Storm调度
Posted Jason__Zhou
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Storm调度相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
调度
资源感应调度器
默认配置文件defaults.yaml
Resource_Aware_Scheduler_overview
调度器
- EventScheduler:将系统中的可用资源均匀地分配给需要资源的topology,其实也不是绝对均匀,后续会详细说明
- DefaultScheduler:和EvenetScheduler差不多,只不过会先将其它topology不需要的资源重新收集起来,再进行EventScheduler
- IsolationScheduler:用户可定义这个topology的机器资源,storm分配的时候会优先分配这些topology,以保证分配给该topology的机器只为这一个topology服务
- Pluggable Schedule 可插拔式的任务分配器,编写自己的task分配算法
- 资源感知调度
- Pluggable Schedule
实现IScheduler接口
public interface IScheduler
void prepare(Map conf);
/**
* Set assignments for the topologies which needs scheduling. The new assignments is available
* through `cluster.getAssignments()`
*
*@param topologies all the topologies in the cluster, some of them need schedule. Topologies object here
* only contain static information about topologies. Information like assignments, slots are all in
* the `cluster` object.
*@param cluster the cluster these topologies are running in. `cluster` contains everything user
* need to develop a new scheduling logic. e.g. supervisors information, available slots, current
* assignments for all the topologies etc. User can set the new assignment for topologies using
* cluster.setAssignmentById()`
*/
void schedule(Topologies topologies, Cluster cluster);
- DefaultScheduler
主要流程梳理:获得当前集群空闲资源-)计算当前topology的executor信息(分配时会用得上)-)计算可重新分配和可释放的资源-)分配
调用cluster的needsSchedualerTopologies方法获得需要进行任务分配的topologies
开始分别对每一个topology进行处理
调用cluster的getAvailableSlots方法获得当前集群可用的资源,以** (node,port) 集合的形式返回,赋值给**available-slots
获得当前topology的executor信息并转化为 ** (start-task-id,end-task-id) 集合存入all-executors,根据topology计算executors信息,采用**compute-executors 算法,稍后会讲解
然后调用EventScheduler的get-alive-assigned-node+port-)executors方法获得该topolog**y已经获得的资源,返回 (node+port,executor) **集合的形式存入alive-assigned,为什么要计算当前topology的已分配资源情况而不是计算集群中所有已分配资源?,猜测可能是进行任务rebalance的时候会有用吧。
接着就调用slot-can-reassign对alive-assigned中的slots信息进行判断,选出其中能被重新分配的slot存入变量can-reassigned
这样可用的资源就由available-slots和can-reassigned两部分组成
- 接下来计算当前topology能使用的全部slot数目total-slots–to-use:min(topology的NumWorker数,available-slots+can-reassigned)
- 如果total-slots–to-use >当前已分配的slots数目,则调用bad-slots方法计算可被释放的slot
- 调用cluster的freeSlots方法释放计算出来的bad-slot
- 最后调用EventScheduler的schedule-topologies-evenly进行分配
继续下一个topology
- EventScheduler
EventScheduler调度算法与Default相比少了一个计算可重新分配资源的环节,直接利用Supervisor中空闲的slot进行分配,在此不再细讲。
调度例子
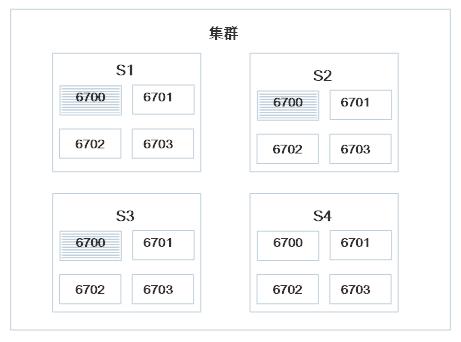
- Worker数3 Executer数8 Task数16
sort-slots算法对可用slots进行处理,结果为[s1 6700] [s2 6700] [s3 6700] [s4 6700] [s1 6701] [s2 6701] [s3 6701] [s4 6701] [s1 6702] [s2 6702] [s3 6702] [s4 6702] [s1 6703] [s2 6703] [s3 6703] [s4 6703]
compute-executors算法计算后得到的Executor列表为:[1 2] [3 4] [5 6] [7 8] [9 10] [11 12] [13 14] [15 16];注:格式为[start-task-id end-task-id],共8个worker,第一个包含2个task,start-task-id为1,end-task-id为2,所以记为[1 2],后面依次类推…compute-executors算法会在下一篇博客中详解
