平衡二叉树的操作(高手进)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了平衡二叉树的操作(高手进)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
做一棵平衡二叉树,其功能如下:1.插入元素,插入节点
2.删除元素,删除节点
3.要求能查看前序遍历
功能要做成菜单!
尽量多一点注释,因为要回答老师提出的问题!写上来前记得在电脑上编译一下,不然有错了都不知道怎么改。高手可以的话加我QQ:241125616
一、 需求分析
1. 本程序是是利用平衡二叉树实现一个动态查找表,实现动态查找表的三种基本功能:查找、插入和删除。
2. 初始,平衡二叉树为空树,可以按先序输入平衡二叉树,以输入0结束,中间以回车隔开,创建好二叉树后,可以对其查找,再对其插入,输入0结束插入,再可以对其删除,输入0结束,每次插入或删除一个结点后,更新平衡二叉树的显示。
3. 本程序以用户和计算机的对话方式执行,根据计算机终端显示:“提示信息”下,用户可由键盘输入要执行的操作。
4. 测试数据(附后)
二、 概要设计
1. 抽象数据类型动态查找表的定义如下:
ADT DynamicSearchTable
数据结构D:D是具有相同特性的数据元素的集合。各个数据元素含有类型相同,可惟一标识数据元素的关键字。
数据关系R:数据元素同属一个集合。
基本操作P:
InitDSTable(&DT);
操作结果:构造一个空的动态查找表DT。
DestroyDSTable(&DT);
初试条件:动态查找表DT存在。
操作结果: 销毁动态查找表DT。
SearchDSTable(DT,key);
初试条件:动态查找表DT存在,key为和关键字类型相同的给定值。
操作结果: 若DT中存在其关键字等于key的数据元素,则函数值为该元素的值或表中的位置,否则为“空”。
InsertDSTable(&DT,e);
初试条件:动态查找表DT存在,e为待插入的数据元素。
操作结果: 若DT中不存在其关键字等于e. key的数据元素,则插入e到DT。
DeleteDSTable(&DT,key);
初试条件:动态查找表DT存在,key为和关键字类型相同的给定值。
操作结果: 若DT中存在其关键字等于key的数据元素,则删除之。
TraverseDSTable(DT,Visit());
初试条件:动态查找表DT存在,Visit()是结点操作的应用函数。
操作结果: 按某种次序对DT的每个结点调用函数Visit()一次且至多
一次。一但Visit()失败,则操作失败。
ADT DynamicSearchTable
2. 本程序包含两个模块:
Void main()
Do
接受命令(根据提示输入终点城市和起点城市的序号);
处理命令;
while(“命令”=“退出”);
3.本程序只有两个模块,调用关系简单
主程序模块
平衡二叉树的模块
三、 详细设计
1. 根据题目要求和查找的基本特点,其结点类型
typedef struct BSTnode
int data;
int bf;
struct BSTnode *lchild,*rchild;
BSTnode,*bstree;
#define LH +1
#define EH 0
#define RH -1
/-----------------------------************对平衡二叉树的操作
bstree InsertAVL(bstree &T, int e);
////////在平衡二叉树中插入结点。
int FindAVL(bstree p,int e);
////////查找平衡二叉树中是否有结点e。
bstree DeleteAVL(bstree &T,int e)
////////删除平衡平衡二叉树的结点e,并保持平衡二叉树的性质。
int Preordertraverse(bstree T)
////////按先序遍历平衡二叉树。
/------------------------************平衡二叉树的操作的详细算法
bstree InsertAVL(bstree &T, int e)
bstree p;
//插入新结点,树长高置taller为TRUE
if(!T)
T=(bstree)malloc(sizeof(BSTnode));
T->data=e;
T->lchild=T->rchild=NULL;
T->bf=EH;
taller=TRUE;
else
//树中存在和e有相同关键字的结点则不再插入
if(e==T->data)
taller=FALSE;
return NULL;
//值小于则继续在树的左子树中搜索
if(e < T->data)
//插入到左子树且左子树长高
p=InsertAVL(T->lchild,e);
if(p)
T->lchild=p;
if(taller)
switch(T->bf) //检查*T的平衡度
case LH: //原本左子树比右子树高,需要做左平衡处理
T=LeftBalance(T);
taller=FALSE;
break;
case EH: //原本左子树和右子树同高,现因左子树争高而使树增高
T->bf=LH;
taller=TRUE;
break;
case RH: //原本右子树比左子树高,现在左右子树等高
T->bf=EH;
taller=FALSE;
break;
///////switch(T->bf)
///////if(taller)
/////if(p)
///////if(e < T->data)
//继续在*T的右子树中搜索
else
//插入到右子树且使右子树长高
p=InsertAVL(T->rchild,e);
if (p)
T->rchild=p;
if(taller)
switch(T->bf) //检查*T的平衡度
case LH: //原本左子树比右子树高,现在左右子树等高
T->bf=EH;
taller=FALSE;
break;
case EH: //原本左子树和右子树同高,现因右子树增高而使树增高
T->bf=RH;
taller=TRUE;
break;
case RH: //原本右子树比左子树高,需要做右平衡处理
T=RightBalance(T);
taller=FALSE;
break;
//////switch(T->bf)
/////if(taller)
/////if (p)
//////if(e > T->data)
///////else
return T;
int Preordertraverse(bstree T)
if(T)
printf(" %d %d\n",T->data,T->bf);
Preordertraverse(T->lchild);
Preordertraverse(T->rchild);
return 1;
int FindAVL(bstree p,int e)
if(p==NULL)return NULL;
else if(e==p->data) return true;
else if(e<p->data)
p=p->lchild;
return FindAVL(p, e);
////左子树上查找
else
p=p->rchild;
return FindAVL( p, e);
////右子树上查找
bstree DeleteAVL(bstree &T,int e)
//删除后要保证该二叉树还是平衡的
int n,m=0;/////标记
bstree q;
if(!T)return NULL;
else
if(e==T->data) ////直接删除
n=Delete(T,e);
m=n;
if(m!=0)
q=T;
DeleteAVL(T,m);
q->data=m;
else
if(e<T->data)////在左子树上寻找
DeleteAVL(T->lchild,e);
if(shorter)
switch(T->bf)
case LH:T->bf=EH;shorter=true;break;
