限流 -- Sentinel 相关实现原理学习总结
Posted 归田
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了限流 -- Sentinel 相关实现原理学习总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简介
Sentinel 是什么?
随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。Sentinel 以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性。
官方地址:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
- 丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
- 完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
- 广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
- 完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口来快速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等。
Sentinel 的主要特性:
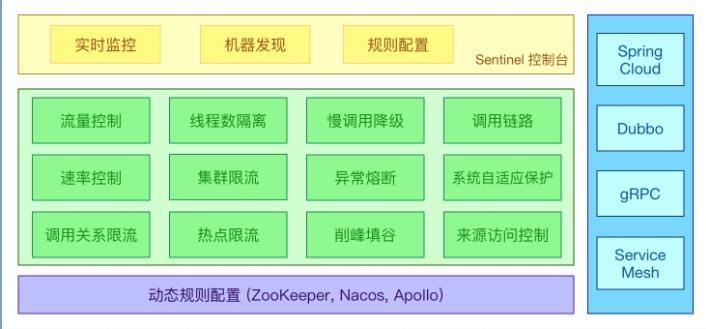
Sentinel 的开源生态:
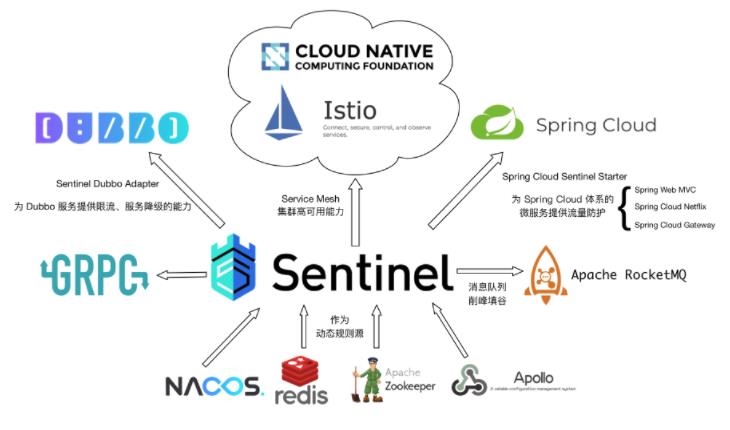
Sentinel 分为两个部分:
- 核心库(Java 客户端)不依赖任何框架/库,能够运行于所有 Java 运行时环境,同时对 Dubbo / Spring Cloud 等框架也有较好的支持。
- 控制台(Dashboard)基于 Spring Boot 开发,打包后可以直接运行,不需要额外的 Tomcat 等应用容器。
服务接入
服务端启动:
将 Sentinel 源码下载下来导入 IDEA 可以看到如下工程结构,启动 DashboardApplication 就可以看到 Sentinel 管理页面
登录 Sentinel 并进入管理页面默认用户名密码(sentinel/amin)

主页面:

客户端接入:
目前 sentinel 官方提供了一些常用框架接入的 demo :https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/tree/master/sentinel-demo
引入相关jar:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>$版本号</version>
</dependency>Spring boot 接入为例:
设置 sentinel 提供的 CommonFilter 来拦截所有的访问
@Configuration
public class webConfig
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean sentinelFilterRegistration()
FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registration.setFilter(new CommonFilter());
registration.addUrlPatterns("/*");
registration.setName("sentinelFilter");
registration.setOrder(1);
return registration;
客户端启动参数:
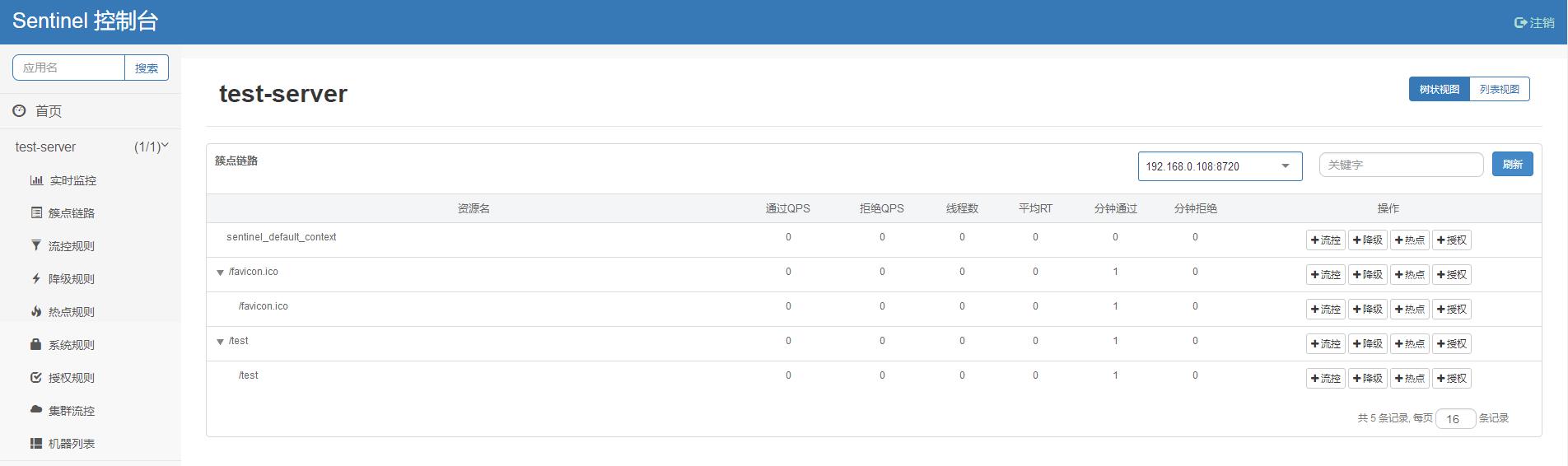
-Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8080 -Dproject.name=test-server启动之后在 Sentinel 的 仪表板上看到客户端上报的一些信息
工作原理
Slot 插槽
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称(resourceName),每次资源调用都会创建一个 Entry 对象。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 SphU API 显式创建。Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain),这些插槽有不同的职责,例如:
