Android面试题
Posted lxn_李小牛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android面试题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.Activity启动模式
如何查看当前的Activity栈以及Activity栈中的Activity信息
adb shell dumpsys activity activities结果如下
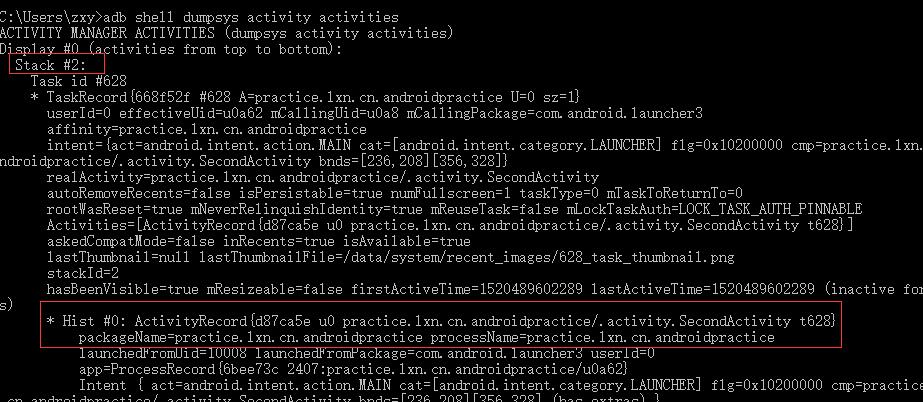
一般会有两个Stack,Stack#0代表Launcher所在的Activity
另外的一个Stack就是我们自己的Activity
Task代表一个任务栈,如果有多个任务栈,会有多个Task
Hist代表任务栈中某个Activity,如果当前任务栈中有多个Activity,则会有多个Hist #
需要说明的是,通过在清单文件中给Activity指定启动模式为singleTask和启动时添加标记FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK效果是一样的,在启动目标Activity的时候,首先在系统中查找当前的Task中有没有和目标Activity的taskAffinity相同的,有的话就在当前Task中启动,没有的话就新建一个Task
2.动态代理
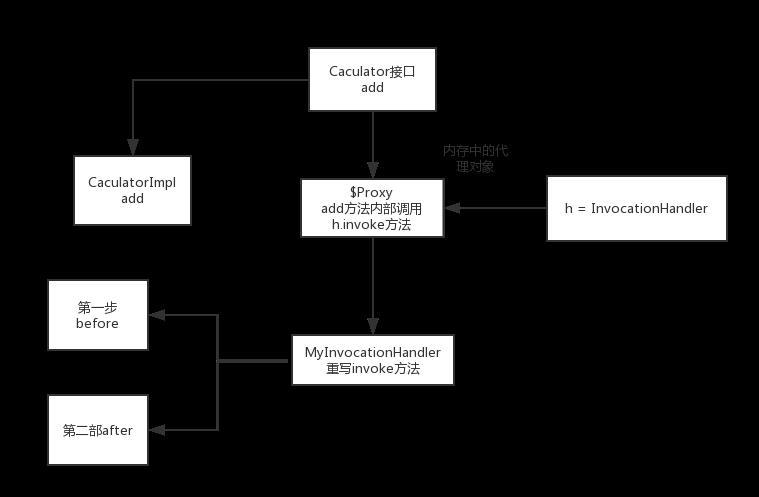
下面我们用代码来解释动态代理
public interface Caculator //统一接口,代理类和真实对象需要实现此接口
int add(int a, int b);
/**
* 真实对象
*/
public class CaculatorImpl implements Caculator
@Override
public int add(int a, int b)
System.out.println("==============add");
return a + b;
/**
* 代理类,需要实现InvocationHandler接口
*/
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler
private Caculator mTarget;
//绑定被代理类,并且返回代理对象
Object bind(Caculator obj)
mTarget = obj;
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(mTarget.getClass().getClassLoader(),mTarget.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
/**
*
* @param o 被代理的真实对象
* @param method 被代理对象的方法
* @param objects 方法参数
* @return 方法返回值
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable
System.out.println("============before");
//调用被代理对象的方法
Object result = method.invoke(mTarget, objects);
System.out.println("============after" + result);
return result;
public class ProxyTest //测试方法
public static void main(String[] args)
Caculator caculator = new CaculatorImpl();//创建被代理对象
Caculator proxy = (Caculator) new MyInvocationHandler().bind(caculator);//创建代理对象,
proxy.add(2,3);
动态代理应用场景
日志集中打印
事物
AOP
权限管理
下面看下生成代理类的流程
我们从源码的角度来看看整个过程
private static final Class<?>[] constructorParams = InvocationHandler.class ;@CallerSensitive public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException Objects.requireNonNull(h);//检查我们传入的InvocationHandler是否为null final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone(); /* * 创建代理类的字节码对象 */ Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs); /* */ try //通过反射获取代理对象的构造函数,这个构造函数的参数为InvocationHandler类型 final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams); if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() public Void run() cons.setAccessible(true); return null; ); return cons.newInstance(new Object[]h);//通过构造函数创建对象,需要InvocationHandler类型的参数 catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); catch (InvocationTargetException e) Throwable t = e.getCause(); if (t instanceof RuntimeException) throw (RuntimeException) t; else throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t); catch (NoSuchMethodException e) throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); 我们看看getProxyClass0方法是如何创建代理对象的
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces)
if (interfaces.length > 65535)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
// If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing
// the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy;
// otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
获取代理类的步骤可以总结为一下的流程:
- 基于代理接口查找ClassLoader中是否有代理对象的类,如果有,从缓存中取一个
- 如果没有,利用ProxyClassFactory生成一个proxy字节码,具体过程是在ProxyClassFactory的apply方法中
private static final class ProxyClassFactory
implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
// 代理类名称前缀
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy";
// next number to use for generation of unique proxy class names
private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong();
@Override
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces)
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces)
/*
* 判断接口对classloader是否可见
*/
Class<?> interfaceClass = null;
try
interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader);