case EH:T->bf=RH;shorter=false;break;
case RH:Delete_Rightbalance(T);shorter=true;break;
////switch(T->bf)
/////if(shorter)
/////if(e<T->data)
else /////////在右子树上寻找
DeleteAVL(T->rchild,e);
if(shorter)
switch(T->bf)
case LH:Delete_Leftbalance(T);shorter=true;break;
case EH:T->bf=LH;shorter=false;break;
case RH:T->bf=EH;shorter=true;break;
////////switch(T->bf)
////////在右子数上寻找完
////////在左右子上完
///////////删除完
return T;
2. 主程序和其他伪码算法
void main()
while(e!=0)
if(e!=0) InsertAVL(T,e);
while(d!=0)
if(d!=0) InsertAVL(T,d);
Preordertraverse(T);
c=FindAVL(T,t);
if(c==1)printf("有要查找的节点\n");
else printf("无要查找的节点\n");
do
DeleteAVL(T,b);
Preordertraverse(T);
while(b==1);
///右旋
bstree R_Rotate(bstree &p)
bstree lc;
lc=p->lchild;
p->lchild=lc->rchild;
lc->rchild=p;
p=lc;
return p;
////左旋
bstree L_Rotate(bstree &p)
bstree rc;
rc=p->rchild;
p->rchild=rc->lchild;
rc->lchild=p;
p=rc;
return p;
/////左平衡处理
bstree LeftBalance(bstree &T)
bstree lc,rd;
lc=T->lchild; //lc指向*T的左子树根结点
switch(lc->bf) //检查*T的左子树平衡度,并做相应的平衡处理
case LH: //新结点插入在*T的左孩子的左子树上,要做单右旋处理
T->bf=lc->bf=EH;
T=R_Rotate(T);
break;
case RH: //新结点插入在*T的左孩子的右子树上,要做双旋处理
rd=lc->rchild; //rd指向*T的左孩子的右子树根
switch(rd->bf) //修改*T及其左孩子的平衡因子
case LH:
T->bf=RH;
lc->bf=EH;
break;
case EH:
T->bf=lc->bf=EH;
break;
case RH:
T->bf=EH;
lc->bf=LH;
break;
//////////switch(rd->bf)
rd->bf=EH;
T->lchild=L_Rotate(T->lchild); //对*T的左孩子做左旋平衡处理
T=R_Rotate(T); //对*T做右旋处理
////////switch(lc->bf)
return T;
////右平衡处理
bstree RightBalance(bstree &T)
bstree rc,ld;
rc=T->rchild; //rc指向*T的右子树根结点
switch(rc->bf) //检查*T的右子树平衡度,并做相应的平衡处理
case RH: //新结点插入在*T的右孩子的右子树上,要做单右旋处理
T->bf=rc->bf=EH;
T=L_Rotate(T);
break;
case LH: //新结点插入在*T的右孩子的左子树上,要做双旋处理
ld=rc->lchild; //ld指向*T的右孩子的左子树根
switch(ld->bf) //修改*T及其右孩子的平衡因子
case LH:
T->bf=EH;
rc->bf=RH;
break;
case EH:
T->bf=rc->bf=EH;
break;
case RH:
T->bf=LH;
rc->bf=EH;
break;
///switch(ld->bf)
ld->bf=EH;
T->rchild=R_Rotate(T->rchild); //对*T的右孩子做右旋平衡处理
T=L_Rotate(T); //对*T做左旋处理
/////switch(rc->bf)
return T;
int Delete(bstree &T,int e)
//删除结点
bstree p,q;
e=0;
p=T;
if(!T->rchild) //右子数为空需要重接它的左子数
T=T->lchild;
free(p);
shorter=true;
else if(!T->lchild) //重接它的右子数
T=T->rchild;
free(p);
shorter=true;
else //左右子数均不空
q=T->lchild;
while(q->rchild!=NULL)//转左,然后向右到尽头
q=q->rchild;
e=q->data;
return e;
void Delete_Rightbalance(bstree &T)
///////////删除在左子树上的,相当于插入在右子树
bstree rc=T->rchild,ld;
switch(rc->bf)
case LH://///////双旋 ,先右旋后左旋
ld=rc->lchild;
rc->lchild=ld->rchild;
ld->rchild=rc;
T->rchild=rc->lchild;
rc->lchild=T;
switch(ld->bf)
case LH:T->bf=EH;
rc->bf=RH;
break;
case EH:T->bf=rc->bf=EH;
break;
case RH:T->bf=LH;
rc->bf=EH;
break;
ld->bf=EH;
T=rc;
shorter=true;break;
case EH:///////删除在左子树,相当于插入在右子树,左单旋
T->rchild=rc->lchild;
rc->lchild=T;
rc->bf=LH;
T->bf=RH;
T=rc;
shorter=EH;break;
case RH:///////删除在左子树,相当于插入在右子树,左单旋
T->rchild=rc->lchild;
rc->lchild=T;
rc->bf=T->bf=EH;
T=rc;
shorter=true;break;
void Delete_Leftbalance(bstree &T)/////删除右子树上的,相当于插入在左子树上
bstree p1,p2;
p1=T->lchild;
switch(p1->bf)
case LH:T->lchild=p1->rchild;//////右旋
p1->rchild=T;
p1->bf=T->bf=EH;
T=p1;
shorter=true;
break;
case EH:T->lchild=p1->rchild;///////右旋
p1->rchild=T;
p1->bf=RH;
T->bf=LH;
T=p1;
shorter=false;
break;
case RH:p2=p1->rchild;//////////右双旋
p1->rchild=p2->lchild;
p2->lchild=p1;
T->lchild=p2->rchild;
p2->rchild=T;
switch(p2->bf)
case LH:T->bf=RH;p1->bf=EH;break;
case EH:T->bf=EH;p1->bf=EH;break;
case RH:T->bf=EH;p1->bf=LH;break;
p2->bf=EH;
T=p2;
shorter=true;break;
3. 函数的调用关系图
Main
