Java多线程基础-第一节2:Thread类
Posted 我擦我擦
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java多线程基础-第一节2:Thread类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
(1)Thread类常见构造方法
Thread类常见构造方法:
Thread():创建线程对象Thread(Runnable target):使用Runnable对象创建线程对象Thread(String name):创建线程对象,并命名Thread(Runnable target, String name):使用Runnable对象创建线程对象,并命名Thread(Thread Group, Runnable target):线程可以分组管理,分好的组即为线程组
例子:
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
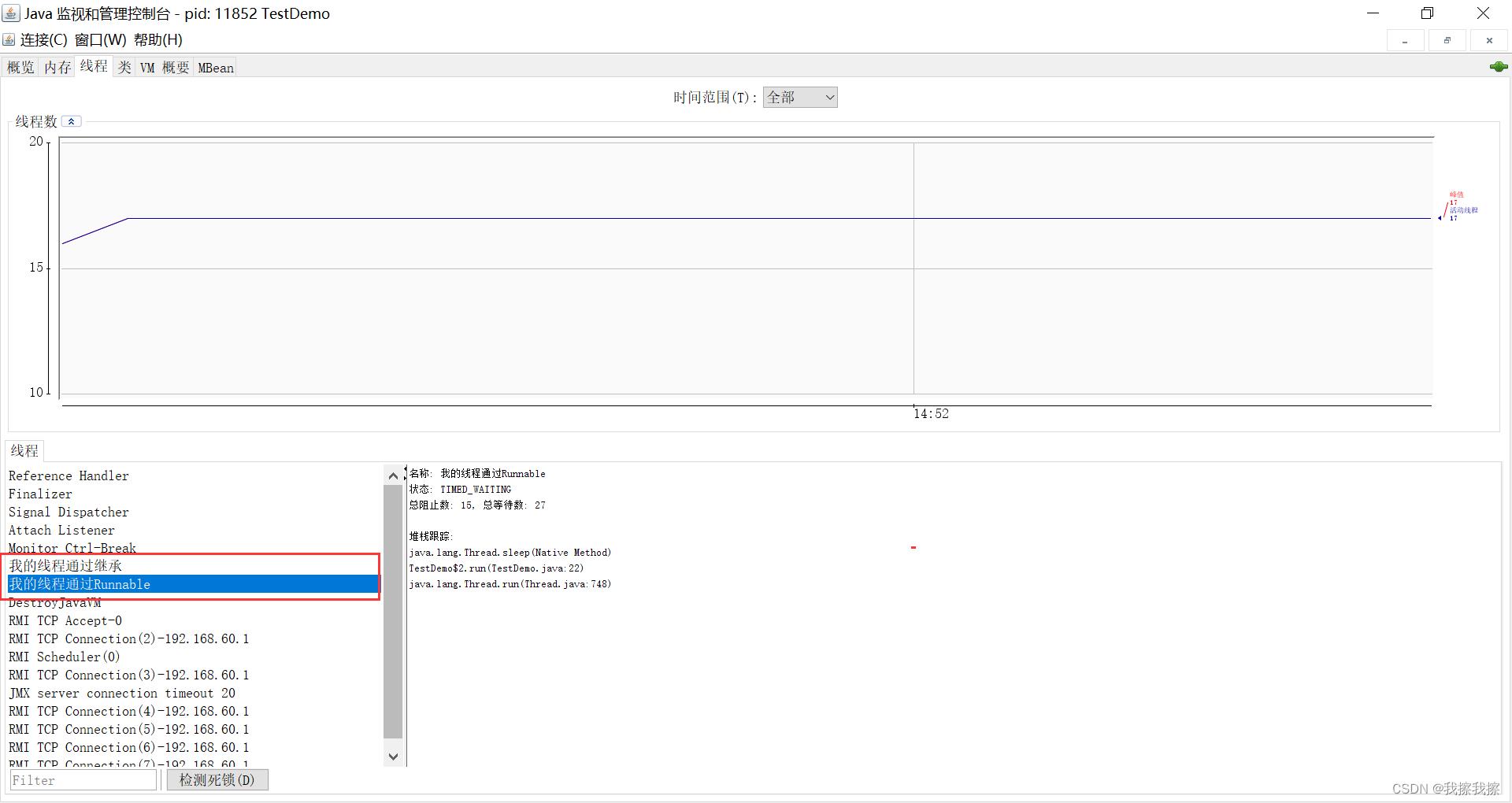
Thread thread1 = new Thread("我的线程通过继承")
@Override
public void run()
try
while (true)
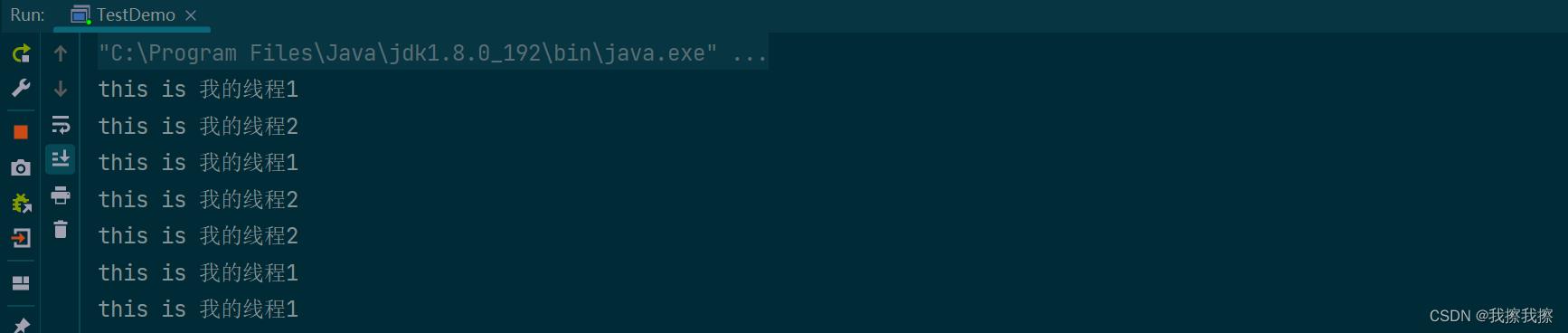
System.out.println("this is 我的线程1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
;
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
while (true)
System.out.println("this is 我的线程2");
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
, "我的线程通过Runnable" //第二个参数
);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
(2)Thread类常见属性
Thread类常见属性:
getId():获取ID,ID是线程的唯一标识getName():获取名称,名称用于各种调试工具getState():获取状态,反映线程当前所处状态getPriority:获取优先级,优先级越高理论上说更容易被调度到isDaemon():判断是否为后台线程,JVM会在一个进程的所有非后台线程结束后才会结束运行isAlive:判断是否存活,简单说就是run方法是否运行完毕isInterrupted():判断是否中断
例子:
public class TestDemo2
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread thread = new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
try
System.out.println(this.getName() + "存活中");
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