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
if (interfaceClass != intf)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
intf + " is not visible from class loader");
/*
* 判断class是否为一个接口
*/
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface())
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface");
/*
* 判断接口是否重复
*/
if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName());
String proxyPkg = null;
int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL;
/*
* Record the package of a non-public proxy interface so that the
* proxy class will be defined in the same package. Verify that
* all non-public proxy interfaces are in the same package.
*/
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces)
int flags = intf.getModifiers();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags))
accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL;
String name = intf.getName();
int n = name.lastIndexOf('.');
String pkg = ((n == -1) ? "" : name.substring(0, n + 1));
if (proxyPkg == null)
proxyPkg = pkg;
else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"non-public interfaces from different packages");
if (proxyPkg == null)
//包名
proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + ".";
/*
* 代理类的名称
*/
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
/*
* 通过ProxyGenerator创建代理类
*/
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
catch (ClassFormatError e)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
我们可以用下面的代码将JDK为我们生成的字节码生成在磁盘上
private static void generateProxy()
FileOutputStream fos = null;
//获取代理类的字节码
byte[] bytes = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("$Proxy", new Class[]Caculator.class);
try
fos = new FileOutputStream("$Proxy0.class");
fos.write(bytes);
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
if (fos != null)
fos.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
生成的字节码对象的代码
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements UserService
private static Method m1;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m0;
private static Method m3;
//构造方法,通过烦着调用创建对象,参数InvocationHandler是通过Proxy.newProxyInstance传过来的
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws
super(var1);//把我们的InvocationHandler对象传递给父类Proxy的h成员变量
public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws
try
return ((Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]var1)).booleanValue();
catch (RuntimeException | Error var3)
throw var3;
catch (Throwable var4)
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);
public final String toString() throws
try
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null);
catch (RuntimeException | Error var2)
throw var2;
catch (Throwable var3)
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
public final boolean getValue() throws
try
return ((Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null)).booleanValue();
catch (RuntimeException | Error var2)
throw var2;
catch (Throwable var3)
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
public final int hashCode() throws
try
return ((Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null)).intValue();
catch (RuntimeException | Error var2)
throw var2;
catch (Throwable var3)
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
public final void getName(String var1) throws
try
super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]var1);
catch (RuntimeException | Error var3)
throw var3;
catch (Throwable var4)
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);
//通过反射获取方法,传给invoke方法
static
try
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m4 = Class.forName("UserService").getMethod("getValue");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
m3 = Class.forName("UserService").getMethod("getName", Class.forName("java.lang.String"));
catch (NoSuchMethodException var2)
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
catch (ClassNotFoundException var3)