InsertAVL Preordertraverse FindAVL DeleteAVL
四、 调试分析
1. 在开始对平衡二叉树的插入后,再做平衡处理时,特别是在做双向旋转平衡处理后的更新时,费了一些时间;
2. 在做平衡二叉树的删除时,当删除结点左右孩子均在时,开始直接用左子树的最大数代替,然后直接删除结点,结果导致删除了将要删除的结点及其孩子均删除了,后来将要删除的结点用左子树的最大树代替后,对左子树的最大结点做好标记,然后再做对其做删除处理。
3. 本程序算法基本简单,没有多大困难,就是在分析做双旋平衡处理的更新时,开始思路有些混乱,后来就好了;
五、 用户手册
1. 本程序的运行环境为DOS操作系统,执行文件为Balanced Tree.exe。
2. 进入演示程序后,按广度遍历输入平衡二叉树,中间以回车键隔开,输入0为结束;再输入要插入的结点,输入0结束,再输入要查找的结点,最后可以输入要删除的结点,输入0结束
六、 测试结果
先按广度遍历创建平衡二叉树(亦可一个一个的插入二叉树的结点)(50 20 60 10 30 55 70 5 15 25 58 90) ,输入0结束,然后可插入结点(39),其会显示插入后的二叉树,输入0,不再插入;输入要查找结点(6),输入要删除的结点(20),其显示如下:
七、 附录
Balance Tree.cpp 参考技术A 平衡二叉树是:左右子树都是平衡二叉树,且左右子树的深度相差<=1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct bitreetype
int item;
int bdegree;/*平衡因子,左子树深度-右子树深度*/
struct bitreetype *lchild;
struct bitreetype *rchild;
bitree;
typedef struct treequeuetype
int head;
int tail;
bitree *items[1000];
treequeue;/*定义一个队列,后面的平衡调整要用层序遍历,于是要用这个队列*/
void resetqueue(treequeue *queue)
queue->head=-1;
queue->tail=-1;
return;
/*把队列清空*/
void inqueue(treequeue *queue,bitree *element)
queue->tail++;
queue->items[queue->tail]=element;
/*入队列*/
bitree *outqueue(treequeue *queue)
queue->head++;
return queue->items[queue->head];
/*出队列*/
int isqueueempty(treequeue *queue)
if(queue->head==queue->tail)
return 1;
else
return 0;
/*判断队列是否为空*/
void fillmemory(char *source,int len,char content)
while(len)
source=source+len;
*source=content;
source=source-len;
len--;
*source=0;
/*用CONTENT的内容去FILL以SOURCE为首,LEN长度的一块空间,初始化内存方便*/
int getnums(int *dst)/*输入字符串并把字符串转化为一串数存入DST指向的内存中去,我们用它采集原始数据*/
char *temp,*num,*p,t;
int len=0;
temp=(char *)malloc(1000*sizeof(char));
num=(char *)malloc(20*sizeof(char));
p=num;
fillmemory(temp,1000,0);
fillmemory(num,20,0);
scanf("%s",temp);
t=*temp;
temp++;
while(t)
if(t!=',')
*num=t;
num++;
t=*temp;
temp++;
/*抽出一个数放入NUM临时空间中*/
else
num=p;
*dst=atoi(num);
len++;
fillmemory(num,20,0);
dst++;
t=*temp;
temp++;
/*将NUM中的数字转化出来存入DST中*/
num=p;
*dst=atoi(num);
len++;
fillmemory(num,20,0);
dst++;
t=*temp;
temp++;
return len;
/*处理最后一个数字*/
/*****唉,写上面的函数时都两个月没写过C了,所以可能上面的函数条理相当差的说*****/
void insertbitree(bitree *head,int source)/*向以HEAD为头结点的排序二叉树中插入一个以SOURCE为内容的点*/
if(source<=head->item)
if(head->lchild==NULL)
head->lchild=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->lchild->item=source;
head->lchild->lchild=NULL;
head->lchild->rchild=NULL;
head->lchild->bdegree=0;
else
insertbitree(head->lchild,source);
else
if(head->rchild==NULL)
head->rchild=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->rchild->item=source;
head->rchild->lchild=NULL;
head->rchild->rchild=NULL;
head->rchild->bdegree=0;
else
insertbitree(head->rchild,source);
/*递归插入的思想:如果SOURCE小于头结点,那么插入头结点的左孩子,否则插入右孩子,递归向下,直到找到空位置为止*/
bitree *createbitree(int *source,int len)/*用SOURCE为首地址,LEN为长度的一段空间中的内容建立一棵二叉数*/
int temp;
bitree *head=NULL;
head=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->lchild=NULL;
head->rchild=NULL;
head->item=*source;
head->bdegree=0;
source++;
len--;
while(len>0)
insertbitree(head,*source);/*这个函数很强大,用心体会吧,哈哈哈*/
source++;
len--;
return head;
int getdepth(bitree *head)/*求排序二叉树的深度*/
int ltemp,rtemp;
if(head==NULL)return 0;
if(head->lchild==NULL && head->rchild==NULL)return 1;
ltemp=1+getdepth(head->lchild);
rtemp=1+getdepth(head->rchild);
if(ltemp>=rtemp)return ltemp;
else return rtemp;
/*递归求深的思想:首先规定好0,1两个递归出口,然后分别求左右子树的深度并返回大者*/
void addbdegree(bitree *head)/*为排序二叉树追加平衡因子*/
if(head==NULL)return;
else
head->bdegree=getdepth(head->lchild)-getdepth(head->rchild);
