Matlab ,数据库和GUi 设计
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Matlab ,数据库和GUi 设计相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
大家好,新手上路,需要用 Matlab 做一个GUI, 总体是这样的: 传感器把实际测到的数据定时传到数据库,之后想通过Matlab读取数据库里的数据并制成GUI界面进一步分析数据。 大概思路就是这样的,由于本人毫无数据库经验,希望大家给点意见如何下手?整体思路该怎么做? 由于数据量还是很大的,Matlab做GUI 能实现如此复杂的程序吗?Matlab能读取实时更新的数据库的数据吗?
从实用角度上讲,你这个监测电机是否正常的最经济的的东西就是用单片机实现实时的报警或者指示。
如果非要用MATLAB做,也不是不可以。那就分为3个部分来说:
(1)数据采集部分。
MATLAB内置了很多接口,包括USB,PCI,声卡等,下面就是一个用麦克风采集数据的例子。
http://zhidao.baidu.com/question/122843581.html
(2)数据库的建立。
这个说白了就是将采集到的数据保存,并做个索引。简单点的直接保存 workspace,复杂点的就用fwrite这个函数了,其实也容易。
(3)GUI界面这个东西也容易实现,界面上面uicontrol uibotton 等就可以了,可以在实时分析和回掉分析两者切换。类似的如下(百度图片中找的)。
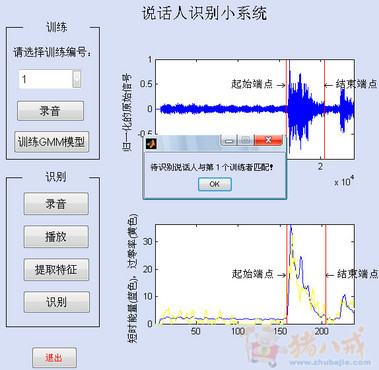
总的来说,这个问题很大,也不可能在百度上就完全说得清楚,理论上肯定可以实现。实际中能够取决于多个方面,比如信号的带宽是否超过传输比特率,信号的处理过程是否过于复杂等等。希望你成功。
追问多谢您的材料,估计是我没有说清楚....我擦拭的参数有80多个,现在的系统已经在数据库里了,所以现在只是想把数据库里的拿到matlab 去分析,所以GUI也主要是分析界面。不能使用单片机,不是那样的系统!
参考技术A 1:如果用matlab来分析你的数据,不一定要做成GUI,直接写m文件和函数就行。2:你如果只是想观察数据特征,不进行一些复杂运算的话。你要设计的其实是个上位机。用labview做个上位机就行。还能通过串口将数据实时更新。
3:你搞的那个数据库是无法实时的实现数据传递更新的。你可以在matlab用串口模块搭建一个上位机。追问
多谢您的答复,我其实是想监测发电机各个数据,主要是过去的数据,这样假如机器坏了,需要找哪些参数不正常就可以找出或者说在某个警报前有哪些参数不正常!这样也可以为以后的操作提供参考。
所以我觉得应该还是对数据的分析占大部分! 可以直接写m文件或者函数,只是GUI不是更直观吗,所以想最好弄成GUI。
您觉得我的思路可行吗?