8个Executor在3个worker上的分布状态为[3,3,2]
分配结果为:
[1 2] [3 4] [5 6] -> [s1 6700]
[7 8] [9 10] [11 12] -> [s2 6700]
[13 14] [15 16] -> [s3 6700]
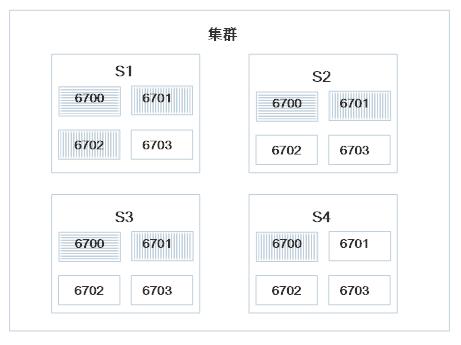
- Worker数5 Executer数10 Task数10
可用的slot经过sort-slots后:[s1 6701] [s2 6701] [s3 6701] [s4 6700] [s1 6702] [s2 6702] [s3 6702] [s4 6701] [s1 6703] [s2 6703] [s3 6703] [s4 6702] [s4 6703]
comput-executors计算后得到的executor列表:[1 1] [2 2] [3 3] [4 4] [5 5] [6 6] [7 7] [8 8] [9 9] [10 10]
10个executor在5个worker上的分布为[2,2,2,2,2]
分配结果为:
[1 1] [2 2] -> [s1 6701]
[3 3] [4 4] -> [s2 6701]
[5 5] [6 6] -> [s3 6701]
[7 7] [8 8] -> [s4 6700]
[9 9] [10 10] -> [s1 6702]
调度算法补充说明
cpmpute->executors
- 从storm配置获取集合
- storm-task-info 获得集合
- 将集合处理为 [compoent-id, tasks]
- 将和 join得到
- 根据[parallelism,tasks]将task均分到数目为parallelism的分区,返回每个parallelism的[ta sk-1,task-2,…]
- 将返回的转换为executor集合[start-task-id,end-task-id]
get-alive-assigned-node+port -> executors:
1.获得当前topology的assignment
2.如不为空,则获得其中的
3.转化为[executors,[node,port]]
4.再次转化为<[node,port],executors>
5.返回结果
- sort-slots
1.将所有可用的slots作为参数传入
2.根据supervisor-id进行分组排序
3.调用intervel-all方法对分组排序后的结果结合colls进行处理
1. colls不为空,则调用map first方法对集合处理:
遍历colls,取每个supervisor的第一条记录,加入到my-elments中。
2. 递归调用interval-all处理剩下的集合。
bad-slots
- 参数需要:此topology已经分配的资源existing-slots、此topology的所有
的executor、此topology可使用的slot数目 - 根据executer数和可使用的slot数计算出一个,executor-count表示一个slot里面的executor数目,slot-count表示这样的slot有多少个。比如 10个executor ,4个slot可能的计算结果为<2,2>,<3,2>
- 再根据传入的existing-slots中的每一项计算其executor-count
把计算得到的executor-count作为键去集合里面取,如果找到的值大于0,说明存在这样的分配,保持这样的分配,将其加入到keeps中,对应的slot-count的值减一,继续下一个计算 - 遍历完existing-slots集合后,可能会未加入keeps集合的元素,此时这些就是可以被释放的资源。具体做法就是:existing-slots和keeps做差值,剩下的,就可以释放。作为结果返回。
- 参数需要:此topology已经分配的资源existing-slots、此topology的所有
使用资源感应调度器
配置conf/storm.yaml
storm.scheduler: "org.apache.storm.scheduler.resource.ResourceAwareScheduler"对于一个 Topology,用户可以指定各个组件(如:Spout 或 Bolt)运行时每个实例所需要的资源数。用户可以通过以下 API 指定一个组件的所需资源。
- 设置所需 Memory
public T setMemoryLoad(Number onHeap, Number offHeap)
- 设置所需 CPU
public T setCPULoad(Double amount)Number amount – 组件的一个实例所使用的 CPU 数量
目前,一个组件所需要的 CPU 资源数或者一个节点的 CPU 可用资源数都是由一个分数来表示的。CPU 的使用量是一个难以定义的概念,不同的 CPU 架构依据不同的执行任务表现不同,用一个精确的数字表示所有的情况是不可能的。相反,我们约定越过配置方法,主要关心粗粒度的 CPU 使用率,同时仍提供指定更细粒度数量的可能性。
通常情况下,一个物理 CPU 核心为 100 分。你可以根据你的处理器的性能相应的调整这个值。重负载任务可以得到 100 分,那样它就可以使用整个核心;中等负载的任务设置 50 分;轻量级负载设置 25 分;微型任务设置 10 分。在某些情况下,你的一个任务需要生成其他的线程用来帮助处理,这些任务可能需要设置超过 100 分来表达他们对 CPU 的使用。如果遵循这些约定,通常情况下一个单线程任务所需要的 CPU 分值是其容量 * 100。
限制 Worker 进程 (JVM) 的堆内存大小
设置节点的可用资源
Storm 管理员可以在 conf/storm.yaml 中添加以下配置项 (单位为 MB) 来指定一个节点的可用内存资源:
supervisor.memory.capacity.mb: [amount<Double>]
supervisor.cpu.capacity: [amount<Double>]
以上是关于Storm调度的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章