addbdegree(head->lchild);
addbdegree(head->rchild);
bitree *leveldetect(bitree *head)/*以层序遍历为基本框架,检查"特殊"点*/
treequeue *tqueue;
bitree *temp;
tqueue=(treequeue *)malloc(sizeof(treequeue));
resetqueue(tqueue);
if(head!=NULL)inqueue(tqueue,head);
while(!isqueueempty(tqueue))
temp=outqueue(tqueue);
if(temp->bdegree<=-2 || temp->bdegree>=2)
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==1)
return temp;
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==-1)
return temp;
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==-1)
return temp;
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==1)
return temp;
if(temp->lchild!=NULL)inqueue(tqueue,temp->lchild);
if(temp->rchild!=NULL)inqueue(tqueue,temp->rchild);
return NULL;
/*(2,1),(2,-1),(-2,-1),(-2,1)完美的卡诺图啊!!*/
bitree *getmother(bitree *head,bitree *child)
bitree *temp;
if(head==child)return NULL;
if(head->lchild==child || head->rchild==child)return head;
if(head->lchild==NULL || head->rchild==NULL)return NULL;
if(head->lchild!=NULL)
temp=getmother(head->lchild,child);
if(temp!=NULL)return temp;
return getmother(head->rchild,child);
/*递归查找一个节点的妈妈*/
bitree *createsuperbitree(int *source,int len)/*不消说了,建立平衡二叉树*/
int itemp;
bitree *head=NULL;
bitree *temp=NULL;
bitree *tmother=NULL;
bitree *p=NULL;
bitree *q=NULL;
head=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->lchild=NULL;
head->rchild=NULL;
head->item=*source;
head->bdegree=0;
source++;
len--;
while(len>0)
insertbitree(head,*source);
addbdegree(head);
temp=leveldetect(head);
if(temp!=NULL)
tmother=getmother(head,temp);
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==1)
p=temp->lchild;
temp->lchild=p->rchild;
p->rchild=temp;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*LL*/
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==-1)
p=temp->lchild->rchild;
q=temp->lchild;
q->rchild=p->lchild;
temp->lchild=p->rchild;
p->lchild=q;
p->rchild=temp;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*LR*/
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==-1)
p=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=p->lchild;
p->lchild=temp;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*RR*/
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==1)
p=temp->rchild->lchild;
q=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=p->lchild;
q->lchild=p->rchild;
p->lchild=temp;
p->rchild=q;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*RL*/
addbdegree(head);
source++;
len--;
return head;
main()/*演示*/
int binums[100],i,len;
bitree *head,*temp;
for(i=0;i<=99;i++)binums[i]=0;
len=getnums(binums);
head=createsuperbitree(binums,len);
temp=getmother(head,head->rchild->rchild->rchild);
参考技术B 找了很久才找到的平衡二叉树实现代码
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct bitreetype
int item;
int bdegree;/*平衡因子,左子树深度-右子树深度*/
struct bitreetype *lchild;
struct bitreetype *rchild;
bitree;
typedef struct treequeuetype
int head;
int tail;
bitree *items[1000];
treequeue;/*定义一个队列,后面的平衡调整要用层序遍历,于是要用这个队列*/
void resetqueue(treequeue *queue)
queue->head=-1;
queue->tail=-1;
return;
/*把队列清空*/
void inqueue(treequeue *queue,bitree *element)
queue->tail ;
queue->items[queue->tail]=element;
/*入队列*/
bitree *outqueue(treequeue *queue)
queue->head ;
return queue->items[queue->head];
/*出队列*/
int isqueueempty(treequeue *queue)
if(queue->head==queue->tail)
return 1;
else
return 0;
/*判断队列是否为空*/
void fillmemory(char *source,int len,char content)
while(len)
source=source len;
