二Spring Security基本原理
Posted 上善若水
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二Spring Security基本原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、Spring Security常见过滤器介绍
Spring Security 本质是一个过滤器链
从启动时,可以获取到过滤器链:
Spring Security中过滤器的介绍:
org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
首当其冲的一个过滤器,作用之重要,自不必多言。
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter主要是使用SecurityContextRepository在session中保存或更新一个SecurityContext,并将SecurityContext给以后的过滤器使用,来为后续filter建立所需的上下文。
SecurityContext中存储了当前用户的认证以及权限信息。org.springframework.security.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter
此过滤器用于集成SecurityContext到Spring异步执行机制中的WebAsyncManagerorg.springframework.security.web.header.HeaderWriterFilter
向请求的Header中添加相应的信息,可在http标签内部使用security:headers来控制org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter
csrf又称跨域请求伪造,SpringSecurity会对所有post请求验证是否包含系统生成的csrf的token信息,如果不包含,则报错。起到防止csrf攻击的效果。org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter
匹配URL为/logout的请求,实现用户退出,清除认证信息。org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
认证操作全靠这个过滤器,默认匹配URL为/login且必须为POST请求。org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
如果没有在配置文件中指定认证页面,则由该过滤器生成一个默认认证页面。org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
由此过滤器可以生产一个默认的退出登录页面org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilter
此过滤器会自动解析HTTP请求中头部名字为Authentication,且以Basic开头的头信息。org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCacheAwareFilter
通过HttpSessionRequestCache内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存HttpServletRequestorg.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
针对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request具有更加丰富的APIorg.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
当SecurityContextHolder中认证信息为空,则会创建一个匿名用户存入到SecurityContextHolder中。Spring Security为了兼容未登录的访问,也走了一套认证流程,只不过是一个匿名的身份。org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilter
SecurityContextRepository限制同一用户开启多个会话的数量org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter
异常转换过滤器位于整个springSecurityFilterChain的后方,用来转换整个链路中出现的异常org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor
获取所配置资源访问的授权信息,根据SecurityContextHolder中存储的用户信息来决定其是否有权限。
二、Spring Security过滤器链加载原理
通过前面15个过滤器功能的介绍,是不是有新的疑惑,我们并没有配置这些过滤器啊?它们都是怎么被加载出来的?
通过查看源码
FilterSecurityInterceptor:是一个方法级的权限过滤器,基本位于过滤链的最底部。
ExceptionTranslationFilter:是一个异常过滤器,用来处理在认证授权过程中抛出的异常。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter:对/login的post请求做拦截,校验表单中用户名、密码。
2.1、DelegatingFilterProxy
DelegatingFilterProxy源码里重要代码进行说明,其中删减掉了一些不重要的代码,大家注意我写的注释就行了。
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.web.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
public class DelegatingFilterProxy extends GenericFilterBean
@Nullable
private String contextAttribute;
@Nullable
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
@Nullable
private String targetBeanName;
private boolean targetFilterLifecycle;
@Nullable
private volatile Filter delegate; // 注:这个过滤器才是真正加载的过滤器
private final Object delegateMonitor;
// 注:doFilter才是过滤器的入口,直接从这看!
