spring注解驱动开发
Posted weixin_42412601
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring注解驱动开发相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
回顾一下使用配置文件是怎么开发的:
<bean id="messageService" class="com.example.demo.service.Impl.MessageServiceImpl"/>
// 用我们的配置文件来启动一个 ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/applicationContext-service.xml");
// 从 context 中取出我们的 Bean,而不是用 new MessageServiceImpl() 这种方式
MessageService messageService = context.getBean(MessageService.class);
// 这句将输出: hello world
System.out.println(messageService.getMessage());
使用注解又是怎样开发的呢
//配置类==配置文件
//@Configurable告诉spring这是一个配置类
@Configurable
public class MainConfig
//给容器中注册一个bean,类型为返回值;id默认使用方法名,可以使用@Bean
//里的value属性设置id
@Bean
public MessageServiceImpl messageServiceImpl()
return new MessageServiceImpl();
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
MessageServiceImpl bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(MessageServiceImpl.class);
System.out.println(bean.getMessage());
组件扫描
- xml怎么扫描:
<!-- 配置包扫描器同时开启注解 -->
<!--包扫描,只要标注了@Controller,@Service,@Repository,@component都会被扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.demo.service"/>
- 注解怎么扫描:
//配置类==配置文件
//@Configurable告诉spring这是一个配置类
@Configurable
//@ComponentScan指定要扫描的包,可以多个 excludeFilters
//excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes=Controller.class, Service.class)
//excludeFilters=Filter[],指定扫描的时候按照什么规则排除那些组件 排除test包下的controller注解的类和service注解的类
//includeFilters=Filter[],指定扫描的时候按照什么规则只要哪些组件 但是要设置useDefaultFilters = false
@ComponentScan(value ="com.example.demo.test",
includeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes=Controller.class, Service.class),
useDefaultFilters = false
)
public class MainConfig
//给容器中注册一个bean,类型为返回值;id默认使用方法名,可以使用@Bean
//里的value属性设置id
@Bean
public Person person()
return new Person();
过滤规则:
- FilterType.ANNOTATION 按照注解
- FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE 按照给定的类型
MessageService.class的子类或者实现类都会被加载进spring上下文 - FilterType.ASPECTJ 使用ASPECTJ表达式’
- FilterType.REGEX 使用正则表达式指定
- FilterType.CUSTOM 使用自定义规则 点进CUSTOM ,可以看到注释说要实现
TypeFilter接口
自定义规则:
public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter
/**
* @param metadataReader 读取到的当前正在扫描的类信息
* @param metadataReaderFactory 可以获取到其他任何类信息的
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException
//获取当前类注解的信心
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
//获取当前正在扫描的类的类信息
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
//获取当前类资源(类路径)
Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource();
String className = classMetadata.getClassName();
System.out.println("--->"+className);
//类名含有er的都会被扫描
if (className.contains("er"))
return true;
return false;
@Configurable
@ComponentScan(value ="com.example.demo.test",
includeFilters =
@ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.CUSTOM,classes=MyTypeFilter.class)
,
useDefaultFilters = false
)
public class MainConfig
//给容器中注册一个bean,类型为返回值;id默认使用方法名,可以使用@Bean
//里的value属性设置id
@Bean
public Person person()
return new Person();
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String s: beanDefinitionNames)
System.out.println(s);
mainConfig 配置类本身,不是包扫描结果
myTypeFilter 扫描结果,含有er
messageController 扫描结果,含有er
person 这个是配置类里@Bean注入的
messageServiceImpl 扫描结果,含有er
组件作用域
singleton 单实例的 默认值
prototype 多实例的
request 同一次请求创建一个实例
session 同一个session创建一个实例
@Configurable
public class MainConfig2
//@Scope设置作用范围 默认singleton
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean
public Person person()
return new Person();
测试:
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad2()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
Object bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("person");
Object bean2 = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(bean==bean2);
false
把bean创建出来放到ioc容器中的方法是何时调用的呢?
当方法@Scope()设置为singleton 时:
@Scope()
@Bean
public Person person()
System.out.println("给容器中添加person....");
return new Person();
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad2()
//什么也不做,只创建一个容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
结果可以看到容器一创建就打印:
给容器中添加person....
