Qt元系统之类型注册
Posted unclerunning
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Qt元系统之类型注册相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Qt元系统之类型注册
Meta Type System
如果库或程序有一个在不知道类型的情况下还能拷贝和销毁对象的需求,怎么实现呢?
如果类型已知,很容易就能拷贝和销毁:
class type
;
int main()
type t;
type t1 = t;
type *pt = new type;
delete pt;
如果类型不可知呢?
在实际应用中,类型在很多情况下都是不可知的,例如,qt库的开发人员就不知道qt库的使用者自定义的类型,而使用者往往希望qt库能对这些类型的对象进行存储、销毁等操作,否则,异步的信号和槽就无法使用用户自定义的类型,因为,qt需要存储调用参数;QVariant也无法使用用户自定义的类型,因为他需要知道怎么存储和销毁该类型的对象。
为了解决这个问题,Qt实现了一个Meta Type System。
想想为什么不用模板呢?
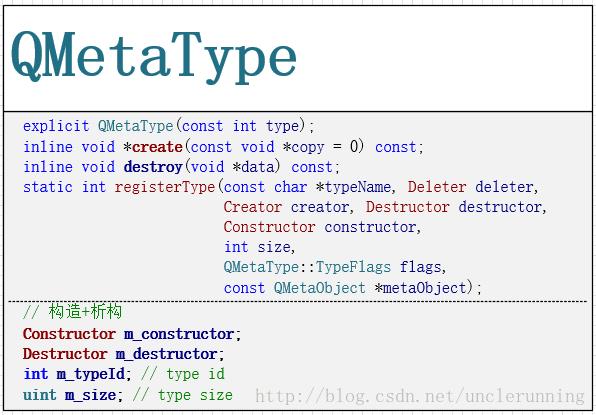
QMetaType是元类型系统提供给外部的接口,上面的类图省略了很多东西,着重给出了构造器、析构器、type id、类型大小这几个成员变量以及从type id构造QMetaType的构造函数、注册类型的接口、从地址指向的数据构造一份数据的接口、对指定地址的数据进行析构并归还内存空间的接口。
qt不可能采取浸入式的设计,因为在设计库的时候不可能知道每一个用户将会定义什么类型,它只可能知道自己定义使用的类型,因此,qt必须采用非浸入式的设计。
元类型系统的背后,是一系列数据结构的组合,例如,系统需要设计数据结构表示类型信息,存储类型信息,还需要接口查询类型信息,注册类型信息。
元类型系统中,每一个注册进去的类型都拥有一个type id,它就是这个类型的身份证编号。
有了这个系统,就能让qt库在不知道我们的类型的情况下拷贝和销毁该类型的对象:
register_type_1.h
#include <QString>
class MyClass
public:
MyClass() = default;
MyClass(const MyClass &_t)
m_str = _t.m_str;
QString m_str;
;
Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(MyClass) //延迟注册,非浸入式的设计 #include "register_type_1.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
//### test 1 ---qt static type
QString str = "test qt static type";
//获取QString的type id
int str_type_id = QMetaTypeId2<QString>::qt_metatype_id();
//从type id构造出元类型对象
QMetaType Str_static_meta_type(str_type_id);
/*
构造出了元对象之后,我们就能用这个对象做一些事情啦
*/
//获取QString类型的大小
int str_type_size = Str_static_meta_type.sizeOf();
//从&str生成str的拷贝,并返回指向它的地址
QString *str_cp = static_cast<QString*>(Str_static_meta_type.create(&str));
//销毁拷贝,析构
Str_static_meta_type.destroy(str_cp);
QString test = *str_cp; //oops...访问一个已经析构的内存
//### test 2 ---qt dynamic[customer] type
MyClass mc;
mc.m_str = "test customer type";
int mc_type_id = QMetaTypeId2<MyClass>::qt_metatype_id();
QMetaType Mc_customer_meta_type(mc_type_id);
int mc_type_size = Mc_customer_meta_type.sizeOf();
MyClass *mc_cp = static_cast<MyClass*>(Mc_customer_meta_type.create(&mc));
Mc_customer_meta_type.destroy(mc_cp);
mc_cp = nullptr;
在test2中:
QMetaType Mc_customer_meta_type(mc_type_id);
Mc_customer_meta_type.create(&mc)
Mc_customer_meta_type.destroy(mc_cp);这三条语句表现出了元类型系统的核心能力:
只需要一个类型的type id,就可以拥有构造和析构该类型的对象的能力!