NodeSelectorSlot负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;ClusterBuilderSlot则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;StatisticSlot则用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;FlowSlot则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;AuthoritySlot则根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;DegradeSlot则通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;SystemSlot则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;
Sentinel 提供了插槽接口 ProcessorSlot,其中提供了方法 enrty 处理进入请求 和 exit 处理请求结束操作
public interface ProcessorSlot<T>
/**
* Entrance of this slot.
*
* @param context current @link Context
* @param resourceWrapper current resource
* @param param generics parameter, usually is a @link com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node.Node
* @param count tokens needed
* @param prioritized whether the entry is prioritized
* @param args parameters of the original call
* @throws Throwable blocked exception or unexpected error
*/
void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, T param, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
/**
* Means finish of @link #entry(Context, ResourceWrapper, Object, int, boolean, Object...).
*
* @param context current @link Context
* @param resourceWrapper current resource
* @param obj relevant object (e.g. Node)
* @param count tokens needed
* @param prioritized whether the entry is prioritized
* @param args parameters of the original call
* @throws Throwable blocked exception or unexpected error
*/
void fireEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
/**
* Exit of this slot.
*
* @param context current @link Context
* @param resourceWrapper current resource
* @param count tokens needed
* @param args parameters of the original call
*/
void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
/**
* Means finish of @link #exit(Context, ResourceWrapper, int, Object...).