结论:bean的作用范围为singleton时,ioc容器启动会调用方法创建对象放到ioc容器中。
以后每次获取就是直接从容器(map.get())中拿。
当方法@Scope()设置为prototype 时:
测试:
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad2()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成。。。");
Object bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("person");
Object bean2 = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(bean==bean2);
结果:
容器创建完成。。。
给容器中添加person....
给容器中添加person....
false
结论:bean作用域为prototype时,ioc容器启动并不会去调用方法创建对象放到ioc容器中。
每次获取的时候才会调用方法创建对象。
懒加载
针对singleton单实例bean:
单实例bean默认在容器启动的时候创建bean。
懒加载:容器启动的时候不创建懒加载的单实例bean。第一次使用bean时,才创建对象并初始化
@Bean
//singleton懒加载
@Lazy
public Person person()
System.out.println("给容器中添加person....");
return new Person();
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad2()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成。。。");
Object bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("person");
Object bean2 = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(bean==bean2);
结果:
容器创建完成。。。
给容器中添加person....
true
按照条件注册(springboot中用的多,重点)
@Conditional 按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器中注册bean。可以放到方法上或者类上。
//当前系统是windows才注册这个bean
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)
@Bean("bill")
public Person person01()
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
//当前系统是linux才注册这个bean
@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)
@Bean("linux")
public Person person02()
return new Person("linux",50);
查看注解@Conditional: 发现value是一个数组且条件要实现Condition接口
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
编写条件:
判断是不是linux系统
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition
/**
* @param context 判断条件使用的上下文
* @param metadata 注释信息
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata)
//是否linux系统
//1.能获取到ioc使用的beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//2.能获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
//3.获取当前环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
//4.获取bean定义的注册类
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
//获取操作系统
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("linux"))
return true;
return false;
判断是不是Windows系统
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata)
//是否windows系统
//获取当前环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
//获取操作系统
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("Windows"))
return true;
return false;
测试:
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad3()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
//获取ioc容器的运行环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getEnvironment();
//动态获取环境变量的值 win10
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println( property);
//拿到所有person的定义
String[] beanNamesForType = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String s: beanNamesForType)
System.out.println(s);
//获取注册了的person对象
Map<String, Person> beansOfType = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(beansOfType);
结果:当前ioc运行环境为windows时,注册bill
当前ioc运行环境为linux时,注册linux
-Dos.name=linux 参数可以改变spring运行环境
给容器中注册bean组件的方式
给容器中注册bean组件的方式:
1、包扫描+组件标注注解
@controller/@Service/@Repository/@Component,标注在类上时,spring扫描出来后,spring会自己new出来一个对象,然后放容器当中去。不能自己控制对象的产生过程。
过程:应用启动,spring扫描类上,是否有
@controller/@Service/@Repository/@Component注解,如果有,spring会
2、 @Bean 导入第三方包里面的组件
对象由自己创建,程序员可以控制对象的产生过程。
3、@Import(重点)
快速给容器中导入一个组件 id默认是组件的全限定名,可以导多个
ImportSelector接口返回需要导入的组件的全限定名数组(Springboot中用的多)ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口手动注册bean到容器中- 使用
Spring提供的FactoryBean(工厂Bean)- 默认获取到的工厂是
bean调用getObject创建的对象 - 要获取工厂
Bean本身 ,我们需要给id前面加一个&
- 默认获取到的工厂是
@Import 使用一:

测试:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
//拿到所有person的定义
String[] beanNamesForType = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String s: beanNamesForType)