这个能力让qt库不必知道类型就能存储和销毁它的对象,只要使用者记得向系统注册这个类型:
template <typename T>
int qRegisterMetaType(const char *typeName)
//qRegisterMetaType<MyClass>("MyClass"); 场景
很多时候,我们需要将自己定义的类型融入到Qt的Meta system中,例如,用QVariant存储自定义的类对象。先看看如果什么都不做,会出现什么问题:
/*
* 示例代码一
*/
#include <QString>
class MyClass
public:
MyClass() = default;
MyClass(const MyClass &_t)
m_str = _t.m_str;
QString m_str;
;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
MyClass mc;
/*
QVariant对类MyClass使用QMetaTypeId2<MyClass>,如果我们不提供QMetaTypeId2<MyClass>的
特化版,那么编译器就会用qt提供的模板自动生成这个类。
*/
QVariant v = QVariant::fromValue(mc);
/*
从v中返回类型为MyClass的数据
*/
mc = v.value<MyClass>();
return 0;
启动编译器进行编译,结果如下:
error C2338: Type is not registered, please use the Q_DECLARE_METATYPE macro to make it known to Qt’s meta-object system
出现编译错误,怎么回事?
qt提供了如下templates:
//偏特化
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeIdQObject<T*, QMetaType::PointerToQObject>
enum
Defined = 1
;
static int qt_metatype_id()
static QBasicAtomicInt metatype_id = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(0);
if (const int id = metatype_id.loadAcquire())
return id;
const char * const cName = T::staticMetaObject.className();
QByteArray typeName;
typeName.reserve(int(strlen(cName)) + 1);
typeName.append(cName).append('*');
const int newId = qRegisterNormalizedMetaType<T*>(
typeName,
reinterpret_cast<T**>(quintptr(-1)));
metatype_id.storeRelease(newId);
return newId;
;
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeIdQObject<T, QMetaType::IsGadget>
enum
Defined = QtPrivate::is_default_constructible<T>::value
;
static int qt_metatype_id()
static QBasicAtomicInt metatype_id = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(0);
if (const int id = metatype_id.loadAcquire())
return id;
const char * const cName = T::staticMetaObject.className();
const int newId = qRegisterNormalizedMetaType<T>(
cName,
reinterpret_cast<T*>(quintptr(-1)));
metatype_id.storeRelease(newId);
return newId;
;
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeIdQObject<T, QMetaType::IsEnumeration>
enum
Defined = 1
;
static int qt_metatype_id()
static QBasicAtomicInt metatype_id = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(0);
if (const int id = metatype_id.loadAcquire())
return id;
const char *eName = qt_getEnumName(T());
const char *cName = qt_getEnumMetaObject(T())->className();
QByteArray typeName;
typeName.reserve(int(strlen(cName) + 2 + strlen(eName)));
typeName.append(cName).append("::").append(eName);
const int newId = qRegisterNormalizedMetaType<T>(
typeName,
reinterpret_cast<T*>(quintptr(-1)));
metatype_id.storeRelease(newId);
return newId;
;
//common templates
template <typename T, int =
QtPrivate::IsPointerToTypeDerivedFromQObject<T>::Value ? QMetaType::PointerToQObject :
QtPrivate::IsGadgetHelper<T>::Value ? QMetaType::IsGadget :
QtPrivate::IsQEnumHelper<T>::Value ? QMetaType::IsEnumeration : 0>
struct QMetaTypeIdQObject
enum
//默认是0 ---false
Defined = 0
;
;
//Defined 默认是0 ---false
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeId : public QMetaTypeIdQObject<T>
;
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeId2
enum Defined = QMetaTypeId<T>::Defined, IsBuiltIn=false ;
static inline Q_DECL_CONSTEXPR int qt_metatype_id()
return QMetaTypeId<T>::qt_metatype_id();
;
//常引用的偏特化,Defined 默认是0 ---false
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeId2<const T&> : QMetaTypeId2<T> ;
//引用的偏特化,Defined 默认是false
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeId2<T&> enum Defined = false ; ;枚举类型用于静态断言:
template <typename T>
inline Q_DECL_CONSTEXPR int qMetaTypeId()
//静态断言
Q_STATIC_ASSERT_X(QMetaTypeId2<T>::Defined, "Type is not registered, please use the Q_DECLARE_METATYPE macro to make it known to Qt's meta-object system");
return QMetaTypeId2<T>::qt_metatype_id();
QMetaTypeId2<T>::Defined是一个枚举常量,如果类型T没有一个Defined值为true的QMetaTypeId2<T>类型的类定义,而且代码使用了qMetaTypeId模板函数,则在编译时就会触发这个静态断言。
QVariant用到了QMetaTypeId2<T>类型:
class Q_CORE_EXPORT QVariant
...
template<typename T>
static inline QVariant fromValue(const T &value)
return qVariantFromValue(value);
...
template <typename T>
inline QVariant qVariantFromValue(const T &t)
//使用qMetaTypeId<T>()模板函数,返回QMetaTypeId2<T>::qt_metatype_id();
return QVariant(qMetaTypeId<T>(), &t, QTypeInfo<T>::isPointer);
...