*
* @param context current @link Context
* @param resourceWrapper current resource
* @param count tokens needed
* @param args parameters of the original call
*/
void fireExit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
总体的框架如下:
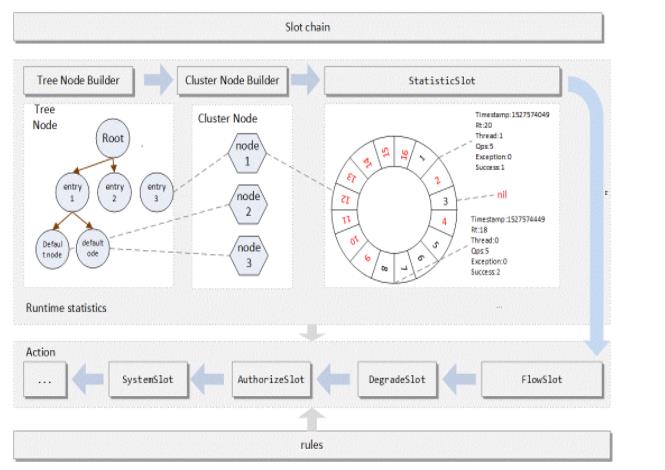
Sentinel 将 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展,使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。您可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。
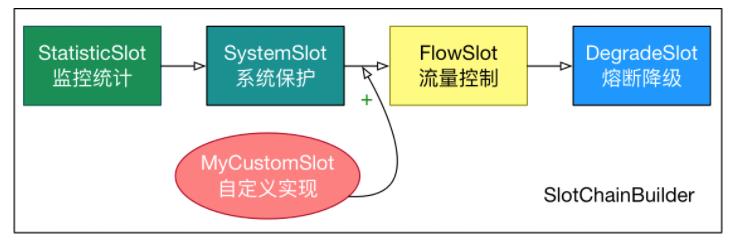
RuleManager 规则管理器
每个 Slot 插槽背后都对应着一个 RuleManager 的实现类,简单理解就是每个 Slot 有一套规则,规则验证处理由对应的 RuleManager 来进行处理。
流量控制:FlowSolt 对应 FlowRuleManager
降级控制:DegradeSlot 对应 DegradeRuleManager
权限控制:AuthoritySlot 对应 AuthorityRuleManager
系统规则控制: SystemSlot 对应 SystemRuleManager
降级控制实现原理
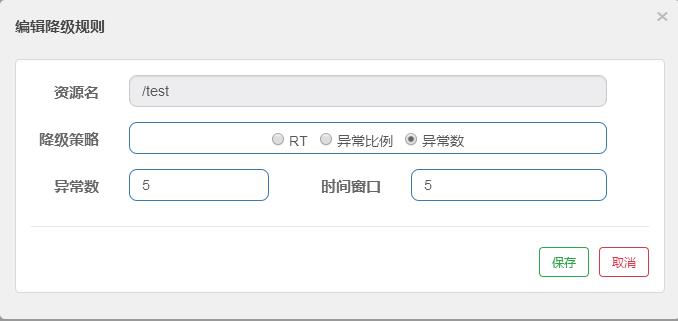
1、新增资源配置降级规则,目前对于降级策有如下三种:
- RT:平均响应时间 (DEGRADE_GRADE_RT):当 1s 内持续进入 5 个请求,对应时刻的平均响应时间(秒级)均超过阈值(count,以 ms 为单位),那么在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule 中的 timeWindow,以 s 为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地熔断(抛出 DegradeException)。注意 Sentinel 默认统计的 RT 上限是 4900 ms,超出此阈值的都会算作 4900 ms,若需要变更此上限可以通过启动配置项 -Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=xxx 来配置。
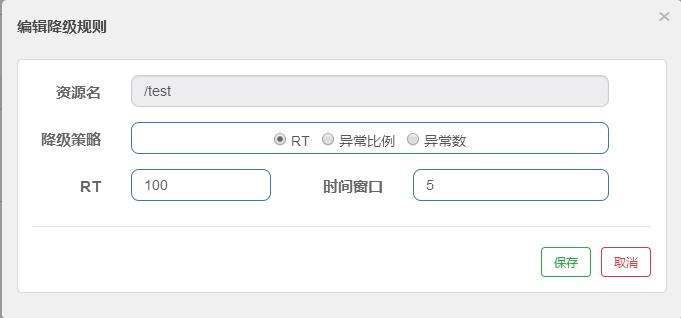
- 异常比例:当资源的每秒请求量 >= 5,并且每秒异常总数占通过量的比值超过阈值(DegradeRule 中的 count)之后,资源进入降级状态,即在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule 中的 timeWindow,以 s 为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地返回。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%。
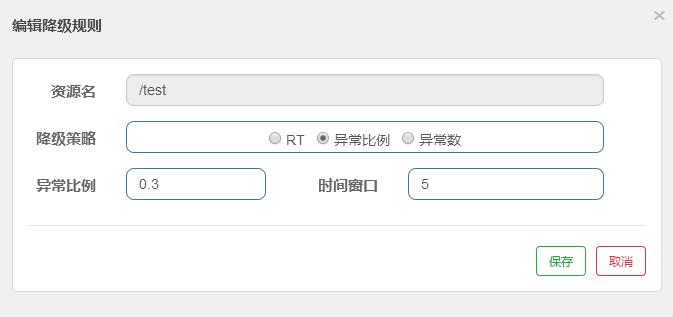
- 异常数:当资源近 1 分钟的异常数目超过阈值之后会进行熔断。注意由于统计时间窗口是分钟级别的,若 timeWindow 小于 60s,则结束熔断状态后仍可能再进入熔断状态。
限流结果信息
Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)2、实现逻辑