*source=content;
source=source-len;
len--;
*source=0;
/*用CONTENT的内容去FILL以SOURCE为首,LEN长度的一块空间,初始化内存方便*/
int getnums(int *dst)/*输入字符串并把字符串转化为一串数存入DST指向的内存中去,我们用它采集原始数据*/
char *temp,*num,*p,t;
int len=0;
temp=(char *)malloc(1000*sizeof(char));
num=(char *)malloc(20*sizeof(char));
p=num;
fillmemory(temp,1000,0);
fillmemory(num,20,0);
scanf("%s",temp);
t=*temp;
temp ;
while(t)
if(t!=',')
*num=t;
num ;
t=*temp;
temp ;
/*抽出一个数放入NUM临时空间中*/
else
num=p;
*dst=atoi(num);
len ;
fillmemory(num,20,0);
dst ;
t=*temp;
temp ;
/*将NUM中的数字转化出来存入DST中*/
num=p;
*dst=atoi(num);
len ;
fillmemory(num,20,0);
dst ;
t=*temp;
temp ;
return len;
/*处理最后一个数字*/
/*****唉,写上面的函数时都两个月没写过C了,所以可能上面的函数条理相当差的说*****/
void insertbitree(bitree *head,int source)/*向以HEAD为头结点的排序二叉树中插入一个以SOURCE为内容的点*/
if(source<=head->item)
if(head->lchild==NULL)
head->lchild=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->lchild->item=source;
head->lchild->lchild=NULL;
head->lchild->rchild=NULL;
head->lchild->bdegree=0;
else
insertbitree(head->lchild,source);
else
if(head->rchild==NULL)
head->rchild=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->rchild->item=source;
head->rchild->lchild=NULL;
head->rchild->rchild=NULL;
head->rchild->bdegree=0;
else
insertbitree(head->rchild,source);
/*递归插入的思想:如果SOURCE小于头结点,那么插入头结点的左孩子,否则插入右孩子,递归向下,直到找到空位置为止*/
bitree *createbitree(int *source,int len)/*用SOURCE为首地址,LEN为长度的一段空间中的内容建立一棵二叉数*/
int temp;
bitree *head=NULL;
head=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->lchild=NULL;
head->rchild=NULL;
head->item=*source;
head->bdegree=0;
source ;
len--;
while(len>0)
insertbitree(head,*source);/*这个函数很强大,用心体会吧,哈哈哈*/
source ;
len--;
return head;
int getdepth(bitree *head)/*求排序二叉树的深度*/
int ltemp,rtemp;
if(head==NULL)return 0;
if(head->lchild==NULL && head->rchild==NULL)return 1;
ltemp=1 getdepth(head->lchild);
rtemp=1 getdepth(head->rchild);
if(ltemp>=rtemp)return ltemp;
else return rtemp;
/*递归求深的思想:首先规定好0,1两个递归出口,然后分别求左右子树的深度并返回大者*/
void addbdegree(bitree *head)/*为排序二叉树追加平衡因子*/
if(head==NULL)return;
else
head->bdegree=getdepth(head->lchild)-getdepth(head->rchild);
addbdegree(head->lchild);
addbdegree(head->rchild);
bitree *leveldetect(bitree *head)/*以层序遍历为基本框架,检查"特殊"点*/
treequeue *tqueue;
bitree *temp;
tqueue=(treequeue *)malloc(sizeof(treequeue));
resetqueue(tqueue);
if(head!=NULL)inqueue(tqueue,head);
while(!isqueueempty(tqueue))
temp=outqueue(tqueue);
if(temp->bdegree<=-2 || temp->bdegree>=2)
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==1)
return temp;
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==-1)
return temp;
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==-1)
return temp;
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==1)
return temp;
if(temp->lchild!=NULL)inqueue(tqueue,temp->lchild);
if(temp->rchild!=NULL)inqueue(tqueue,temp->rchild);
return NULL;
/*(2,1),(2,-1),(-2,-1),(-2,1)完美的卡诺图啊!!*/
bitree *getmother(bitree *head,bitree *child)
bitree *temp;
if(head==child)return NULL;
if(head->lchild==child || head->rchild==child)return head;
if(head->lchild==NULL || head->rchild==NULL)return NULL;
if(head->lchild!=NULL)
temp=getmother(head->lchild,child);
if(temp!=NULL)return temp;
return getmother(head->rchild,child);
/*递归查找一个节点的妈妈*/
bitree *createsuperbitree(int *source,int len)/*不消说了,建立平衡二叉树*/
int itemp;
bitree *head=NULL;
bitree *temp=NULL;
bitree *tmother=NULL;
bitree *p=NULL;
bitree *q=NULL;
head=(bitree *)malloc(sizeof(bitree));
head->lchild=NULL;
head->rchild=NULL;