所以 示例代码一用到了QMetaTypeId2<MyClass>, 由于没有给出特化版,所以编译器根据模板:
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeId2
enum Defined = QMetaTypeId<T>::Defined, IsBuiltIn=false ;
static inline Q_DECL_CONSTEXPR int qt_metatype_id()
return QMetaTypeId<T>::qt_metatype_id();
;生成类型QMetaTypeId2<MyClass>:
//编译器根据模板生成的QMetaTypeId<MyClass>
struct QMetaTypeId<MyClass> : public QMetaTypeIdQObject<MyClass>
;
struct QMetaTypeId2<MyClass>
//Defined是编译器常量值0
enum Defined = QMetaTypeId<MyClass>::Defined, IsBuiltIn=false ;
static inline Q_DECL_CONSTEXPR int qt_metatype_id()
return QMetaTypeId<MyClass>::qt_metatype_id();
;Defined值为0(false),所以编译器编译qVariantFromValue中调用的qMetaTypeId<MyClass>()模板函数时就会触发上面的静态断言,编译不能通过。
如果想要编译通过,就要给出一个特化版的QMetaTypeId<MyClass>, 使Defined值为1(true),像这样:
template <>
struct QMetaTypeId<MyClass>
//Defined值现在是1 !
enum Defined = 1 ;
//如果已注册,返回MyClass注册的id,否则注册并返回注册上的id
static int qt_metatype_id()
//静态原子变量,用来存储type id
static QBasicAtomicInt metatype_id = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(0);
if (const int id = metatype_id.loadAcquire()) return id;
/*
将类型注册到系统中
*/
const int newId =
qRegisterMetaType<MyClass>("MyClass",
reinterpret_cast<MyClass*>(quintptr(-1)));
metatype_id.storeRelease(newId);
return newId;
;
或者使用宏定义Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(TYPE)让预编译器自己生成:
#define Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(TYPE) Q_DECLARE_METATYPE_IMPL(TYPE)
#define Q_DECLARE_METATYPE_IMPL(TYPE) \\
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE \\
template <> \\
struct QMetaTypeId< TYPE > \\
\\
enum Defined = 1 ; \\
static int qt_metatype_id() \\
\\
static QBasicAtomicInt metatype_id = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(0); \\
if (const int id = metatype_id.loadAcquire()) \\
return id; \\
const int newId = qRegisterMetaType< TYPE >(#TYPE, \\
reinterpret_cast< TYPE *>(quintptr(-1))); \\
metatype_id.storeRelease(newId); \\
return newId; \\
\\
;
QT_END_NAMESPACE给出了这个特化版的类定义之后,就不会触发静态断言了,通过上面的模板类,qt以非浸入的方式将TYPE和type id绑定在一起。
特化版的QMetaTypeId<TYPE>类与使用common template推导生成的类最大的区别在于qt_metatype_id(), 从模板推导的类没有这个函数,特化版的类则定义了一个这样的函数:
static int qt_metatype_id()
//静态原子变量,用来存储type id
static QBasicAtomicInt metatype_id = Q_BASIC_ATOMIC_INITIALIZER(0);
if (const int id = metatype_id.loadAcquire()) return id;
/*
将类型注册到系统中
*/
const int newId =
qRegisterMetaType<MyClass>("MyClass",
reinterpret_cast<MyClass*>(quintptr(-1)));
metatype_id.storeRelease(newId);
return newId;
这个函数内部调用的模板函数qRegisterMetaType需要TYPE的类名字符串作为第一参数,这是模板机制推导不出来的,所以qt利用预处理器的#TPYE生成这样的字符串。
qt_metatype_id函数返回的type id对应类型TYPE注册到meta type system中的查找下标,通过这个type id就能找到TYPE的注册信息。
调用
QMetaTypeId<TYPE>::qt_metatype_id保证能够返回TYPE注册到系统中的type id
好了,现在可以放心的使用QVariant存储Myclass的对象了。
原因
为什么需要对非qt静态类型的类型进行注册呢?或者说,注册的含义是什么呢?为什么所谓的类型需要注册之后才能融入qt类型系统架构中呢?