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
3.加载大图片
android3.0之前,bitmap的像素数据存放在Native内存,native内存的释放是不确定的,容易出现溢出,所以不用的时候需要
调用recycle()方法回收bitmap占用的内存。
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
//只解析图片的宽高信息,不在内存中申请空间
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground,options);
int width = options.outWidth;
int height = options.outHeight;
//获取采样率
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
options.inSampleSize = 4;
//加载图片
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground, options);
options.inBitmap = bitmap;
//使用inBitmap的时候inMutable要设置为true,才能够重用bitmap
options.inMutable = true;如果不想压缩图片的话,可以使用BitmapRegionDecoder
4.拍照并且保存图片到本地
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_four_th);
imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageview);
public void start(View view)
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
File dir = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"myimg");
if (!dir.exists())
dir.mkdirs();
long fileName = System.currentTimeMillis();
file = new File(dir,fileName + ".jpg");
if (!file.exists())
try
file.createNewFile();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
//指定拍照后图片保存地址
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, Uri.fromFile(file));
startActivityForResult(intent,1);
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data)
if(resultCode == RESULT_OK && requestCode == 1)
String filePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
//解析原始图片,比较大
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(filePath);
//获取压缩后的图片,采样率
Bitmap smallBitmap = getSmallBitmap(file, 500, 500);
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
public Bitmap getSmallBitmap(File file,int reqWidth,int reqHeight)
String filePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
//只是解析尺寸信息,不加载到内存中
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(filePath,options);//此时返回bitmap为null
//计算采样率
options.inSampleSize = caculateInSampleSize(options,reqWidth,reqHeight);
//真正去加载图片
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(filePath, options);
try
//质量压缩,压缩图片到本地,只改变存储在磁盘上的大小,bitmap的大小不会变,质量压缩不会改变像素
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG,80,bos);
return bitmap;
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
/**
* 计算采用率
*/
public int caculateInSampleSize(BitmapFactory.Options options,int reqWidth,int reqHeight)
int outWidth = options.outWidth;
int outHeight = options.outHeight;
int inSampleSize = 1;
if (outWidth > reqWidth || outHeight > reqHeight)
int widthRatio = Math.round((float) outWidth/(float) reqWidth);
int heightRatio = Math.round((float) outHeight/(float) reqHeight);
//返回比例小的一个
inSampleSize = widthRatio < heightRatio ? widthRatio : heightRatio;
return inSampleSize;
public Bitmap crossBitmap(Bitmap bitmap,String filePath)
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//质量压缩,100表示不压缩,把压缩后的数据保存到bos中
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG,100,bos);
int quality = 100;
//循环判断压缩后的图片大小是否大于100kb,大于继续压缩
while(bos.toByteArray().length/1024 > 100)
bos.reset();//清空bos
quality -= 10;
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG,quality,bos);
//压缩好写到文件中
try
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
fos.write(bos.toByteArray());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
return bitmap;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
5.Loader
public class DownLoadTask extends AsyncTaskLoader<String>
private static final String TAG = "DownLoadTask";
DownLoadTask(Context context)
super(context);
@Override
protected void onStartLoading()
Log.d(TAG, "onStartLoading: ");
super.onStartLoading();
forceLoad();//必须调用此方法,loadINBackground方法才能执行
@Override
public String loadInBackground()
Log.d(TAG, "loadInBackground: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try
Thread.sleep(2000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return "finish";
以上是关于Android面试题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章