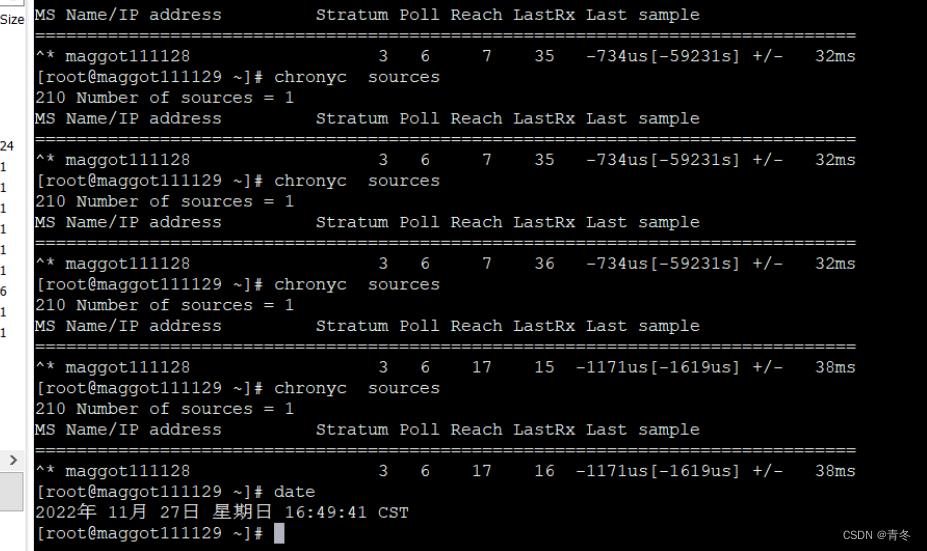
chronyc 命令
使我们操控 chrony 的命令方式,主要有:
| 参数 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
| sources | 查看所有服务器同步情况 |
| accheck | 检查NTP访问是否对特定主机可用 |
| activity | 该命令会显示有多少NTP源在线/离线 |
| add server | 手动添加一台新的NTP服务器。 |
| clients | 在客户端报告已访问到服务器 |
| delete | 手动移除NTP服务器或对等服务器 |
| settime | 手动设置守护进程时间 |
| tracking | 显示系统时间信息 |
集群搭建注意事项
一般我们进行搭建的时候可能都是只选择了一台节点作为时间服务器,但是其实在超大型集群搭建的时候,我们应该按照网段进行区别,采用多时间服务器的方式进行搭建。不要像一棵树,只有一个根。
以上是关于Linux 时间同步 ntpd&chrony 内网的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章