System.out.println(s);
mainConfig2
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Color 组件的全限定名
@Import 使用二:
实现ImportSelector接口
//自定义逻辑返回需要导入的组件
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector
//返回值就是要导入到容器中的组件全限定名
// AnnotationMetadata 当前标注了@Import注解的类的所有注解信息
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata)
return new String[]"com.example.demo.test.pojo.Blue","com.example.demo.test.pojo.Yellow";
配置类:
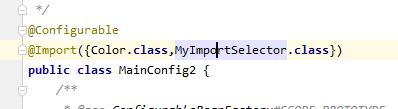
测试:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
//拿到所有person的定义
String[] beanNamesForType = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String s: beanNamesForType)
System.out.println(s);
mainConfig2
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Color
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Blue
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Yellow
@Import 使用三:
实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口:
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
//importingClassMetadata 当前标注了@Import注解的类的所有注解信息
//BeanDefinitionRegistry BeanDefinition注册类
//把所有需要添加到容器中的bean:调用BeanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition()
//手工注册进来
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
boolean blue = registry.containsBeanDefinition("com.example.demo.test.pojo.Blue");
boolean yellow = registry.containsBeanDefinition("com.example.demo.test.pojo.Yellow");
//如果blue yellow 注册了就注册rainBow
if (blue && yellow)
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(RainBow.class);
//指定beanName为rainBow,设置BeanDefinition
registry.registerBeanDefinition("rainBow",rootBeanDefinition);
配置类:
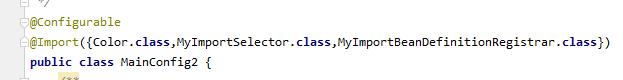
测试:
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad4()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
//拿到所有person的定义
String[] beanNamesForType = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String s: beanNamesForType)
System.out.println(s);
mainConfig2
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Color
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Blue
com.example.demo.test.pojo.Yellow
rainBow
使用Spring提供的FactoryBean(工厂Bean)
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42412601/article/details/103549059
实现FactoryBean接口:
//创建一个spring定义的FactoryBean
public class ColorFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Color>
//是单例吗 true 是单例,在容器中保存一份
//false 多实例,在容器中保存多分
@Override
public boolean isSingleton()
return true;
//返回一个Color对象,这个对象会添加到容器中
//如果isSingleton()返回true,则该实例会放到Spring容器中
//存放的方式为名字是colorFactoryBean ,类型ColorFactoryBean的对象,但是如果直接使用名字为colorFactoryBean的方式去
//获取bean,底层获取到ColorFactoryBean对象后,然后调了getObject()方法,把getObject方法里的对象返回了。所以造成了
//一个假象,容器里存的是key为colorFactoryBean ,value为Color的Bean。当使用&拼接colorFactoryBean时,底层会做一个判断
//如果说传入的beanName带了&符,就不调用getObject方法了,直接把ColorFactoryBean对象返回。
@Override
public Color getObject() throws Exception
return new Color();
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType()
return Color.class;
配置类:
@Configurable
public class MainConfig2
@Bean
public ColorFactoryBean colorFactoryBean()
return new ColorFactoryBean();
测试:
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad4()
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
//获取所有beanName
String[] beanNamesForType = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String s: beanNamesForType)
System.out.println(s);
//工厂bean获取的是调用getObject创建的对象
// 实际上是一个beanName为colorFactoryBean的com.example.demo.test.pojo.Color的bean
Object colorFactoryBean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("colorFactoryBean");
System.out.println("colorFactoryBean类型:"+colorFactoryBean.getClass());
//我就要获取factoryBean,不要获取getObject返回的对象,怎么获取呢?