(1)在之前我们已经提及 Sentinel 是通过 slot 链来实现的,对于降级功能其提供了 DegradeSlot,实现源码如下:
public class DegradeSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode>
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable
DegradeRuleManager.checkDegrade(resourceWrapper, context, node, count);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args)
fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
(2)通过上面代码我们可以了解到,限流规则的实现是在 DegradeRuleManager 的checkDegrade中来处理的,限流可以-配置多个规则,依次按照规则来处理。
public static void checkDegrade(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count)
throws BlockException
Set<DegradeRule> rules = degradeRules.get(resource.getName());
if (rules == null)
return;
for (DegradeRule rule : rules)
if (!rule.passCheck(context, node, count))
throw new DegradeException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);
(3)在 DegradeRule 的 passCheck 方法中我们可以看到可以根据 RT、异常数和异常比例来进行熔断降级处理。
@Override
public boolean passCheck(Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount, Object... args)
if (cut.get())
return false;
ClusterNode clusterNode = ClusterBuilderSlot.getClusterNode(this.getResource());
if (clusterNode == null)
return true;
// 请求处理时间
if (grade == RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT)
double rt = clusterNode.avgRt();
if (rt < this.count)
passCount.set(0);
return true;
// Sentinel will degrade the service only if count exceeds.
if (passCount.incrementAndGet() < rtSlowRequestAmount)
return true;
else if (grade == RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO)
//异常比例
double exception = clusterNode.exceptionQps();
double success = clusterNode.successQps();
double total = clusterNode.totalQps();
// If total amount is less than minRequestAmount, the request will pass.
