java中异步调用,Callable,Future,FutureTask,CompletableFuture如何使用
Posted Leo Han
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java中异步调用,Callable,Future,FutureTask,CompletableFuture如何使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们知道,在java中一般多线程编程时经常会使用Thread或者Runnable来进行自定义的线程运行逻辑,但是如果我们需要在一个线程运行结束时返回给另外一个线程结果,上面两个实现都不是很容易实现,一般可能需要另外的实现,比如通过一个临时变量共享。
在java中,提供了Callable能够返回结果的线程方法调用。我们看一下下面这个实现:
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>()
@Override
public String call() throws Exception
Thread.sleep(5000);
return "hello world";
;
Future<String> future = executor.submit(callable);
// do something
String result = future.get();
System.out.println(result);
这里通过向线程池提交了一个自定义的Callable实现,然后主线程可以先去处理其他逻辑,需要获取结果时主线程通过Futrue.get来等待结果返回。
这样我们通过Callable能够异步执行任务,并且通过Futrue.get来获取执行的结果。我们看下其具体实现:
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
上面这个方法具体实现在AbstractExecutorService中:
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Callable<T> callable)
return new FutureTask<T>(callable);
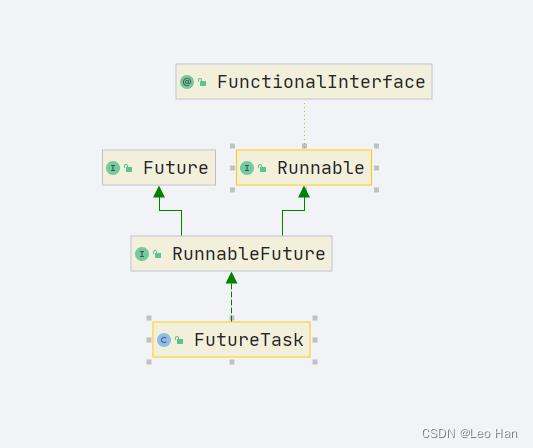
实际上我们提交一个Callable任务的时候,在AbstractExecutorService会将Callable转换为一个FutureTask任务,而FutureTask则实现了Future和Runable两个接口,通过Callable参数构造的时候,内部会只有一个Callable的引用。
private volatile int state;
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
这里又看到了和AQS中熟悉的state变量,一看到这个,就知道要通过这个状态量来控制一些行为。
这里在线程池的submit方法后,将Callable封装成了一个FutureTask(实现了Runnable接口),然后调用线程池的execute方法执行任务,这块就不说了,如果想要知道线程池怎么执行的,可以看之前写的博客: java同步之线程池ThreadPoolExecutor实现原理
当线程池调度到该任务执行时,会调用FutureTask.run方法:
public void run()
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW)
V result;
boolean ran;
try
result = c.call();
ran = true;
catch (Throwable ex)
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
if (ran)
set(result);
finally
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
这就是FutureTask执行逻辑的代码,我们大致说下流程:
- 通过
state状态量判断任务是否正常(是否执行过,或者被取消) - 执行任务,获取任务结果result
- 如果任务执行成功,设置返回结果,同时会唤醒在等待返回结果的线程队列
设置返回结果逻辑如下:
protected void set(V v)
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING))
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
private void finishCompletion()
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;)
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null))
for (;;)
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null)
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
break;
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
可以看到,当任务正确执行完成之后,通过CAS先设置state变量,然后设置返回值outcome,然后唤醒等待阻塞队列里的线程。
这样任务就执行完成了。
然后我们看下怎么获取返回值FutureTask.get:
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;)
if (Thread.interrupted())
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING)
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed)
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L)
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
else
LockSupport.park(this);
FutureTask.get有两种方式,一种是阻塞一直等待知道有返回值,另外一种是阻塞等待超时退出。在判断任务没有完成的时候,调用awaitDone方法,然当前获取结果线程阻塞等待。这里会将所有等待的线程当如到waiters这个单链表中。
如果指定了等待超时的时长,那么会调用LockSupport.parkNanos让获取线程阻塞指定时长,如果没有指定时长,则一直阻塞,知道任务完成唤醒阻塞对垒
对于超时方式而言:
else if (timed)
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L)
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
这里面外面是个for循环,当线程指定时间休眠到期唤醒后,到这里休眠时间结束,那么就会从等待队列移除,并返回state状态。然后调用方判断state发现超时,抛出TimeoutException异常。
除了通过Future.get阻塞方式来获取结果,还可以通过Futrue.isDone方法来判断任务是否完成,这个方法是非阻塞的,逻辑就是判断上面的state字段的值是否是变化,因此如果需要获取最终结果,需要不断循环判断。
public boolean isDone()
return state != NEW;
到这里我们可以看到,Future异步调用主要基于如下逻辑:
- 调用线程提交的Callable任务到线程池中会被转换为一个FutureTask然后在执行execute逻辑,返回的是一个Futrue
- 调用线程通过
Future.get阻塞方式获取结果,调用该方法后,当前线程会被阻塞 - 线程池执行提交的FutureTask任务,任务执行成功后会修改state变量并唤醒阻塞等待的线程
虽然FutureTask能够实现异步编程,但是在获取结果的时候必须通过循环调用Futrue.isDone或者调用Future.get阻塞等待结果返回。在java8中提供了CompletableFuture能够进行异步编程。
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->
try
Thread.sleep(5000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(String.format("[%s] 1. %s",Thread.currentThread().getName(),format.format(new Date())));
return "Hello world";
,executor);
String temp = "complete future";
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = completableFuture.thenApply((String result1)->
System.out.println(String.format("[%s] 2. %s",Thread.currentThread().getName(),format.format(new Date())));
return result1+temp;
);
上述就是CompletableFuture的一个应用。一般CompletableFuture有两个方法来返回CompletableFuture:
- runAsync 返回无返回结果的CompletableFuture
- supplyAsync 返回有返回结果的CompletableFuture
当我们获得这个CompletableFuture之后,接下来可以对根据这个异步对象进行处理,主要是如下几个方法:
- thenApply / thenApplyAsync 当任务执行完之后执行,相当于回调方法
- thenAccept / thenRun 和上面一样,但是方法没有返回值
- exceptionally 当执行任务发生异常,异步回调该方法
- whenComplete 当某个任务执行完成之后调用的方法,会将结果或异常传递给回调方法。\\
上面这几个方法都是在任务执行完之后回调的(注意在创建任务、回调方法之间不要用get方法),并且这些方法都是在线程池里面执行的,不会影响主逻辑。
以上是关于java中异步调用,Callable,Future,FutureTask,CompletableFuture如何使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章