System.out.println(this.getName() + "即将死亡");
;
System.out.println("【线程创建后情况:】");
System.out.println("获取线程ID:" + thread.getId());
System.out.println("获取线程名称:" + thread.getName());
System.out.println("获取线程优先级:" + thread.getPriority());
System.out.println("获取线程状态:" + thread.getState());
System.out.println("判断是否为后台线程:" + thread.isDaemon());
System.out.println("判断线程是否存活:" + thread.isAlive());
System.out.println("判断是否被中断:" + thread.isInterrupted());
thread.start();
(3)获取当前线程引用
获取当前线程引用:可以使用public static Thread currentThread()返回当前线程对象的引用
public class TestDemo7
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread.getName());
(4)线程的启动、中断、等待和休眠
A:线程启动
线程启动之start:通过重写run方法可以创建一个线程对象,但线程对象创建出来并不意味着线程就开始运行了,可是需要通过调用Thread类的start方法来启动一个线程。而run方法只是类的一个普通方法而已,如果直接调用run方法,那么程序中依然只有主线程这一个线程,所以只有调用start方法后才会使新线程运行起来然后去执行run方法中的逻辑
例子
如下,创建线程后,只执行run方法,会发现并没有实现多线程
class myThread extends Thread
@Override
public void run()
while(true)
System.out.println("hello thread");;
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
public class TestDemo3
public static void main(String[] args)
myThread myThread = new myThread();
myThread.run();
while(true)
System.out.println("hello main");;
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
B:线程中断
①:通过共享标志中断
由于线程共享进程的地址空间,所以我们可以通过设置一个标志为来决定线程是否需要退出,如下
public class TestDemo4
private static boolean Quit = false;//退出标志