head->item=*source;
head->bdegree=0;
source ;
len--;
while(len>0)
insertbitree(head,*source);
addbdegree(head);
temp=leveldetect(head);
if(temp!=NULL)
tmother=getmother(head,temp);
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==1)
p=temp->lchild;
temp->lchild=p->rchild;
p->rchild=temp;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*LL*/
if(temp->bdegree==2 && temp->lchild!=NULL && temp->lchild->bdegree==-1)
p=temp->lchild->rchild;
q=temp->lchild;
q->rchild=p->lchild;
temp->lchild=p->rchild;
p->lchild=q;
p->rchild=temp;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*LR*/
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==-1)
p=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=p->lchild;
p->lchild=temp;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*RR*/
if(temp->bdegree==-2 && temp->rchild!=NULL && temp->rchild->bdegree==1)
p=temp->rchild->lchild;
q=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=p->lchild;
q->lchild=p->rchild;
p->lchild=temp;
p->rchild=q;
if(tmother!=NULL)
if(tmother->lchild==temp)tmother->lchild=p;
else tmother->rchild=p;
else
head=p;
/*RL*/
addbdegree(head);
source ;
len--;
return head;
main()/*演示*/
int binums[100],i,len;
bitree *head,*temp;
for(i=0;i<=99;i )binums[i]=0;
len=getnums(binums);
head=createsuperbitree(binums,len);
temp=getmother(head,head->rchild->rchild->rchild);
第二个:
#define LH 1 /* 左高 */
#define EH 0 /* 等しい */
#define RH -1 /* 右高 */
#define True 1
#define False 0
#define Boolean int
#define RET_FOUND 0
#define RET_NOFOUND 1
typedef struct user_list_
char mail_address[512 +1]; /* 送信者address */
char mail_domain[255 +1]; /*domain*/
int count1; /* 送信件数, doman别送信通数, NDR送信通数 */
int count2; /* 送信通数 */
int bf; /* 平衡因子 */
struct user_list_ * ptnLeft; /* 左指针 */
struct user_list_ * ptnRight; /* 右指针 */
USER_LIST;
typedef USER_LIST * PUSER_LIST;
/* 全局変数 */
Boolean taller;
/*平衡二叉树调整操作*/
void R_Rotate(PUSER_LIST *p)
/*对以*p指向的结点为根的子树,作右单旋转处理,处理之后,*p指向的结点为子树的新根*/
PUSER_LIST lp;
lp=(*p)->ptnLeft; /*lp指向*p左子树根结点*/
(*p)->ptnLeft=lp->ptnRight; /*lp的右子树挂接*p的左子树*/
lp->ptnRight=*p;
*p=lp; /* *p指向新的根结点*/
void L_Rotate(PUSER_LIST *p)
/*对以*p指向的结点为根的子树,作左单旋转处理,处理之后,*p指向的结点为子树的新根*/
PUSER_LIST lp;
lp=(*p)->ptnRight; /*lp指向*p右子树根结点*/
(*p)->ptnRight=lp->ptnLeft; /*lp的左子树挂接*p的右子树*/
lp->ptnLeft=*p;
*p=lp; /* *p指向新的根结点*/
void LeftBalance(PUSER_LIST *p)
/*对以*p指向的结点为根的子树,作左平衡旋转处理,处理之后,*p指向的结点为子树的新根*/
PUSER_LIST lp, rc;
lp=(*p)->ptnLeft; /*lp指向*p左子树根结点*/
[color=Red][size=4][b]switch((*p)->bf) /*检查*p平衡度,并作相应处理 ??(是否应该是检查lp的平衡度 )*/[/b][/size][/color]
case LH: /*新结点插在*p左子女的左子树上,需作单右旋转处理*/
(*p)->bf=lp->bf=EH;
R_Rotate(p);
break;
case EH: /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
(*p)->bf=LH;
break;
case RH: /*新结点插在*p左子女的右子树上,需作先左后右双旋处理*/
rc=lp->ptnRight; /*ptnRight指向*p左子女的右子树根结点*/
switch(rc->bf) /*修正*p及其左子女的平衡因子*/
case LH:
(*p)->bf=RH;
lp->bf=EH;
break;
case EH:
(*p)->bf=lp->bf=EH;
break;
case RH:
(*p)->bf=EH;
lp->bf=LH;
break;
/*switch(ptnRight->bf)*/
rc->bf=EH;
L_Rotate(&((*p)->ptnLeft)); /*对*p的左子树作左旋转处理*/
R_Rotate(p); /*对*t作右旋转处理*/
/*switch((*p)->bf)*/
/*LeftBalance*/
void RightBalance(PUSER_LIST *p)
/*对以*p指向的结点为根的子树,作左平衡旋转处理,处理之后,*p指向的结点为子树的新根*/
PUSER_LIST lp, lc;
lp=(*p)->ptnRight; /*lp指向*p右子树根结点*/
switch((*p)->bf) /*检查*p平衡度,并作相应处理*/
case RH: /*新结点插在*p左子女的右子树上,需作单左旋转处理*/
(*p)->bf=lp->bf=EH;
L_Rotate(p);
break;
case EH: /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
(*p)->bf=RH;
break;
case LH: /*新结点插在*p左子女的左子树上,需作先右后左双旋处理*/
