Java数据结构与算法解析——二叉查找树
Posted 4K_WarCraft
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java数据结构与算法解析——二叉查找树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二叉查找树简介
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),又被称为二叉搜索树。
它是特殊的二叉树:对于二叉树,假设x为二叉树中的任意一个结点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值记为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y] <= key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个结点,则key[y] >= key[x]。那么,这棵树就是二叉查找树。如下图所示:
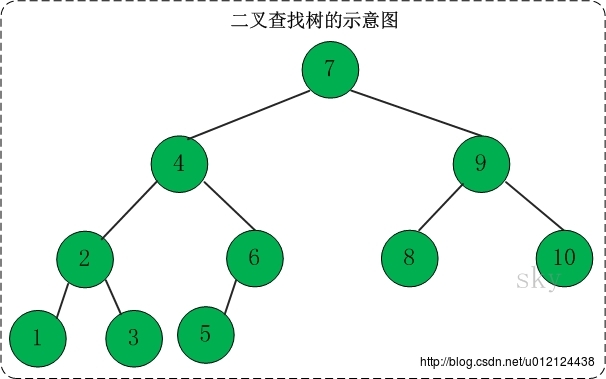
在二叉查找树中:
(1) 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(2) 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(3) 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
(4) 没有键值相等的节点(no duplicate nodes)。
二叉查找树的实现
1.二叉查找树节点实现
public class BinaryNode<T>
private T element;
private BinaryNode<T> left;
private BinaryNode<T> right;
public BinaryNode(T element, BinaryNode<T> left, BinaryNode<T> right)
this.element = element;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
public BinaryNode(T element)
this(element, null, null);
(1) element–当前节点的值
(2) right – 它指向当前节点的右孩子。
(3) parent – 它指向当前节点的父结点。
2.contains方法的实现
如果在树T中存在含有项X的节点,那么contains方法返回true,否则返回false.如果树T是空集,则返回false.
public boolean contains(T t, BinaryNode<T> node)
if (t == null)
return false;
int campareResult = t.compareTo(node.element);
if (campareResult < 0)
return contains(t, node.left);
else if (campareResult > 0)
return contains(t, node.right);
else
return true;
从根节点开始查找该值,如果根节点匹配,则直接返回true,否则和根节点的值进行比较,然后递归遍历左子树或右子树进行查找。
3.findMin方法和findMax方法
public T findMax()
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return findMax(mRoot).element;
private BinaryNode<T> findMax(BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node != null)
while (node.right != null)
node = node.right;
return node;
对于findMax方法,如果存在右子树,则递归遍历,终止点就是最大的元素。否则,根节点就是最大的元素。
public T findMin()
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return findMin(mRoot).element;
private BinaryNode<T> findMin(BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node != null)
while (node.left != null)
node = node.left;
return node;
对于findMin方法,如果存在左子树,则递归遍历,终止点就是最小的元素。否则,根节点就是最小的元素。
4.insert方法
将一个新的元素X插入到树T中,可以先通过contains方法去查找该元素是否存在,如果存在,则什么都不做,否则将X插入到遍历路径上的最后一点。
public void insert(T t)
mRoot = insert(t, mRoot);
public BinaryNode<T> insert(T t, BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node == null)
return new BinaryNode<T>(t, null, null);
int compareResult = t.compareTo(node.element);
if (compareResult > 0)
node.right = insert(t, node.right);
else if (compareResult < 0)
node.left = insert(t, node.left);
return node;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
5.remove方法
public void remove(T t)
mRoot = remove(t, mRoot);
public BinaryNode<T> remove(T t, BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node == null)
return node;
int compareResult = t.compareTo(node.element);
if (compareResult > 0)
node.right = remove(t, node.right);
else if (compareResult < 0)
node.left = remove(t, node.left);
else if (node.left != null && node.right != null)
node.element = findMin(node.right).element;
node.right = remove(node.element, node.right);
else
node = (node.left != null) ? node.left : node.right;
return node;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
对于删除,最复杂的是该将被删除的节点A具有两个儿子的情况,一般是该节点的右子树最小的节点B代替节点A,然后在B原来的位置删除掉节点B。
上面的代码能够完成删除工作,但效率并不高,因为它沿着树进行两趟搜索来查找和删除右子树中最小的节点。
如果删除的次数不多,通常使用懒惰删除:当一个元素要被删除时,它仍在树中,而只是标记为删除。
特别是删除算法会使得左子树比右子树深,因为我们总是用右子树的一个来代替删除的节点。会造成二叉查找树,严重的不平衡。
5.二叉查找树完整代码
public class BinarySearchTree<T extends Comparable<?
