paper reading:PARTIES:Qos-Aware Resource Partitioning for Multiple Interative Services
Posted 银灯玉箫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了paper reading:PARTIES:Qos-Aware Resource Partitioning for Multiple Interative Services相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
PARTIES:Qos-Aware Resource Partitioning for Multiple Interative Services
2019, Shuang Chen,Chritistia Delimitrou, ASPOLOS
引用格式
Summary
写完笔记之后最后填,概述文章的内容,以后查阅笔记的时候先看这一段。注:写文章summary切记需要通过自己的思考,用自己的语言描述。忌讳直接Ctrl + c原文。
Research Objective(s)
We present PARTIES, a Qos-aware resoruce manager that enables an arbitrary number of interative, latency-crtitical services to share a physical node without Qos violations.
Background / Problem Statement
Unfortunately, mutli-tenancy oftern comes at a performance penalty, as co-scheduled applications contend for shared resources, leading to interference and performance unpredictability. Interference is partitcularly destructive for interative, latency-critical(LC) services, which must meet strict quality of service(QoS) guarantees.
Cloud applications are progressively shifting from batch to low-latency services. For example, traditionally throughput-bouand applications, like big data and graph analytics,are now moving to in-memory computation, with frameworks like Spark[60], which brings task execution latencies to a few milliseconds or seconds. Furthermore, cloud applications are undergoing a major redesign form large, monolithic services that encompass the entire application functionality in a single binary, to hundreds or thousands of loosely-coupled microsevices[28-30,52]. While the end-to-end latency of a large-scale service remains in the granularity of serveral milliseconds or seconds, each microservice must meet much tighter latency constraints, often in the order of a few hundrends of microseconds.
Method(s)
作者解决问题的方法/算法是什么?是否基于前人的方法?基于了哪些?
PARTIES leverages an online monitoring framework that operates at the granularity of a few hundred milliseconds, to quickly detect QoS violations. Upon detection, the runtime boosts the allocation of one or more resources to the LC service whose latency suffers the most. PARTIES assumes no a priori knowledge of incoming applications, making it applicable in settings like public clouds where user-submitted applications are not known in advance. PAPRTIES uses both OS- and hardware-level partitioning mechanisms available in modern platforms, including containers, tread pinning, cahe partitioning, frequency scaling, memory capacity partitioning, and disk and network bandwidth partitioning to sastisfy the instantaneous resource needs of each co-scheduled interative service.
We then introduce the concept of resource fungibility,i.e., the fact that resources can be traded for each other to arrive to equivalent application performance. Fungibility improves the controller’s flexibility and convergence speed.
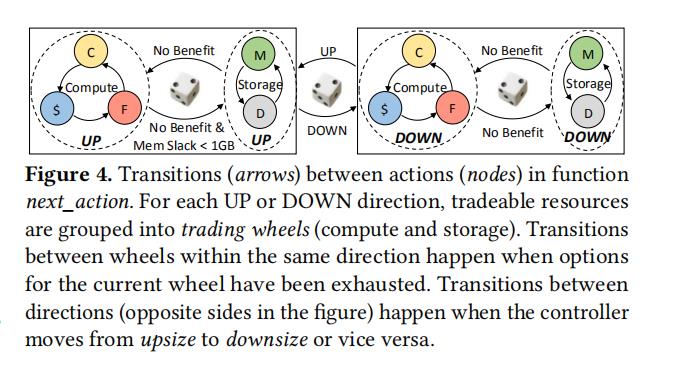
Unlike resources in the storage wheel where the benefit in performancee is almost always immediate, adjusting compute resources may require multiple rounds befeore there are noticeable peformance gains. Indeed, when an aplication is servely starved for compute resoruces, fine-grained adjustments, e.g., in frequency, are not enough to dissipate the long queues taht have built up in the system. Every time the cotroller completes a turn in the compute wheel, it checks memory utilization before deciding whether to initiate another round or to jump to the storage wheel. If memoy slack is large and latency does not drop after scaling compute up, there is high probability that the allocated compute resources are not yet sufficient. On the other hand, if memory is almost saturated, the QoS violation is likely due to an increasing dataset, in which case the controller jumps to the storage wheel.
Evaluation
作者如何评估自己的方法?实验的setup是什么样的?感兴趣实验数据和结果有哪些?有没有问题或者可以借鉴的地方?
Conclusion
作者给出了哪些结论?哪些是strong conclusions, 哪些又是weak的conclusions(即作者并没有通过实验提供evidence,只在discussion中提到;或实验的数据并没有给出充分的evidence)?
Notes
(optional) 不在以上列表中,但需要特别记录的笔记。
References
(optional) 列出相关性高的文献,以便之后可以继续track下去。
以上是关于paper reading:PARTIES:Qos-Aware Resource Partitioning for Multiple Interative Services的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章