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread thread = new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
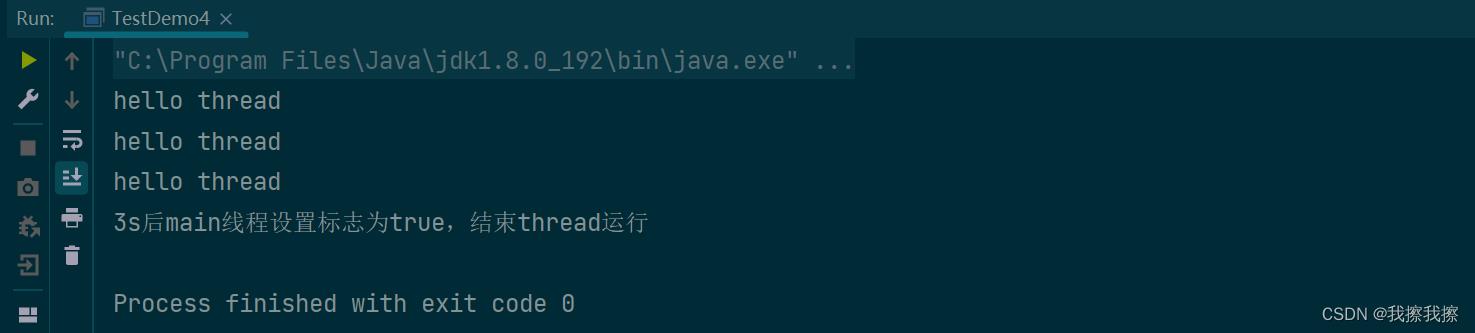
while(!Quit)
System.out.println("hello thread");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
;
thread.start();
try
Thread.sleep(3000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
Quit = true;
System.out.println("3s后main线程设置标志为true,结束thread运行");
②:通过interrupt方法中断
Thread类内部包含了一个boolean类型的变量作为线程是否被中断的标记,可以使用Thread.interrupted()或Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()代替自定义标志位
public void interrupt():中断对象关联的进程,如果线程正在阻塞,则会以异常的方式通知,否则设置标志位public static boolean interrupted():判断当前线程的中断标志位是否设置,调用后清除标志位public boolean isInterrupted():判断对象关联的线程的标志位是否设置,调用后不清除标志位
特别注意,在调用interrupt方法时,会有以下两种情形
- 线程在运行状态:会将
isInterrupted设置为true - 线程在阻塞状态(例如
sleep):不会设置标志位,而是触发InterruptedException异常
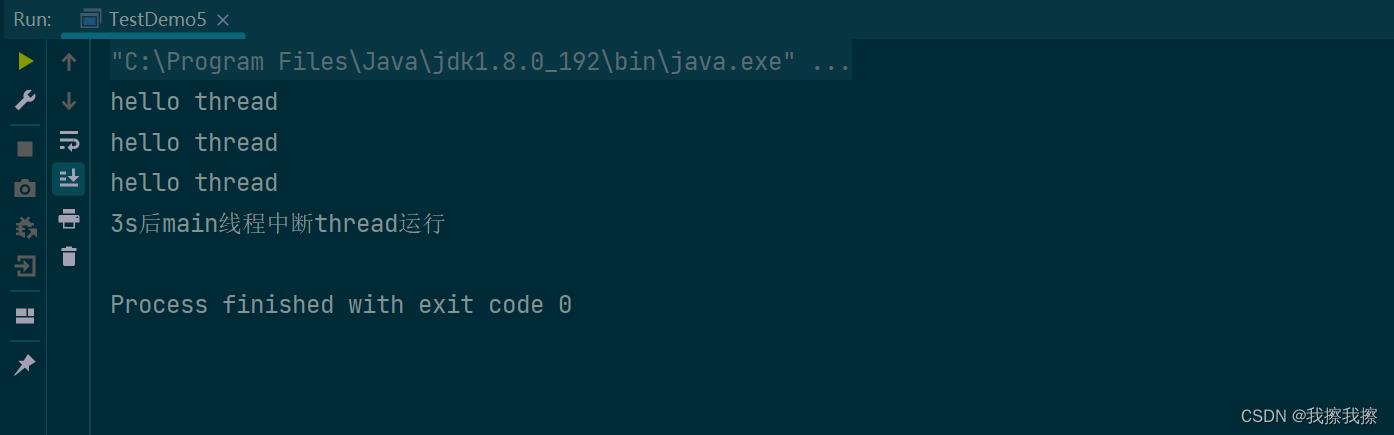
public class TestDemo5
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread thread = new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted())
System.out.println("hello thread");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
//注意跳出,中断后由于线程在sleep所以会触发异常
break;
;
thread.start();
try
Thread.sleep(3000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
thread.interrupt(); //中断
System.out.println("3s后main线程中断thread运行");
C:线程等待
线程等待:线程之间的调度顺序是不确定的,但我们可以通过一些特殊的操作,对线程的执行顺序做出干预。其中join方法就可以控制线程之间的结束顺序,例如如果在mian中调用thread.join,那么效果就是让main阻塞等待,等到thread执行完毕之后,main才能继续执行