那就可以的。没必要搞什么数据库,你把数据写到txt里面。将来用matlab处理就行。
不过还是不建议你用GUI。毕竟掌握起来需要时间。写个m文件其实也很方便。
你可以在考虑一下!望采纳!谢谢
数据分析基于matlab GUI学生成绩管理系统含Matlab源码 1981期
一、案例简介(仅供参考)
1 设计目标
1.1 设计一个基于GUI的学生成绩管理与分析系统
(1)设计一个插入背景的登录界面
(2)以某班某课成绩为研究对象,设计几个对话框,实现:
1.2 查询功能
点击学生姓名,在列表视图显示相应的学号、成绩
1.3 统计功能
读取数据库的学生成绩信息,进行统计从而绘制该课程学生成绩直方图(注释:学生成绩分几段,统计每段分数的人数,选择分数段中间数据,以此数据与人数为横、纵坐标,绘制直方图)以及饼图(对各分数段进行统计,便于直观的看出该课程成绩分布情况)
分析功能:
(1)该课的最低分、最高分以及相对应的学号
(2)该课程的平均分和均方差
(3)将该课程成绩按照从大到小排列、显示相对应学号
(4)按照学号显示学生成绩的原始分
1.4 设计退出系统的结束界面
2 实现方法
2.1 利用matlab语言指令编写程序和GUI设计对话框。
2.2 直接利用matlab中的函数来求最低分、最高分、平均分、标准方差、对成绩进行排序。
2.3 利用matlab中函数进行统计、分析,绘制直方图以及饼状图。
3 设计内容
3.1 GUI图形设计
(1)建立GUI对象添加需要的控件,加入需要的按钮、菜单控件、静态文本框、列表框等。
(2)修改控件属性,属性查看器提供了一系列属性,可以通过修改相应属性来改变控件。
3.2 编写m文件
当建立GUI后,在执行或存储界面时,会产生一个M文件,单击M-file Editor 图标按钮来编写该GUI下每个对象的Cllback与一些初始设置。直接在各对象callback下输入当用户按下这个对象后所应该调用执行的操作所对应的程序代码即可。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = chengjiguanli(varargin)
% CHENGJIGUANLI MATLAB code for chengjiguanli.fig
% CHENGJIGUANLI, by itself, creates a new CHENGJIGUANLI or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = CHENGJIGUANLI returns the handle to a new CHENGJIGUANLI or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% CHENGJIGUANLI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in CHENGJIGUANLI.M with the given input arguments.
%
% CHENGJIGUANLI('Property','Value',...) creates a new CHENGJIGUANLI or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before chengjiguanli_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to chengjiguanli_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help chengjiguanli
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 16-Jun-2022 16:54:23
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @chengjiguanli_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @chengjiguanli_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin1)
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin1);
end
if nargout
[varargout1:nargout] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin:);
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin:);
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before chengjiguanli is made visible.
function chengjiguanli_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to chengjiguanli (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for chengjiguanli
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes chengjiguanli wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = chengjiguanli_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout1 = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton_open.
function pushbutton_open_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton_open (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile('*.xls','打开成绩文件');%选择要打开的文件
if isequal(filename,0)|isequal(pathname,0)
errordlg('用户没有选择文件','出错'); %如果没有选择,弹出出错窗口
return;
else
str=[pathname,filename];
[mark,txt]=xlsread(str); %获取当前文件信息
name=txt(2:end,1);
set(handles.namelist,'string',name); %显示姓名
set(handles.marklist,'string',num2str(mark)); %显示成绩
handles.count=length(name);
handles.mark=mark; %定义成绩全局变量
handles.name=name; %定义姓名全局变量
guidata(hObject,handles);
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton_save.
function pushbutton_save_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton_save (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename,pathname]=uiputfile('*.xls','保存的文件'); %选择文件
if isequal(filename,0)|isequal(pathname,0)
errordlg('没有保存文件','出错'); %如果没有选择,弹出出错窗口
else
str=[pathname,filename];
name=handles.name;
mark=handles.mark;
oldcount=handles.count;
[row,co]=size(mark);
col=co+1;
if row<oldcount
M=cell(oldcount,col);
else
M=cell(row,col);
end
M(1:row,1)=name;
M(1:row,2:col)=num2cell(mark);
xlswrite(str,M,1,'A2');
handles.count=row;
guidata(hObject,row);
end
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
三、运行结果

四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 由伟,刘亚秀.MATLAB数据分析教程[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[2]王岩,隋思涟.试验设计与MATLAB数据分析[M].清华大学出版社,2012.
以上是关于Matlab ,数据库和GUi 设计的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章