if (total < minRequestAmount)
return true;
// In the same aligned statistic time window,
// "success" (aka. completed count) = exception count + non-exception count (realSuccess)
double realSuccess = success - exception;
if (realSuccess <= 0 && exception < minRequestAmount)
return true;
if (exception / success < count)
return true;
else if (grade == RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT)
//异常数
double exception = clusterNode.totalException();
if (exception < count)
return true;
if (cut.compareAndSet(false, true))
ResetTask resetTask = new ResetTask(this);
pool.schedule(resetTask, timeWindow, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return false;
流量控制实现原理
接下来我们了解学习一下 Sentinel 是如何实现流量控制的
流量控制(flow control),其原理是监控应用流量的 QPS 或并发线程数等指标,当达到指定的阈值时对流量进行控制,以避免被瞬时的流量高峰冲垮,从而保障应用的高可用性。
FlowSlot 会根据预设的规则,结合前面 NodeSelectorSlot、ClusterNodeBuilderSlot、StatisticSlot 统计出来的实时信息进行流量控制。
限流的直接表现是在执行 Entry nodeA = SphU.entry(resourceName) 的时候抛出 FlowException 异常。FlowException 是 BlockException 的子类,您可以捕捉 BlockException 来自定义被限流之后的处理逻辑。
同一个资源可以创建多条限流规则。FlowSlot 会对该资源的所有限流规则依次遍历,直到有规则触发限流或者所有规则遍历完毕。
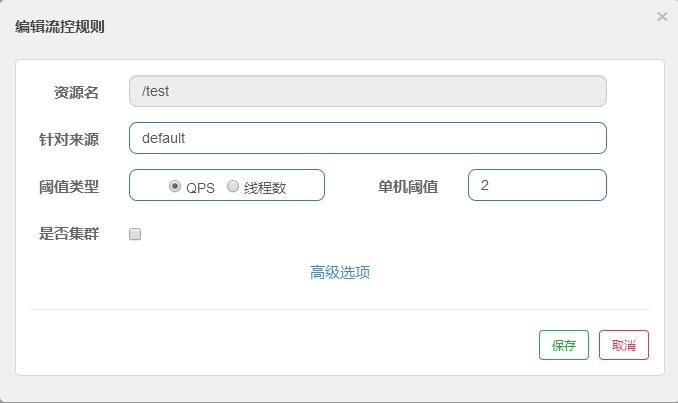
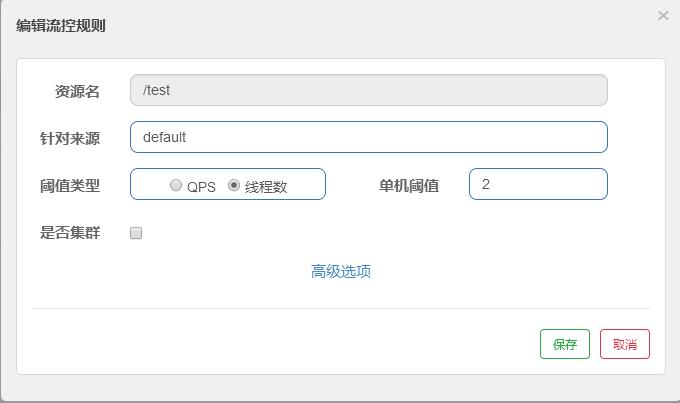
一条限流规则主要由下面几个因素组成,我们可以组合这些元素来实现不同的限流效果:
- resource:资源名,即限流规则的作用对象
- count: 限流阈值
- grade: 限流阈值类型(QPS 或并发线程数)
- limitApp: 流控针对的调用来源,若为 default 则不区分调用来源
- strategy: 调用关系限流策略
- controlBehavior: 流量控制效果(直接拒绝、Warm Up、匀速排队)
流控-QPS配置
流控-线程数配置
限流结果信息
Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)实现流程
(1)Sentinel 提供了 FlowSlot 用来进行流量控制,流量规则的最终实现在 FlowRuleChecker 的 checkFlow 中实现的。
public class FlowSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode>
private final FlowRuleChecker checker;
public FlowSlot()
this(new FlowRuleChecker());
/**
* Package-private for test.
*
* @param checker flow rule checker
* @since 1.6.1
*/
FlowSlot(FlowRuleChecker checker)
AssertUtil.notNull(checker, "flow checker should not be null");
this.checker = checker;
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable
checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized)
throws BlockException
checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized);
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args)
fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
private final Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider = new Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>>()
@Override
public Collection<FlowRule> apply(String resource)
// Flow rule map should not be null.
Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap();
return flowRules.get(resource);
;
(2)在 checkFlow 中会依次获取我们配置的流控规则,然后依次进行流控判断处理,如果被流控则抛出异常 FlowException
public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource,
Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException
if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null)
return;
Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());
if (rules != null)
for (FlowRule rule : rules)
if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized))
throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);
(3)在 canPassCheck 中会判断是集群限流还是本地限流
public boolean canPassCheck(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized)
String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();
if (limitApp == null)
return true;
if (rule.isClusterMode())
return passClusterCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
return passLocalCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
(4)如果是本地限流则获取节点信息,然后根据流控规则进行流控判断
private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized)
Node selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node);
if (selectedNode == null)
return true;
return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized);
(5)当 QPS 超过某个阈值的时候,则采取措施进行流量控制。流量控制的手段包括以下几种:直接拒绝、Warm Up、匀速排队。对应 FlowRule 中的 controlBehavior 字段。
直接拒绝(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT)方式是默认的流量控制方式,当QPS超过任意规则的阈值后,新的请求就会被立即拒绝,拒绝方式为抛出FlowException。这种方式适用于对系统处理能力确切已知的情况下,比如通过压测确定了系统的准确水位时。具体的例子参见 FlowQpsDemo。
Warm Up(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP)方式,即预热/冷启动方式。当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过"冷启动",让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。详细文档可以参考 流量控制 - Warm Up 文档
目前 Sentinel 对于流量控制提供了如下几种方式:
- 直接拒绝(DefaultController):支持抛出异常
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized)
int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);
if (curCount + acquireCount > count)
if (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS)
long currentTime;
long waitInMs;
currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count);
if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout())
node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount);
node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);
sleep(waitInMs);
// PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for @link @waitInMs.
throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs);
return false;
return true;
- 匀速排队(RateLimiterController):判断等待时间,如果等待时间过长也是会限流,并且使用 Thread.sleep 如果配置不正确可能会导致线程过多。
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized)
// Pass when acquire count is less or equal than 0.
if (acquireCount <= 0)
return true;
// Reject when count is less or equal than 0.
// Otherwise,the costTime will be max of long and waitTime will overflow in some cases.
if (count <= 0)
return false;
long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
// Calculate the interval between every two requests.
long costTime = Math.round(1.0 * (acquireCount) / count * 1000);
// Expected pass time of this request.
long expectedTime = costTime + latestPassedTime.get();
if (expectedTime <= currentTime)
// Contention may exist here, but it's okay.
latestPassedTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
else
// Calculate the time to wait.
long waitTime = costTime + latestPassedTime.get() - TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeMs)
return false;
else
long oldTime = latestPassedTime.addAndGet(costTime);
try
waitTime = oldTime - TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeMs)
latestPassedTime.addAndGet(-costTime);
return false;
// in race condition waitTime may <= 0
if (waitTime > 0)
Thread.sleep(waitTime);
return true;
catch (InterruptedException e)
return false;
- Warm Up(WarmUpController 和 WarmUpRateLimiterController):预热启动
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized)
long passQps = (long) node.passQps();
long previousQps = (long) node.previousPassQps();
syncToken(previousQps);
// 开始计算它的斜率
// 如果进入了警戒线,开始调整他的qps
long restToken = storedTokens.get();
if (restToken >= warningToken)
long aboveToken = restToken - warningToken;
// 消耗的速度要比warning快,但是要比慢
// current interval = restToken*slope+1/count
double warningQps = Math.nextUp(1.0 / (aboveToken * slope + 1.0 / count));
if (passQps + acquireCount <= warningQps)
return true;
else
if (passQps + acquireCount <= count)
return true;
return false;
总结:其他的限流规则我们就不一一去查看源码学习了,通过了解降级和流控这两个规则的实现原理,我们可以了解其他的实现原理都是类似的。当然这些目前是 Sentinel 提供的一些 限流等功能,这对于我们业务中使用响应的限流实现方案有一些借鉴意义,当然限流也可以通过其他方案来实现,可以读一下博主之前整理的一篇博客《业务学习 -- 高并发系统保护之限流和降级熔断》
以上是关于限流 -- Sentinel 相关实现原理学习总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章