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException
Filter delegateToUse = this.delegate;
if (delegateToUse == null)
synchronized(this.delegateMonitor)
delegateToUse = this.delegate;
if (delegateToUse == null)
WebApplicationContext wac = this.findWebApplicationContext();
if (wac == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: no ContextLoaderListener or DispatcherServlet registered?");
// 第一步:doFilter中最重要的一步,初始化上面私有过滤器属性delegate
delegateToUse = this.initDelegate(wac);
this.delegate = delegateToUse;
//第三步:执行FilterChainProxy过滤器
this.invokeDelegate(delegateToUse, request, response, filterChain);
//第二步:直接看最终加载的过滤器到底是谁
protected Filter initDelegate(WebApplicationContext wac) throws ServletException
//debug得知targetBeanName为:springSecurityFilterChain
String targetBeanName = this.getTargetBeanName();
Assert.state(targetBeanName != null, "No target bean name set");
//debug得知delegate对象为:FilterChainProxy
Filter delegate = (Filter)wac.getBean(targetBeanName, Filter.class);
if (this.isTargetFilterLifecycle())
delegate.init(this.getFilterConfig());
return delegate;
protected void invokeDelegate(Filter delegate, ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException
delegate.doFilter(request, response, filterChain);
第二步debug结果如下:
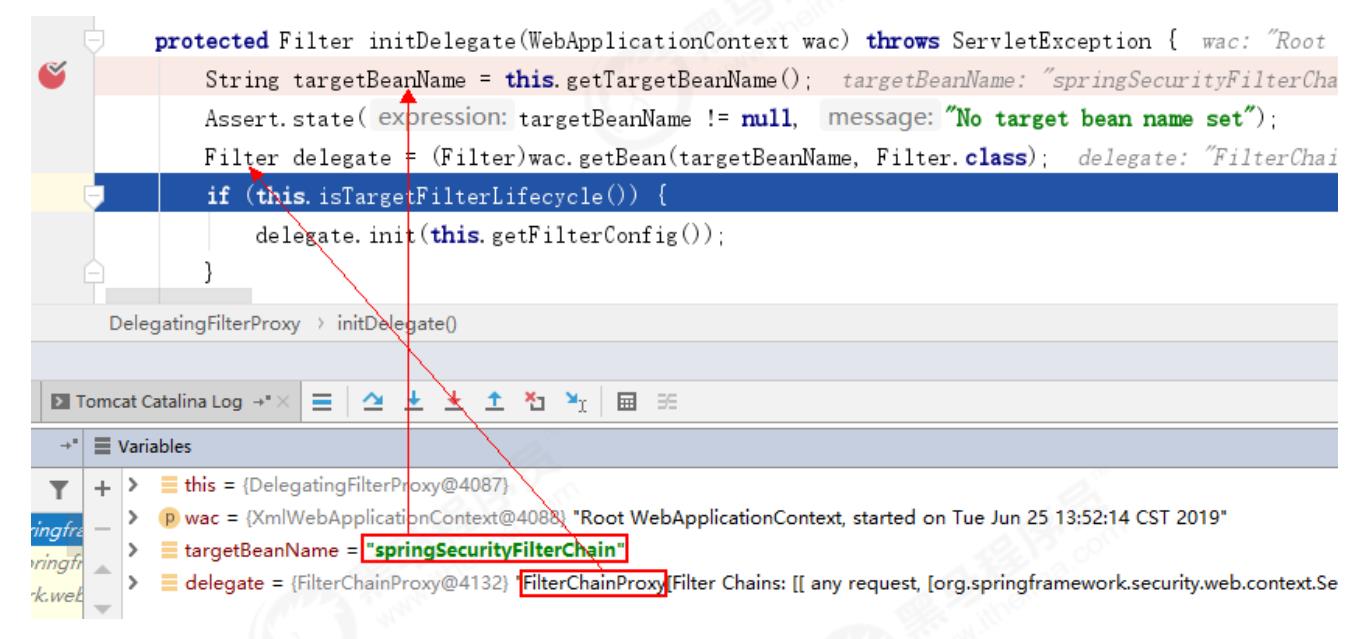
由此可知,DelegatingFilterProxy通过springSecurityFilterChain这个名称,得到了一个FilterChainProxy过滤器,
最终在第三步执行了这个过滤器。
2.2、FilterChainProxy
注意代码注释!注意代码注释!注意代码注释!