lc=lp->ptnLeft; /*ptnLeft指向*p右子女的左子树根结点*/
switch(lc->bf) /*修正*p及其右子女的平衡因子*/
case RH:
(*p)->bf=LH;
lp->bf=EH;
break;
case EH:
(*p)->bf=lp->bf=EH;
break;
case LH:
(*p)->bf=EH;
lp->bf=RH;
break;
/*switch(ptnLeft->bf)*/
lc->bf=EH;
R_Rotate(&((*p)->ptnLeft)); /*对*p的右子树作右旋转处理*/
L_Rotate(p); /*对*t作左旋转处理*/
/*switch((*p)->bf)*/
/*RightBalance*/
int insertNewAddress( PUSER_LIST * pptnHead, char *mailAddr, int cnt1, int cnt2, int cnt3, int errcnt Boolean *taller)
PUSER_LIST ptnCurr;
ptnCurr = *pptnHead;
if(ptnCurr == NULL)
ptnCurr = (PUSER_LIST)malloc(sizeof(USER_LIST));
ptnCurr->ptnLeft = NULL;
ptnCurr->ptnRight = NULL;
strcpy(ptnCurr->mail_address, mailAddr);
ptnCurr->count1 = cnt1;
ptnCurr->count2 = cnt2;
ptnCurr->count3 = cnt3;
ptnCurr->errcnt = errcnt;
*taller = True;
ptnCurr->bf = EH;
*pptnHead = ptnCurr;
else if(strcmp(oneUser->fee_number, ptnCurr->fee_number) < 0)
insertNewAddress(&(ptnCurr->ptnLeft), mailAddr, cnt1, cnt2, cnt3, errcnt, taller);
if(*taller) /*已插入到(*t)的左子树中,且左子树增高*/
switch(ptnCurr->bf) /*检查*t平衡度*/
case LH: /*原本左子树高,需作左平衡处理*/
LeftBalance(pptnHead); *taller=False;break;
case EH: /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
ptnCurr->bf=LH; *taller=True;break;
case RH: /*原本右子树高,使左、右子树等高*/
ptnCurr->bf=EH; *taller=False;break;
else
insertNewAddress(&(ptnCurr->ptnRight), mailAddr, cnt1, cnt2, cnt3, errcnt, taller);
if(*taller) /*已插入到(*t)的左子树中,且左子树增高*/
switch(ptnCurr->bf) /*检查*t平衡度*/
case LH: /*原本左子树高,使左、右子树等高*/
ptnCurr->bf=EH; *taller=False;break;
case EH: /*原本左、右子树等高,因右子树增高使树增高*/
ptnCurr->bf=RH; *taller=True;break;
case RH: /*原本右子树高,需作右平衡处理*/
RightBalance(pptnHead); *taller=False;break;
return 0;
int searchAndAdd( PUSER_LIST *pptnHead, char *mailAddr, int cnt1, int cnt2, int cnt3, int errcnt)
PUSER_LIST ptnCurr;
ptnCurr = *pptnHead;
if (NULL == pptnHead)
return RET_NOFOUND;
while(ptnCurr != NULL)
if(strcmp(ptnCurr->mail_address, mailAddr) == 0)
ptnCurr->count1 += cnt1;
ptnCurr->count2 += cnt2;
ptnCurr->count3 += cnt3;
ptnCurr->errcnt += errcnt;
return RET_NOFOUND;
else if(strcmp(ptnCurr->mail_address, mailAddr) > 0)
ptnCurr = ptnCurr->ptnLeft;
else
ptnCurr = ptnCurr->ptnRight;
return RET_NOFOUND;
参考技术C 去网上找吧 平衡二叉树的旋转是一个很有趣的问题,自己理解了很有好处
平衡二叉树的定义及基本操作(查找插入删除)及代码实现
文章目录
平衡二叉树的定义
为了避免树的高度增长过快,降低二叉排序树的性能,我们规定在插入和删除二叉树结点时,要保证在任意结点的左、右子树高度差的绝对值不超过1,将这样的树称为平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree),简称平衡树(AVL)。此外,AVL树又称为高度平衡的二叉查找树。
定义结点左子树与右子树的高度差为该结点的平衡因子,则平衡二叉树结点的平衡因子的值只可能是-1,0或1 。
平衡二叉树可定义为:
或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:它的左子树和右子树都是平衡二叉树,且左子树和右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。

平衡二叉树的结点类型描述:
typedef struct AVLNode{
int data; //数据域
int bf; //平衡因子
struct AVLNode *lchild, *rchild; //指针域
}AVLNode, *AVLTree;
平衡二叉树的查找
平衡二叉树上进行查找的过程与二叉排序树相同,详细完整代码请参照二叉排序树的定义及基本操作(构造、查找、插入、删除)递归及非递归算法。因此,在查找过程中,与给定值进行比较的关键字个数不超过树的深度。
可以证明,含有n个结点的平衡二叉树的最大深度为O(log2n),因此平衡二叉树的平均查找长度为O(log2n)。
平衡二叉树的平衡旋转
二叉排序树保证平衡的基本思想如下:
每当在二叉排序树中插入(或删除)一个结点时,首先检查其插入路径上的结点是否因为此次操作导致了不平衡。若导致了不平衡,则先找到插入路径上离插入结点最近的平衡因子的绝对值大于1的结点A,再对以A为根的子树,在保持二叉排序树特性的前提下,调整各结点的位置关系,使之重新达到平衡。
一般可将失去平衡后进行调整的规律归纳为下列四种情况:LL平衡旋转,RR平衡旋转,LR平衡旋转,RL平衡旋转。
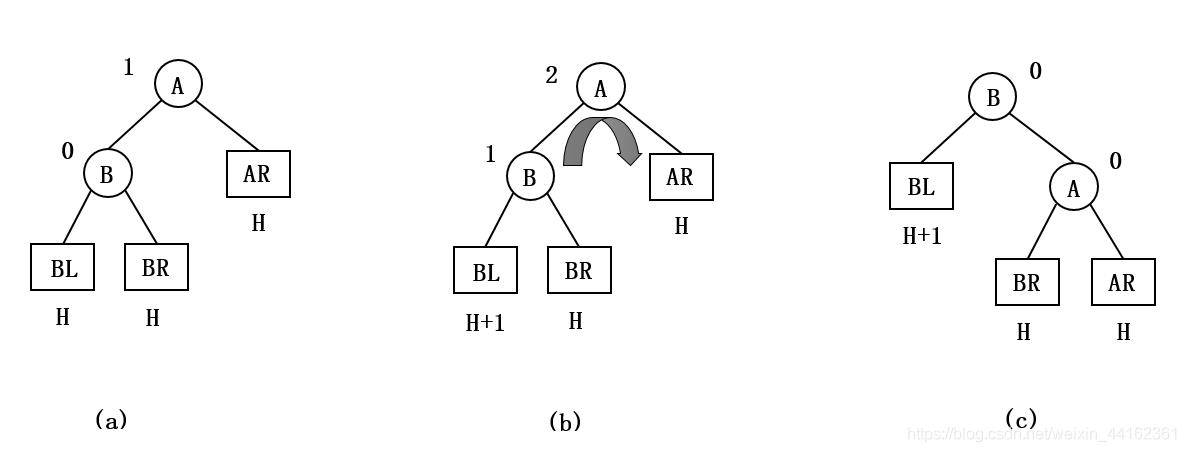
LL平衡旋转(右单旋转)
由于在结点A的左孩子(L)的左子树(L)上插入了新结点,A的平衡因子由1增至2,导致了以A为根的子树失去平衡。
需要一次向右的旋转操作:将A的左孩子B向右上旋转代替A成为根结点,将A结点向右下旋转成为B的右子树的根结点,而B的原右子树则作为A结点的左子树。
如下图所示,结点旁的数值代表结点的平衡因子,方块表示相应结点的子树,方块下的数值代表该子树的高度,以下相同,不再赘述。
实现代码:
void Rotate_LL(AVLNode *&p){
AVLNode *s = p; //要右旋转的结点
p = s->lchild;
s->lchild = p->rchild; //卸掉p右边的负载