- 注意:如果
main在调用join之前,thread线程已经结束了,那么main就不需要等待了
其中join方法有如下三种重载形式
public void join():等待线程结束public void join(long millis):等待线程结束,最多millis毫秒public void join(long millis, int nanos):同理,但可以提高精度
例子
如果main线程不等待thread线程,那么main线程会自己结束,而thread线程仍在运行
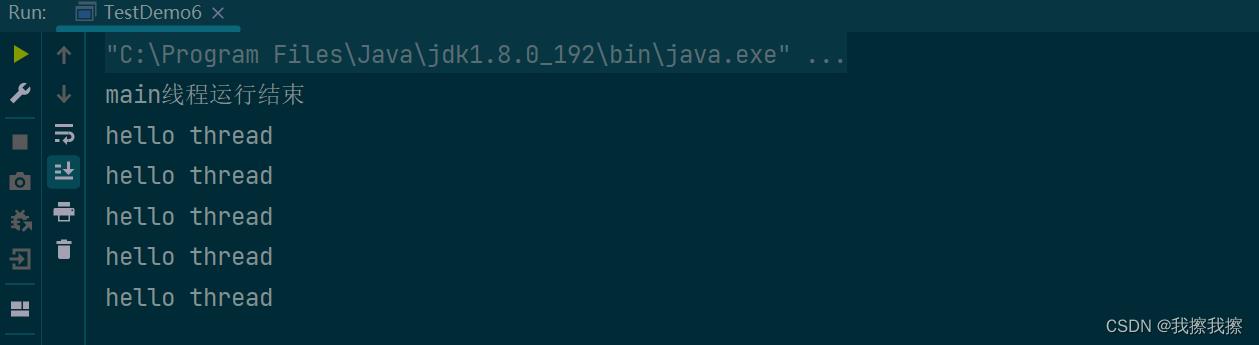
public class TestDemo6
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread thread = new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
System.out.println("hello thread");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
;
thread.start();
System.out.println("main线程运行结束");
而如果加入thread.join(),那么main线程必须要等待thread运行完毕之后才能结束
public class TestDemo6
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread thread = new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
System.out.println("hello thread");
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
;
thread.start();
System.out.println("main线程join之前");
try
thread.join();
catch (InterruptedException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
System.out.println("main线程join之后");

D:线程休眠
线程休眠:使线程暂停运行一段时间,但要注意由于线程调度不可控,所以只能保证实际休眠时间大于等于参数所设置的休眠时间
public static void sleep(long millis):休眠当前线程mills毫秒public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos):同理,提高精度
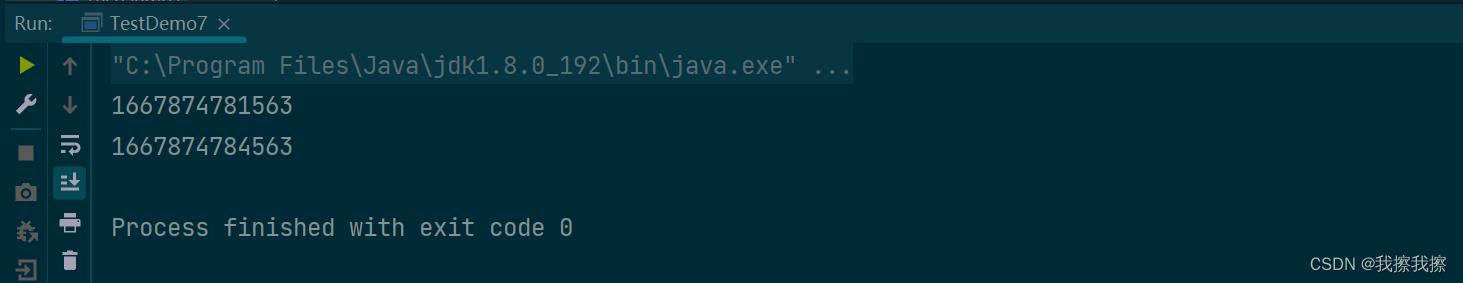
public class TestDemo7
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
以上是关于Java多线程基础-第一节2:Thread类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章