来看QVariant的一个构造函数:
/*!
\\internal
flags is true if it is a pointer type
*/
QVariant::QVariant(int typeId, const void *copy, uint flags)
if (flags) //type is a pointer type
d.type = typeId;
d.data.ptr = *reinterpret_cast<void *const*>(copy);
else
create(typeId, copy);
d.is_null = false;
当要拷贝的是一个指针类型,那好办,赋值给万能的void型指针。关键在else部分:
如何
拷贝一个对象。进一步地,拷贝之后,如何销毁一个对象。
说了这么多,这才是要解决的关键问题:
void QVariant::create(int type, const void *copy)
d.type = type;
handlerManager[type]->construct(&d, copy);
我们如果要将类的对象存储在QVariant,就要:
- 提供数据—就是要放入QVariant中的该类的对象。
- 提供对象的大小—分配内存空间以及释放空间。
- 提供外部可访问的构造函数—构造数据。
- 提供外部可访问的析构函数—删除数据。
实现细节
QMetaType::registerNormalizedType函数
从registerNormalizedType函数展开貌似是个不错的选择,俯瞰全局,易于理解:
...
//注册
const int id = QMetaType::registerNormalizedType(
//正规化调整后的类型名字符串
normalizedTypeName,
//析构器
QtMetaTypePrivate::QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<T>::Destruct,
//构造器
QtMetaTypePrivate::QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<T>::Construct,
//对象大小
int(sizeof(T)),
flags,
//MetaObject or 0
QtPrivate::MetaObjectForType<T>::value());
...
/*!
Registers a user type for marshalling, with \\a normalizedTypeName,
a \\a destructor, a \\a constructor, and a \\a size. Returns the type's
handle, or -1 if the type could not be registered.
\\note normalizedTypeName is not checked for conformance with
Qt's normalized format, so it must already conform.
*/
int QMetaType::registerNormalizedType(const NS(QByteArray) &normalizedTypeName,
Destructor destructor,
Constructor constructor,
int size, TypeFlags flags,
const QMetaObject *metaObject)
// 获取静态全局的QCustomTypeInfo数组,里面存放的非qt静态类型的注册信息:
// QCustomTypeInfo
QVector<QCustomTypeInfo> *ct = customTypes();
if (!ct || normalizedTypeName.isEmpty() || !destructor || !constructor)
return -1;
//search
int idx = qMetaTypeStaticType(normalizedTypeName.constData(),
normalizedTypeName.size());
...
if (idx == UnknownType)
QWriteLocker locker(customTypesLock());
int posInVector = -1;
//search
idx = qMetaTypeCustomType_unlocked(normalizedTypeName.constData(),
normalizedTypeName.size(),
&posInVector);
//如果在注册系统查找不到该类型的注册信息,那就构造它的类型信息并注册到系统中
if (idx == UnknownType)
QCustomTypeInfo inf;
//正规化调整后的类名
inf.typeName = normalizedTypeName;
#ifndef QT_NO_DATASTREAM
inf.loadOp = 0;
inf.saveOp = 0;
#endif
inf.alias = -1;
//构造器和析构器
inf.constructor = constructor;
inf.destructor = destructor;
//对象大小
inf.size = size;
inf.flags = flags;
inf.metaObject = metaObject;
if (posInVector == -1)
idx = ct->size() + User;
//注册类型
ct->append(inf);
else
//注册类型
idx = posInVector + User;
ct->data()[posInVector] = inf;
return idx;
...
...
return idx;
registerNormalizedType函数将正规化类名为normalizedTypeName的类的QCustomTypeInfo信息填充好,然后注册到全局静态的QVector<QCustomTypeInfo>数组中,返回注册的type id。
QMetaTypeFunctionHelper模板类
QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<T>封装了T的析构函数和构造函数:
template <typename T, bool Accepted = true>
struct QMetaTypeFunctionHelper
static void Destruct(void *t)
Q_UNUSED(t) // Silence MSVC that warns for POD types.