super T>>
private BinaryNode<T> mRoot;
public void makeEmpty()
mRoot = null;
public boolean isEmpty()
return mRoot == null;
public boolean contains(T t)
return contains(t, mRoot);
public boolean contains(T t, BinaryNode<T> node)
if (t == null)
return false;
int campareResult = t.compareTo(node.element);
if (campareResult < 0)
return contains(t, node.left);
else if (campareResult > 0)
return contains(t, node.right);
else
return true;
public T findMax()
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return findMax(mRoot).element;
private BinaryNode<T> findMax(BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node != null)
while (node.right != null)
node = node.right;
return node;
public T findMin()
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return findMin(mRoot).element;
private BinaryNode<T> findMin(BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node != null)
while (node.left != null)
node = node.left;
return node;
public void insert(T t)
mRoot = insert(t, mRoot);
public BinaryNode<T> insert(T t, BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node == null)
return new BinaryNode<T>(t, null, null);
int compareResult = t.compareTo(node.element);
if (compareResult > 0)
node.right = insert(t, node.right);
else if (compareResult < 0)
node.left = insert(t, node.left);
return node;
public void remove(T t)
mRoot = remove(t, mRoot);
public BinaryNode<T> remove(T t, BinaryNode<T> node)
if (node == null)
return node;
int compareResult = t.compareTo(node.element);
if (compareResult > 0)
node.right = remove(t, node.right);
else if (compareResult < 0)
node.left = remove(t, node.left);
else if (node.left != null && node.right != null)
node.element = findMin(node.right).element;
node.right = remove(node.element, node.right);
else
node = (node.left != null) ? node.left : node.right;
return node;
private static class BinaryNode<T>
private T element;
private BinaryNode<T> left;
private BinaryNode<T> right;
public BinaryNode(T element, BinaryNode<T> left, BinaryNode<T> right)
this.element = element;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
public BinaryNode(T element)
this(element, null, null);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
二叉树的遍历
1.前序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(1) 访问根结点;
(2) 先序遍历左子树;
(3) 先序遍历右子树。
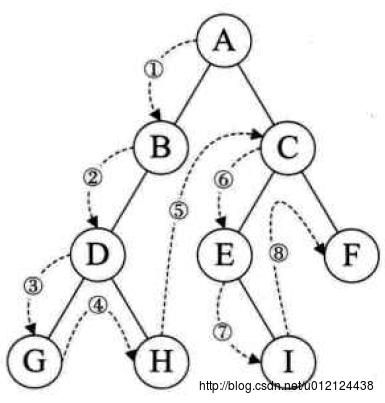
前序遍历代码
private void preOrder(BinaryNode<T> tree)
if(tree != null)
System.out.print(tree.element+" ");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
public void preOrder()
preOrder(mRoot);
2.中序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(1) 中序遍历左子树;
(2) 访问根结点;
(3) 中序遍历右子树。
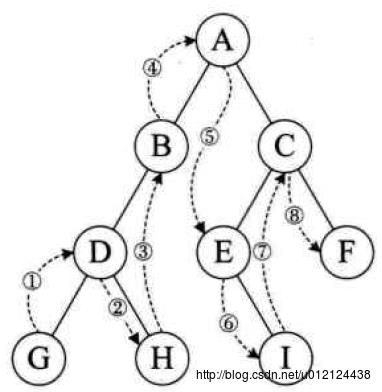
中序遍历代码
private void inOrder(BinaryNode<T> tree)
if(tree != null)
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.element+" ");
inOrder(tree.right);
public void inOrder()
inOrder(mRoot);