Object colorFactoryBean2 = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("&colorFactoryBean");
System.out.println("colorFactoryBean自己:"+colorFactoryBean2.getClass());
结果:
mainConfig2 配置类本身
colorFactoryBean 一个benaName为colorFactoryBean的Color类型的bean
colorFactoryBean类型:class com.example.demo.test.pojo.Color
factoryBean自己:class com.example.demo.test.pojo.ColorFactoryBean factoryBean的beanName为&colorFactoryBean
4、Spring.factories扩展机制
通过在 META-INF/spring.factories文件中指定自动配置类入口,从而让框架加载该类实现jar的动态加载。
想要往容器中注入一个bean,但是这个bean不再启动类的包扫描路径下,怎么办?比如第三方的jar,可能需要往容器中注入一些bean,但是这些bean并不在包扫描路径下。
1、可以通过@Import注解导入第三方jar中的bean
2、spring.factories 文件中添加要注入到容器中的类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\
com.xxx.cloud.megarock.autoconfig.MegarockSecurityCodeAutoConfiguration
springboot通过这种方式就能把配置类注入到容器中,同时这个配置类中本身可能已经配置了多个bean,通过@Bean或者@ComponentScan
注意:
如果第三方jar的包名和当前项目的包名相同,那么第三方jar的被@Configuration,@Component注释的bean,也是可以被当前项目扫描到的。
如果第三方jar的包路径,与当前项目的包路径不同,第三方需要注入到IOC容器中的bean,可以通过spring.factories方式导入或者通过@Import注解
Bean生命周期
生命周期指:
bean创建->初始化->销毁的过程
容器管理bean的生命周期:
我们可以自定义初始化和销毁方法,容器在bean进行到当前生命周期的时候来调用我们自定义的初始化和销毁方法。
- 通过@Bean指定初始化和销毁方法:
使用配置文件的时候我们可以在<bean>指定初始化方法和销毁方法:init-method="" destroy-method=""
注解的方式:
实体类:
public class Car
//构造函数
public Car()
System.out.println("Car constructor....");
//自定义初始化方法
public void init()
System.out.println("Car ... init ....");
//自定义销毁方法
public void destroy()
System.out.println("Car ... destroy ....");
配置类:通过 @Bean(initMethod ="init",destroyMethod = "destroy")配置
@Configurable
public class MainConfig2
@Bean(initMethod ="init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Car car()
return new Car();
测试:
@Test
public void test()
//1.创建IOC容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext mainConfig2 = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成。。。");
//关闭容器
mainConfig2.close();
Car constructor....
Car ... init ....
容器创建完成。。。
Car ... destroy ....
结论:
单例bean:
对象创建->在启动容器时创建对象
初始化->在对象创建完成并赋值好,调用初始化方法
销毁->在关闭容器时销毁bean
多实例bean(prototype):
对象创建->在启动容器时不会创建对象,在获取对象的时候才创建对象
初始化->在对象创建完成并赋值好,调用初始化方法
销毁->容器不会管理这个bean,自己销毁
- 通过让Bean实现
InitializingBean(定义初始化逻辑),DisposableBean(定义销毁逻辑)
Bean:
@Component
public class Cat implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean
public Cat()
System.out.println("cat constructor...");
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception
System.out.println("cat....afterPropertiesSet...");
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception
System.out.println("cat....destroy...");
配置类:
@Configurable
@ComponentScan("com.example.demo.test.pojo")
public class MainConfig2
测试:
@Test
public void test()
//1.创建IOC容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext mainConfig2 = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成。。。");
//关闭容器
mainConfig2.close();
cat constructor...
cat....afterPropertiesSet...
容器创建完成。。。
cat....destroy...
- 可以使用JSR250
@PostConstruct:在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成,来执行初始化方法;
@PreDestroy 在容器销毁bean之前通知我们进行清理工作
bean:
@Component
public class Dog
public Dog()
System.out.println("dog...constructor...");
//对象创建并赋值之后调用初始化
@PostConstruct
public void init()
System.out.println("Dog...@PostConstruct...");
//容器移除对象之前调用销毁
@PreDestroy
public void destroy()
System.out.println("Dog ...@PreDestroy...");
配置类,测试,同上。
- BeanPostProcessor:bean的后置处理器
在bean初始化之前后进行一些处理工作:
postProcessBeforeInitialization:在初始化之前工作
postProcessAfterInitialization:在初始化之后工作
BeanPostProcessor:
后置处理器,初始化前后进行处理工作,将后置处理器加入到容器中
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean);
return bean;
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean);
return bean;
配置类,测试同上。
结果:
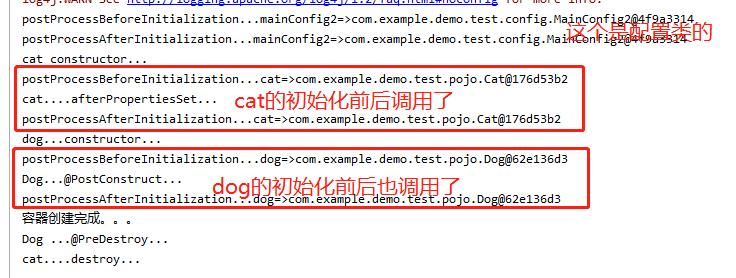
BeanPostProcessor原理:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42412601/article/details/103546435
以上是关于spring注解驱动开发的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章