//调用T的析构函数
static_cast<T*>(t)->~T();
static void *Construct(void *where, const void *t)
//调用placement operator new for type T
if (t)
return new (where) T(*static_cast<const T*>(t));
return new (where) T;
#ifndef QT_NO_DATASTREAM
static void Save(QDataStream &stream, const void *t)
stream << *static_cast<const T*>(t);
static void Load(QDataStream &stream, void *t)
stream >> *static_cast<T*>(t);
#endif // QT_NO_DATASTREAM
;
template <typename T>
struct QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<T, /* Accepted */ false>
static void Destruct(void *)
static void *Construct(void *, const void *) return 0;
#ifndef QT_NO_DATASTREAM
static void Save(QDataStream &, const void *)
static void Load(QDataStream &, void *)
#endif // QT_NO_DATASTREAM
;
template <>
struct QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<void, /* Accepted */ true>
: public QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<void, /* Accepted */ false>
;qMetaTypeStaticType函数:
从qt库的静态类型中查找typeName的type id
static const struct const char * typeName; int typeNameLength; int type;
types[] =
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_TYPE(QT_ADD_STATIC_METATYPE)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_ALIAS_TYPE(QT_ADD_STATIC_METATYPE_ALIASES_ITER)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_HACKS_TYPE(QT_ADD_STATIC_METATYPE_HACKS_ITER)
0, 0, QMetaType::UnknownType
;
/*!
\\internal
Similar to QMetaType::type(), but only looks in the static set of types.
*/
static inline int qMetaTypeStaticType(const char *typeName, int length)
int i = 0;
while (types[i].typeName &&
((length != types[i].typeNameLength)
|| memcmp(typeName, types[i].typeName, length)))
++i;
return types[i].type;
qMetaTypeCustomType_unlocked函数:
作用:查找类名为typeName的类是否已经注册,如果注册,则返回type id,否则,返回QMetaType::UnknownType。
/*!
\\internal
Similar to QMetaType::type(), but only looks in the custom set of
types, and doesn't lock the mutex.
The extra \\a firstInvalidIndex parameter is an easy way to avoid
iterating over customTypes() a second time in registerNormalizedType().
*/
static int qMetaTypeCustomType_unlocked(const char *typeName, int length,
int *firstInvalidIndex = 0)
const QVector<QCustomTypeInfo> * const ct = customTypes();
if (!ct)
return QMetaType::UnknownType;
if (firstInvalidIndex)
*firstInvalidIndex = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < ct->count(); ++v)
const QCustomTypeInfo &customInfo = ct->at(v);
if ((length == customInfo.typeName.size())
&& !memcmp(typeName, customInfo.typeName.constData(), length))
//已经注册过,直接返回
if (customInfo.alias >= 0)
return customInfo.alias;
return v + QMetaType::User;
if (firstInvalidIndex &&
(*firstInvalidIndex < 0)
&& customInfo.typeName.isEmpty())
*firstInvalidIndex = v;
//没有找到
return QMetaType::UnknownType;
QCustomTypeInfo类
class QMetaTypeInterface
public:
QMetaType::SaveOperator saveOp;
QMetaType::LoadOperator loadOp;
//指向QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<Type>::Construct函数的函数指针变量
QMetaType::Constructor constructor;
//指向QMetaTypeFunctionHelper<Type>::Destruct函数的函数指针变量
QMetaType::Destructor destructor;
//注册类的大小
int size;
quint32 flags; // same as QMetaType::TypeFlags
//指向注册类的QMetaObject地址
const QMetaObject *metaObject;
;
class QCustomTypeInfo : public QMetaTypeInterface
public:
QCustomTypeInfo()
: alias(-1)
QMetaTypeInterface empty = QT_METATYPE_INTERFACE_INIT(void);
*static_cast<QMetaTypeInterface*>(this) = empty;
//类名
QByteArray typeName;
int alias;
;source code
Qt5-QMetaType
Qt5-QVariant
Qt5- Private
通过定义一个全局静态的对象,利用构造函数调用AFUNC,编译器保证构造函数在main之前被调用
Q_CONSTRUCTOR_FUNCTION0(AFUNC)
QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_TYPE(F)
结合QT_FOR_EACH_STATIC_TYPE,生成了所有qt的静态类型的特化的 QMetaTypeId2<T>类
Q_DECLARE_BUILTIN_METATYPE(TYPE, METATYPEID, NAME)
全局静态初始化的所有qt的静态类型的<类名,类对象大小,type id>三元组
types[]
全局的QVector<QCustomTypeInfo>静态变量
customTypes()
封装构造、析构等函数的调用
Qt5-QMetaTypeFunctionHelper
以上是关于Qt元系统之类型注册的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章