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.security.web;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.web.firewall.FirewalledRequest;
import org.springframework.security.web.firewall.HttpFirewall;
import org.springframework.security.web.firewall.StrictHttpFirewall;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.UrlUtils;
import org.springframework.web.filter.GenericFilterBean;
public class FilterChainProxy extends GenericFilterBean
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(FilterChainProxy.class);
private static final String FILTER_APPLIED = FilterChainProxy.class.getName().concat(".APPLIED");
private List<SecurityFilterChain> filterChains;
private FilterChainProxy.FilterChainValidator filterChainValidator;
private HttpFirewall firewall;
//可以通过一个叫SecurityFilterChain的对象实例化出一个FilterChainProxy对象
//这FilterChainProxy又是何方神圣?会不会是真正的过滤器链对象呢?先留着这个疑问!
public FilterChainProxy(SecurityFilterChain chain)
this(Arrays.asList(chain));
//又是SecurityFilterChain这家伙!嫌疑更大了!
public FilterChainProxy(List<SecurityFilterChain> filterChains)
this.filterChainValidator = new FilterChainProxy.NullFilterChainValidator();
this.firewall = new StrictHttpFirewall();
this.filterChains = filterChains;
//注:直接从doFilter看
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException
boolean clearContext = request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) == null;
if (clearContext)
try
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
this.doFilterInternal(request, response, chain);
finally
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
else
//第一步:具体操作调用下面的doFilterInternal方法了
this.doFilterInternal(request, response, chain);
private void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException
FirewalledRequest fwRequest = this.firewall.getFirewalledRequest((HttpServletRequest)request);
HttpServletResponse fwResponse = this.firewall.getFirewalledResponse((HttpServletResponse)response);
//第二步:封装要执行的过滤器链,那么多过滤器就在这里被封装进去了!
List<Filter> filters = this.getFilters((HttpServletRequest)fwRequest);
if (filters != null && filters.size() != 0)
FilterChainProxy.VirtualFilterChain vfc = new FilterChainProxy.VirtualFilterChain(fwRequest, chain, filters);
//第四步:加载过滤器链
vfc.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
else
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug(UrlUtils.buildRequestUrl(fwRequest) + (filters == null ? " has no matching filters" : " has an empty filter list"));
fwRequest.reset();
chain.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
private List<Filter> getFilters(HttpServletRequest request)
Iterator var2 = this.filterChains.iterator();
//第三步:封装过滤器链到SecurityFilterChain中!
SecurityFilterChain chain;
do
if (!var2.hasNext())
return null;
chain = (SecurityFilterChain)var2.next();
while(!chain.matches(request));
return chain.getFilters();
第二步debug结果如下图所示,惊不惊喜?十五个过滤器都在这里了!

再看第三步,怀疑这么久!原来这些过滤器还真是都被封装进SecurityFilterChain中了。
2.3、SecurityFilterChain
最后看SecurityFilterChain,这是个接口,实现类也只有一个,这才是web.xml中配置的过滤器链对象!
接口:SecurityFilterChain.java
package org.springframework.security.web;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public interface SecurityFilterChain
boolean matches(HttpServletRequest var1);
List<Filter> getFilters();
实现类:DefaultSecurityFilterChain.java
package org.springframework.security.web;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcher;
public final class DefaultSecurityFilterChain implements SecurityFilterChain
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(DefaultSecurityFilterChain.class);
private final RequestMatcher requestMatcher;
private final List<Filter> filters;
public DefaultSecurityFilterChain(RequestMatcher requestMatcher, Filter... filters)
this(requestMatcher, Arrays.asList(filters));
public DefaultSecurityFilterChain(RequestMatcher requestMatcher, List<Filter> filters)
logger.info("Creating filter chain: " + requestMatcher + ", " + filters);
this.requestMatcher = requestMatcher;
this.filters = new ArrayList(filters);
public RequestMatcher getRequestMatcher()
return this.requestMatcher;
public List<Filter> getFilters()
return this.filters;
public boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request)
return this.requestMatcher.matches(request);
public String toString()
return "[ " + this.requestMatcher + ", " + this.filters + "]";
总结:对SpringSecurity工作原理有了一定的认识。但理论千万条,功能第一条,探寻底层,是为了更好的使用框架。
以上是关于二Spring Security基本原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
#yyds干货盘点#从零学习spring security基本原理了解