p->rchild = s; //右单旋, p成为新根
p->bf = 0;
s->bf = 0;
}
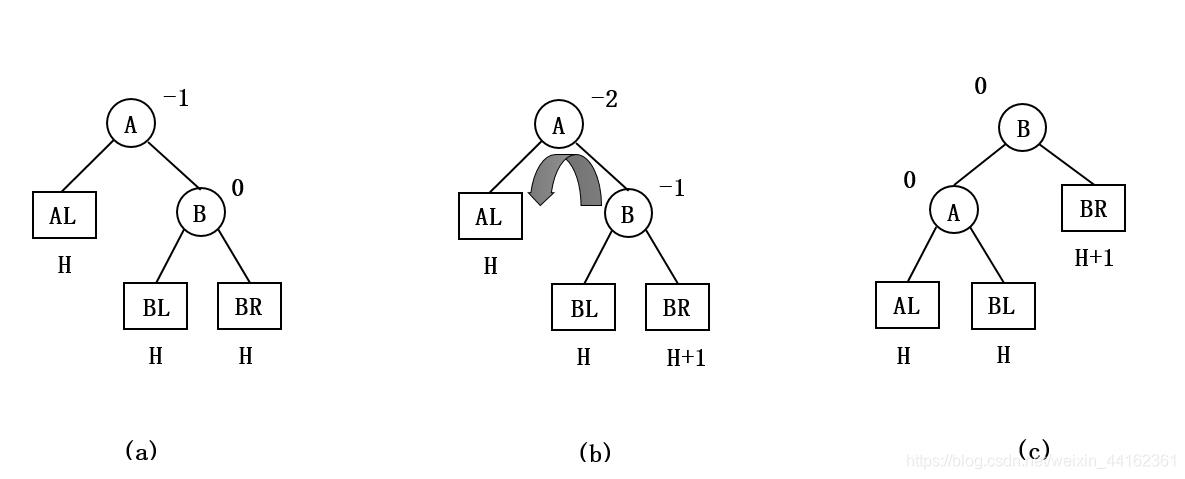
RR平衡旋转(左单旋转)
由于在结点A的右孩子(R)的右子树(R)上插入了新结点,A的平衡因子由-1减至-2,导致以A为根的子树失去平衡。
需要一次向左的旋转操作:将A的右孩子B向左上旋转代替A成为根结点,将A结点向左下旋转成为B的左子树的根结点,而B的原左子树作为A结点的右子树。如下图所示:
实现代码:
void Rotate_RR(AVLNode *&p){
AVLNode *s = p; //要左旋转的结点
p = s->rchild; //卸掉p左边的负载
s->rchild = p->lchild;
p->lchild = s; //左单旋, p成为新根
p->bf = 0;
s->bf = 0;
}
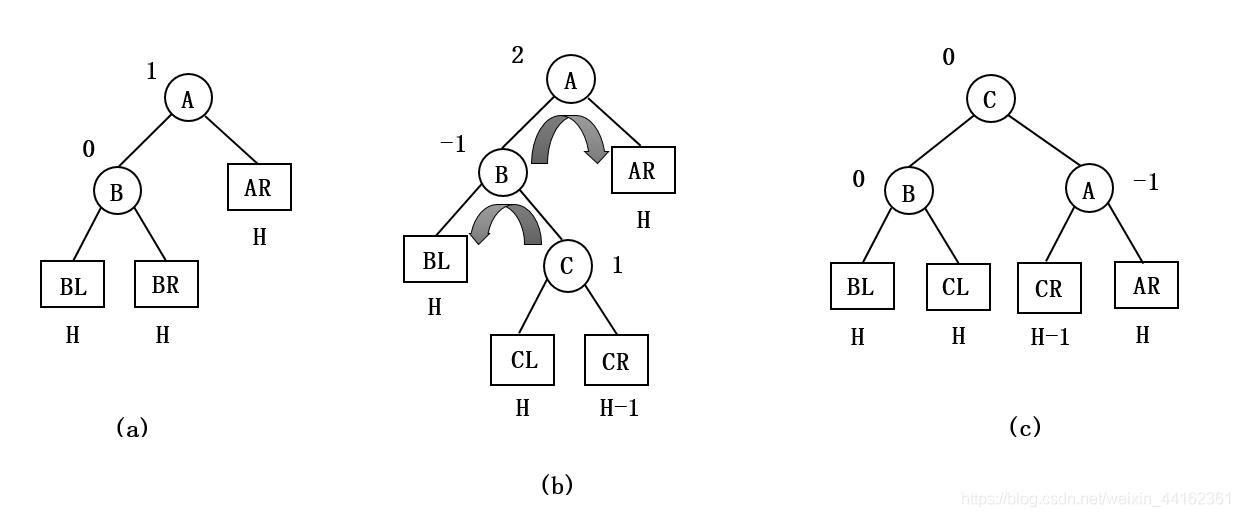
LR平衡旋转(先左后右双旋转)
由于在A的左孩子(L)的右子树(R)上插入新结点,A的平衡因子由1增至2,导致以A为根的子树失去平衡。
需要进行两次旋转操作:先左旋转后右旋转。先将A结点的左孩子B的右子树的根结点C向左上旋转提升到B结点的位置,然后再把该C结点向右上旋转提升到A结点的位置。如下图所示:
【注意】LR和RL旋转时,新结点究竟是插入C的左子树还是插入C的右子树均不影响旋转过程,在下面的图中以插入C的左子树中为例。
实现代码:
void Rotate_LR(AVLNode *&p){
AVLNode *sr = p, *sl = sr->lchild;
p = sr->rchild; //p成为新根
sl->rchild = p->lchild; //卸掉p左边的负载
p->lchild = sl;
sr->lchild = p->rchild; //卸掉p右边的负载
p->rchild = sr;
if(p->bf == 1){ //原p左子树高
sl->bf = 0;
sr->bf = -1;
}else if(p->bf == -1){ //原p右子树高
sl->bf = 1;
sr->bf = 0;
}else{ //原p两子树同高
sl->bf = 0;
sr->bf = 0;
}
p->bf = 0;
}
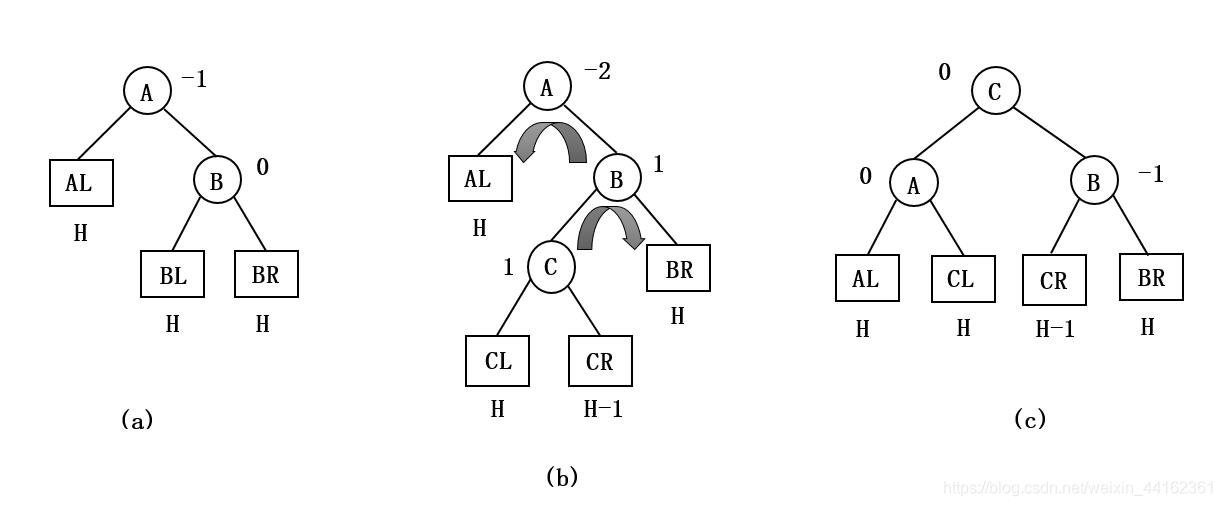
RL平衡旋转(先右后左双旋转)
由于在A的右孩子(R)的左子树(L)上插入新结点,A的平衡因子由-1减至-2,导致以A为根的子树失去平衡。
需要进行两次旋转操作:先右旋转后左旋转。先将A结点的右孩子B的左子树的根结点C向右上旋转提升到B结点的位置,然后再把该C结点向左上旋转提升到A结点的位置。如下图所示:
实现代码:
void Rotate_RL(AVLNode *&p){
AVLNode *sl = p, *sr = p->rchild; //p成为新根
p = sr->lchild;
sr->lchild = p->rchild; //卸掉p右边的负载
p->rchild = sr;
sl->rchild = p->lchild; //卸掉p左边的负载
p->lchild = sl;
if(p->bf == 1){ //原p左子树高
sl->bf = 0;
sr->bf = -1;
}else if(p->bf == -1){ //原p右子树高
sl->bf = 1;
sr->bf = 0;
}else{ //原p两子树同高
sl->bf = 0;
sr->bf = 0;
}
p->bf = 0;
}
平衡二叉树的插入
平衡二叉树的插入过程前半部分与二叉排序树相同,但是在新结点插入后,若造成查找路径上的某个结点不再平衡,则需要做出相应的调整。
在新结点作为叶结点插入后,必须从插入位置沿到根结点的路径回溯,检查在此路径上的结点是否变得不平衡。若是,则找出其中的最小不平衡子树,在保持二叉查找树特性的情况下,调整最小不平衡子树中结点之间的关系,使之达到新的平衡;否则,本次插入结束。
所谓最小不平衡子树,是指插入后在所有失去平衡性的结点中,以离插入结点最近的结点作为根的那棵子树,这个根结点一定处于在查找插入位置时所经过的路径上。
然后,在找到的最小不平衡子树上识别平衡旋转类型(LL、RR、LR、RL),做完平衡旋转后,本次插入即可结束。
平衡二叉树的删除
平衡二叉树的删除过程与二叉查找树类似。不同之处在于:若删除后破坏了AVL树的高度平衡性,还需要做平衡旋转。
<1>如果被删除结点*p有两个子女。首先查找*p在中序下的直接前驱*q(同样可以查找中序下的直接后继)。再把结点*q的内容传送给结点*p,把问题转移到删除最多只有一个子女的结点*q,把结点*q当作被删结点*p。(就是二叉排序树中的删除情况3的过程)
<2>如果被删除结点*p只有一个子女*q,可以把*p的双亲*f中原来指向*p的指针指到*q;(二叉排序树中的删除情况2)
<3>如果被删除结点*p没有子女,*p的双亲*f的相应指针置为NULL。(二叉排序树中的删除情况1)然后将原来以结点*f为根的子树的高度减1,并沿着*f到根的路径方向追踪高度变化对路径上各个结点的影响。
若*p是*f的左子女,则*f的左子树高度降低,平衡因子减1;若*p是*f的右子女,则*f的右子树高度降低,平衡因子加1。
根据修改后的*f的平衡因子,按三种情况处理:1.结点*f的平衡因子原来为0;2.结点*f的平衡因子原不为0,且较高子树的高度降低;3.结点*f的平衡因子原来不为0,且较矮子树的高度降低。
被删除结点的双亲原平衡因子为0
结点*f的平衡因子原来为0,在它的左子树或右子树高度降低后,它的平衡因子改为1或-1。由于以*f为根的子树高度没有改变,从*f到根结点的路径上的所有结点不需要调整。如下图所示:

被删除结点的双亲原平衡因子不为0且较高子树高度降低
结点*f的平衡因子原不为0,且较高的子树的高度降低,则*p的平衡因子改为0。此时以*f为根的子树平衡,但其高度减1。为此需要继续上溯,考察结点*f的双亲的平衡状态。如下图所示:
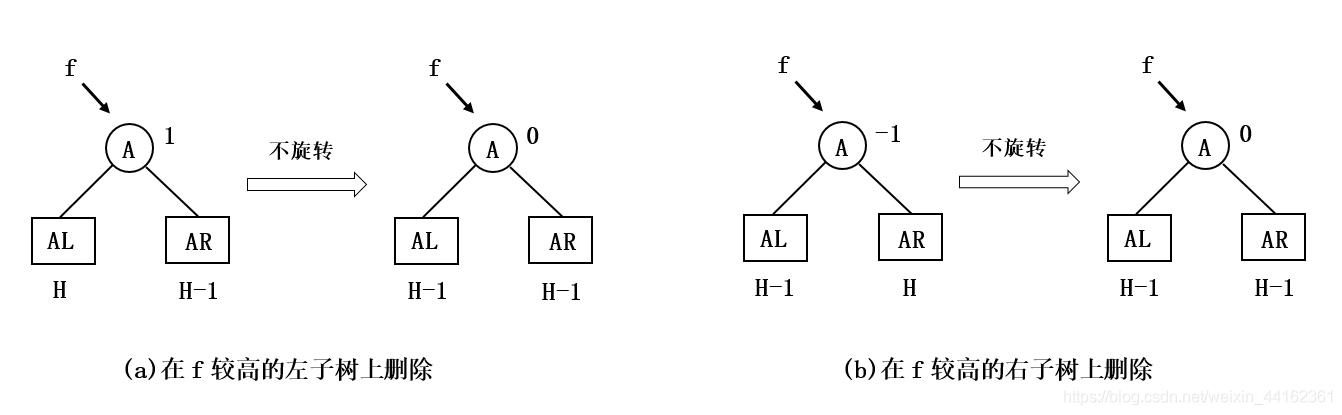
被删除结点的双亲原平衡因子不为0且较矮子树高度降低
结点*f的平衡因子原不为0,且较矮的子树的高度降低,则在结点*f处发生不平衡。需要进行平衡旋转来恢复平衡。
令*f的较高的子树的根为*q(该子树的高度未发生变化),根据*q的平衡因子,有以下三种平衡化操作。
<一> *q的平衡因子为0
如果*q的平衡因子为0,执行一个单旋操作来恢复结点*f的平衡,如下图所示:
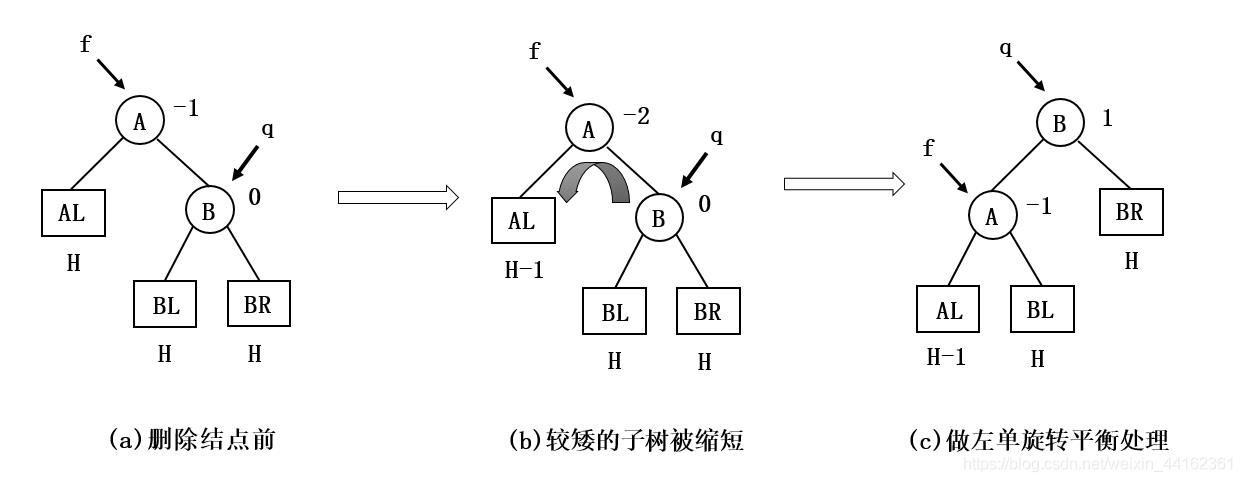
上图是左单旋转的例子,右单旋转的情形可以对称的处理。由于平衡旋转后以*q为根的子树的高度没有发生改变,此时可以结束平衡化处理过程。
<二> *q的平衡因子与双亲*f的平衡因子正负号相同
如果*q的平衡因子与双亲*f的平衡因子正负号相同,则执行一个单旋转来恢复平衡,结点*f和*q的平衡因子均改为0,如下图所示:
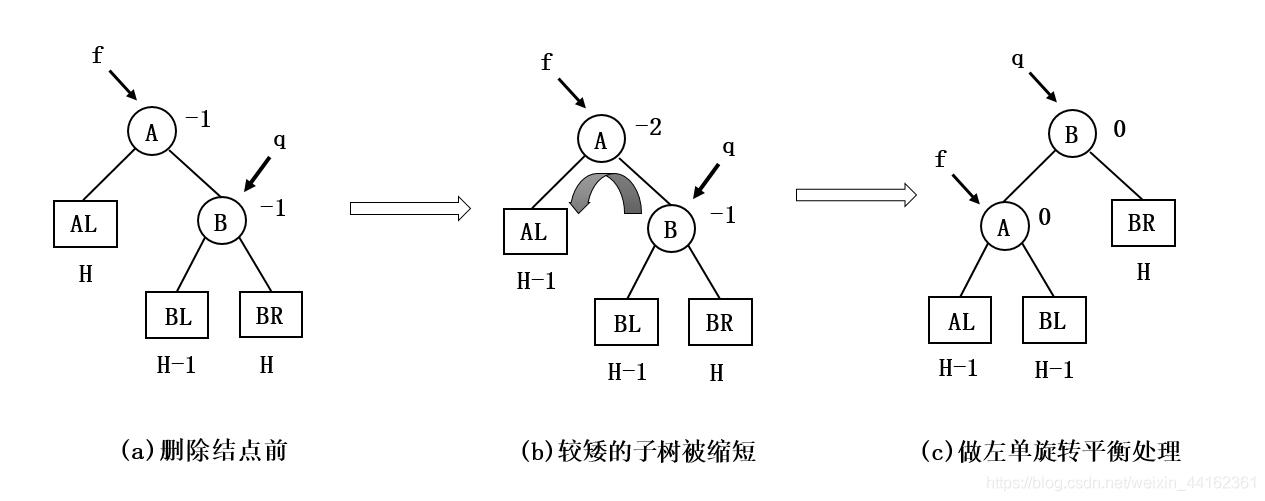
图中是做单旋转的例子,右单旋转的情形可以对称的处理。由于经过平衡旋转后结点*q的子树高度降低1,故需要继续沿插入路径上溯考察结点*q的双亲的平衡状态。
<三> *q的平衡因子与双亲*f的平衡因子正负号相反
如果*f与*q的平衡因子正负号相反,则执行一个双旋转来恢复平衡,如下图所示:
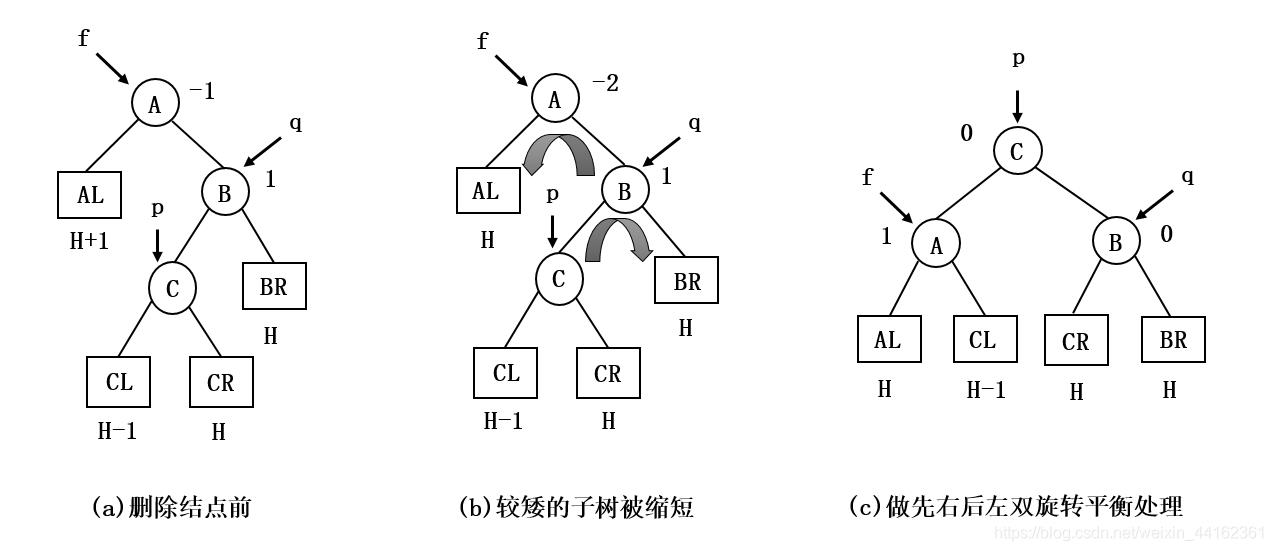
先围绕*q转再围绕*f转。新的根结点的平衡因子置为0,其他结点的平衡因子相应的调整。还需要上溯考察它的双亲,继续向上层进行平衡化工作。
最极端的情形是:如果回溯路径上每个结点都需要平衡旋转,可能导致AVL树的高度降低,甚至原来的根结点都可能旋转下去,被旋转上来的结点替代。
以上是关于平衡二叉树的操作(高手进)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章